
Photoluminescence Characterization of Zn- and Cs-Vanadate
Phosphors
Tingting Li, Zentaro Honda, Takeshi Fukuda, Jiaolian Luo and Norihiko Kamata
Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Saitama University, 255 Shimo-Ohkubo,
Sakura-ku, Saitama 338-8570, Japan
Keywords: Zn
3
V
2
O
8
,
Csvo
3
,
Cs
3
VO
4
, Sol-gel Process, Quantum Yield.
Abstract: We synthesized Zn
3
V
2
O
8
, CsVO
3
and Cs
3
VO
4
by sol-gel process and studied their crystalline and
luminescent properties. By optimizing the sintering conditions, pure phases of aim samples including
Cs
3
VO
4
were obtained. The annealing temperatures of 450℃ for CsVO
3
, 600℃ for Cs
3
VO
4
, respectively,
are lower than that of 750℃ for Zn
3
V
2
O
8
at the same duration of 12h. The Cs
3
VO
4
showed quantum yield of
90% with the half-width of 120nm. It became clear that the Cs-V-O system, especially Cs
3
VO
4
, is
promising for white LED applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
White light-emitting diodes (W-LEDs) are replacing
traditional incandescent and fluorescent lamps due
to their superior efficiency, lifetime, and
controllability of lighting environment (Li et al.,
2013). However, recent widespread W-LEDs,
realized by blue LED and yellow phosphor of Ce-
doped yttrium aluminum garnet, lack red emission
component and show a low color rendering index
(CRI) (Kim et al., 2009). It is necessary, therefore,
to find phosphor materials with higher CRI together
with keeping efficiency and reliability. As a kind of
efficient phosphor materials, a family of vanadates
has been widely investigated for various types of W-
LEDs and flat-panel displays due to their better
chromaticity (Huang et al., 2012); (Nakajima et al.,
2009).
The VO4 unit of a central vanadium ion and
coordinating four oxygen ions in a tetrahedral (Td)
symmetry is known as the luminescent center of the
vanadate group. Unlike sharp emission lines due to
4f transitions of rare earth ions as Eu3+, Tb3+ etc., a
family of zinc and cesium vanadates, Zn3V2O8,
CsVO3 and Cs3VO4, shows efficient and broad
emission spectra in a visible wavelength region.
Each VO4 tetrahedron in Zn3V2O8 is isolated in an
orthorhombic structure, while that in CsVO3 is two-
dimensionally arrayed as the VO4 sheet in an
orthorhombic pyroxene structure (Nakajima et al.,
2010).
In the present work, we synthesized Zn3V2O8,
CsVO3 and Cs3VO4 by a sol-gel method and
studied their X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns,
surface images, photoluminescence (PL), PL
excitation (PLE) spectra and the value of PL-
quantum yield (QY). The synthesized Cs3VO4 was
most efficient with the PL-QY of 90%. Different
luminescence properties and synthesis conditions
among three phosphors were discussed.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
2.1 Preparation
We chose Zn(CH3COO)2•2H2O, Cs2CO3 and
NH4VO3 as starting materials of Zn3V2O8, CsVO3
and Cs3VO4 by a sol-gel process. First, we weighed
these starting materials, and dissolved them in
aqueous ammonia, respectively. The first stirring
step was performed for two hours with 250 rpm at
room temperature (RT) in order to prevent the
evaporation of aqueous ammonia and make sure that
materials fully react with each other in ionic states.
Then the temperature was increased to 80ºC with
keeping 250 rpm stirring until the solution became a
semitransparent gel. Second, the semitransparent gel
was dried at 120ºC about 4h, then ground thoroughly
by a mortar, and transferred into a crucible which
63
Li T., Honda Z., Fukuda T., Luo J. and Kamata N..
Photoluminescence Characterization of Zn- and Cs-Vanadate Phosphors.
DOI: 10.5220/0004704800630065
In Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS-2014), pages 63-65
ISBN: 978-989-758-008-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
was put into a sintering oven. After the sintering
process, a yellowish powder of CsVO3 (450ºC, 12h)
or a white powder of Cs3VO4 (600ºC, 12h) were
obtained.
In case of Zn3V2O8 (750ºC, 24 h), it also
contained the phase of Zn2V2O7 or Zn4V2O9. (Li
et al., 2013) In order to obtain a uniform crystalline
phase, the inchoate sample was placed into ethanol
solution again. It was stirred first at 250 rpm for 2h
at RT, then raised the temperature to 80ºC until the
ethanol solution was completely removed. After
that, we sintered it again at the temperature of 750ºC
during 24h, and at last obtained a yellowish powder
of pure Zn3V2O8.
2.2 Characterization
Synthesized samples were ground again and then
transferred onto a glass plate, and the X-ray
diffraction (XRD) patterns were measured by using
a RINTUltimaIII (RIGAKU) diffractometer with Cu
Ka radiation (40 kV 9 40 mA). The samples were
identified by Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction
Standards (JCPDS) files, and the relative
percentages of each phase were estimated from the
total area under the most intense diffraction peaks
(Francisco et al., 2007). The surface morphology
was observed by using a S-4100 (HITACHI)
scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
The photoluminescence (PL) and PL excitation
(PLE) spectra of each sample, pressed inside a
circular dip of 4 mm diameter with 1 mm depth on a
Cu-holder, were measured by a FluoroMax-3
(Horiba Jovin-Yvon) spectrophotometer. The PL-
QY was determined by a QEMS-2000 (Systems
Engineering) by an excitation light of an LED with
the peak wavelength of 375 nm. The PL-QY was
obtained by a comparison between the PL spectrum
of the sample and the scattered excitation light when
a standard diffuser was placed at the sample position
(Li et al., 2013). All measurements were performed
at room temperature.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Crystalline Phase Formations
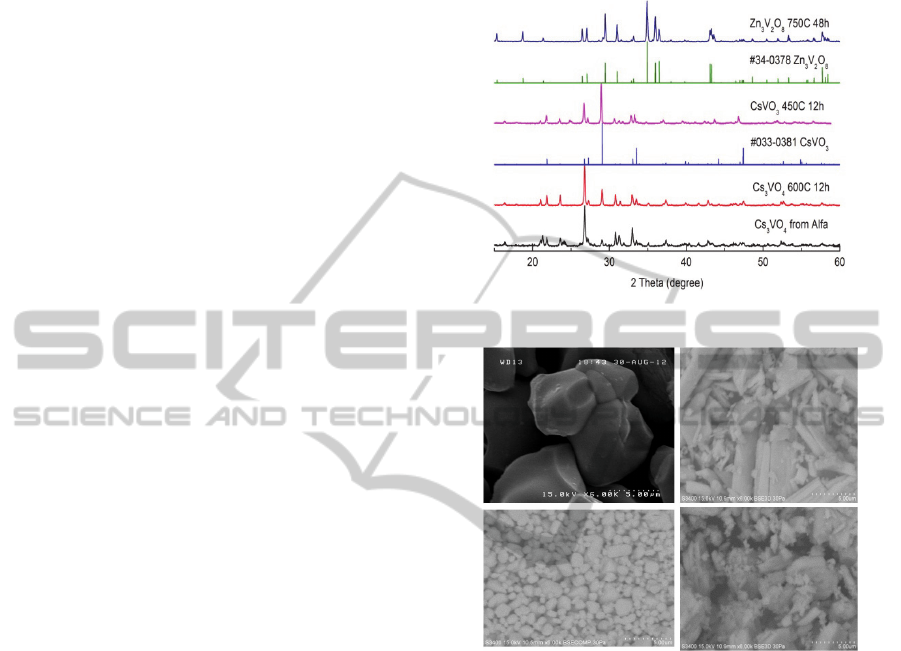
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of synthesized
samples with corresponding homologous databases.
We can see that our experimental data of Zn3V2O8
and CsVO3 agreed well with the standard PDF cards
of No.34-0378 (Zn3V2O8) and No.033-0381
(CsVO3), respectively. No PDF data were found as
for the case of Cs3VO4 phosphor, but the principal
patterns of our synthesis were consistent with those
of a commercial powder from Alfa.
Figure 1: XRD patterns for vanadates.
Figure 2: SEM images for vanadate phosphors: (a)
Zn3V2O8 750Ԩ12h, (b) CsVO3 450Ԩ12h, (c) Cs3VO4
600Ԩ12h, and (d) Cs3VO4 450Ԩ12h.
Surface morphologies of synthesized samples
were observed by SEM. Resultant images of
synthesized vanadates were shown in Figure 2(a)-
(d). In case of Zn3V2O8 (750ºC 12h), each block
throughout the observing volume seems to be
homogeneously crystallized with a typical size of
several µm as shown in Fig. 2(a).
Fairly irregular particles both on size and shape
were observed in CsVO3 (450ºC 12h) as shown in
Figure 2 (b). In contrast, the morphology of Cs3VO4
(600ºC 12h) was relatively homogeneous with
particle sizes about 1-3µm as shown in Figure 2 (c).
At 450 ºC 12h, however, the dregs-like particles
were found at the surface of the Cs3VO4 as shown
in Figure 2(d).
PHOTOPTICS2014-InternationalConferenceonPhotonics,OpticsandLaserTechnology
64
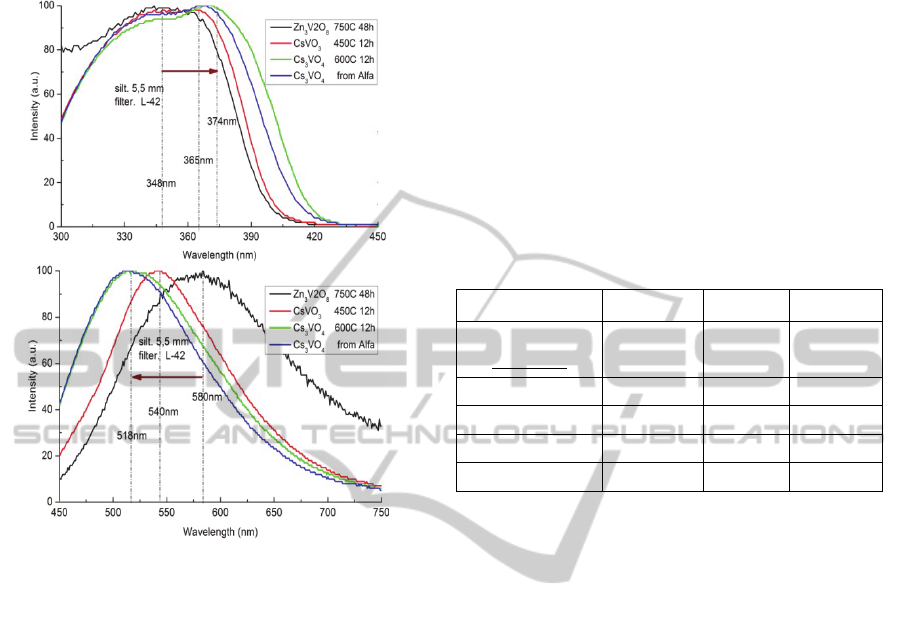
3.2 The Excitation and Emission
Spectra
(a)
(b)
Figure 3: The PLE (a) and PL (b) spectra of the vanadate
phosphors.
Figure 3(a) and (b) show the PLE and PL spectra
of these vanadate phosphors, respectively. The broad
PLE band ranging from 300nm to 400nm enables
these vanadates to be combined with UV or blue
LEDs. Meanwhile, Zn3V2O8, CsVO3 and Cs3VO4
produce intense emission from yellowish white to
mid white band with the FWHM of 180, 110 and
120nm, respectively. Meaningful spectral shifts were
observed, though these originate from the same
luminescence center VO4 at transitions among 3T2,
3T1 and 1A1 levels. Compared with the PLE and PL
peaks of Zn3V2O8, those of CsVO3 shift about 20
and 40nm, and those of Cs3VO4 about 30 and
60nm, respectively.
3.3 The PL-Quantum Yield (PL-QY)
The PL-QY at 375nm excitation is listed in Table 1
together with the synthesis condition, the FWHM,
the peak wavelengths of the PLE and PL spectra.
The QY value of 90% was obtained in the case of
Cs3VO4 which is higher than that of 76% obtained
by commercial powder from Alfa. We consider that
the difference between Cs3VO4 and CsVO3 is
important for their application to W-LEDs.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, vanadate phosphors of Zn3V2O8,
CsVO3 and Cs3VO4 were synthesized by the sol-gel
method. By comparing the difference of crystalline
structure and luminescence properties among the
three, the Cs3VO4 with the heating process at 600ºC
during 12h showed highest PL-QY of 90% and is
promising for the application to the W-LEDs.
Table 1: Comparison between the three vanadate
phosphors.
Samples
Zn
3
V
2
O
8
CsVO
3
Cs
3
VO
4
Synthesis
conditions
750 ºC
48h
450 ºC
12h
600 ºC
12h
FWHM (nm)
180 110 120
λex (nm)
348 365 374
λem (nm)
580 540 518
PL-QY (%)
52 81 90
REFERENCES
C. Li et al, 2013. ‘Photoluminescence and energy transfer
studies on Ce3+/Eu2+ co-doped Ba3Si6O12N2
phosphor for white light emitting diodes’. Opt.
Communications 295, pp. 129-133.
J. Kim et al, 2009. ‘Nanocrystalline Y3Al5O12:Ce
phosphor-based white light-emitting diodes embedded
with CdS:Mn/ZnS core/shell quantum dots’. Mater
Lett 63, pp. 614-616.
Y. Huang et al, 2012. ‘Novel yellow-emitting phosphors
of Ca5M4 (VO4)6 (M=Mg, Zn) with isolated VO4
tetrahedra’. Opt. Express 20(4), pp. 4360-4367.
T. Nakajima et al, 2009. ‘A revisit of photoluminescence
property for vanadate oxides AVO3 (A:K, Rb and Cs)
and M3V2O8 (M:Mg and Zn)’. J. Lumin. 129(12), pp.
1598–1601.
T. Nakajima et al. 2010. ‘Correlation between
Luminescence Quantum Efficiency and Structural
Properties of Vanadate Phosphors with Chained,
Dimerized, and Isolated VO4 Tetrahedra’. J, Phys,
Chem. C, 114, pp. 5160-5167.
T. Li, Z. Honda et al, 2013. ‘Fabrication and
characterization of Zn3V2O8 phosphor by sol–gel
process’. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 66, pp. 225–230.
M. M. Francisco, J. V. Miriam, P. Heriberto, 2007.
‘Micro-structural development of ZnO pellets doped
with different Vanadium Oxides (V2O5 and V2O3)’,
Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 4(6), pp. 564-570.
PhotoluminescenceCharacterizationofZn-andCs-VanadatePhosphors
65
