
System Improvement for the Management of Subcontracted Service
Performance Information in Korea’s Public Construction
Kim SeongJin, Kim Namgon and Ok Hyun
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology, Goyang-si, Republic of Korea
Keywords: Subcontract, Construction Technology Services, Service Performance, Prevention of Low-Priced
Subcontracts.
Abstract: To date, in South Korea, construction subcontracted services have been illicitly conducted without clear
grounds, but to establish a sound trading order between the principal contractors and the subcontractors, the
government recently began complementing the relevant system to legalize and systematically manage
subcontracted services. In line with this move, this study prepared a system designed to manage
construction subcontractors’ service performance results in a bid to legalize subcontracted services.
Towards this end, measures were worked out to integrate subcontracted services and contracted services
based on the system for the management of contracted construction technology service performance results.
The study findings can be used to formulate measures to protect subcontractors, such as the prevention of
low-priced subcontracts, by managing objective, reliable subcontracted service performance results.
1 INTRODUCTION
Subcontract refers to the arrangement by which
when the principal contractor commissions a
subcontractor to carryout construction work or
service, or when the principal contractor re-
commissions the construction work or service
commissioned by another project operator to the
subcontractor, the subcontractor performs the
commissioned construction work or service and
supplies, delivers, or provides the output to the
principal contractor and receives the corresponding
price (MOLIT, 2013).
To date, in South Korea, many subcontracted
construction technology services have been illicitly
and unfairly conducted between principal
contractors and subcontractors, through the later
issue of written contracts, breach of obligation of
notice, delay and adjustment of design changes, non-
payment of interests on delay, and failure to
maintain certain cash settlement rates. To resolve
these problems, the government is currently taking
measures to legalize subcontracted services, with a
view to establishing a sound trading order between
principal contractors and subcontractors; to revise
the relevant laws, with a view to systematically
managing the transactions; and to prepare the
grounds for implementing construction technology
service subcontracts in a bid to improve the relevant
systems (KICT, 2013).
In an effort to legalize subcontracted services,
this study sought to prepare a system designed to
manage subcontractors’ service performance results.
Towards this end, measures were worked out to
integrate the management of contracted and
subcontracted services based on the system for the
management of contracted construction technology
service performance results. As a result, the output
of this study can identify the objective, reliable
service status between contractors and
subcontractors, and can prevent low-priced
subcontracts, thus achieving the transparent
management of subcontracted services.
2 PROCEDURE FOR THE
MANAGEMENT OF
SUBCONTRACTED SERVICE
PERFORMANCE
South Korea does not have procedures for inquiring,
confirming, or approving subcontracted services
according to individual ordering agencies.
382
Seong Jin K., Namgon K. and Hyun O..
System Improvement for the Management of Subcontracted Service Performance Information in Korea’s Public Construction.
DOI: 10.5220/0005155303820386
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2014), pages 382-386
ISBN: 978-989-758-050-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
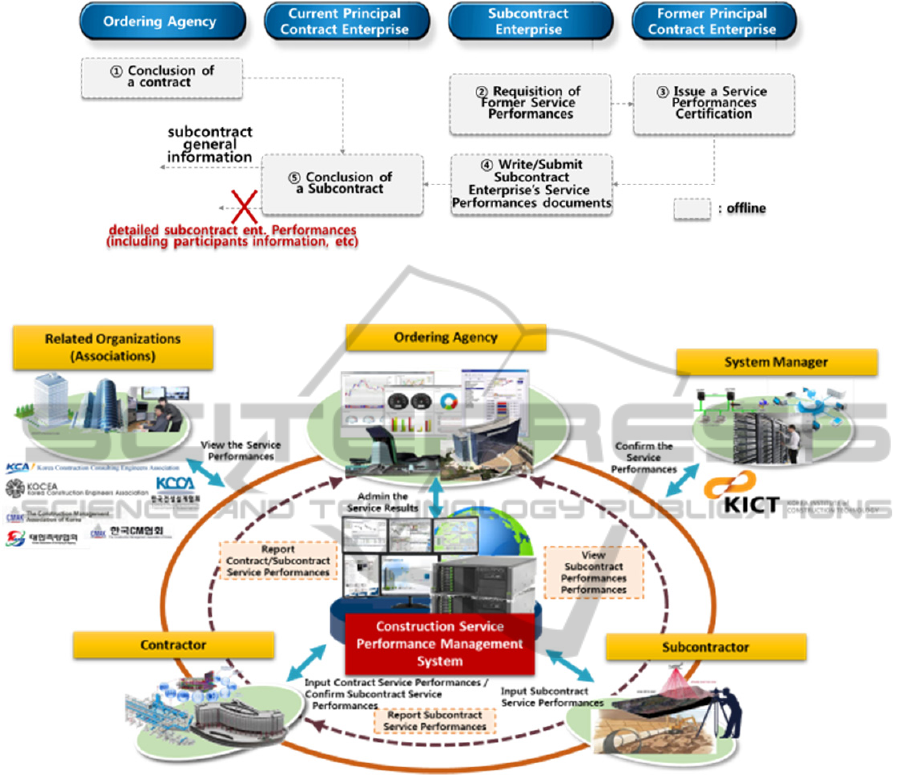
Figure 1: Flow of managing contracted and subcontracted Service Performances (As-Is).
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of the subcontracted service performance management system.
Yet, in domestic public construction projects, when
bidding for construction projects preferably with the
lowest prices, the bidders should submit the types
and volume of the works to be subcontracted to the
ordering agency for approval, and the subcontract
plans specifying the method and criteria for selecting
subcontractors. When signing the contract, the
bidder should submit the subcontract plan to the
ordering agency, specifying the subcontractors’
name, location, and selection methods by work type,
as well as the construction amount to be
subcontracted and the price thereof, and the
subcontract ratio.
As shown in Figure 1, the subcontract enterprise
is issued the service performance certifications by
the former principal contract enterprises, and submit
the service performance documents to the current
contract enterprise. But, the contract enterprise don’t
submit the service performance documents of
subcontract enterprise to the ordering agency.
Therefore , it is impossible for the ordering agency
to search subcontract enterprise ’ s service perfo-
rmance information until now.
Thus, this study worked out a system for the
management of subcontracted construction services
similar to the system for the management of
subcontracted construction work. In the proposed
procedure, the principal service contractor receives
the subcontracted service results from the
subcontractor, and reports such subcontracted
service results as well as the contracted service
results to the ordering agency. Figure 2 is the
schematic diagram of the subcontracted service
performance management system.
The subcontractor inputs the subcontracted service
results in the system for the management of the
SystemImprovementfortheManagementofSubcontractedServicePerformanceInformationinKorea'sPublic
Construction
383
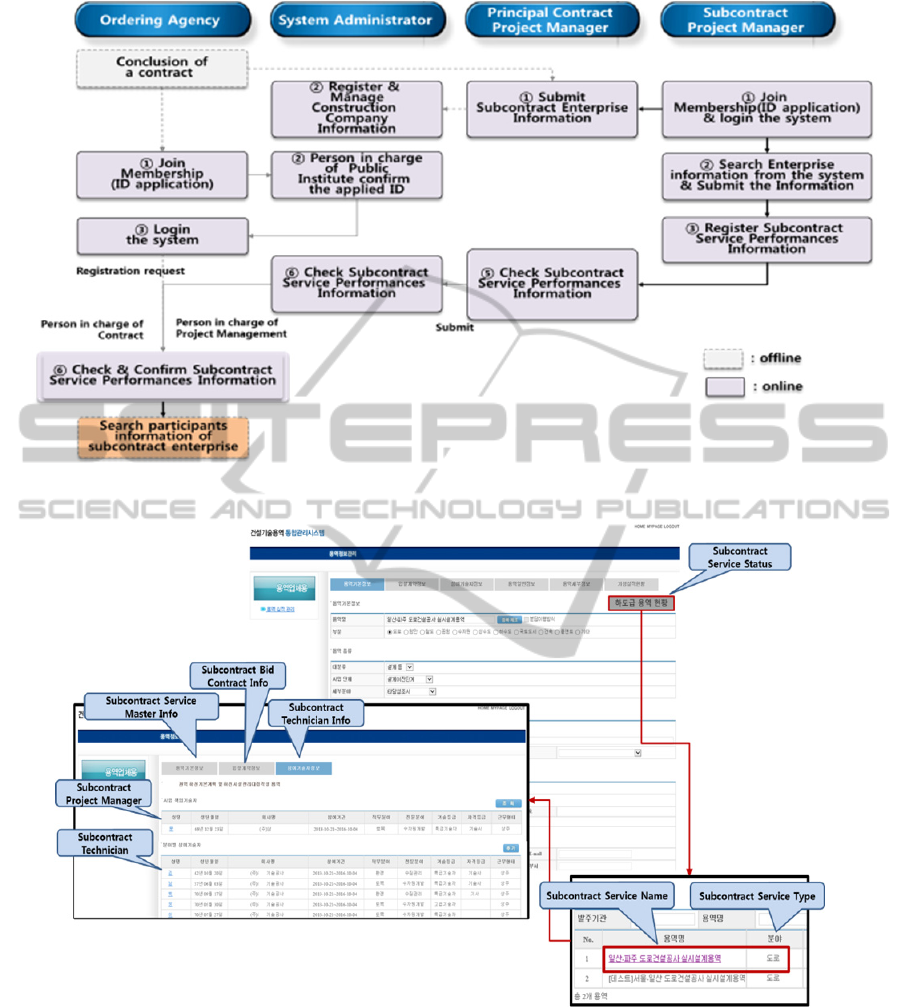
Figure 3: Flow of managing contracted and subcontracted Service Performances (To-Be).
Figure 4: Contractors’ screen for inputting & managing about the subcontracted service performance information.
construction technology service results, and reports
this fact to the principal contractor, who confirms
the subcontracted service performance information
and inputs his contracted service performance
information in the system. The input service
performance information is reported online to the
ordering agency by the principal contractor’s service
manager.
The ordering agency reviews and approves or rejects
the reported contracted/subcontracted service
performance information. The approved service
performance information is used in submitting
service performance confirmation data in other
service bids. The following diagram shows the
procedure for managing contracted and
subcontracted service results (Seongjin Kim, 2013).
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
384
As shown in Figure 3, the principal contractor’s
service manager reports the service performance
information, and the system administrator reviews it
and then reports it to the ordering agency. At the
ordering agency, the contract staffer and the project
manager review the service performance information
by relevant area, and approve or reject it.
3 DEVELOPMENT THE
MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OF
SUBCONTRACTED SERVICE
PERFORMANCE
According to the hitherto proposed measures for the
management of subcontracted service results, the
subcontracted service performance is not directly
reported by the subcontractor to the ordering agency,
but by the principal contractor.
In this study, a screen was configured where the
contracted service name can be inputted in the
system for the management of construction
technology service results, and then the
subcontracted service performance information can
be inputted. Also, the screen was configured in such
a way that when configuring the subcontracted
service performance information screen, only the
basic service information, bid and contract
information, and participating engineer information
can be inputted and managed, excluding the detailed
information on roads, water, harbors, and other
service areas included in the contracted service
performance information. Figure 4 shows the screen
shot of the subcontracted service performance
management system:
As shown in Figure 4, the principal contractor
can inquire about the subcontracted service
performance information according to the
subcontracts by work type. The subcontracted
service performance information, however, can be
revised directly by the subcontractor.
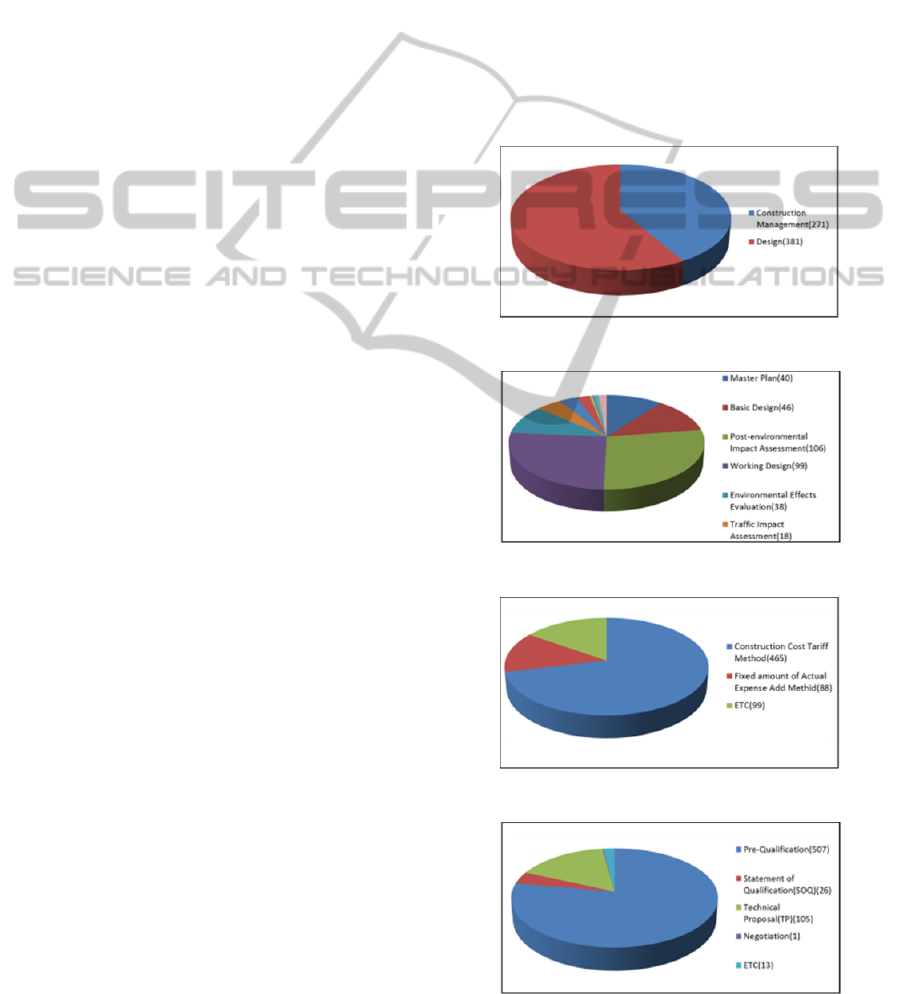
The study test operated the management of service
performance results of five local national land
agencies under the control of Ministry of Land,
infrastructure and Transport(MOLIT). As a result,
national land management agencies were found to
perform services in diverse areas, such as roads and
water, and contractors with relevant agencies and
relevant parties were surveyed, revealing that the
service contracts were concluded in diverse types.
The following shows an overview of national land
management agencies’ services:
As shown in Figure 4, the principal contractor
can inquire about the subcontracted service
performance information according to the
subcontracts by work type. The subcontracted
service performance information, however, can be
revised directly by the subcontractor.
The study test operated the management of
service performance results of five local national
land agencies under the control of Ministry of Land,
infrastructure and Transport(MOLIT). As a result,
national land management agencies were found to
perform services in diverse areas, such as roads and
water, and contractors with relevant agencies and
relevant parties were surveyed, revealing that the
service contracts were concluded in diverse types.
The following shows an overview of national land
management agencies’ services:
Figure 5: Construction technology service areas.
Figure 6: Detailed service areas.
Figure 7: Contracted service price payment.
Figure 8: Method of selecting service firms methods.
SystemImprovementfortheManagementofSubcontractedServicePerformanceInformationinKorea'sPublic
Construction
385

4 CONCLUSIONS
To date, in South Korea, the management of
subcontracted construction technology services has
not been properly conducted, leading to many
disputes between principal contractors and
subcontractors. To resolve these problems, there was
a need to ensure the transparent management of the
subcontracted service performance results with the
participation by all the parties, including the
ordering agency, principal contractor, and
subcontractor.
To prepare a system for the management of such
subcontracted construction technology service
performance results, this study established the
relations between contracted and subcontracted
services and prepared the procedure for handling the
subcontracted service performance results. Also, a
screen was prepared for managing service
performance results, and the system for the
management of service results was test-operated
targeting national land management agencies.
The proposed system can integrate the
management of all contracted and subcontracted
service performance results – which have been
managed by individual public agencies –to enable
the identification of the overview of the public
sector’s service contract conclusion methods in this
country. Also, the subcontracted service
performance is reported to the ordering agency,
enabling inquiry about the overview of bans on re-
subcontracts and subcontractors’ qualifications, and
enhancing the transparency and fairness of
subcontracts, as well as contributing to the
protection and fostering of small and medium-sized
subcontractors.
The research on the integrated service
management system should continue to link all
construction technology service performance
information and service evaluation information so as
to enable the one-stop service management service
in the public sector.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was carried out as part of Korea Agency
for Infrastructure Advancement’s research project on
the promotion of construction and transport
technologies [12 Construction Innovation E05, the
development of technologies for updating,
evaluating, and managing public agencies’ orders
for services].
REFERENCES
Korea Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport
(MOLIT), Master Act for Construction Industry –
Enformance Ordaince – Article 34–2 (Submissin of
Subcontract Plans), 2013.
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building
Technology (KICT), “A Study on Measures to
Leagnalize the Subcontrcting of Construction
Technology Services,” 2013.
SeongJin Kim and NamGon Kim, “Development of an
Information System for managing the Service
Performances in Public Construction Technique
Fields”, Journal of The Korea Academia-Industrial
cooperation Society, vol.14 no.11, 2013, pp.5993-
5999.
KyongHo Jin, “An Improvement Plan on Business
Bounded System of Construction Technical Services”,
Korea Institute of Construction Engineering and
Management, vol.13, no.1, 2012, pp.36-39.
KMIS2014-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
386
