
A Serious Game Application using EEG-based Brain Computer
Interface
Francisco José Perales and Esperança Amengual
Mathematics and Computer Science Department, University of the Balearic Islands,
Crta. Valldemossa Km 7.5, 07122, Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Keywords: Brain Computer Interface (BCI), Electroencephalography (EEG), Rehabilitation, Serious Games, Neu-
rofeedback, Cerebral Palsy, Motor Impairment, Focus Feature, Alpha Channel.
Abstract: Serious games have demonstrated their effectiveness as a therapeutic resource to deal with motor, sensory
and cognitive disabilities. In this article we consider Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) as a new interaction
mechanism that could be used in serious games to improve their rehabilitation activity thanks to the ability
of neurofeedback to stimulate the cortical plasticity. We present the brief state-of-the-art of BCI serious
games and the factors to be considered in order to develop this particular kind of software that could be
highly complex and require experts with different knowledge and skills. We propose a new approach based
on the detection of focus features in the game activity. We introduce a system able to assess the Alpha band
variations in particular game tasks. Our initial target users are children with cerebral palsy and motor disa-
bilities. The system is currently under evaluation with control users before to be operated with the target us-
ers in rehabilitation centers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human Computer Interaction (HCI) is the discipline
concerned with the study of the information ex-
change between humans and computer systems. Its
main objective is to achieve an efficient information
interchange, while minimizing the number of errors
and improving user satisfaction. Ultimately, the final
goal is to improve the productivity of the tasks that
people carry out using computers. Usually the inter-
action between human and computers is performed
through common peripheral devices such as the
keyboard, the mouse and the display. This type of
interaction unavoidably involves the operation of the
neuromuscular system as intermediary. When we
use the mouse or the keyboard, the brain communi-
cates with movements which are managed through
impulses that run the nervous system until they
reach the appropriate muscle. But, what happens
with a muscular or nervous disease? It is at this point
when Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) gains im-
portance. This emerging technology makes direct
communication interchange possible. Thanks to
BCI, communication between human and computers
does not inevitably imply the use of the neuromus-
cular system. These interfaces can be used as an
additional communication band, or even as the
unique possible one for people with serious diseases.
The possibility of direct communication between
a computer and the user’s brain, without any addi-
tional peripheral devices, opens a wide range of
possibilities to develop new software applications.
One of them is neuromotor rehabilitation with com-
puter games, which in this case are named “serious
games”. In general, the main goal of computer
games is entertainment. Serious games are a special
type of computer games which have been designed
with medical or educational purposes. Like all the
games, serious games have to be entertaining and
fun to improve the motivation of the patient, thus
improving the final results.
The use of BCI in serious games design rises to
the challenge of using non-invasive brain signal
acquisition devices. The choice of non-invasive
techniques, such as electroencephalography (EEG),
is particularly important since these techniques do
not require surgery. In this way the patient will be
able to use the serious game the time that will be
required, whether adult or child, without added risks.
Electroencephalography (EEG) is the recording of
electrical activity along the scalp. EEG measures
voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current
249
Perales F. and Amengual E..
A Serious Game Application using EEG-based Brain Computer Interface.
DOI: 10.5220/0004678102490255
In Proceedings of the International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics (BrainRehab-2013), pages 249-255
ISBN: 978-989-8565-80-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

flows within the neurons of the brain. In clinical
contexts, EEG refers to the recording of the brain's
spontaneous electrical activity over a short period of
time as recorded from multiple electrodes placed on
the scalp. Currently, it has been shown that there is
some relation between variations in EEG signals and
some processes such as perception, language, psy-
chomotor skills, arithmetical calculus, and several
emotions. Another advantage of EEG is the availa-
bility of commercial devices for electroencephalog-
raphy at an affordable cost (Carrino et al., 2012).
The main goal of this paper is to plot the landscape
of the application of BCI to medical serious games.
In section 2 we present the state-of-the-art of the use
of BCI in medical serious games. In section 3 we
show our proposal system designed to evaluate the
user activity based in a portable and wireless EEG
low cost system that measure the Alpha band ampli-
tude variations. Finally, the conclusions and some
proposals for future work are exposed in section 4.
2 BCI FOR SERIOUS GAMES
A relevant number of BCI systems have been de-
signed to improve the quality of life of people with
diseases (Kaur et al., 2012). In these cases BCI is
used to perform a direct and precise control of pros-
thetic devices, wheelchairs (Carrino et al., 2012) and
computers. However, the approach we are interested
in for serious games is quite different since it focus-
es on the treatment or on the improvement of the
disease, not in palliative care. Within this field, seri-
ous games have demonstrated their capability to
boost the rehabilitation activity with regard to tradi-
tional therapy which is frequently repetitive and
monotone. In contrast, serious games can include
changing stimulant elements which even can not to
be directly related with the therapy. In (Diaz et al.,
2012) their authors describe how a simple adaptation
of the game scenarios (background images) can
result in positive or negative effects over the results
obtained by the player, and this is a kind of stimulus
that can be frequently changed with little effort in a
computer program. In this sense, it is possible to find
a number of serious games developed for rehabilita-
tion purposes, but only a few of them include BCI.
In (Rego et al., 2010) a taxonomy of serious games
is proposed, but there is not any reference to BCI in
the article. The criteria used for the classification of
serious games neither consider any BCI specific
aspect.
2.1 Application of BCI to Serious
Games
In (Nijholt, 2009) two different approaches for the
integration of BCI in games are described. The first
one is aimed at controlling the game through the
development of a mental gamepad. The second one
is intended to get feedback, in this case named “neu-
rofeedback”, for the improvement of the user expe-
rience by adapting the contents or the difficulty level
of the game to the mental state of the player. In
medical applications in particular, BCI has been
integrated with the aim of neurofeedback and its
effectiveness to improve cognitive skills, pain treat-
ment, schizophrenia, depression, alcoholism, epilep-
sy, as well as and other psychological or neurologi-
cal affections, has been demonstrated. The reason
for the effectiveness of this strategy seems to be that
it induces cortical plasticity, that is, the function
which was performed by a part of the cerebral cortex
which was damaged is now performed by other
region of the cortex. A multimodal interaction strat-
egy is also possible by combining the usual periph-
eral devices with BCI. In this way, it is possible to
perform a cognitive training which can be improved
by BCI neurofeedback (Sung et al., 2012).
2.2 Serious Games Development with
BCI
In (Sung et al., 2012) the complexity of BCI serious
game development is highlighted. This kind of de-
velopments involves different experts with distinct
knowledge and skills: EEG and neuro rehabilitation
experts, EEG signal treatment experts, and game
development experts. The first group of experts has
to design the rehabilitation strategy and the patterns
to extract from the EEG signals. The second group
has to develop the BCI component able to treat the
signal. Finally, the game developers have to deal
with the graphical interface, the sound and other
elements of the game. Other qualities that are desir-
able for BCI serious games, and which still empha-
size the difficulties, are the need for low-cost EEG
devices and a wide range of possible users. The
development of BCI serious games which satisfy the
specified requirements at a reasonable cost and time
is possible. A recommended strategy is the integra-
tion of a BCI framework with the drivers of the EEG
device to be used and a game motor.
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
250

3 THE PROPOSED METHOD
Our objective is to assess the ability to focus on a
specific mental task. We have designed a mental
concentration tests based on visual and acoustic
stimulus. The main idea is to evaluate if the stimulus
increases or decreases the user concentration over
the mental task. The user is in front of the computer
screen and is required to direct his/her attention
towards a specific task.
To perform this test it has been necessary to de-
velop a system which is composed of BCI interac-
tion and measurement physical devices, together
with the software applications that support the data
integration for each patient. The main limitation of
this work is the inability to use standard wired EEG
because of the systematic involuntary movements of
the final user. Therefore, the system hardware
should be the least invasive as possible. The initial
constraints of our system are: wireless and a mini-
mal set of electrodes. Several commercial systems
have been evaluated and finally we have selected the
NeuroBit Optima 4 and BioEraPro Software tool
(BioEraPro Software, 2012) to develop the initial
application.
The system architecture used in this experiment
is shown in Figure 1. For the proposed study the
maximum number of electrodes is limited to a max-
imum of 4 at frontal position. Although this con-
straint the analysis range, there is not currently any
available version with less electrodes. Figure 2
shows a use case of the system. In any case, the
initial measurements have been performed with 2
electrodes to simplify the initial configuration of the
system.
More concretely, we are particularly interested
on the variations of the alpha frequency components.
From an initial reference we analyze the variation
Figure 1: System architecture.
Figure 2: Control user.
ASeriousGameApplicationusingEEG-basedBrainComputerInterface
251
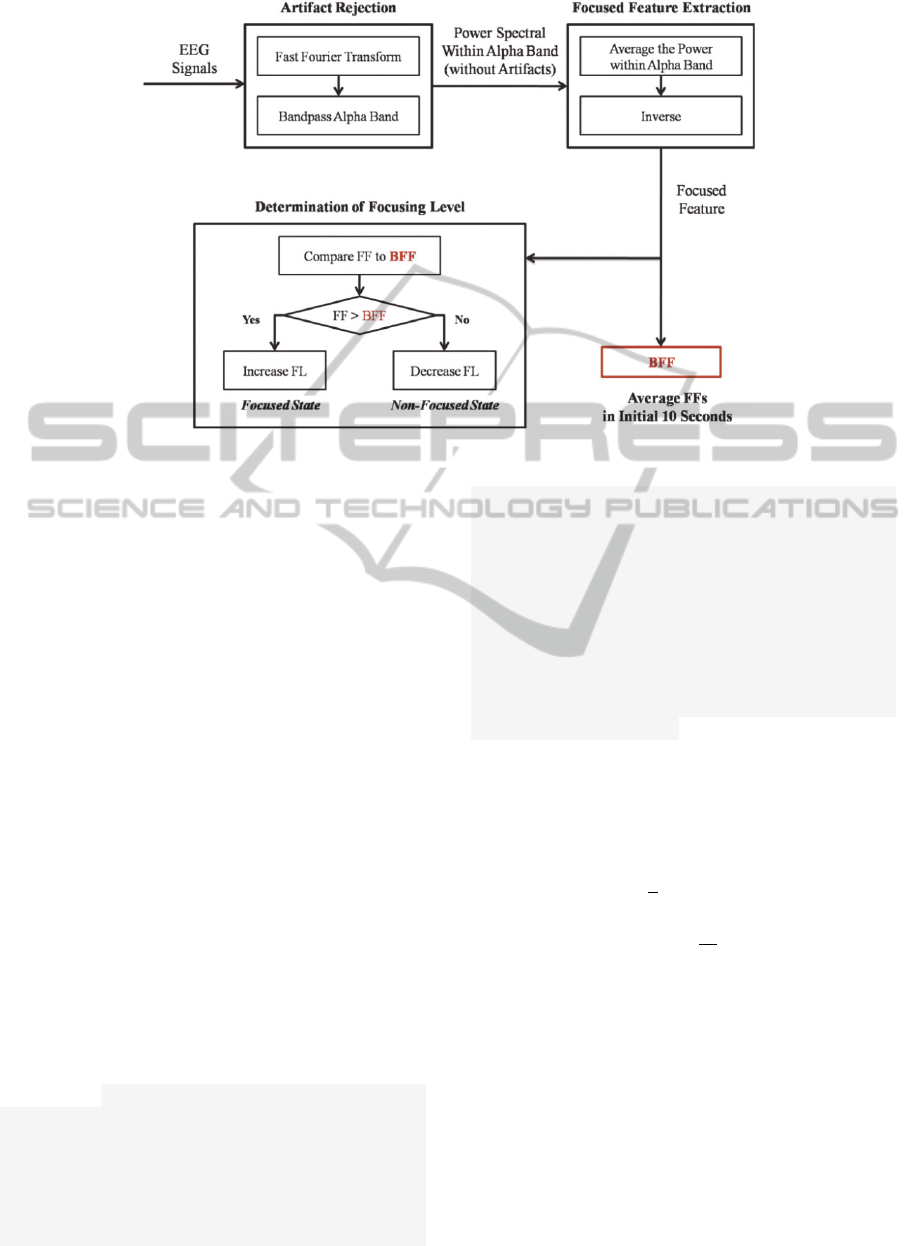
Figure 3: FF (Focus Feature) classification procedures.
through successive acoustic and visual stimuli. Our
idea is based on a variant of the work developed by
Lun-De Liao (Lun-De Liao et al., 2012) which fo-
cuses on the analysis of the influence of using dry or
wet electrodes. We have a totally different purpose
because our technique is based, not in the analysis of
a particular hardware, but on the possible influence
of the acoustic and visual stimuli over the concentra-
tion ability of the user. The proposed procedure
follows the classical steps in a BCI system. The
main objective is to capture the input signals from
the electrodes and apply the Fourier transform and
then apply a specific filter where we exclusively
select the Alpha band whose signals describe the
rhythmic activity between 8Hz and 13Hz. From
these data we perform an average of the five values
within the range and invert the signal. At this point
we consider important to remark that ocular artifacts
only affect the EEG delta and theta bands (Romero
et al.,2010). Therefore it has not been necessary to
use any artifact reduction method to minimize the
signal interference. Formulas in (1) describe these
operations. The reason of using the Alpha band is
that several studies [9, 10] have demonstrated that
the EEG alpha rhythm frequency decreases with
changes from a relaxed state to a focused or concen-
trated state. Previous neurophysiologic studies
(Kramer, 1991) have postulated that the mental
workload could be detected in a decrease of the
alpha band activity in the parietal and occipital
brain areas. Moreover, as demonstrated in (Klimesh,
1999) there is a decrease of the alpha band activity
when we are doing a learning task. Other recently
studies (Walter et al., 2011) prove that we can classi-
fy mental states with machine learning algorithms
with the analysis of the variations in time of the
alpha band. These studies use sixteen electrodes
placed according to the International Electrode (10-
20). In the particular case of our experiment this
EEG configuration is not viable due the special
motor disabilities of the final users (cerebral palsy
with significant spastic movements). In addition, the
proposed mental task must be adapted to the cogni-
tive level of these users. Therefore, we assume that
the alpha band is the main feature used to classify
the concentration state.
…
…
1
5
1
(1)
Figure 3 shows the flow diagram of the software
application. In this work we have adapted the flow
diagram presented in (Lun-De Liao et al., 2012) to
our problem with different architecture and objec-
tives. The EEG data are captured during a period of
10 seconds and the rolling average is calculated
every 10 seconds to see the tendency (Lee and Tan,
2006). This average is initially stored in a BFF
(Baseline Focus Feature) which is used as a refer-
ence for the successive measurements. The average
is stored in the buffer only one single time and a
threshold is defined. If this threshold is exceeded,
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
252

this indicates the user is moving to a concentration
state. On the contrary, if activity falls below the
threshold, this means the user is moving to a relaxa-
tion state. Concentration gradations are not initially
considered. The performed test is composed by the
following 10 second measurement steps:
1. Measurement of the initial concentration thresh-
old
2. Measurement without any stimuli, only numeri-
cal feedback (0 = relaxation, 1 = concentration)
3. Measurement with pleasing musical sound
4. Measurement with unpleasant musical sound
(>80db)
5. Measurement without sound
6. Measurement with images of a ball motion in a
pathway
7. Measurement with relaxing video (smooth see
waves)
8. Measurement with stressing video (city with
activity)
9. Measurement without video
This procedure is repeated three times for each con-
trol user.
4 SOME INITIAL RESULTS
IN TWO SET OF CONTROL
USERS
As discussed in the preceding section, to obtain
visual results we have established two states: con-
centrated and relaxed. The following table shows the
values registered in 7 different control users.
From the obtained results the average of the 7
control users has been calculated. In any case, it can
be observed that two of the users, user 6 and user 7
specifically, have high BFF values, as well as the
rest of the values when compared with the other
control users. The reason could be that they are
stressed users or users with an alpha band activity
which is out of the ordinary. From this sample it is
difficult to infer convincing conclusions about varia-
tions in the alpha rhythms depending on the stimuli.
If we construct a variations table (+ indicates an
increase, - indicates a decrease), we have:
Table 1: Seven control users.
User BFF BFF(Without Feedback) FF (Music) FF (Noise) FF(Ball Tracking) FF(Calm Image) FF(City Image)
User 1 18670 3500 5870 3600 8900 6000 6500
User 2 20840 4000 7200 7000 6000 3000 4300
User 3 59720 74000 34000 20700 40000 50000 35000
User 4 49970 100000 209000 70000 155000 270000 200000
User 5 22370 12000 11700 15000 30000 35000 45000
User 6 75830 137300 349000 186000 134000 180000 105000
User 7 100500 250000 450000 320000 149000 350000 200000
Mean 49700 82971 152396 88900 74700 127714 85114
Table 2: BFF variations seven control users.
User BFF BFF (Without Feedback) FF (Music) FF (Noise) FF(Ball Tracking) FF(Calm Image) FF(City Image)
User 1 18670 - + - + - +
User 2 20840 - + - - - +
User 3 59720 + - - + + -
User 4 49970 + + - + + -
User 5 22370 - - + + + +
User 6 75830 + + - - + -
User 7 100500 + + - - + -
Mean 49700 82971 152396 88900 74700 127714 85114
ASeriousGameApplicationusingEEG-basedBrainComputerInterface
253

Table 3: Ten control users (new stimuli sequence).
User BFF BFF(Witho
ut Feed-
back)
FF
(Music)
FF
(Noise)
FF(Calm
Image)
FF(City
Image)
FF(Ball
Track-
ing)
User 1
42004 34695 94657 48105 60421 85311 127647
User 2
33091 77423 82677 53220 102204 138000 96341
User 3
39240 57022 81677 49649 20375 95671 136361
User 4
16000 19961 78001 84430 124430 81704 143382
User 5
69271 95530 96006 314551 119806 114728 201283
User 6
15818 18000 185200 131747 101230 161300 220300
User 7
134132 227733 461333 198666 227350 217300 495285
User 8
282551 375950 560000 455500 716650 345600 391550
User 9
84901 140200 244320 374115 271111 583433 443452
User10
47154 153450 208115 145937 342769 648486 523440
Mean
76416 119996 209199 185592 208635 247153 277904
Variation
BFF
+ + - + + +
It is perhaps possible to deduce that music in par-
ticular enhances the capacity of concentration since
in 5 users the signal increases. Something similar
happens with the image of a calm beach. Further-
more, we observe that in 6 of the users the shrill
noise stimulus exceeding 80 decibels results in a loss
of concentration. An unexpected result is that an
increment of attention appears only in 4 users. A
possible reason could be that 10 seconds between
stimuli are not enough to recover concentration due
to the “carry over effect" (Hsieh and Lin-Chao,
2005). Based on these reflections we have consid-
ered that more experiments with control users are
necessary in order to gain greater distinction among
stimuli and calculate the average values of each of
them at repeated intervals. A new sequence of stimu-
li is defined: the ball tracking stimulus is the last
one, the calm and city images are interchanged. In
this experiment the number of control users has
been increased to 10 (7 overlapped with the ones
from table 1 and table 2).
From the previous table it is possible to conclude
that, although there are some divergences in the
data, the average is that calm music and beach stim-
uli increase concentration, noise decreases concen-
tration and the surprising finding is that the image of
the city in motion also increases concentration, it
does not distract. Finally the ball tracking implies
concentration, which seems logical. However, it is
not possible to strictly state that the acoustic or visu-
al stimulus increase concentration for the task to
perform or initially imagined because it would be
possible that the increment in the attention was due
to the stimulus itself. Accordingly, we would ana-
lyze more cases based on a concrete activity and
combine the stimuli to see if they improve or not the
goal or the performance of the main task (hybrid
endogenous + exogen paradigm).
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Serious games have demonstrated to be effective as
a therapeutic resource in motor, sensory and cogni-
tive disabilities. There is a great variety of serious
games and they can be classified depending on their
application area, interaction technology, monitoring
capability, feedback possibilities and other proper-
ties. Advances in the treatment of EEG signals have
reached the point at which there are an important
number of characteristics that can be extracted and
classified as the basis for BCI systems design with
different objectives and forms of application. There
are currently some games which integrate BCI by
fundamentally following two strategies: to control
some aspects of the game or to get feedback and
adapt the level of difficulty of the game environ-
ment. However, in the particular case of serious
games the strategy always consists in applying BCI
to get neurofeedback to deal with psychopathology
or neuropathology. The development of serious
games is a costly and complex task which involves
experts in different areas. This cost and complexity
can be managed with existent frameworks which
help to increase the level of abstraction of the com-
ponents to be developed.
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
254

A prototype of a BCI system which assesses the
concentration skills has been presented. The system
is based on a classification of the Alpha band varia-
tions. The assessed users are control users who do
not suffer any motor disease. The proposed system is
simple, low cost, wireless, requires very little train-
ing, and has a minimum number of electrodes. Re-
sults identify certain logical trends such that relaxing
music and pleasant images promote concentration,
likewise a harsh noise reduces it. At all events, it is
not possible to precisely infer that this is in fact what
happens due to problems in video editions that do
not properly separate the proposed events. This work
is at a very early stage and it is still necessary to
validate the results with more users, particularly
with the final users which would be people who
suffer from cerebral palsy. We plan to improve the
defined experiments using a main task and addition-
al visual or acoustic stimulus in order to improve the
final performance of the user. The cognitive skills of
each specific user will also be considered in order to
adapt the game to their level of mental cognition.
REFERENCES
Carrino, F., Dumoulin, J., Mugellini, E., Khaled, O., and
Ingold, R. 2012. A self-paced bci system to control an
electric wheel-chair: Evaluation of a commercial, low-
cost eeg device. In Biosignalsand Biorobotics Confer-
ence (BRC), 2012 ISSNIP. IEEE, 1–6.
Diaz, B., Sloot, L., Mansvelder, H., and Linkenkaer-
Hansen, K. 2012. Eeg-biofeedback as a tool to modu-
late arousal: Trends and perspectives for treatment of
ad hd and insomnia.
Kaur, M., Ahmed, P., and Rafiq, M. 2012. Technology
development for unblessed people using bci: A survey.
International Journal of Computer Applications 40.
Nijholt, A. 2009. Bci for games: a ‘state of the art’ survey.
Entertainment Computing-ICEC 2008, 225–228.
Rego, P., Moreira, P., and Reis, L. 2010. Serious games
for rehabilitation: A survey and a classification to-
wards a taxonomy. In Information Systems and Tech-
nologies (CISTI), 2010 5th Iberian Conference on.
IEEE, 1–6.
Sung Y., Cho, K., and Um, K. 2012. A development archi-
tecture for serious games using bci (brain computer in-
terface) sensors. Sensors 12, 15671–15688.
Sina 2009. SINA. Sistema de interacción natural avanza-
do. El ordenador al alcance de todos. 1-84 Editorial
Eines. ISBN / ISBN: 978-84-613-1740-0. 2009.
Dipòsit legal. PM-481-2009.
Lun-De Liao, Chi-Yu Chen,I-Jan Wang, Sheng-Fu Chen,
Shih-Yu Li , Bo-Wei Chen, Jyh-Yeong Chang, Chin-
Teng Lin. “Gaming Control Using a Wearable and
Wireless EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interface De-
vice with Novel Dry Foam-based Sensors, Journal of
NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation” 2012, 9:5.
ISSN 1743-0003.
C.-T. Lin, L.-W. Ko, J.-C. Chiou, J.-R. Duann, R.-S.
Huang, T.-W. Chiu, S.-F. Liang and T.-P. Jung, "Non-
invasive neural prostheses using mobile and wireless
EEG," Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 96, pp. 1167-
1183, 2008.
C. T. Lin, I. F. Chung, L. W. Ko, Y. C. Chen, S. F. Liang
and J. R. Duan, "EEG-based assessment of driver cog-
nitive responses in a dynamic virtual-reality driving
environment," IEEE Transactions on Biomedical En-
gineering, vol. 54, pp. 1349-1352, 2007.
Hsieh S., Lin-Chao L., The nature of switch cost: task set
configuration or carry-over effect?, Cognitive Brain
Research 22, pp. 165-175, Elsevier,2005.
A. F. Kramer. Physiological metrices of mental workload:
A review of recent progress, In D. Damon (Ed.), Mul-
tiple Task Perfomance, pages 279- 328, London, Tay-
lor& Francis, 1991.
W. Klimesch. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect
cognitive and memory performance: a review and
analysis, Brain Research Reviews, 29:169-195, Else-
vier, 1999.
Classifying mental states with machine learning algo-
rithms using alpha activity decline. Carina Walter,
Gabriele Cierniak, Peter Gerjets, Wolfgang Rosenstiel,
Martin Bogdan. ANN 2011 proceedings, European
Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computa-
tional Intelligence and Machine Learning. Bruges
(Belgium), 27-29 April 2011, i6doc.com publ., ISBN
978-2-87419-044-5. Available from http://
www.i6doc.com/en/livre/?GCOI=28001100817300.
BioEraPro visual designer for biofeedback. URL:
http://www.bioera.net/. 2012.
Johnny Chung Lee, and Desney S. Tan, “Using a low-cost
electroencephalograph for task classification in HCI
research”, Symposium on User Interface Software and
Technology, Proceedings of the 19th annual ACM,
Switzerland, Sensing from head to toe, 81 – 90, 2006.
Romero, S. et al.: Filtrado ocular de señales EEG en el
análisis de fármacos mediante topografía y tomografía
cerebral. A: Simposio de Bioingenieía 2010. "Simposio
de Bioningeniería 2010 (Redes REDINBIO y
RETADIM)". 2010, p. 152-158.
ASeriousGameApplicationusingEEG-basedBrainComputerInterface
255
