
The Analysis of Relationship between Diabetes and Cancer from
2006-2013 Hospital Inpatients
Shumei Miao
1
, Xiaoping Zhou
1
, Xin Zhang
1
, Hongwei Shan
1
, Xinyi Huang
1
, Yixin Zhu
1
,
Kai Leng
1
, Zhongmin Wang
1
, Jianqiu Kou
1
and Yun Liu
2
1
Department of Information, the First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
2
Department of Geratology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
Keywords: Diabetes, Cancer, Big-Data, Statistical Analysis.
Abstract: Diabetes and cancer have become two major chronic diseases concerning human health. More and more
studies indicate that diabetes can increase the risk of cancer and affect the prognosis of cancer patients. In
this paper, the information technology tools and statistical knowledge are used to analyse the clinical data of
hospital inpatients from year 2006 to year 2013, and explore the relationship between diabetes and cancer.
This paper analyses statistical characteristics and reasoning of suffering diabetes and cancer, makes
preliminary research on clinical big-data, and provides statistical basis for clinical researchers, thus helps to
enhance the level of diagnosis and treatment of disease and improve public health.
1 INTRODUCTION
As economic develops, lifestyles changes, and
environmental pollution aggravated, incidence of
diabetes have been increasing over the past decades.
Meanwhile, the incidence of neoplastic diseases is
rising year by year, which has become the leading
killer threatening public health. Both cancer and
diabetes have become two major chronic diseases
concerning human health (Y.Liu et al., 2013; G.
Yang et al., 2013). In early twenties, Maynard
(Maynard GD, 1910) proposed that the incidence of
diabetes and cancer was statistically positively
correlated. In recent years, more and more studies
indicate that diabetes can cause increased risk of
cancer and affect cancer prognosis. In 2010,
American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the
Cancer Society (ACS) issued a joint statement that
the risk of cancers increased on patients with
diabetes, and this demonstrates that the complex
relationship between diabetes and cancer
(Giovannuci E. et al., 2010). In addition, a large
number of domestic and international studies have
found that there is a certain etiology relationship
between diabetes and cancer, namely the incidence
of malignant tumors increased significantly among
diabetic population.
IDC (International Data Corporation) predicted
that China’s big data market will increase by five
times in 2012 to 2016. With the accelerating
development of health information, the type and size
of medical data is growing at an unprecedented rate,
the health sector has entered the "era of big data".
These valuable health information resources are vital
for disease management, control and medical
research. A better way to utilize this massive
information resources to serve the management,
treatment, research and teaching in healthcare has
been popular research focus (Gao Hansong et al.,
2013; CaiJiahui, 2013).
In this paper, the information technology and
related statistical knowledge are used to analyze
clinical data of hospitalized patients during January
2006 to December 2013. The analyses of statistical
characteristics were explored and the relationship
between diabetes and cancer was analyzed. This
paper makes preliminary attempts in the aspect of
big-data, and provides statistical evidence for
researchers of cancer and diabetes diseases, thus
helps to improve public health.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials Resources
Our research objects are patients who have been
hospitalized from January 2006 to December 2013,
483
Miao S., Zhou X., Zhang X., Shan H., Huang X., Zhu Y., Leng K., Wang Z., Kou J. and Liu Y..
The Analysis of Relationship between Diabetes and Cancer from 2006-2013 Hospital Inpatients.
DOI: 10.5220/0005233104830488
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2015), pages 483-488
ISBN: 978-989-758-068-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

and the data we used are from MRS (Medical
Records System) and HIS (Hospital Information
System) of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing
Medical University (Jiangsu Province Hospital). The
paper focuses on diabetes and cancer patients.
2.2 Disease Classification
Discharge diagnosis is coded by professional
medical record coders according to ICD-10 (World
Health Organization, 2005). Based on primary
diagnosis and other diagnosis, we established a
clinical database to classify different types of
diseases and calculated the number of patients of
each disease. The paper focuses on diabetes and
cancer patients, the principal diagnosis and eight
other diagnosis of HIS should be analysed all
together.
2.3 Statistical Methods
Entry data with Excel and set up database with
ACCESS software, then valuable information is
chosen and analysed. SPSS software is also used for
statistical analysis. Chi-square calibration equation
is used to calculate P-value, P-value and OR value
are used to analyse the relationship between two
difference diseases.
Chi-square calibration equation is:
2
22
0
df
()
~
e
e
ff
f
()
(1)
Where, the actual observation number is fo, the
theoretical number is fe, we check χ2 table to get P-
values. When P is less than 0.005, the factor analysis
has a very significant difference. When P is less than
0.01, the comparison differences are statistically
significant, While P is larger than 0.05, the
comparison difference is not statistically significant.
OR value is calculated as:
OR= ad/ bc (2)
In statistics , OR refers to odds ratio, which means
the indicators of disease are associated with the risk
factors described in case control study. If OR is not
less than 3, the disease associated with the
correlation index greatly.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Overview of the Investigation
During the eight years from 2006 to 2013, there
were 531718 discharges in our hospital. The average
number is 66465 per year. Women account for
50.64%. The number of discharged patients
increased year by year from 37105 in 2006 to 93040
in 2013. Both cancer and type II diabetes are ranked
in the top ten diseases in our hospital in 2013. They
have common risk factors such as age, high body
weight index, central obesity, sedentary lifestyle,
excessive intake of carbohydrates, and lack of
physical activity, drinking and smoking (Haidong
Wang et al., 2012). In this paper, information of
eight years is used to do analyses, the common
features and relationship of cancer patients and
diabetes patients are proposed from statistical view.
3.2 Overview of Diabetes Disease
During the eight years from 2006 to 2013, the
number of diabetes patients increased year by year,
it increased from 2422 cases in 2006 to 9704 cases
in 2013. The data in Table 1 shows the patients in
year 2006 to 2011 with diabetes in elderly group was
significantly higher than non-elderly group, age
differences were highly significant (P <0.005, OR>
3), which proves diabetes and age have a significant
positive correlation. Age differences of patients in
year 2012 to 2013 were significant (P <0.005, OR>
2). The non-elderly group of diabetes has increased
annually, this conclusion is consistent with Yang
Wenying‘s (Yang W et al., 2010) paper in 2010.
Rapid urbanization and disordered unhealthy diet
style leads to diabetes threatening the younger’s
health more obvious (Bener A et al., 2014).
3.3 Overview of Cancer Disease
During the eight years from 2006 to 2013, the
number of cancer patients also increased year by
year, it increased from 9381 cases in 2006 to 30599
cases in 2013. The incidence of cancer is also
increasing every year. The data in Table 2 shows
that the patients in year 2006 to 2011 with cancer in
the elderly group were significantly higher than the
non-elderly group. Age differences were statistically
significant (P <0.005, OR> 1.4), which proves
diabetes and age have a significant positive
correlation. Cancer is also a disease of old age, but
in comparison with diabetes, the age of onset cancer
is more advanced. In recent years, OR value
becomes less, which indicates that the age of onset
of tumors growing in advance, the results remain
consistent with the phenomenon of early onset
diabetes, unhealthy living diet has a significant
impact on this phenomenon (F. Bray et al., 2012; J.
Traebert et al., 2013).
HEALTHINF2015-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
484
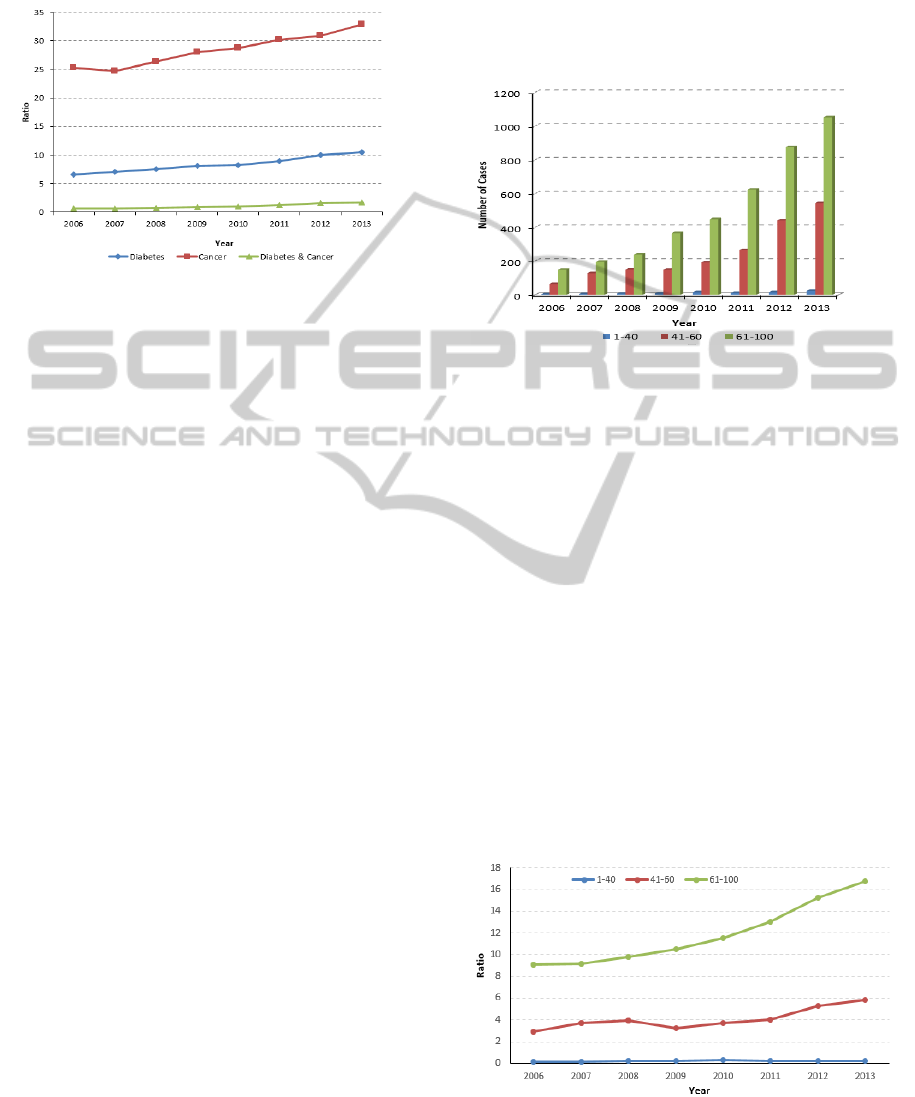
3.4 General Situation of Patients with
Diabetes and Cancer
Figure 1: Trend of Diabetes, Cancer, and both in 2006-
2013. The horizontal axis represents year and the vertical
axis represents the ratio between number of different
disease cases and the total number of inpatients every
year.
Last two sections analyzed the diabetes and cancer
respectively, and the correlation of them is explored.
Both of them are closely related to age. The
occurrence of diabetes and cancer is related to age,
economic development, lifestyle, and environmental
etc (R. Prakash et al., 2013). We combined the
primary diagnosis and other diagnosis of
hospitalization data to analyze diabetes and cancer,
the number of patients with both diabetes and cancer
rose from 220 cases in 2006 to 1623 cases in 2013.
The proportion of cancer patients in diabetes patients
has also increased every year. Table 3 describes
annual cases of diabetes, cancer, and both from year
2006 to year 2013. The ratio between the cases and
the annual total number of hospitalizations is also
shown. Figure 1 describes the percentage change of
the three categories of patients in visually showed.
All of them are in an increasing trend, especially
since year 2010, the rate of increase is more evident.
The cancer incidence in diabetic patients is
calculated from data in Table 3. It rose from 9.08%
in 2006 to 16.72% in 2013. Compared to society
crowd cancer incidence 0.29% announced in 2013,
cancer incidence in diabetes patients was
significantly greater than in the general population,
and the relationship between cancer and diabetes
deserve further study.
3.4.1 Age Distribution of Patients with
Diabetes and Cancer
The age distribution of Cancer patients with diabetes
is shown in Figure 2. Age is divided into three
Categories: under 41 years-old, 41 to 60 years-old,
above 60 years-old. Cancer with diabetes is common
for the elders. In recent years, especially since 2010,
patients under age 41 years-old group and 41 to 60
years-old group are increasing year by year,
suggesting a trend of younger age with diabetes and
cancer disease (J.M. Lopez et al., 2014).
Figure 2: The Age Distribution of Diabetes with Cancer
Patients. The horizontal axis represents year and the
vertical axis represents the number of cases with both
diabetes and cancer diseases.
Figure 3 shows the incidence rate of cancer for
diabetes patients at different age group. Diabetic
patients over 60 years account for the largest
percentage of incidence of cancers, especially in
recent year, and the cancer incidence rate of the
older increased significantly. Diabetic patients
between 41 years and 60 years took the second
largest percentage of incidence of cancers, the
indicator also has slightly improvement. The cancer
incidence rate of diabetic patients under 41 years old
remained virtually unchanged in recent years. The
analysis result shows high risk of cancer in elderly
diabetes mellitus patients (Trosko J. E. et al., 1980;
Zoncu R. et al., 2011).
3.4.2 Gender Distribution of Patients with
Diabetes and Cancer
Figure 3: The Incidence of Cancer in Diabetes Patients.
The horizontal axis represents year and the vertical axis
present the ratio between the cases of cancer patients in
diabetes and the cases of diabetes every year.
TheAnalysisofRelationshipbetweenDiabetesandCancerfrom2006-2013HospitalInpatients
485
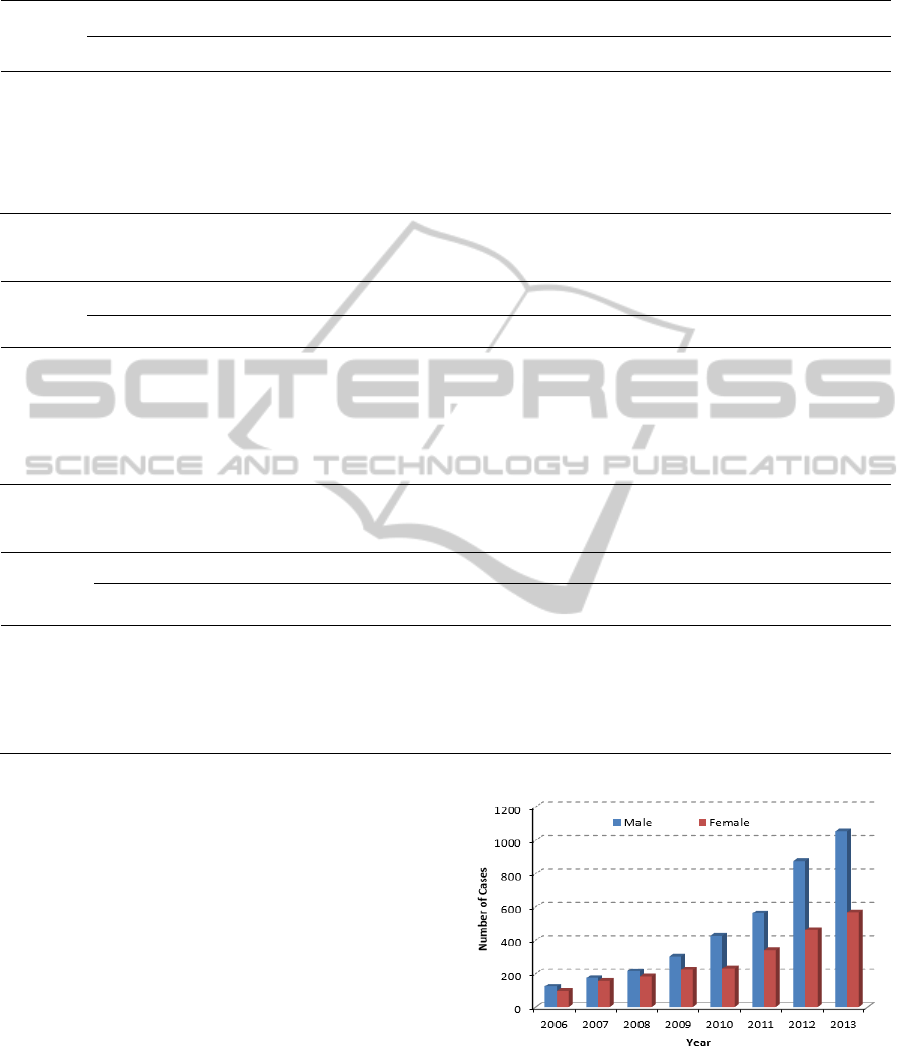
Table 1: The analysis of diabetes patients in year 2006-2013.
Year 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Age
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
Total 18624 18481 25947 25323 26666 27233 28544 33661 31943 37358 34694 42927 38144 49128 39328 53683
Number
of Cases 411 2011 583 3028 705 3368 797 4203 930 4787 1210 5699 1931 6824 1993 7711
P <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005
OR 4.93 5.32 4.68 4.47 4.40 3.81 2.74 2.83
Table 2: The Analysis of Cancer Patients in Year 2006-2013.
Year 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Age
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
1-49
≥
50
Total 18624 18481 25947 25323 26666 27233 28544 33661 31943 37358 34694 42927 38144 49128 39328 53683
Number
of Cases 3400 5981 4553 8099 5022 9173 6002 11438 6935 13001 8176 15177 9266 17678 10469 20130
P <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005
OR 1.77 1.82 1.79 1.62 1.60 1.50 1.48 1.41
Table 3: The Gender situation of Diabetes with Cancer Patients in Year 2006-2013.
Year 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
No. of
Cases
%
No. of
Cases
%
No. of
Cases
%
No. of
Cases
%
No. of
Cases
%
No. of
Cases
%
No. of
Cases
%
No. of
Cases
%
Total 37105 51270 53903 62205 69301 77621 87273 93040
Diabetes 2422 6.53 3611 7.04 4073 7.56 5000 8.04 5717 8.25 6909 8.90 8755 10.03 9704 10.43
Cancer 9381 25.28 12652 24.68 14195 26.33 17440 28.04 19936 28.77 23353 30.09 26944 30.87 30599 32.89
Diabetes
& Cancer
220 0.59 331 0.65 400 0.74 527 0.85 660 0.95 903 1.16 1337 1.53 1623 1.74
The gender composition of diabetes with cancers
patients is shown in Figure 4. The figure shows,
cancer patients suffering from diabetes mellitus
occurs more in male patients than female patients,
and in recent years the proportion is increasing more
evidently.
3.4.3 Gender Distribution of Patients with
Diabetes and Cancer
The gender composition of diabetes with cancers
patients is shown in Figure 4. The figure shows,
cancer patients suffering from diabetes mellitus
occurs more in male patients than female patients,
and in recent years the proportion is increasing more
evidently.
Figure 4: The Gender Distribution of diabetes with cancer
patients. The horizontal axis represents year and the
vertical axis represent the number of patients suffering
both diabetes and cancer.
HEALTHINF2015-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
486

3.4.4 Cancer Types of Different Gender with
Diabetes
Patients suffering from both diabetes and cancers are
chosen to analyse cancer types of different gender.
Liver cancer is ranked at top for male diabetes
patients. For female diabetes patients, the incidence
of breast cancer and uterine cancer is the highest. To
briefly illustrate the situation, Table 4 only list top
five cancer disease for male and female in 2013.
Table 4: Top five cancer disease in 2013.
POS.
Male Female
1
Liver Cancer Colorectal cancer
2
Prostate Cancer Uterine fibroids
3
Esophageal Breast Cancer
3
Pancreatic Cancer Lung Cancer
5
Colorectal cancer Pancreatic Cancer
4 DISCUSSIONS
The incidence of diabetes and cancer is rising, both
of them have become the major diseases threatening
human health and a worldwide epidemic,
meanwhile, the prevalence of both diseases is rising.
Cancer is a kind of disease of high consumption. For
diabetes patients, due to a lack of insulin, sugar,
protein and imbalance of fat metabolism, many
complications are caused. When the two diseases
coexist, they interact with each other, affects
prognosis, and worsen patient’s wellbeing. (Wan
Guilin et al., 2005).
In this paper, clinical data of inpatients from year
2006 to year 2013 is used for analysis, which
includes 46191 cases of diabetes, and 6001 cases of
diabetes with cancer. The numbers of diabetes
disease and cancer disease grow rapidly in recent
year, so is the number of diabetes with cancer
patients. The number also increases with age growth.
Both of them are significantly correlated to age. The
number of diabetes and cancer cases over 40 years
increased obviously, as the aging population is one
factor. Meanwhile, statistical analysis showed that
the prevalence of non-elderly group also increased
year by year, this conclusion is consistent with Yang
Wenying’s (CaiJiahui et al., 2013) findings in an
article. Disorderly rapid urbanization life and
unhealthy diet leads to these two chronic diseases
appearing in younger population.
From the perspective of gender, there are more
male patients than female patients. In the analyses of
diabetes mellitus with cancers patients, the incidence
of liver cancer makes a comparatively large
proportion in male patients. Many men have
drinking, smoking and other bad habits, which lead a
direct impact on this. While uterine fibroids and
breast cancer make a large proportion in female
patients. The identity of gender is obvious, which
also explain impact of diabetes on sex hormones
from the statistical view. Meanwhile, epidemiology
confirmed obesity, insulin resistance state and
diabetes significantly increased the incidence of
cancer. Basic science presents reasonable
mechanism leading to cancer disease. Once the
diabetic disease is diagnosed, the inspection of liver
cancer, colorectal cancer, uterine cancer, breast
cancer and etc are recommended to add in their
regular medical examinations. Thus early cancer
detection and intervention is recommended. The
occurrence of cancer is a complex and slow process,
and is influenced by many factors. The follow-up
studies need to further consider the type of diabetes,
duration of treatment, the degree of control and etc.
The complex mechanism between diabetes and
cancer need more epidemiological studies to verify
the relationship.
As healthcare information technology develops, a
lot of data has been accumulated. The level of
medical information has great influence on medical,
teaching and research. To better support clinical
decisions and scientific researches, the construction
of data exchange platform and clinical data
repository become the emphasis in information
technology development. In this paper, the data
warehouse of diabetes and cancer is built to perform
data analysis. Then the clinical big-data is used in
clinical medical research. As medical information
systems develop, a lot of data has already been
accumulated. Healthcare workers can promote
health care reformation through information
technology, by fully exploiting big data for medical
to support clinical research paramedic, and
improving the quality of medical management.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by grants from the
National Natural Science Foundation of China
(Grant no. 81270952), the Jiangsu Province’s Key
Provincial Talents Program (BE 2011802), the
Project funded by the Priority Academic Program
Development of Jiangsu Higher Education
Institutions, the Program for Development of
Innovative Research Team in the First Affiliated
Hospital of NJMU (no. 20113012), and Nanjing
TheAnalysisofRelationshipbetweenDiabetesandCancerfrom2006-2013HospitalInpatients
487

Medical University Science and Technology
Development Foundation (2012NJMU122). Yun Liu
is the guarantor of this paper.
REFERENCES
Y. Liu, G. Yang, Y. Zeng, R. Horton, and L. Chen, Policy
dialogue on China’s changing burden of disease. The
Lancet, vol. 381, pp. 1961-1962, 2013.
G. Yang, Y. Wang, Y. Zeng et al., Rapid health transition
in China, 1990–2010: findings from the Global
Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet, vol. 381,
no. 9882, pp. 1987–2015, 2013.
Maynard GD. A statistical study in cancer death-
rates[J].Biometrika,1910,7( 3) : 276 -304.
Wilson EB, Maher HC. Cancer and tuberculosis with
some comments on cancer and other diseases[J]. Am
J Cancer, 1932, 16(2) : 227 -250.
Giovannucci E,Harlan MD,Archer MC, et a1. Diabetes
and Cancer
:
A consensus report [J]. A Cancer
Journal for Clinicians, 2010, 60(4):207-221.
Wan Guilin, Wu Shiguang, Wei kuixiu. Correlation
between malignant tumors and diabetes mellitus [J].
Med Qilu. 2005, 20(6): 478-480.
GaoHansong, Xiao Ling, XuDewei, et al. Medical data
mining platform based on cloud computing[J]. 2013
(5): 7-12.
CaiJiahui, Zhang Tao, ZongWenhong. Challenges and
consideration of the big data of medicine. Chinese
Journal of health information and management. 2013
(4): 292-295.
World Health Organization, ICD-10, vol. 2, World Health
Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2nd edition, 2005.
Haidong Wang, Laura Dwyer-Lindgren, Katherine T
Lofgren, et al. Age-specific and sex-specific mortality
in 187 countries,1970-2010: a systematic analysis for
the global burden of disease study 2010.Lancet 2012;
380: 2071–94.
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes
among men and women in China[J]. New England
Journal of Medicine, 2010, 362(12): 1090-1101.
Bener A, Al-Laftah F, Al-Hamaq AO, et al. A study of
diabetes complications in an endogamous population:
An emerging public health burden. Diabetes
MetabSyndr. 2014.8(2):108-114.
F. Bray, A. Jemal, N. Grey, J. Ferlay, and D. Forman,
Global cancer transitions according to the Human
Development Index: a population-based study, The
Lancet Oncology. vol. 13, pp. 790–801, 2012.
J. Traebert, I,JayceCeola Schneider, C. Flemming Colussi,
et al. Burden of disease due to cancer in a Southern
Brazilian state. Cancer Epidemiology, vol. 37, pp.
788–792, 2013.
R. Prakash, P.Misrab, and V. G. Chellaiyan, Burden of
diabetes mellitus and prediabetes in tribal population
of India: a systematic review. Diabetes Research and
Clinical Practice, vol. 102, pp. 1–7, 2013.
J.M. Lopez, R. A. Bailey, M. F. T. Rupnow, et al.
Characterization of type 2 diabetes mellitus burden by
age nd ethnic groups based on a nationwide survey.
Clinical Therapeutics, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 494–506,
2014.
Trosko J E, Chang C C. An integrative hypothesis linking
cancer, diabetes and atherosclerosis: the role of
mutations and epigenetic changes [J]. Medical
hypotheses, 1980, 6(5): 455-468.
Zoncu R, Efeyan A, Sabatini D M. mTOR from growth
signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing[J].
Nature reviews Molecular cell biology, 2011, 12(1):
21-35.
HEALTHINF2015-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
488
