
Physiology-based Affect Recognition During Driving in Virtual
Environment for Autism Intervention
Dayi Bian
1
, Joshua Wade
3
, Amy Swanson
6
, Zachary Warren
4,5,6
and Nilanjan Sarkar
1,2
1
Department of Electrical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, U.S.A.
2
Mechanical Engineering and
3
Computer Science, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, U.S.A.
4
Department of Pediatrics and Psychiatry, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, U.S.A.
5
Department of Special Education, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, U.S.A.
6
Vanderbilt Kennedy Center, Treatment and Research Institute of Autism Spectrum Disorders, Vanderbilt University,
Nashville, TN, U.S.A.
Keywords: Virtual Reality, Autism intervention, Affect recognition, Physiological sensing.
Abstract: Independent driving is believed to be an important factor of quality of life for individual with autism
spectrum disorder (ASD). In recent years, several computer technologies, particularly Virtual Reality (VR),
have been explored to improve driving skills in this population. In this work a VR-based driving
environment was developed for skill training for teenagers with ASD. Eight channels of physiological
signals were recorded in real time for affect recognition during driving. A large set of physiological features
were investigated to determine their correlation with four categories of affective states: engagement,
enjoyment, frustration and boredom, of teenagers with ASD. In order to have reliable reference points to
link the physiological data with the affective states, the subjective reports from a therapist were recorded
and analyzed. Six well-known classifiers were used to develop physiology-based affect recognition models,
which yielded reliable predictions. These models could potentially be used in future physiology-based
adaptive driving skill training system such that the system could adapt based on individual affective states.
1 INTRODUCTION
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has a prevalence
rate as high as 1 in 68 children in U.S. (CDC 2014).
While at present there is no single accepted
intervention, treatment, or known cure for ASD,
there is growing consensus that intensive behavior
and educational intervention programs can
significantly improve long-term outcomes for
individuals and their families (Rogers 1998; Cohen,
Amerine-Dickens et al. 2006). However, many
current intervention approaches show limited
improvements in functional adaptive skills because
traditional skill-based methodologies often failed to
systematically match intervention strategies to
specific underlying processing deficits associated
with targeted skills. Additionally, such intervention
approaches may have difficulties creating
opportunities for addressing such skills and deficits
within and across naturalistic settings in
appropriately intensive dosages (Goodwin 2008). In
this regard, technological intervention paradigms,
including Virtual Reality (VR) platforms, have been
suggested as potentially powerful tools for
addressing these limits of current intervention
paradigms. Moreover, given the limited availability
of professionals trained in autism intervention, it is
likely that emerging technology will play an
important role in providing more accessible and
individualized adaptive intervention in the future
(Standen and Brown 2005; Tartaro and Cassell 2007;
Lahiri, Bekele et al. 2013).
VR-based intervention could be utilized to help
children with ASD generalize learned skill to the
real world not only by providing more control over
how the basic skills are taught, but also the ability to
systematically employ and reinforce these skills
within many different, controllable, realistic
interaction environments. In addition, the virtual
world can be designed to break down, repeat, add
and subtract aspects of the environment in any
manner necessary to achieve a task goal. While VR-
based ASD intervention has become an active
research field in recent years, more in-depth studies
137
Bian D., Wade J., Swanson A., Warren Z. and Sarkar N..
Physiology-based Affect Recognition During Driving in Virtual Environment for Autism Intervention.
DOI: 10.5220/0005331301370145
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Physiological Computing Systems (PhyCS-2015), pages 137-145
ISBN: 978-989-758-085-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

are required to explore how skills learned in virtual
environment are translated into real-world situations.
Historically, VR environments applied to
assistive intervention for children with ASD were
designed to develop skills based on performance
only (e.g., correct or incorrect and some other
performance metrics). However, current research
focuses the development of VR and other
technologies that respond not only to explicit
human-computer interactions (e.g., keyboard, mouse,
joystick, etc.), but also to implicit interactions like
eye gaze and physiological signals (Wilms,
Schilbach et al. 2010; Bekele, Lahiri et al. 2013;
Lahiri, Bekele et al. 2013). Such methods may offer
potential to individualize applications. Ultimately,
VR systems that not only assess performance in
specific task but also measure eye gaze or
physiological markers of engagement may lead to
optimization of learning (Welch, Lahiri et al. 2009;
Lahiri, Bekele et al. 2013).
The main objective of this paper is to explore the
reliability of using physiological signals to detect
affective states in a VR-based driving simulation
environment. The results show that physiological
signals can be used as a reliable way to detect
participants’ affective states in a driving task and
these affective states together with performance
could potentially be used to alter VR interactions.
While there exists a body of literature that
discusses interventions for individuals with ASD to
develop social skills, language development and
emotion recognition (Sundberg and Partington 1998;
Bauminger 2002; Golan, Ashwin et al. 2010), only a
few studies have addressed how to improve driving
skills of ASD population. Cox and his colleagues’
study (Cox, Reeve et al. 2012) reported parents’
experiences about driving of young adults with ASD
and provided suggestions to teach driving skills for
ASD teenagers. Huang et al. (Huang, Kao et al. 2012)
also addressed the factors associated with driving in
teenagers with ASD. Reimer and his colleagues
(Reimer, Fried et al. 2013) explored the differences
between an ASD group and a control group in terms
of physiology. However, only standard statistical
techniques were used in this study instead of
detecting affective states by using physiological
signals. Our previous study (Wade, Bian et al. 2014)
explored the differences between these two groups
in a more comprehensive way. These studies provide
us with useful information to design the driving
system and are the foundation of the proposed work.
As far as we know, there is no work on physiology-
based affect detection in driving skill training system
for the ASD population.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section II, we
provide a brief background on VR-based driving
task - the overall system description and how
physiology is used to measure the affective states of
the participants. This section is followed by a
description of the driving task. In Section IV, we
focus on the physiology-based affect detection
system description and results of physiological data
analysis. The implication of our results and future
work are discussed in the last section.
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The Virtual Reality (VR) based driving system
contained a VR module and three subsystems, which
were a peripheral physiological data acquisition
module, an EEG data acquisition module and an eye
tracker module (Fig. 1).
The virtual environment was developed via the
Unity game engine (www.unity3d.com). Within
Unity, we developed a graphical user interface,
created behavior for vehicles, pedestrians and traffic
lights, designed the driving scenario and embedded
traffic rules. Participants interacted with the driving
environment by operating a Logitech G27 driving
controller that was mounted on a playseat (Fig. 2).
The VR system was modeled as a video game with
three difficulty levels: easy, medium and hard. Each
level contained three assignments. Each assignment
had eight trials which were designed in order to
improve specific driving skill such as turning, speed-
maintenance, merging and following traffic laws.
Physiological data, EEG data and eye gaze data were
recorded continuously from the beginning of the
experiment to the end. A therapist rated the
participant’s affective states via a custom-designed
online rating program. More details of VR module
could be found in our previous papers (Bian, Wade
et al. 2013; Wade, Bian et al. 2014).
In this work, we only focused on the physiology-
based affect recognition during driving in VR. Four
categories of affective states, engagement,
enjoyment, frustration, boredom, were chosen
because of their importance in driving (Baker,
D'Mello et al. 2010) as well as their detectability
using peripheral physiological signals (Bradley and
Lang 2000; Sarkar 2002; Rani, Sarkar et al. 2003;
Liu, Rani et al. 2006; Welch, Lahiri et al. 2009). As
can be seen from the framework of our study (Fig. 1),
establishing an affect recognition model could lead
to the development of an adaptive closed-loop
driving skill training system.
PhyCS2015-2ndInternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
138
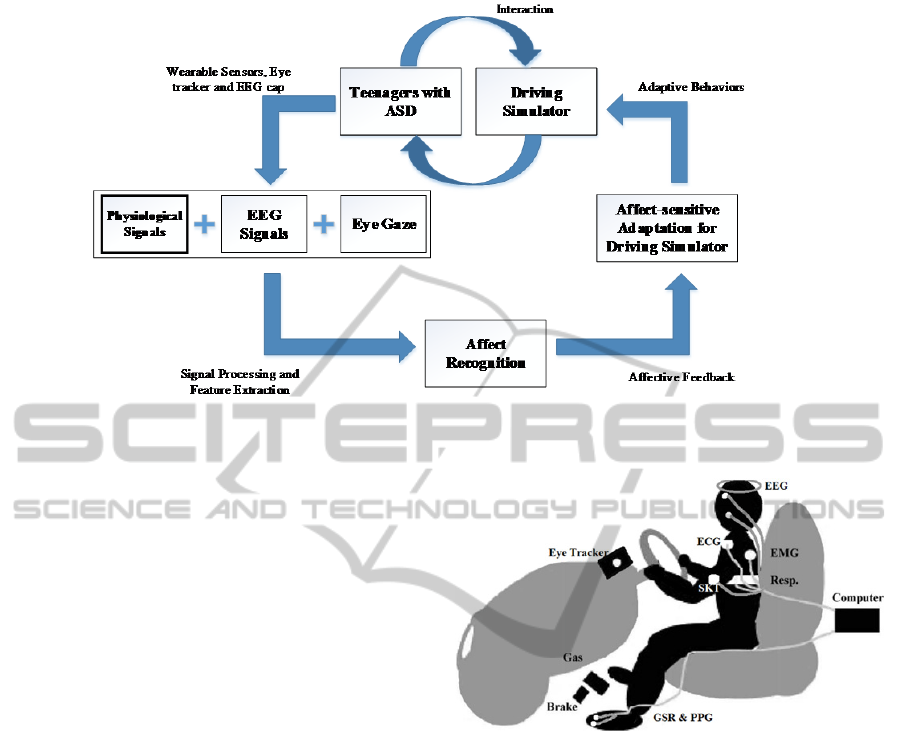
Figure 1: Framework overview.
3 METHODS AND MATERIALS
3.1 Experimental Setup
The physiological signals were collected using the
Biopac MP150 physiological data acquisition system
(www.biopac.com) with a sampling rate of 1000 Hz.
Several physiological signals were investigated. The
acquired physiological signals were broadly
classified as cardiovascular activities including
electrocardiogram (ECG), photoplethysmogram
(PPG); electrodermal activities (EDA) including
tonic and phasic responses from galvanic skin
response (GSR); electromyogram (EMG) activities
from Corrugator Supercilii, Zygomaticus Major, and
Upper Trapezius muscles; respiration and skin
temperature.
These signals were measured by using light-
weight, non-invasive wireless sensors (Fig. 2). ECG
signal was collected from the chest using two
disposable electrodes to record electrical activity
generated by the heart muscle. PPG and GSR were
measured from toes instead of fingers in order to
reduce the motion artifact from driving. EMG was
measured by placing surface electrodes on
Corrugator Supercilii and Zygomaticus Major and
Upper Trapezius muscles. Respiration was used to
measure changes in thoracic circumference that
occur as a participant breathes. Skin temperature was
collected from the upper arm by using a temperature
sensor. In addition, an EEG cap and an eye tracker
were also used to detect EEG signal and eye gaze in
this setup.
Figure 2: Physiological sensors setup.
A socket-based communication module was
developed to transmit task-related (e.g., trial
start/stop) event triggers from the virtual driving
environment to the Biopac. Physiological signals
along with task-related event triggers were sent over
an Ethernet link to a physiological data logger
computer to enable acquiring and logging of the
signals in a time-synchronized manner with the VR-
based driving task (Fig. 3).
3.2 Procedure
Each participant completed six sessions in different
days. The first and last session were pre and post
sessions, which contained the exact same
assignments. Participants usually completed a single
session within approximately 60 minutes. At the
start of each session, physiological sensors and EEG
cap were placed on a participant’s body and the eye
tracker was calibrated. Participants watched a short
Physiology-basedAffectRecognitionDuringDrivinginVirtualEnvironmentforAutismIntervention
139
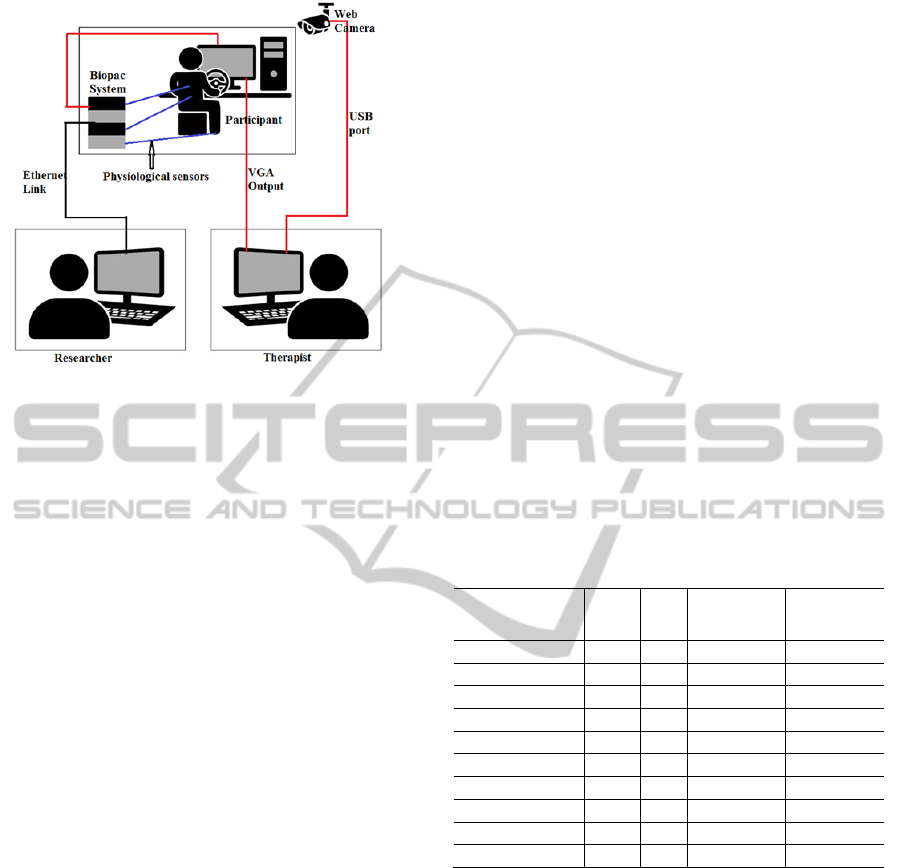
Figure 3: Experimental setup diagram.
instruction video which explained basic instructions
and game controls. After the tutorial, participants
were asked to remain calm and relax for three
minutes during which physiological, EEG, and eye
gaze baseline data were collected. The baseline data
were later used to offset environmental variability.
Participants also had three minutes free practice in
which there were no pedestrians and no other
vehicles in the VR environment. This practice mode
allowed participants to familiarize themselves with
the game controls and virtual environment.
After the three-minute practice, participants
began the first of three assignments. Through the
assignment, participants followed the navigation
system and tried to obey traffic rules. Disobeying
any traffic rules (i.e., running red light) caused a
performance failure. In addition, in gaze contingent
group, failing to look at a specific region of interest
in specific trials (i.e., did not look at speedometer in
school zone) also caused a gaze failure. Four failures
would cause the assignment end and the game would
go back to assignment selection menu. Time
duration for each assignment varied from 2 minutes
to 5 minutes depending on the participants’
performance.
Because of suspected unreliability of self-report of
teenagers with ASD, an experienced therapist was
involved in the experiment. The therapist was seated
next to the experiment room, watching the
experiment from the view of two cameras (Fig. 3).
The therapist rated the participants’ affective states
in four categories: engagement, enjoyment,
frustration and boredom by using a continuous rating
scale from 0 to 9 via an online rating program. For
each assignment, an overall rating was given after
the assignment. Also, the therapist provided ratings
when she felt the participants had obvious affective
state changes.
3.3 Participants
We have recruited 12 male teenagers with ASD for
this phase of the study. While it was not our
intention to recruit all male participants, they were
recruited randomly through the existing university
clinical research registry and happened to be all
males. This may partially be due to the fact that
ASD prevalence in male population is four times as
high as it is for female population (CDC 2014). All
participants had a clinical diagnosis of ASD from a
licensed clinical psychologist as well as cores at or
above clinical cutoff on the Autism Diagnostic
Observation Schedule (Lord, Risi et al. 2000). The
Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval was
sought and received for conducting the experiment.
Ten participants’ physiological data were used for
this paper because two of them were not able to
follow the instructions to get valid physiological
data.
Table 1: Participant data.
Participant NO. Age IQ
ADOS total
raw core
ADOS CSS
ASD01 13.6 -- -- --
ASD02 15.1 80 16 9
ASD03 14.3 86 14 8
ASD04 14.6 99 -- --
ASD05 17.1 118 8 5
ASD06 13.2 108 14 8
ASD08 17.5 125 13 8
ASD09 15.5 117 11 7
ASD10 16.6 88 22 10
ASD12 14.1 -- 11 7
Note: ADOS_CSS = Autism Diagnostic Observation
Schedule Calibrated Severity Score; IQ = composite score:
Differential Ability Scales (General Conceptual Ability) or
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (Full Scale IQ).
4 PHYSIOLOGICAL DATA
ANALYSIS
In this study, a group model was developed to
classify affective states in four categories:
engagement, enjoyment, frustration and boredom. A
90-s window was chosen for sampling the
continuously-recorded physiological data. The 90-s
window was chosen for several reasons: it
approximates the time needed for autonomic signal
PhyCS2015-2ndInternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
140

such as skin conductance to recover and it also
provides a level of smoothing when the features
were extracted. The samples were labeled by the
therapist’s overall rating for each assignment. The
therapist’s ratings were mapped into high and low
intensity for each category for binary classification.
The recorded physiological signals were
preprocessed for feature extraction. First, each signal
was filtered using different filters such as high/low
pass filter, notch filter etc. to reject outliers and
artifacts. The signals were then standardized to be
zero mean and unity standard deviation. In addition,
baseline wander was removed from the PPG signal
before peak detection as this signal is known to be
affected by baseline wander.
Several features were extracted for each channel
of physiological signal. A brief explanation for all
the features are listed in Table 2.
The Waikato Environment for Knowledge
Analysis (WEKA) (Hall, Frank et al. 2009), which is
recognized as a landmark system in machine
learning nowadays, was used to do feature selection
and classification in this study. For each category,
CorrelationAttributeEval (Hall 1999) algorithm was
used to select features. This algorithm evaluated the
value of a feature by measuring the correlation
between it and the class. It ranked feature subsets
according to a correlation based heuristic evaluation
function. The bias of the evaluation function was
toward subsets that contain features that were highly
correlated with the class and uncorrelated with each
other. Irrelevant features were ignored because they
would have low correlation with the class.
Redundant features were screened out as they would
be highly correlated with one or more of the
remaining features. Top ten features (Table 3) that
had the highest correlations with the classes were
chosen for further classification.
Six different well-known classifiers were used
for classification for each category. These classifiers
were:
BayesNet: SimpleEstimatior estimator and K2
search algorithm were chosen.
NaiveBayes: Numeric estimator precision values
were chosen based on analysis of the training data.
SVM: Radial basis function was chosen with a
degree of 3.
MultiLayerPerceptron: HiddenLayers were
chosen by using (attribs + classes) / 2, learningRate
was 0.3.
RandomForest: The number of trees to be
generated was 10, maxDepth was unlimited.
J48 DecisionTree: The minimum number of
instances per leaf was 2, 1 of 3 folds data was used
for reduced-error pruning.
10-fold cross validation was used. The
classification accuracies for each category from
different classifiers are shown in Figure 4.
The highest accuracy for engagement, enjoyment,
frustration and boredom were 77.78%, 79.63%,
79.63% and 81.48%, respectively. These results are
comparable to the accuracy of most up-to-date
affective computing systems (Tao and Tan 2005;
Jerritta, Murugappan et al. 2011).
As we can see from the selected 10 features of
each category, PPG, RSP, SCR, EMG_C and
EMG_Z are most common for the chosen affective
states. This indicates the possibility of using a
smaller set of features with a relatively low
computational cost for a potential closed-loop
system.
In this study, we focused on developing a group
affective state prediction model instead of model for
each individual. In the future, we want to use this
group model to provide affective state feedback in a
closed-loop system and potentially develop a more
efficient driving system to teach teenagers with ASD
basic driving skills.
5 DISCUSSION
There is a growing consensus that development of
computer assistive therapeutic tools can make
application of intensive intervention for teenagers
with ASD more readily accessible. In recent years,
several applications of advanced intervention that
address deficit in driving for teenagers with ASD
were investigated. However, these application
lacked the ability of detect the affective cues of the
teenagers, which could be crucial given the affective
factors of teenagers with ASD have significant
impacts on the intervention practice.
In this work, we presented a physiology-based
affect recognition framework for teenagers with
ASD. 68 features were extracted from the recorded
physiological data. Subsequently 10 features were
selected by using CorrelationAttributeEval algorithm
to overcome the overfitting problem. Six most
commonly used machine leaning algorithms were
used to classify four category of affective states. The
developed model could reliably recognize affective
states of the teenagers with ASD and provide the
basis for physiology-based affect-sensitive driving
skill training system.
In the future, a real-time affect recognition
system which dynamically shape the driving task
will be developed. We will also incorporate EEG
Physiology-basedAffectRecognitionDuringDrivinginVirtualEnvironmentforAutismIntervention
141

Table 2: Physiological features.
Physiological signal Feature extracted Label used Unit of measurement
Electrocardiogram
(ECG/EKG)
Sympathetic power
Parasympathetic power
Very low-frequency power
Ratio of powers
Mean Interbeat Interval (IBI)
Std. of IBI
power_sym
power_para
power_vlf
para_vlf
para_sym
vlf_sym
mean_ibi_ekg
std_ibi_ekg
Unit/s
2
Unit/s
2
Unit/s
2
No unit
ms
Standard deviation(no
unit)
Photoplethysmogram
(PPG)
Mean and std. of amplitude of the peak
values
Mean and std. of heart rate variability
ppg_peak_mean
ppg_peak_std
hrv_mean
hrv_std
µV
No unit
ms
No unit
Electrodermal activity
(EDA)
Mean and std. of tonic activity level
Slope of tonic activity
Mean and std. of amplitude of skin
conductance response (phasic activity)
Rate of phasic activity
Mean and std. of rise time
Mean and std. of recovery time
SCL_mean
SCL_sd
SCL_slope
SCR_mean
SCR_sd
SCR_rate
tRise_mean
tRise_std
tHRecovery_mean
tHRevovery_sd
µS
µS/s
µS
µS
Response peaks/s
Electromyographic
Activity
(EMG)
Mean of Corrugator, Zygomaticus and
Trapezius activities
Std. of Corrugator, Zygomaticus and
Trapezius activities
Slope of Corrugator, Zygomaticus and
Trapezius activities
Number of burst activities per minute of
Corrugator, Zygomaticus and Trapezius
Mean of Corrugator, Zygomaticus and
Trapezius burst activities
Std. of Corrugator, Zygomaticus and
Trapezius burst activities
Mean and Median frequency of
Corrugator, Zygomaticus and
Trapezius
Mean of the amplitude of Corrugator,
Zygomaticus and Trapezius burst
activities
Cemg_mean
Zemg_mean
Temg_mean
Cemg_std
Zemg_std
Temg_std
Cemg_slope
Zemg_slope
Temg_slope
Cburst_count
Zburst_count
Tburst_count
Cburst_mean
Zburst_mean
Tburst_mean
Cburst_std
Zburst_std
Tburst_std
Cfreq_mean
Cfreq_med
Zfreq_mean
Zfreq_med
Tfreq_mean
Tfreq_med
Cburst_amp_mean
Zburst_amp_mean
Tburst_amp_mean
µV
No unit
µV/s
/min
mS
No unit
Hertz
µV
PhyCS2015-2ndInternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
142
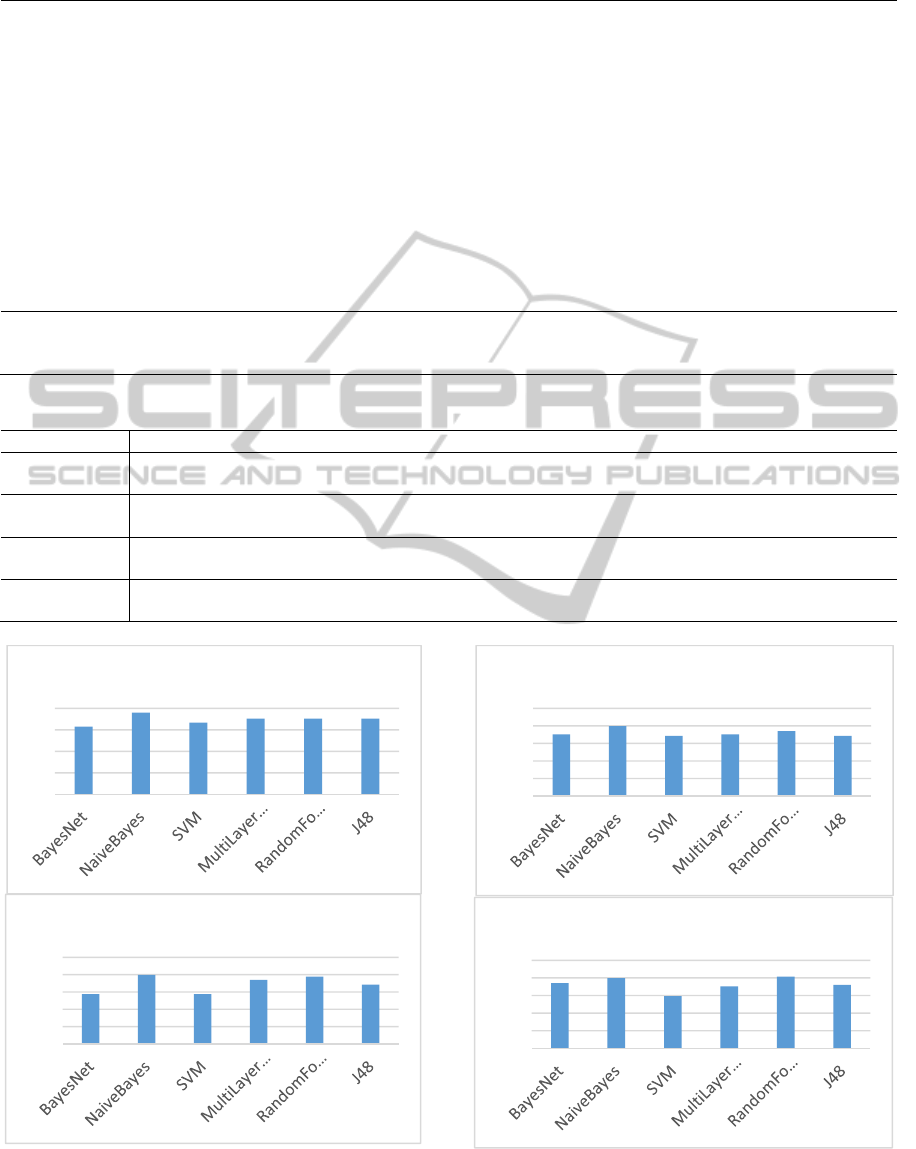
Table 2: Physiological features (cont.).
Respiration
(RSP)
Mean amplitude
Std. of amplitude
Subband spectral entropy
Minimum and maximum difference
Change rate
Power spectrum density
Std. of Poincare plot geometry
Mean and std. of peak valley magnitude
Mean and std. of breath per minute
RSP_mean
RSP_std
RSP_subbandSpectr
alEntropy({1,2,3})
RSP_minmax_diff
RSP_rate
RSP_low_power
RSP_high_power
RSP_firstOrder_std
RSP_poincare_SD1
RSP_poincare_SD2
PVM_mean
PVM_std
RRI_mean
RRI_std
No unit
Peripheral temperature
(SKT)
Mean temperature
Slope of temperature
Std. of temperature
temp_mean
temp_slope
temp_std
F
F/s
No unit
Table 3: Selected features for each category of affective states.
Category Features selected
Engagement
RSP_subbandSpectralEntropy(1), hrv_mean, SCR_rate, Zemg_mean, RSP_mean, PVM_std, SCL_sd,
SCL_slope, Cburst_amp_mean, ppg_peak_mean
Enjoyment
hrv_mean, RSP_mean, ppg_peak_mean, Cburst_count, Cemg_slope, Zburst_count, Temg_slope,
PVM_std,Zburst_mean,Cburst_amp_mean
Frustration
Cemg_std, RSP_subbandSpectralEntropy(2), RSP_subbandSpectralEntropy(3), PVM_mean,
RSP_firstOrder_std, temp_slope, RSP_std, RRI_std, Zfreq_med, RSP_low_power
Boredom
tRise_sd, hrv_mean, temp_mean, tRise_mean, SCR_sd, SCR_rate, RSP_subbandSpectralEntropy(3),
RSP_subbandSpectralEntropy(2), Zfreq_mean, Cburst_count
Figure 4: Classification accuracies for each category of
affective states.
Figure 4: Classification accuracies for each category of
affective states (cont.).
0
20
40
60
80
Classification accuracy of engagement
0
20
40
60
80
100
Classification accuracy of enjoyment
0
20
40
60
80
100
Classification accuracy of frustration
0
20
40
60
80
100
Classification accuracy of boredom
Physiology-basedAffectRecognitionDuringDrivinginVirtualEnvironmentforAutismIntervention
143

signal and eye gaze in order to give more
individualized feedback.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the participants and
their families for making this study possible. We
also gratefully acknowledge National Science
Foundation Grant 0967170 and National Institute of
Health Grant 1R01MH091102-01A1 that partially
supported the research presented here.
REFERENCE
Baker, R. S., S. K. D'Mello, et al. (2010). "Better to be
frustrated than bored: The incidence, persistence, and
impact of learners’ cognitive–affective states during
interactions with three different computer-based
learning environments." International Journal of
Human-Computer Studies 68(4): 223-241.
Bauminger, N. (2002). "The facilitation of social-
emotional understanding and social interaction in
high-functioning children with autism: Intervention
outcomes." Journal of autism and developmental
disorders 32(4): 283-298.
Bekele, E. T., U. Lahiri, et al. (2013). "A step towards
developing adaptive robot-mediated intervention
architecture (ARIA) for children with autism." Neural
Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE
Transactions on 21(2): 289-299.
Bian, D., J. W. Wade, et al. (2013). A novel virtual reality
driving environment for autism intervention.
Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction.
User and Context Diversity, Springer: 474-483.
Bradley, M. M. and P. J. Lang (2000). "Measuring
emotion: Behavior, feeling, and physiology."
Cognitive neuroscience of emotion 25: 49-59.
CDC (2014). "Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder
among children aged 8 years-autism and
developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11
sites, United States, 2010." Morbidity and mortality
weekly report. Surveillance summaries (Washington,
DC: 2002) 63: 1.
Cohen, H., M. Amerine-Dickens, et al. (2006). "Early
intensive behavioral treatment: Replication of the
UCLA model in a community setting." Journal of
Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics 27(2): S145-
S155.
Cox, N. B., R. E. Reeve, et al. (2012). "Brief Report:
Driving and young adults with ASD: Parents’
experiences." Journal of autism and developmental
disorders 42(10): 2257-2262.
Golan, O., E. Ashwin, et al. (2010). "Enhancing emotion
recognition in children with autism spectrum
conditions: An intervention using animated vehicles
with real emotional faces." Journal of autism and
developmental disorders 40(3): 269-279.
Goodwin, M. S. (2008). "Enhancing and accelerating the
pace of autism research and treatment." Focus on
Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities 23(2):
125-128.
Hall, M., E. Frank, et al. (2009). "The WEKA data mining
software: an update." ACM SIGKDD explorations
newsletter 11(1): 10-18.
Hall, M. A. (1999). Correlation-based feature selection
for machine learning, The University of Waikato.
Huang, P., T. Kao, et al. (2012). "Factors associated with
driving in teens with autism spectrum disorders."
Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics
33(1): 70-74.
Jerritta, S., M. Murugappan, et al. (2011). Physiological
signals based human emotion recognition: a review.
Signal Processing and its Applications (CSPA), 2011
IEEE 7th International Colloquium on, IEEE.
Lahiri, U., E. Bekele, et al. (2013). "Design of a virtual
reality based adaptive response technology for
children with autism." Neural Systems and
Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE Transactions on
21(1): 55-64.
Liu, C., P. Rani, et al. (2006). Affective state recognition
and adaptation in human-robot interaction: A design
approach. Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2006
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on, IEEE.
Lord, C., S. Risi, et al. (2000). "The Autism Diagnostic
Observation Schedule—Generic: A standard measure
of social and communication deficits associated with
the spectrum of autism." Journal of autism and
developmental disorders 30(3): 205-223.
Rani, P., N. Sarkar, et al. (2003). Affective
communication for implicit human-machine
interaction. Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2003.
IEEE International Conference on, IEEE.
Reimer, B., R. Fried, et al. (2013). "Brief report:
examining driving behavior in young adults with high
functioning autism spectrum disorders: a pilot study
using a driving simulation paradigm." Journal of
autism and developmental disorders 43(9): 2211-2217.
Rogers, S. J. (1998). "Empirically supported
comprehensive treatments for young children with
autism." Journal of clinical child psychology 27(2):
168-179.
Sarkar, N. (2002). Psychophysiological control
architecture for human-robot coordination-concepts
and initial experiments. Robotics and Automation,
2002. Proceedings. ICRA'02. IEEE International
Conference on, IEEE.
Standen, P. J. and D. J. Brown (2005). "Virtual reality in
the rehabilitation of people with intellectual
disabilities: review." Cyberpsychology & behavior
8(3): 272-282.
Sundberg, M. L. and J. W. Partington (1998). "Teaching
language to children with autism and other
developmental disabilities." Pleasant Hill, CA:
Behavior Analysts.
PhyCS2015-2ndInternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
144

Tao, J. and T. Tan (2005). Affective computing: A review.
Affective computing and intelligent interaction,
Springer: 981-995.
Tartaro, A. and J. Cassell (2007). "Using virtual peer
technology as an intervention for children with
autism." Towards universal usability: designing
computer interfaces for diverse user populations.
Chichester: John Wiley 231: 62.
Wade, J., D. Bian, et al. (2014). Design of a Virtual
Reality Driving Environment to Assess Performance
of Teenagers with ASD. Universal Access in Human-
Computer Interaction. Universal Access to
Information and Knowledge, Springer: 466-474.
Welch, K. C., U. Lahiri, et al. (2009). An affect-sensitive
social interaction paradigm utilizing virtual reality
environments for autism intervention. Human-
Computer Interaction. Ambient, Ubiquitous and
Intelligent Interaction, Springer: 703-712.
Wilms, M., L. Schilbach, et al. (2010). "It’s in your eyes—
using gaze-contingent stimuli to create truly
interactive paradigms for social cognitive and affective
neuroscience." Social cognitive and affective
neuroscience: nsq024.
Physiology-basedAffectRecognitionDuringDrivinginVirtualEnvironmentforAutismIntervention
145
