
Knowledge Process Models in Health Care Organisations
Ideal-typical Examples from the Field
Lars Rölker-Denker and Andreas Hein
Department of Health Services Research, University of Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Germany
Keywords: Knowledge Processes, Organisational Learning, Learning Organisation, Modelling.
Abstract: This paper summarizes the recent work of analysing knowledge process in health care organisations with a
special focus on the geriatric disciplines. A study has been performed consisting of observations in the field
and interviews with the professionals. It is shown that knowledge processes have evolved over the past
years. New knowledge processes are introduced and modelled by using a combined method (3LGM
2
and
KMDL
®
). An outlook is given on measuring the dissemination of knowledge through the identified
processes in ongoing work.
1 INTRODUCTION
The increase of knowledge and information is a
general phenomenon and thus also applies to
healthcare. Emerging cooperation between health
care organisations (HCO) and in addition Mergers &
Acquisitions by highly integrated health care groups
extend the organisational knowledge base even
more. In addition medical schools and medical
university hospitals represent key actors in medical
knowledge development (Rölker-Denker and Hein,
2012b).
Organisational learning routines are key factors
for learning organisations. This applies to hospitals
in general (Pfaff, 1997) and individual departments
(Lipshitz and Popper, 2000) but also for larger
network structures (Rölker-Denker, 2010).
Organisational learning routines are key factors
for learning organisations. This applies to hospitals
in general (Pfaff, 1997) and individual departments
(Lipshitz and Popper, 2000) but also for larger
network structures (Rölker-Denker, 2010).
2 LEARNING ORGANISATIONS
Learning organisations can be described from
different viewpoints. In this paper the learning
organisation is analysed in sense of Wengelowski.
He defines three main areas: learning levels,
learning types and learning determinants, which all
can be practically mapped over an organisation for
analysing its accordance with the learning
organisation concept (Wengelowski, 2000).
Four learning levels can be distinguished:
individual learning, group (team) learning,
organisational learning and inter-organisational
learning. Individual learning means the changes in
behaviour, theories and concepts by an individual
whereas group learning means the same in a group
context. Organisational learning focuses on the
changes in organisational behaviour or theory. If
more than one organisation is involved in the
learning process then inter-organisational learning
can be identified.
Learning types can be differentiated into single-
loop learning, double-loop learning and deutero
learning (Hislop, 2009). Single-loop learning
focuses on incremental changes inside a constant
framework while double-loop learning focuses on
the framework. Finally, the process of learning and
extending an organisation’s awareness itself is in the
focus of deutero learning. The learning types are
based on each other. The abstract theories of
learning levels and types are brought together into
the organisation by the learning determinants. Three
determinants are discussed in literature:
organisational member, organisational structure and
organisational culture (Wengelowski, 2000). The
specific utilization and advancement of
competencies and qualifications among the
organisational members are fundamental tasks in
learning organisations. Each organisational member
has its unique setting of competencies and qualifica-
tions, e. g. professional or social competence.
312
Rölker-Denker L. and Hein A..
Knowledge Process Models in Health Care Organisations - Ideal-typical Examples from the Field.
DOI: 10.5220/0005192003120317
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2015), pages 312-317
ISBN: 978-989-758-068-0
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Important levers are human resource development
(further and advanced education) as well as staffing.
The formal organisational structure gives the
framework for all intra-organisational and partly
inter-organisational processes and sets the scope of
action for the organisational members. Following the
organisational view a differentiation can be made
between organisational structure, process
organisation, communicational / knowledge
organisation and informational organisation. The
organisational structure describes the long-term
primary organisation (functional, divisional, matrix
organisation) and flexible short-term organisation
(such as project organisation); the process
organisation describes how organisational tasks are
executed. The communicational / knowledge
organisation describes how knowledge is shared
inside organisations and which communicational
areas can be used. The informational organisation
contains written, spoken and IT-based information
systems. Organisational culture can be interpreted as
the informal organisational structure. In context of
the learning organisation three different types of
culture can be distinguished: learning culture,
communication culture and culture of trust (Rölker-
Denker, 2010). This definition of learning
organisations has been already used in previous
studies and ensures the comparability of actual and
future work with recent studies. As a result of this
recent work a method for modelling organisational
learning processes was declared to be useful
(Rölker-Denker et al., 2011).
3 MODELLING APPROACH
3.1 State of the Art
Modelling knowledge processes can be achieved
with different languages. UML (Unified Modelling
Language) is one approach which is used for this
purpose (Schreiber and Akkermans, 2000), other
approaches are EPCs (Event-driven process chains)
or petri nets (Fröming, 2009). These modelling
approaches have been developed without a guiding
knowledge management theory like the knowledge
management model from Nonaka and Takeuchi
(Nonaka and Takeuchi, 1995). This applies for the
Knowledge Modeling and Description Language -
KMDL
®
(Gronau and Fröming, 2006), see chap. 3.3.
In the area of modelling clinical IT
infrastructures a key concept is a conceptual
architecture showing the included systems and areas
(Locatelli et. al., 2012). These approaches lack a
detailed technical view, e.g. showing tasks and
subtasks. This applies to the Three-Level Graph-
Based Meta Model for the Management of Hospital
Information Systems - 3LGM
2
(Winter and Haux,
1995), (Winter et. al., 2003), see chap. 3.2.
For the description and modelling of
organisational learning routines these two well-
proven concepts have been selected and combined
for the first time to meet the demand for modelling
organisational learning routines in health care
organisations. Both concepts are introduced in brief,
for more details see (Rölker-Denker and Hein,
2012a).
3.2 3LGM
2
3LGM
2
is used for modelling hospital information
systems and architectures. Models build with
3LGM
2
use a simple intuitive notation. It can not
only be used for modelling hospital information
system but also connections to hospital’s
environment like physicians, care-givers and other
HCOs. 3LGM
2
is based on three layers: domain
layer, logical tool layer and physical layer. The
domain layer describes typical tasks and subtasks in
a HCO like patient scheduling or radiological
reporting. The logical tool layer comprises concrete
systems like hospital information systems (HIS),
radiology information systems (RIS) or picture
archive and communication systems (PACS).
Finally the physical layer describes physical
hardware (PCs, server, switches) and social-
technical elements (mail in-trays, archive) and the
connections between these elements. The physical
layer is left out at the moment due to its subordinate
relevance in analysing knowledge processes (Winter
and Haux, 1995), (Winter et. al., 2003).
3.3 KMDL
®
KMDL
®
is used for modelling knowledge processes
in organisations. It is based on the knowledge
management model from Nonaka and Takeuchi
(Nonaka and Takeuchi, 1995) with its four phases of
socialisation, externalisation, combination and
internalisation. KMDL
®
is divided into process layer
and activity layer. Tasks, the order of tasks,
information systems, functions (provided through
information systems), roles and persons are part of
the process layer. Objects of the activity layers are
information and knowledge objects, single persons
(or teams), requirements and the different
transformations between the four knowledge
management phases (Gronau and Fröming, 2006).
KnowledgeProcessModelsinHealthCareOrganisations-Ideal-typicalExamplesfromtheField
313
3.4 Consolidation
On the functional layer 3LGM
2
solely describes
typical hospital task and is not process-oriented.
However KMDL
®
describes processes and focuses
on information systems, roles and especially tasks
on the process layer. The connection of both
concepts can be achieved by mapping 3LGM
2
‘s
domain and logical tool layer and KMDL
®
‘s process
layer. The result is a fourth layer above the
functional layer of 3LGM
2
and can be understood as
a knowledge layer. The knowledge layer is
connected to the domain layer by tasks and roles and
to the logical tool layer by information systems.
Using the knowledge layer it is possible to map
knowledge processes into a HCO and identify key
success factors for these processes (Rölker-Denker
and Hein 2012a).
3.5 Graphical Representation
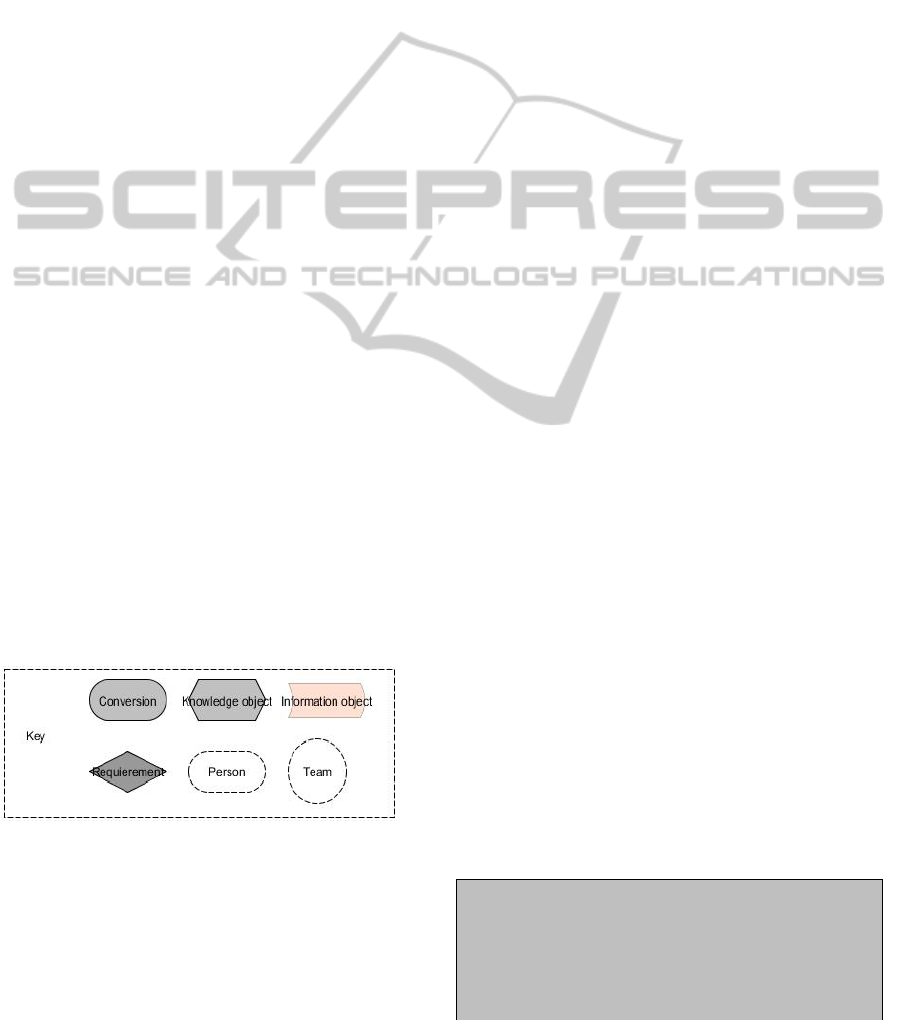
The following symbols are used in this work:
Conversion: A knowledge conversion
following Nonaka/Takeuchi, e.g. externalisa-
tion or internalisation.
Knowledge Object: A complex object of
knowledge, describing how knowledge is
acquired for the organisation e.g. creating a
sophisticated report or staffing well-educated
personnel.
Information Object: A simple information
object, e.g. letter, x-ray image or laboratory
report.
Requirement: A functional or technical
requirement, e.g. a software system to be used
Person: A person taking part in the process
Team: Multiple persons forming a durable
team
Figure 1: Key (activity view).
4 MODELLED LEARNING
PROCESSES
In a first step the learning processes were identified
in field studies by shadowing the daily work in
different clinical departments (acute geriatric,
neurology, stroke unit, neurosurgery, and
nephrology) in two hospitals, one municipally and
one confessionally owned. Each department was
visited for one to two days (depending on the unique
work flows) by one observer, afterwards draft
models were developed and in the end discussed in
semi-structured narrative interviews with selected
professionals involved in the processes (Rölker-
Denker and Hein, 2012b).
The following organisational learning routines
have been identified and observed (Rölker-Denker
and Hein, 2014):
Physician rounds
Reflection meetings
In/after surgery meetings
Staff meetings
Consultation
Early Stand-up Meeting
Multi-professional geriatric team session
Interdisciplinary clinical case conferences
Discharge management
These learning routines have been identified in
all clinical departments except the multi-professional
geriatric team session which is specific to geriatrics.
The learning routines have been also validated by
expert interviews in a research project for building a
health services research network (Rölker-Denker et.
al., 2014). These interviews have been conducted
with the medical and/or economic management of
more than 20 hospitals in the northern part of
Lower-Saxony, Germany. Some of these learning
routines (physician rounds, reflection meetings,
in/after surgery meetings, staff meetings) have been
already discussed in literature (e.g. Lipshitz and
Popper, 2000) and have been confirmed during this
study. Some of the new identified organisational
learning routine will be described in the next
paragraphs.
Each routine will be introduced by a so-called
storyboard, derived from clinical practice. Based on
these storyboards the routines are modelled and
described in detail.
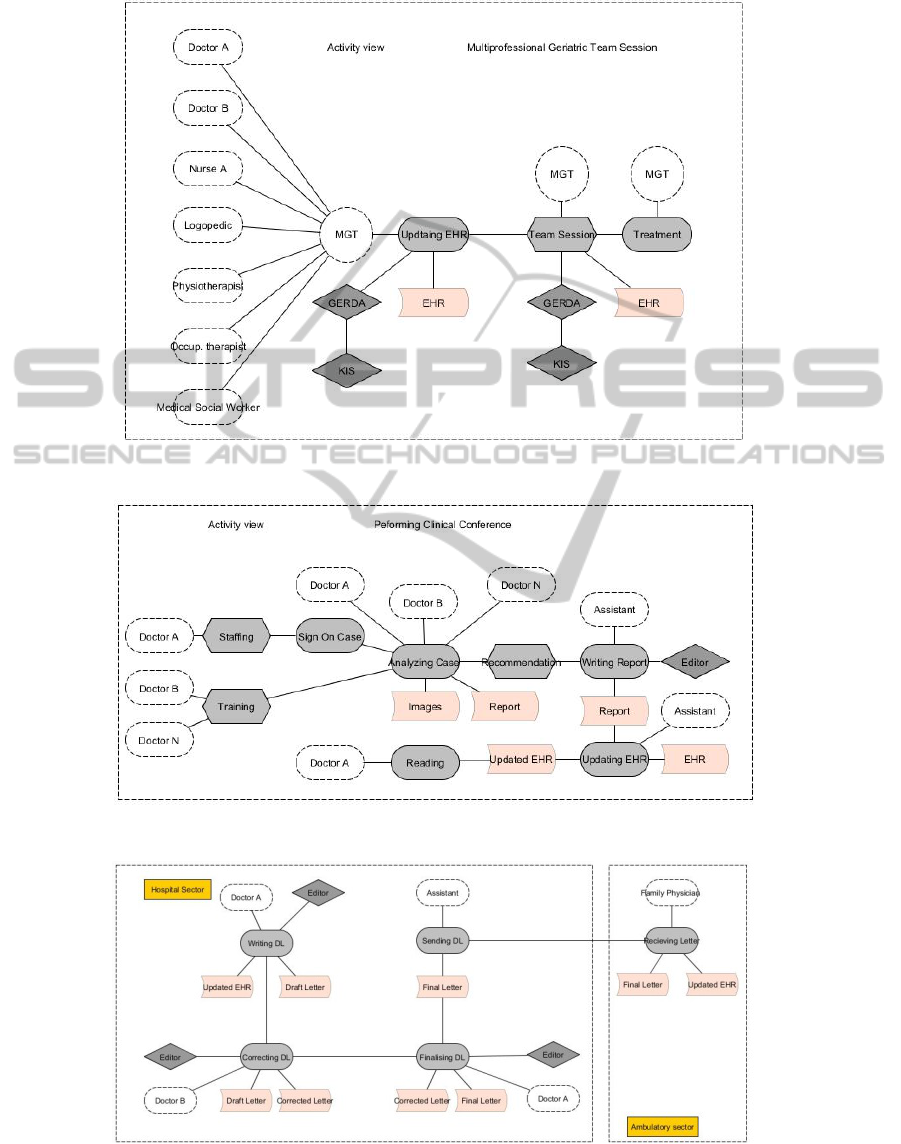
4.1 Multi-professional Geriatric Team
Session
Storyboard
In the morning, Doctor A, an assistant
geriatrician, is updating the EHR of his/her
geriatric patients. He/she uses the GERDA
(Geriatric Database), a software component
integrated into the HIS. He/she updates his/her
observations on the patient regarding the general
HEALTHINF2015-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
314

state, his/her interpretation of laboratory values
etc. He/she also sees the entries of the members
of the multi-professional geriatric team. In the
afternoon he(she meets with the other members
and discusses the patient development. As the
patient’s discharge is planned for end of the week
the medical social worker reports the current state
of negotiations with an ambulatory care service in
the city which will take care of the patient after
discharge.
The multi-professional geriatric team session
process is shown in figure 2, particular process steps
are:
MGT - Multi-professional Geriatric Team: The
team consists of doctors, nurses, logopedics,
physiotherapeutists, occupational therapeutists
and medical social workers.
Updating EHR: All team members update the
EHR with the relevant professional
information. Each profession has its own input
fields. This is the externalisation step.
Team Session: The MGT meets and discusses
all patients on the basis of the information
within the EHR. This includes the current state,
future developments and treatments as well as
all other business regarding the patient. This is
the combination step.
Treatment: With the combined information out
of the team session all members can continue
with the coordinated treatment.
4.2 Interdisciplinary Clinical Case
Conferences
Storyboard
The internist Doctor A has a patient with an
unclear oncological diagnosis. He/she decides to
sign on this case for the clinical conference. All
oncologist of the hospital meet at weekly basis
and discuss patients with difficult/severe
diagnoses. The conference participants examine
the documents (reports, medical images) and give
a recommendation and report. The assistant of a
doctor attending writes the final report and
updates the EHR. In the end Doctor A reads the
updated EHR and the report and can use this for
the further treatment of his/her patient.
The clinical conference is shown in figure 3,
particular process steps are:
Sign on Case: Doctor A signs up his/her
patient for the clinical conference to be
discussed.
Analyzing Case: All attending doctors,
including Doctor A, analyse the provided
information objects (e.g. images, reports;
internalisation step) and discuss
recommendations for further treatment
(internalisation). The result is a consolidated
recommendation (combination) as new
knowledge object.
Writing Report: The assistant writes a report
containing the recommendation, resulting in a
new information object.
Updating EHR: The assistant loads the report
into the EHR.
Reading: Doctor A reads the updated EHR
and can use this knowledge for the further
treatment of his/her patient.
4.3 Discharge Letter
Storyboard
Doctor A, a senior geriatrician, starts writing the
discharge letter for his/her patient. When he/she
has finished his/her draft the discharge letter is
corrected by the chief geriatrician Doctor B.
Doctor A can finalise the discharge letter. The
discharge letter is forwarded to the department
assistant who sends to letter by regular mail to the
family physician of the patient.
The discharge letter (DL) process is shown in figure
4, particular process steps are:
Writing DL: Doctor A writes the DL draft by
using the updated EHR with images, reports
etc. This is the externalisation step.
Correcting DL: Doctor B corrects the draft
DL, the result is the corrected DL. This is the
combination step.
Finalising DL: Doctor A finalises the
corrected DL and forwards it to the
department assistant.
Sending DL: The department assistant sends
the DL to the family physician in charge. This
is the step where the sector boundaries are
overcome.
Receiving DL: The family physician in charge
receives the DL and updates the patient EHR
in his/her office. Reading the patient’s DL is
the internalisation step.
5 CONCLUSION AND OUTLOOK
5.1 Conclusion
Health care has evolved in the recent years and this
KnowledgeProcessModelsinHealthCareOrganisations-Ideal-typicalExamplesfromtheField
315

also applies to organisational learning routines.
Emerging specialisation in medicine regarding more
specialised disciplines (e.g. geriatrics as a
specialisation of internal medicine) or occupational
profiles (e.g. case management, palliative care
nurses) and enforced inter-profession cooperation
between physicians, nursing and other professions
have changed organisational learning routines like
the multi-professional geriatric team session. The
scope of organisational learning has also changed,
starting from learning routines inside hospital
boundaries up to inter-organisational (between
several hospitals) and even inter-sectoral (between
hospitals, rehabilitation organisation and ambulatory
actors).
Well-described learning routines have been
proven in the field but also new ideal-typical
organisational learning routines have been identified
and have been introduced in detail. The
demonstrated organisational learning routines have
been modelled from field observations and can be
stated as ideal-typical routines.
5.2 Outlook
In a next step the velocity of knowledge
dissemination will be measured and factors
influencing the velocity will be identified, e.g. how
long does it take to use the knowledge from a
consultation report in the patient treatment process.
These measurements and influencing factors will
be the basis for remodelling proposals. These
proposals could focus on remodelling the learning
routine itself by rearranging the process steps,
eliminating negative influencing factors, or
reinforcing positive influencing factors. New
process steps or links between actors are possible.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Metropolregion
Bremen-Oldenburg (reference number: 23-03-13)
for partly supporting this work.
REFERENCES
Fröming, J., 2009. Ein Konzept zur Simulation
wissensintensiver Aktivitäten in Geschäftsprozessen,
GITO, Berlin.
Gronau, N., Frömming, J., 2006. KMDL® Eine
semiformale Beschreibungssprache zur Modellierung
von Wissenskonversionen. In WIRTSCHAFTS-
INFORMATIK. Gabler Verlag. Wiesbaden. (German).
Hislop, D., 2009. Knowledge Management in
Organizations. A critical Introduction, Oxford
University Press. New York.
Lipshitz, R., Popper, M., 2000. Organizational Learning in
a Hospital. In Journal of Applied Behavioral Science.
Locatelli, P., Restifo, N., Gastaldi, L., Corso, M., 2012.
Health Care Information Systems: Architectural
Models and Governance. In Innovative Information
Systems Modelling Techniques, Kalloniatis, C. (Ed.),
InTech, DOI: 10.5772/38212.
Nonaka, I., Takeuchi, H., 1995. The Knowledge-Creating
Company: How Japanese Companies Create the
Dynamics of Innovation. Oxford University Press.
Oxford.
Pfaff, H., 1997. Das lernende Krankenhaus. In Zeitschrift
für Gesundheitswissenschaften. (German).
Rölker-Denker, L., 2010. Hospitals as Learning
Organizations. In Proceedings of the IADIS
International Conference e-Health.
Rölker-Denker, L., et. al., 2011. The organizational
learning cube. Adopting the data cube model for
analyzing organizational learning in healthcare
organizations and networks. In Proceedings of 9th
International Conference On Information
Communication Technologies In Health. National and
Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece.
Rölker-Denker, L., Hein, A., 2012a. Modelling
Knowledge Processes In Health Care Organizations.
In Proceedings of The International Workshop on
Applied Modeling & Simulation.
Rölker-Denker, L., Hein, A., 2012b. Lernende
Krankenhäuser aus versorgungsforscherischer
Perspektive. Studiendesign und Methodeninventar. In
DMW. Thieme (German).
Rölker-Denker, L., Hein, A., 2014. Organisationale
Lernroutinen in der geriatrischen Akutbehandlung und
Rehabilitation. Ergebnisse einer qualitativen Studie. In
Zeitschrift für Palliativmedizin. Thieme. (German).
Rölker-Denker, L., Seeger, I., Sass, D., Hein, A., 2014.
Projektvorstellung „Netzwerk Versorgungsforschung
Metropolregion Bremen – Oldenburg“. In Zeitschrift
für Palliativmedizin. Thieme. (German).
Schreiber, G. T., Akkermans, H., 2000. Knowledge
engineering and management: the CommonKADS
methodology, MIT Press Cambridge.
Wengelowski, P., 2000. Entwicklung organisationalen
Lernens. Ein Lenkungsmodell, Deutscher Universitäts-
verlag Wiesbaden. (German).
Winter, A., Haux, R., 1995. A Three-Level Graph-Based
Model for the Management of Hospital Information
Systems. In Methods of Information in Medicine
.
Winter, A., et. al., 2003. 3LGM2: Methode und Werkzeug
zur Modellierung von Unternehmensarchitekturen im
Krankenhaus. In Proceedings der Frühjahrskonferenz
2003 des GI-Arbeitskreises Enterprise Architecture.
Institute for information management, University St.
Gallen, Switzerland. (German).
HEALTHINF2015-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
316
APPENDIX
Figure 2: Multi-professional Geriatric Team Session (activity view).
Figure 3: Clinical conference process (activity view).
Figure 4: Discharge letter (activity view).
KnowledgeProcessModelsinHealthCareOrganisations-Ideal-typicalExamplesfromtheField
317
