
A Novel Human Interaction Game-like Application to Learn,
Perform and Evaluate Modern Contemporary Singing
“Human Beat Box”
S. K. Al Kork
2,3
, D. Uğurca
1
, C. Şahin
1
, P. Chawah
4,5
, L. Buchman
4,5
, M. Adda-Decker
4.5
, K. Xu
2,3
,
B. Denby
2,3
P. Roussel
2,3
,
B. Picart
6
, S. Dupont
6
, F. Tsalakanidou
7
, A. Kitsikidis
7
, F. M. Dagnino
8
,
M. Ott
8
F. Pozzi
8
, M. Stone
9
and E. Yilmaz
1
1
Argedor Information Technologies, Ankara, Turkey
2
Universite Pierre Maire Curie, Paris, France
3
Signal Processing and Machine Learning Lab ESPCI, Paris, France
4
Phonetics and Phonology Laboratory, LPP-CNRS, Paris, France
5
University Paris 3 Sorbonne Nouvelle, Paris, France
6
Unversity of Mons, Mons, Belgium
7
Information Technologies Institute, Centre for Research and Technology Hellas, Thessaloniki, Greece
8
Institute for Educational Technology, National Research Council (ITD-CNR), Palermo, Italy
9
Vocal Tract Visualization Lab, University of Maryland Dental School, Baltimore, U.S.A.
Keywords: Human Computer Interaction, Interactive Game, 3D Model, Ultrasound Sensor, Portable System, Human
Beat Box, Game based Learning.
Abstract: The paper presents an interactive game-like application to learn, perform and evaluate modern contemporary
singing. The Human Beat Box (HBB) is being used as a case study. The game consists of two main modules.
A sensor module that consists of a portable helmet based system containing an ultrasonic (US) transducer to
capture tongue movements, a video camera for the lips, Kinect camera for face gestures, and a microphone
for sound. A 3D environment game module is used to visualize a 3D recording studio as game world with all
of its unique elements like guitars, mixer, amplifier, speakers and a microphone in front of the 3D avatar to
simulate the recording ambience. The game also features a 2D virtual tutor to help the learner by giving oral
and written feedback during the game. He also gives feedbacks during the practice session to improve the
student’s performance. The game is still at its early stages of development and it is been tested using simple
HBB plosive sounds for percussion such as “PTK”.
1 INTRODUCTION
The adoption of Serious Games (SGs), namely games
expressly designed with explicit educational purposes
(Breuer & Bente, 2010), in the teaching practice is
a quite well consolidated trend in the Technology
Enhanced Learning field. At present digital games are
increasingly adopted to sustain learning and training
in a variety of educational fields: school education as
well as military and medical training, etc. (Bellotti, et
al., 2012) (Graafland, et al., 2012) (Chatam, 2009).
This is done for a wide range of target populations,
ranging from children to adults (Charlier, et al.,
2012).
The use of digital games also is not new in the
field of Cultural Heritage (Ott & Pozzi, 2008). As
could be expected, games are more widespread in the
Tangible Cultural Heritage (TCH) area, but a number
of games have also been developed in the field of
Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH), where they are
also considered very promising (Mortara, et al.,
2014). The educational potential of games has been
widely explored and highlighted by researchers
within the wider research area of Game Based
Learning. Beside other important advantages, such as
promoting learners motivation (Garris, et al., 2002)
engagement (Susi, et al., 2007) and self-regulated
learning (Zap & Code, 2009), games are also widely
recognized as potentially adaptive to support the
learning of procedures and gestures (and also of
sequences of gestures, physical actions); in this flow,
they are widely adopted in professional training
640
Al Kork S., U
˘
gurca D., ¸Sahin C., Chawah P., Buchman L., Adda-Decker M., Xu K., Denby B., Roussel P., Picart B., Dupont S., Tsalakanidou F., Kitsikidis
A., Dagnino F., Ott M., Pozzi F., Stone M. and Yilmaz E..
A Novel Human Interaction Game-like Application to Learn, Perform and Evaluate Modern Contemporary Singing - "Human Beat Box".
DOI: 10.5220/0005429506400650
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (MMS-ER3D-2015), pages 640-650
ISBN: 978-989-758-090-1
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
(Martínez-Durá, et al., 2001). The i-Treasures project
(i-Treasures, 2013) aims to exploit this potential of
SGs in the ICH field: their capability of training
motor skills and then the possibility to support
sensorimotor learning for the teaching/learning of
intangible cultural expressions, which are based
mainly on procedural knowledge (namely, knowing
how to do something).
Performing arts such as traditional or modern
singing is usually learned under the supervision of a
master or an expert. So it can be said that such
features requires physical actions to survive as they
are transferred through a master apprentice approach.
A major objective of the i-Treasures project is to
provide students with innovative multi-media human
game-like application for sensorimotor learning
feedback to train specific articulatory strategies for
different type of rare singing, considered an
endangered Intangible Cultural Heritage (UNESCO,
2012).
The i-Treasures project also includes research
about a newly expanding contemporary singing style:
the “Human Beat Box”, where the vocalist imitates
percussive and drum instrument sounds. Beatboxing
is a form of vocal percussion primarily involving the
art of producing drum beats, rhythm, and musical
sounds using one's mouth, lips, tongue, and voice. It
may also involve singing, vocal imitation of
turntables, and the simulation of horns, strings, and
other musical instruments. Beatboxing today is
connected with hip-hop culture, being one of "the
elements", although it is not limited to hip-hop music.
The proposed game-like application is expected to
help those who want to learn the basic of singing or
even make a practice. The game will use 3D
visualization techniques and tools to support the users
in learning or mastering different type of singing
styles. The domain knowledge of real masters will be
transferred to the virtual tutor. Thus, the virtual tutor
will be able to evaluate the user as a real master does.
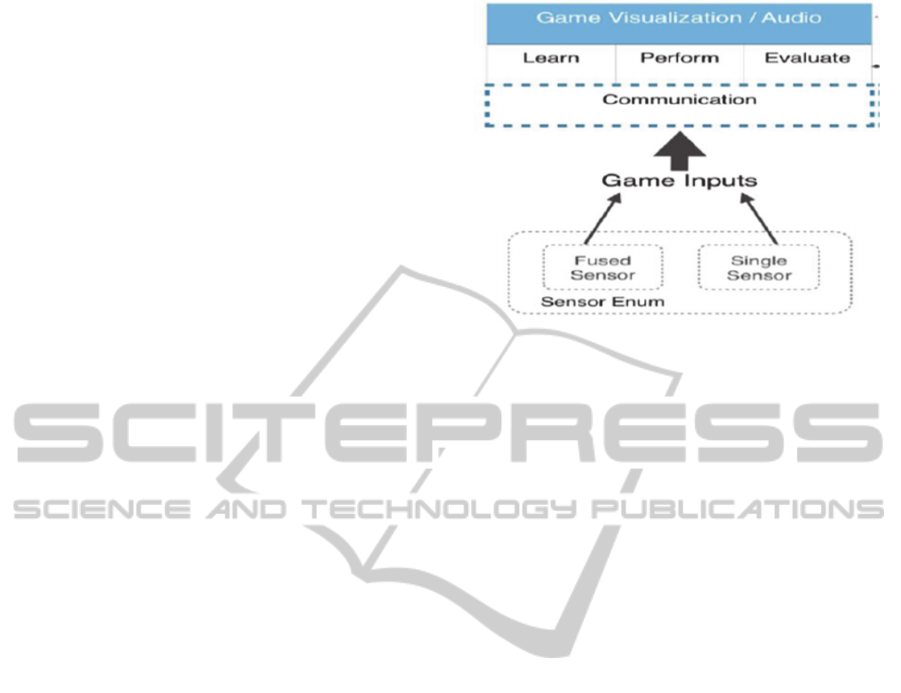
2 GAME ARCHITECTURE
The game architecture of the system is shown in
Figure 1.The system is composed of the following
modules: Sensor input capture module,
Communication module and 3D game environment
module.
Figure 1: Game System Architecture.
2.1 Data Acquisition Module
One of the challenging tasks in developing the
proposed game apprentice is to interface little known
sensors in the game industry such as ultrasound. To
meet the requirement, a portable helmet based system
has been used to capture motor behaviour during
singing and other oral-motor functions in a non-
laboratory experimental environment (Al Kork, et al.,
2014) (Chawah, et al., 2014) (A Jaumard-Hakoun, et
al., 2013). The system, based on vocal tract sensing
methods developed for speech production and
recognition, consists of a lightweight “hyper-helmet”
containing an ultrasonic (US) transducer to capture
tongue movement, a video camera for the lips, and a
microphone for audio capturing as seen in Figure 2.
Moreover, facial data are captured using a Kinect
v1 sensor. Synchronized colour and depth image
streams are used for facial feature tracking and
recognition of facial action units based on an
improved version of the approach presented in
(Tsalakanidou & Malassiotis, 2010).This data is used
to visualize the facial movements of the 3D avatars.
2.2 Architecture of the Communication
Module
The communication module is responsible for
providing bilateral data transfer between the sensors
and the game .The application communicates with
various external entities such as the hyper-helmet,
audio comparison and evaluation server. Figure 3
illustrates the communication architecture.
The module is capable of acquiring multiple video
streams in real-time from the sensors of the hyper-
helmet by using a third party sensor integration and
controlling software called as RTMaps
(S.A.-RTMaps, 2012). Thus the system actually
ANovelHumanInteractionGame-likeApplicationtoLearn,PerformandEvaluateModernContemporarySinging-
"HumanBeatBox"
641
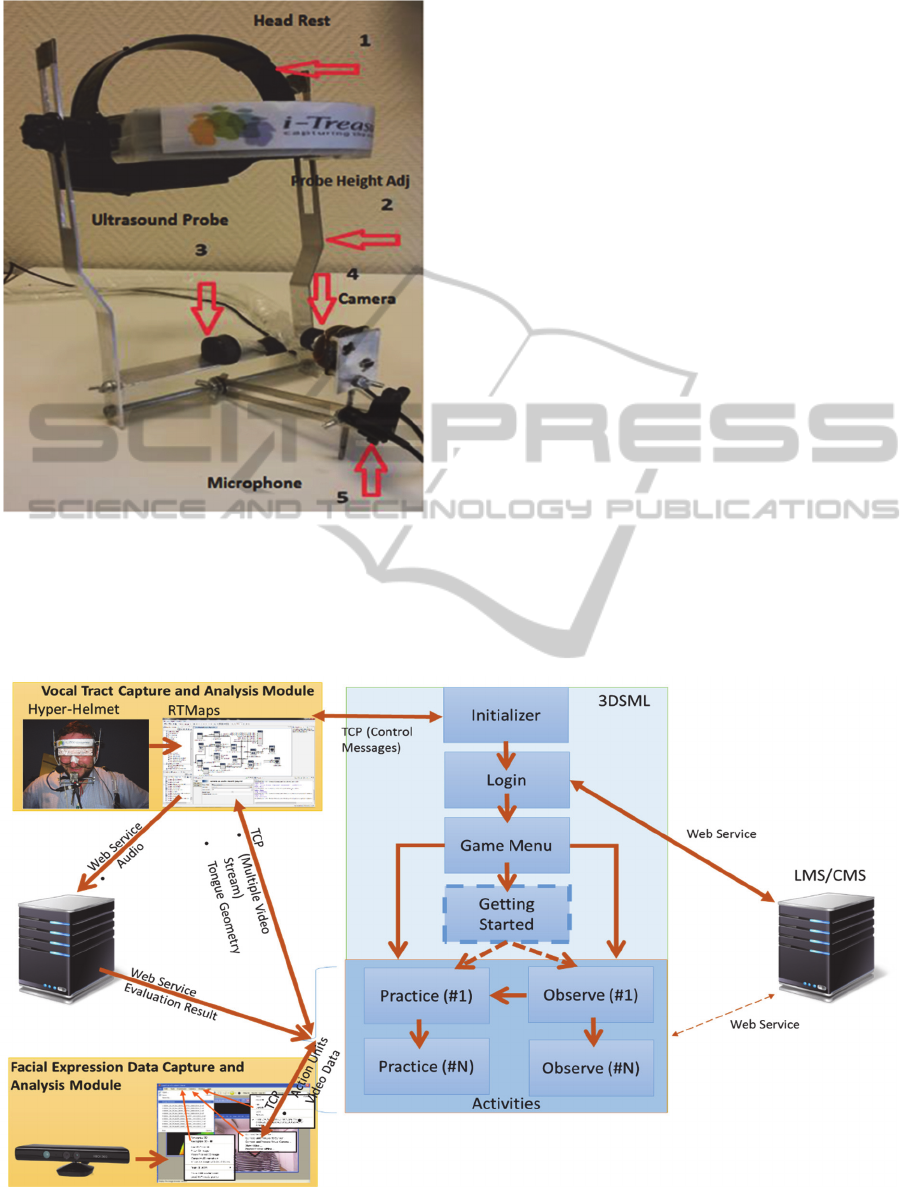
Figure 2: Multi-sensor Hyper-Helmet.
communicates with RTMaps via Transmission
Control Protocol. Besides video, the module also
supports real-time transfer of the 3D Tongue Model’s
vertex positions. The module supports up to 60 fps
data transfer either for video or 3D animation. The
game also gets facial data from the facial expression
data capture and analysis module using TCP/IP
messaging. The communication module also lets the
player control the data capture by sending relevant
commands to the data capture system as well.
The sensor capture module also streams audio data
from leaners to an external server. This
communication is done by a web service. This server
provides the result of audio comparison to the game
via web service. 3DSML communicates with
LMS/CMS via web services. This communication
covers user authentication, expert data download and
learner performance upload. Currently only user
authentication is supported in this first version.
2.3 3D Game Environment Module
The game module will basically provide an interface
for students to learn, and practice HBB and it will also
evaluate the performance and progress of the student.
The performance of the student will be assessed based
on his/her tongue movements and the pitch of the
student’s sound as compared to the expert’s.
2.3.1 Learning Scenario
The Human Beatbox is an artistic form of human
sound production in which the vocal organs are used
Figure 3: Communication Architecture of Singing Game-like Application.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
642

to imitate percussion instruments, but also wind and
string instruments. Therefore, facial and intra-oral
movements of the tongue, lips and jaw are involved
in sound production. The apprentice will be guided by
some description of the sound to be produced and
listening to the sounds to imitate them. These
descriptions can be related to natural sounds such as
imitating animal sounds or mouth noise.
The apprentice will also look at the mouth and
tongue of the expert to try to produce different
sounds. The rhythm is an important dimension in
HBB and hand movement or a metronome can be
added in the scenario. The HBB game will consist
initially of a single lesson, where each isolated sound
will be described and will be demonstrated by the
expert and then imitated by the learner. The
apprentice will go from one step to another until he
succeed and finishes all the stages of the lesson. The
Stages are described as follows:
Stage 1: Imitate the plosive sounds for percussion
“PTK”.
During this stage the student will repeat several
times the three consonants at different rhythm, slow
Pp; Tt; Kk…and fast… prolong each consonant, try
to make an “echo” (Ppppp, Tttttt…). In reverse order
KTP aiming in maintaining the rhythm and the speed
of the articulators’ movement and quality of sound
Play with loudness P(loud) tk (whisper) and alternate
pTk ; ptK The time it takes the student to perform this
task will also be taken into account.
Stage 2: Introduce vowels.
During this stage the student will add a vowel
(PTKKi; Peu; Ti…). The vowels will be produced in
loud and whispered mode.
Stage 3: Add sound effects and nasality.
During this stage the student will add other
consonants (PTK e PT one = Wan ; Wa a wan…)
make a fricative sound (Tsss ; Tsi ; Pfff ; Kiwi …)
Stage 4: Succession of sounds, rhythms and
loudness.
The learner should practice each stage a number
of times, and finally perform all the stages at once.
Once the evaluation score of the student increases, he
will be asked to make other sounds from other
instruments and try to combine then in a harmonious
way. The game will provide auditory and visual
feedback. Figure 4 shows the learning progress
approach of this game.
ivy
1Figure 4: Learning Progress of the HBB Game.
2.3.2 Game Play
In order to develop the human beat box game, the
following assets were prepared: a 2D virtual tutor, 3D
avatars for expert and learner, a 3D tongue model and
a 3D sound recording studio environment.
2.3.2.1 2D Virtual Tutor
The virtual tutor is a 2D illustrated NPC (Non Player
Character), who is designed as a young male beat box
artist. His role is to navigate and help the student by
giving oral and written feedback during the game. He
also gives feedback during the practice phase to
improve the student’s performance. Besides, he
explains the sensors used in this game such as the
components of the hyper-helmet during the getting
started phase. The Virtual Tutor has five different
states for different moods such as happy, explanatory,
unsatisfied, neutral and not bad as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: 2D Virtual Tutor Moods in HBB.
The mood posture is selected by the system based on
the student’s performance during the practice phase.
In addition, all the written feedback provided by the
virtual tutor can be configured via XML files, which
ensures which ensures easy manipulation and
multilingual capabilities. It is also possible to set the
visual style of the expert throughout the game.
2.3.2.2 3D Expert and Learner Avatars
The avatars of the HHB expert and learner are
prepared by using 31 bones for the face and a simple
skeleton for the body. It is possible to map Face
Action Units to these facial animation bones.
Currently, we have prepared 52 blend shapes for the
face. Blend Shapes, which is also known as morph
target animation, is a popular computer animation
technique mainly used for facial animation (Joshi,
2005). Even though this technique is very labour-
intensive, it is useful for generating good looking
animations. For the following versions of the game,
Activity1
Activity2
Activity3 Activity4
ANovelHumanInteractionGame-likeApplicationtoLearn,PerformandEvaluateModernContemporarySinging-
"HumanBeatBox"
643
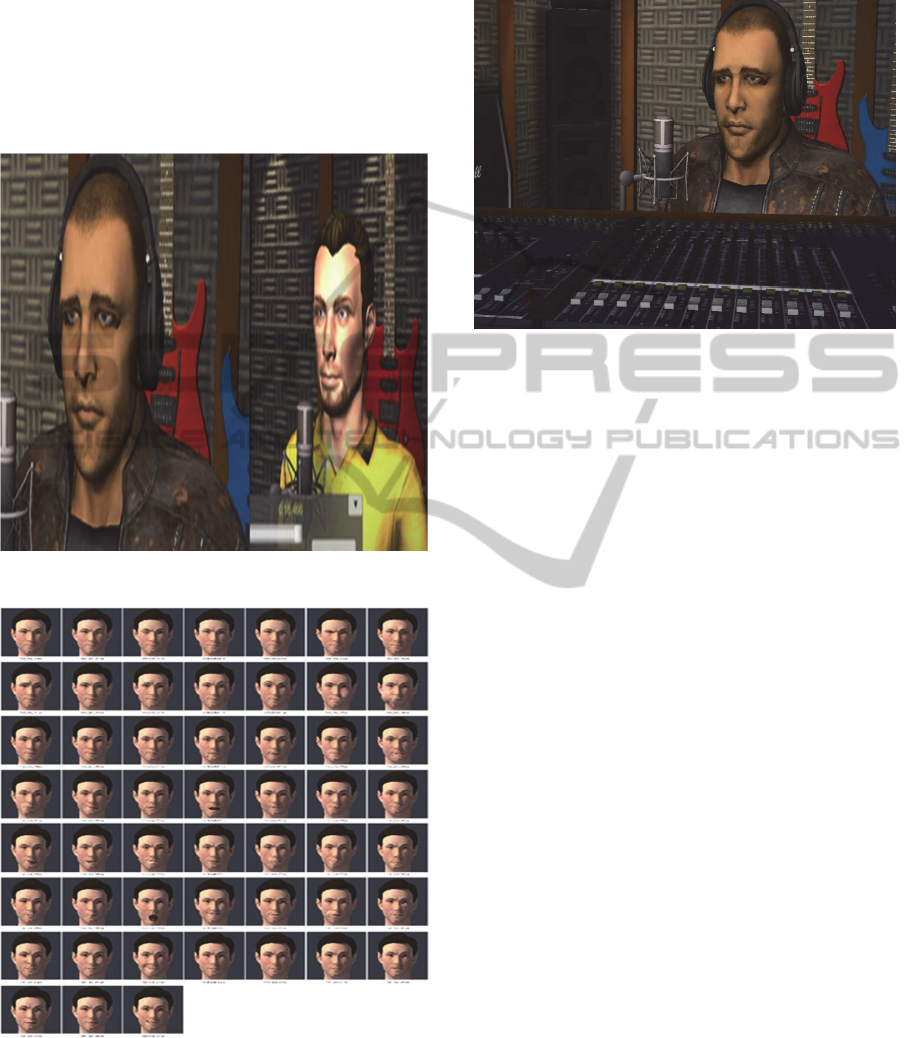
we plan to mainly focus on lips, since the lip
movement is quite important in singing, and produce
more blend shapes for lips. In this way, it will be
possible to visualize the lips more realistically.
3D expert and learner avatars are shown in Figure
6. Figure 7 shows the blend shapes and various
interpolations used for the current version. The expert
avatar is designed as a professional musician while
the learner avatar is designed with casual clothes.
Figure 6: Expert Avatar (Left) and Learner Avatar (Right).
Figure 7: Blend Shapes Prepared for Face Modelling.
2.3.2.3 3d Studio Environment
A 3D recording studio is designed as the game’s
world with all of its unique elements like guitars,
mixer, amplifier, speakers and a microphone in front
of the 3D avatar to simulate the recording ambience
as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: 3D Environment of HBB.
2.3.2.4 User Interface
Distinctive parts of the beat box game are explained
in this section.
2.3.2.4.1 Main Screen
As explained in section 2.3.1, there are four Activities.
Each activity has two different options, which are
“observe” and “practice”, and also a “Getting
Started” activity, which serves as game tutorial, as
shown in Figure 9. The user can click the “Observe”
button to observe the expert performing or click the
“Practice” button to start practicing the beat box
himself. A short description of each activity is
provided on each activity panel, so that the learners
can track the content of the selected activity. Under
each activity description, there is a progress bar that
represents the success rate of the student. Activity 2,
3 and 4 are locked and this is represented with a key
lock on the related panels, because of the fact that the
progress of the student is not enough to unlock further
activities. Activity 1 is also locked at the beginning.
However, when the user completes the “Getting
Started” the first activity is unlocked without any
further process. All of the description texts, buttons,
labels etc. are configurable via the configuration
XML.
2.3.2.4.1.1 Getting Started
When the student clicks on the “Begin” button of the
“Getting Started” panel of the Main Menu, the tutorial
of the beat box game starts. The main purpose of the
“Getting Started” is to teach the basics of the game to
the student. To do so, the 2D virtual tutor explains
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
644
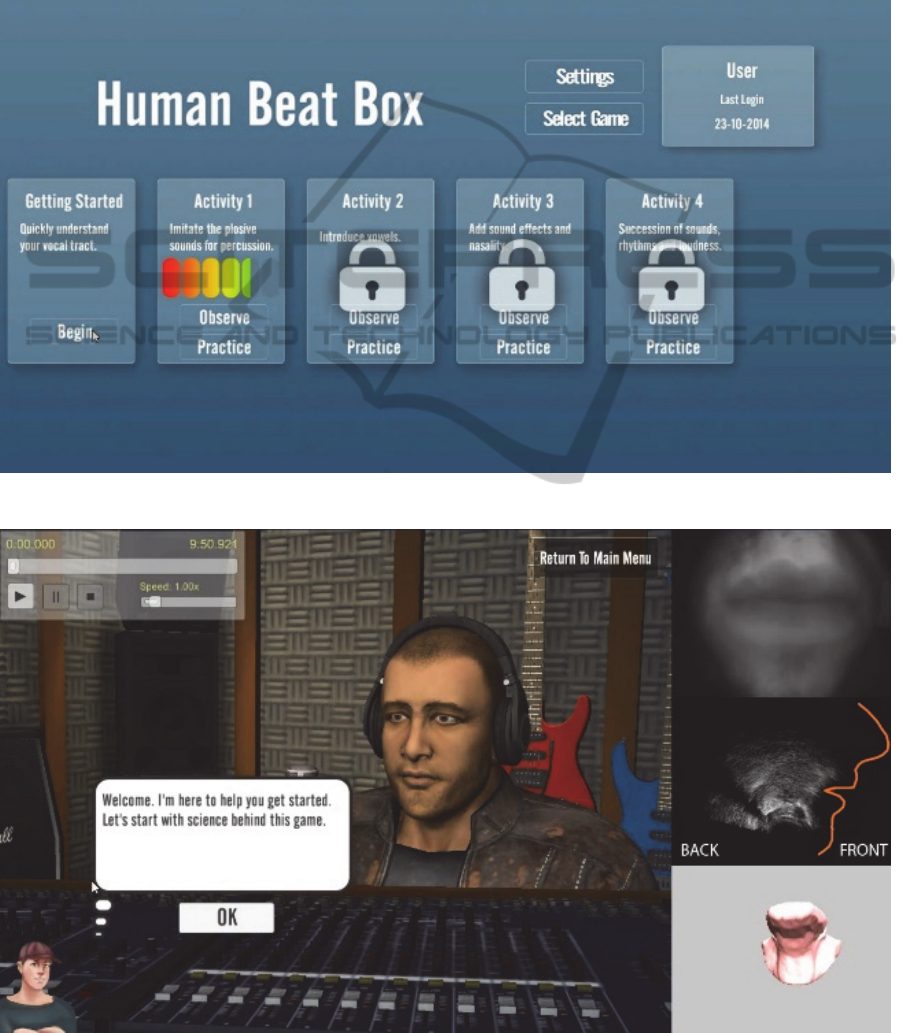
each user interface element and how to use them to
play the game. The 2D virtual tutor comes up from
bottom left of the screen to say what will happen next
as shown in Figure 10.
Afterwards, tutorial continues with the
explanation of the techniques, which are used for
giving feedbacks to the student in beat boxing,
respectively; (a) Tongue position, (b) Using
ultrasound for tongue movement, (c) Description of
the tongue-air interface, (d) Ultrasound image of
tongue, (e) The tongue model. This is shown in Figure
11.
The tutorial proceeds to observe screen
as illustrated. Virtual tutor continues with the
Figure 9: Game Main Menu Screen of HBB Game.
Figure 10: Tutorial beginning of HBB Game with 2D virtual avatar.
ANovelHumanInteractionGame-likeApplicationtoLearn,PerformandEvaluateModernContemporarySinging-
"HumanBeatBox"
645
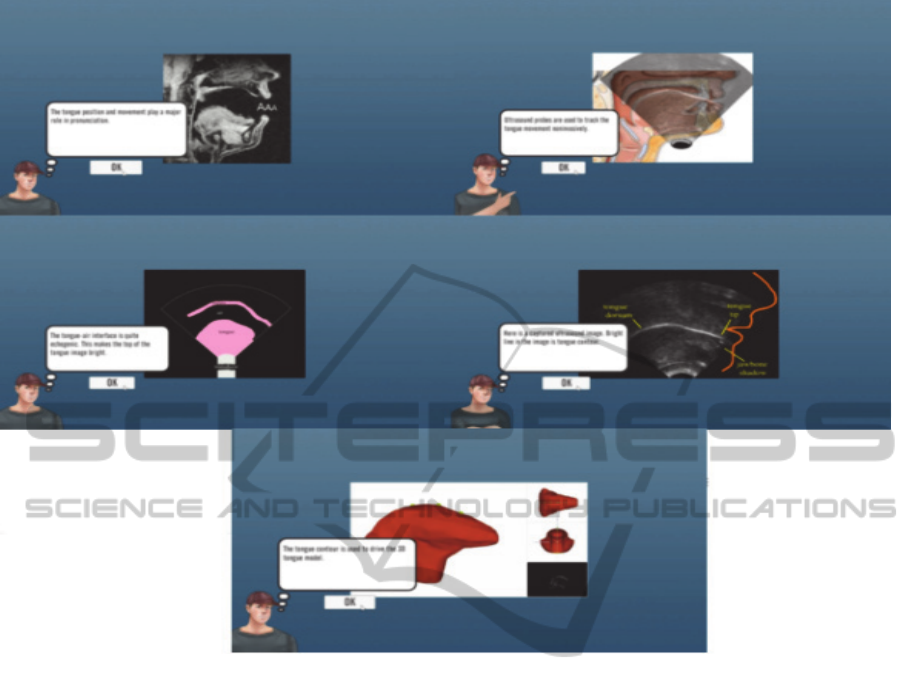
Figure 11: Illustrations of HBB Game Components.
explanation of observe screen elements respectively;
(a) 3D avatar, (b) Animation player, (c) Expert video
clip, (d) Ultrasound image of the tongue, (e) 3D
tongue model. Then 2D virtual tutor navigates student
to practice tutorial. This tutorial works exactly like
observe tutorial. 2D virtual tutor explains each
element on the screen in plain text and verbally. In
practice tutorial, 2D virtual tutor describes each
element respectively: (a) Animation controller of
practice section, (b) All other views on the screen.
Thereafter the virtual tutor explains the usage and
functionality of the sensors and software used in this
game. It is planned to include video tutorial for the
sensors that are not well-known and not easy to use.
In this way it is believed that the user will have the
required knowledge. When the “Getting Started”
ends, it is expected from student to continue to play
the game-like application to learn and improve his
knowledge about human beat box.
2.3.2.4.1.2 Observe Screen
All of the four activities in this game have an observe
scene, which shows the performance of the expert
captured by various sensors. The aim is to let the user
observe the details of each performance before s/he
starts the practice. All of the sensor outputs and
recordings are synchronized. These outputs are all
controlled by the animation controller, which is
located at the bottom center of the screen as shown in
Figure 12. The Observe screen consists of different
visual and functional elements such as the animation
player, expert lip video (window on right top corner),
ultrasound image of the tongue (second window on
the right) and 3D tongue model view (window on
bottom right corner) as shown in Figure 12.There are
also several windows on the right part of the screen
that show the outputs of different sensors.
It is possible to determine which sensor output
windows will be displayed via configuration XML.
Another important aspect of the observe screen is the
way we can change the size of the windows. By
default, the 3D recording studio is displayed as the
big central view. However when the user double
clicks on any window, the views are changed and the
selected window is displayed at the big central
window as shown in Figure 13.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
646
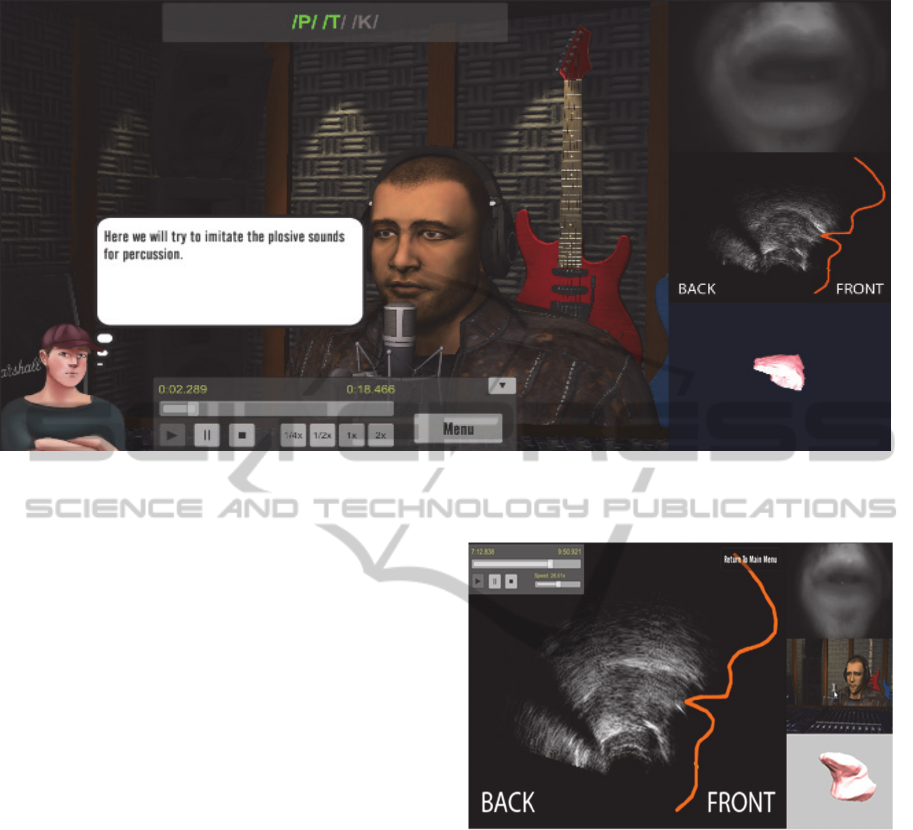
Figure 12: Observe Screen of HBB Game.
Throughout the observe phase, the 2D virtual tutor
comes up from the bottom left of the screen and
explains the HBB sounds to the student. The text of
the virtual tutor’s narration can be modified via the
XML file. The features of the observe screen are all
described in the following sections.
2.3.2.4.1.3 Animation Player
The student controls the animation of the expert
lip/face video, expert tongue ultrasound video, 3D
tongue model and 3D expert avatar through the
animation player. These are all synchronized. It
should also be noted that the audio is also
synchronized with these data. The user is free to
control both the 3D expert avatar and tongue model
by using a freely navigable camera. The animation
player has “Play”, “Pause” and “Stop” buttons like
most of the video players. The animation can be
rewind or forwarded. The speed of the animation can
be controlled as well. The total time of the animation
and video with the current time position on the
animation timeline is also provided as labels on the
animation player.
2.3.2.4.1.3.1 Expert Video Lips
The expert video is provided at the top right of the
observe screen. This video shows either the lips or
face of the expert. Currently, only the lips video is
provided. However, we can display any type of video
content. It is also possible to change the video content
in real-time if both the lip and face videos are
available.
Figure 13: Maximized window of 2D Tongue Ultrasound
mid-sagittal view.
2.3.2.4.1.3.2 Expert Video (Ultrasound)
The observe screen provides the ultrasound sensor
video output which is captured by the “hyper-helmet”
system. The user is expected to observe the upper
contour of the tongue on the mid-sagittal plane. The
video shows the movement of the tongue during
singing. In this window a face silhouette and
directional info are provided to help the user to easily
distinguish the tongue movements. These features are
drawn as an overlay.
2.3.2.4.1.3.3 3D Tongue Model Visualization
The observe screen provides the 3D interactive
ANovelHumanInteractionGame-likeApplicationtoLearn,PerformandEvaluateModernContemporarySinging-
"HumanBeatBox"
647

tongue model (Kele Xu, et al., 2014) which shows the
animation of the tongue of the expert Our simulations
use ArtiSynth (J. E. Lloyd, et al., 2012), a 3D finite
mesh model of the tongue consisting of 14,000 nodes.
In Figure 14, six nodes (yellow points) are chosen as
anchor nodes corresponding to the hyoid bone and the
short tendon as discerned in the ultrasound image.
These anchor nodes are held fixed during the
simulation. We must then set several constraint nodes
(green points) lying on the mid-sagittal contour in the
ultrasound images, in order to drive tongue motion.
The assumption is that the behaviour of the 3D model
will be approximately correct if the movement of the
driven 2D sagittal points is correct. Linear constraints
on 3D movements can be integrated into an Euler-
Lagrange equation using the Lagrange multiplier
method. In Figure 15, the smaller images next to the
main 3D display show two ultrasound frames, from
which displacements are calculated. These
displacements are then passed to the constraint nodes
on the 3D tongue model mid-sagittal surface in order
to drive the model.
Figure 14: An overview of interface for the proposed
system.
Figure 15: : Six Anchor nodes (yellow nodes) on the tongue
mesh at the rest position and Constraint Nodes (green
nodes) on the mid-sagittal contour at the rest position of
tongue model.
Currently, we visualized and presented the same
tongue model used in ArtiSynth in Unity 3D as an
interactive window. The learner can freely navigate
this tongue model. It is possible to change the view to
top, lateral etc, and to zoom in and out. The research
to transfer animation results to the game environment
is still under progress. However, the technical
implementation for tongue animation has been
completed; thus, in future versions the game will
display the full tongue animation The system has
been tested with simulation data and real time data
streaming. Figure 16 shows the highly detailed 3D
tongue model which is made of 14.000 vertices.
Figure 16: 3D Interactive Tongue Model in Game
Environment.
2.3.2.4.1.4 Main Window-3D Expert Avatar
This 3D virtual environment represents a recording
studio. In this environment, the user is free to navigate
by using the virtual camera. The face of the avatar is
animated by using the data derived from the Kinect
sensor through the facial analysis software. This
animation is also synchronized with the rest of the
other sensor outputs.
2.3.2.4.1.4.1.1 Sound Progress Window
The sound that the expert imitates is shown at the
center top as shown in figure 12. Here the plosive
sounds P/T/K are visualized. It should be noted that
this text is also synchronized with the other outputs.
This text and the length are also defined in the
configuration XML. The played part is highlighted
with green to show the current location of the
performed sound.
2.3.2.4.1.5 Practice Screen
All of the four activities in this game have a practice
scene enabling the learner to practice the selected
activity. The practice scene shows the 3D avatar at the
center screen, the sensor data of the expert on the right
panel and the sensor data of the player on the left as
shown in Figure 17.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
648

Similar to the observe scene, the sensor data
windows are all configurable. Thus, whenever it is
required to simplify the scene, some windows may
not be displayed. This can be easily set via the
configuration XML. The practice starts with the
introduction of the virtual tutor. After providing some
basic instructions, the virtual tutor asks the user to get
ready and counts down. The learner imitates the
requested sound.
Figure 17: Practice Screen of HBB Game.
After the performance is completed, the recorded
sound is sent to the remote server that is responsible
of audio analysis and comparison. This server
receives the audio file including the sound produced
by the learner and compares it with the corresponding
expert sound (which is part of the Human Beat Box
experts’ database). Following the completion of
comparison, the software generates a detailed text file
that contains the similarity ratio, sub-parts and
corresponding similarities etc. This text file is send
back to the game via web-service. This output is used
to evaluate the performance of the learner. It should
be noted that this remote evaluation takes very short
time and it does not introduce any lag or latency. This
evaluation approach was designed for the first version
of the game However, in future versions there will be
improvements regarding this approach and more
information will be taken into account by the
evaluation algorithm such as the position of the
tongue, the opening of the mouth, etc.
After getting the evaluation result, the virtual tutor
provides feedback about the performance of the
learner by using the corresponding grading text, e.g.
“You need to improve! Let’s do it again!”, “Good
performance! Just needs a little bit more!”,
“Outstanding performance! You are ready for the
next activity” etc. The animation controller in the
practice screen is used to record the learner’s
performance and repeat it whenever needed.
3 CONCLUSIONS
A first version of an interactive game-like application
to learn, perform and evaluate modern contemporary
singing focusing on the Human Beat Box case study
was developed in the context of the i-Treasures
project. The game integrates several state-of-the-art
sensors such as Kinect for facial data capture and a
prototype multi-sensor hyper-helmet for vocal tract
capture. It provides a user-friendly interface including
an engaging 3D recording studio environment and
singer avatars and visualizes a variety of sensor
outputs on user demand. A virtual tutor guides the
user through the game and provides real-time
feedback for the evaluation of the user‘s performance
in different singing activities.
The developed game framework is capable of
providing bilateral communication with external
sensors and third party sensor control software such
as RTMaps. The framework supports UDP and
TCP/IP based network communication as well as web
services. More sensors can be included in the system
without additional effort. Besides communication
utilities, the framework enables game designers and
domain experts to configure the application easily by
setting the fields of an XML file.
4 FUTURE WORK
An updated version of the HBB game is currently
under development. We plan to update the game
design, improve the game play and integrate learning
analytics so as to increase user engagement and
improve the game’s educational effectiveness. We
also plan to focus more on educational aspects, since
without meeting specific educational targets, the final
output will be more a technology demonstration
rather than an educational tool.
From a technical perspective, we plan to integrate
Kinect v2 in future versions. This sensor will help us
to better visualize and animate the lips and the face.
We also plan to develop a mobile version of this
game, mainly intended for observation and learning
rather than practicing HBB.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is funded by the European Commission via
the i-Treasures project (Intangible Treasures -
Capturing the Intangible Cultural Heritage and
Learning the Rare Know-How of Living Human
ANovelHumanInteractionGame-likeApplicationtoLearn,PerformandEvaluateModernContemporarySinging-
"HumanBeatBox"
649

Treasures FP7-ICT-2011-9-600676-i-Treasures). It is
an Integrated Project (IP) of the European Union's 7th
Framework Programme 'ICT for Access to Cultural
Resources.
REFERENCES
A Jaumard-Hakoun, et al., 2013. Capturing, Analyzing, and
Transmitting Intangible Cultural Heritage with the i-
Treasures Project. Edinburgh, UK, s.n.
Al Kork, S. K. et al., 2014. A Multi-Sensor Helmet to
Capture Rare Singing, An Intangible Cultural Heritage
Study. Cologne, Germany, s.n.
Bellotti, F. et al., 2012. Designing a course for stimulating
Entrepreneurship in higher education through Serious
Games. Procedia Computer Science, Volume 15, pp.
174-186.
Breuer, J. & Bente, G., 2010. Why so serious? On the
Relation of Serious Games and Learning - Eludamos.
Journal for Computer Game Culture,, 4(1), pp. 7-24.
Charlier, N., Ott, M., Remmele, B. & Whitton, N., 2012.
Not Just for Children: Game-Based Learning for Older
Adults. Cork,Ireland, In 6th European Conference on
Games Based Learning,, pp. 102-108.
Chatam, R., 2009. The 20th-century revolution in military
training. In: E. K, ed. Development of professional
expertise. Toward measurement of expert performance
and design of optimal learning environements. New
York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 27-60.
Chawah, P. et al., 2014. An educational platform to capture,
visualize and analyze rare singing. Singapore, s.n.
Garris, R., Ahlers, R. & Driskell, J. E., 2002. Games,
motivation, and learning: A research and practice
model. Simulation & Gaming, 33(4), pp. 441-467.
Graafland, M., Schraagen, J. M. & Schijven, M. P., 2012.
Systematic review of serious games for medical
education and surgical skills training.. British Journal
of Surgery, Volume 99, p. 1322–1330.
i-Treasures, 2013. The i-Treasures project. (Online)
Available at: www.i-treasures.eu/
J. E. Lloyd, Stavness, I. & S. Fels, 2012. “ArtiSynth: A fast
interactive biomechanical modeling toolkit combining
multibody and finite element simulation. Springer,, pp.
344-394.
Joshi, P., 2005. Learning controls for blend shape based
realistic facial animation. s.l., ACM SIGGRAPH 2005
Courses.
Kele Xu, et al., 2014. 3D tongue motion visualization based
on ultrasound image sequences. Singapore, s.n.
Martínez-Durá, M. et al., 2001. Serious Games for Health
and Safety Training. In: M. Prensky, ed. Digital game-
based learning. New York: Mc Graw-Hill.
Mortara, M. et al., 2014. Learning Cultural Heritage by
serious games. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 15(3), pp.
318-325.
Ott, M. & Pozzi, F., 2008. ICT and Cultural Heritage
Education: Which Added Value?. In: M. e. a. Lytras,
ed. Emerging Technologies and Information Systems
for the Knowledge Society - Lecture Notes in Computer
Science. Berlin: Springer , pp. 131-138.
S.A.-RTMaps, I., 2012. Intempora S.A.-RTMaps. (Online)
Available at: http://www.intempora.com/
Susi, T., Johanesson, M. & Backlund, P., 2007. Serious
Games - An Overview, Skövde, Sweden: University of
Skövde.
Tsalakanidou, F. & Malassiotis, S., 2010. Real-time 2D+3D
Facial Action and Expression Recognition. Pattern
Recognition, 43(5), pp. 1763-1775.
UNESCO, 2012. UNESCO. (Online)
Available at: http://www.unesco.org/culture/ich/en/
convention.
Zap, N. & Code, J., 2009. Self-Regulated Learning in Video
Game Environments. In: R. Ferdig, ed. Handbook of
Research on Effective Electronic Gaming in Education.
s.l.:Hershey, pp. 738-756.
VISAPP2015-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
650
