
A Data Cube Model for Surveillance Video Indexing and Retrieval
Hansung Lee, Sohee Park
and Jang-Hee Yoo
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, Daejeon, Korea
Keywords: Data Cube, Surveillance Video, OLAP, Video Indexing, Video Retrieval.
Abstract: We propose a novel data cube model, viz., SurvCube, for the multi-dimensional indexing and retrieval of
surveillance videos. The proposed method provides the multi-dimensional analysis of interesting objects in
surveillance videos according to the chronological view, events and locations by means of data cube
structure. By employing the OLAP operation on the surveillance videos, it is able to provides desirable
functionalities such as 1) retrieval of objects and events at a different level of abstraction, i.e., coarse to fine
grained retrieval; 2) providing the tracing of interesting object trajectories across the cameras; 3) providing
the summarization of surveillance video with respect to interesting objects (and/or events) and abstract level
of time and locations.
1 INTRODUCTION
The CCTV video surveillance system has been
developed for the public and private security, and
safety. The main purposes of the CCTV surveillance
systems are real-time monitoring of the interesting
areas and supporting criminal investigation at initial
stage. The CCTV cameras at the most public areas
are working and recording a huge numbers of
surveillance videos for the criminal prevention and
investigation. With the recent exploding of
surveillance videos, it is more difficult to find
meaningful information in manual way from large
data collections. Therefore, the surveillance video
databases have extensively studied for over past
decade to provide indexing, browsing, retrieval and
analysis of surveillance videos.
The conventional surveillance video database
systems, which are developed as a part of the video
surveillance systems, simply parse and index the
surveillance videos. In addition, only one-
dimensional indexing can be performed, separately
on respective pieces of footage captured by a
plurality of cameras, regardless of relationships
between several correlated pieces of footage.
To meet aforementioned problems, the intelligent
surveillance video databases have recently been
developed as a significant component of the
intelligent video surveillance system. Su et al. (2009)
proposed the surveillance video segmentation
method based on moving object detection for
surveillance video indexing and retrieval. Le et al.
(2010) provided an analysis on existing research
results (i.e., object and event detection) for
surveillance video retrieval. Yang et al. (2009)
presented the framework and a data model for
CCTV surveillance videos on RDBMS which
provides the function of a surveillance monitoring
system, with a tagging structure for event detection.
Le et al. (2009) proposed novel data model which
consists of two main abstract concepts (objects and
events). Zhang et al. (2009) proposed a framework
for mining and retrieving events. It is based on video
segmentation and object tracking. Despite of great
achievements in surveillance video databases, there
are few attempts for managing the surveillance
videos in centralized manner.
On the other hand, there are on-going efforts to
apply the data cube model, which is a framework for
supporting the Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)
operations on a huge volume of multi-dimensional
numeric dataset, to multimedia dataset such as text
documents, graphs, and news videos (Lin et al.,
2008; Zhang et al., 2009; Gonzalez et al., 2006; Tian
et al., 2008; Arigon et al., 2007; Lee 2008; Lee et al.,
2009).
The primary objective of this paper is to provide
a multimedia warehousing model for managing the
surveillance videos which are acquired by CCTV
cameras at different locations in centralized manner.
The central control centres of surveillance
systems usually manage and maintain a number of
163
Lee H., Park S. and Yoo J..
A Data Cube Model for Surveillance Video Indexing and Retrieval.
DOI: 10.5220/0004612101630168
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications and 10th International Conference on Wireless
Information Networks and Systems (SIGMAP-2013), pages 163-168
ISBN: 978-989-8565-74-7
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
CCTV cameras which are installed at different
places. In general, humans and vehicles are only
interesting objects when analysing and retrieving
surveillance videos. The surveillance videos include
the specific objects and events may be captured and
recorded by multiple cameras with the different
locations and times. Because of its multi-
dimensional nature, accordingly, we need a new
database model for multi-dimensional indexing and
retrieval of surveillance videos with time, location
and visual constraints.
In this paper, we propose a framework for
surveillance video analysis based on a new data cube
structure, called the SurvCube, which provides the
multi-dimensional indexing and retrieval of the
interesting objects in the surveillance videos
according to time, location and events. Since the
data cube structure supporting standard OLAP
operations, it provides various functions of the
surveillance video databases such as 1) providing the
coarse to fine grained retrieval of objects and events
from surveillance videos; 2) tracking the trajectories
of interesting objects; 3) summarizing the
surveillance videos with respect to interesting
objects (and/or events) and abstract level of time and
locations.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we present a framework for surveillance
video indexing and retrieval, viz., SurvCube, which
consists of the pre-processing module, data cube
model and retrieval/analysis module. The OLAP
operations and example scenarios are introduced in
Section 3. Finally, in Section 4, we conclude with a
brief summary and suggest future research directions.
2 SURVCUBE: A FRAMEWORK
FOR SURVEILLANCE VIDEO
INDEXING AND RETRIEVAL
In this section, we present the SurvCuve, framework
for multi-dimensional indexing and retrieval of
surveillance videos, which can analyse the long-term
massive surveillance videos by OLAP operations at
different levels of abstraction.
The proposed framework aims to retrieve objects
of a particular event or a sequence of the events with
time and location constraints. For example, it can be
retrieved a person wearing a blue jacket and a person
who abandoned luggage at street during last night.
Indexing and retrieval of the surveillance video is
based on the video analytics such as object detection,
object tracking, object classification and semantic
event recognition. The video analytics is defined as
understanding (or interpreting) events occurring in a
scene monitored by multiple CCTV cameras. The
surveillance videos coming from cameras at
different locations will be analysed by the video
analytics modules at the first to be indexed and
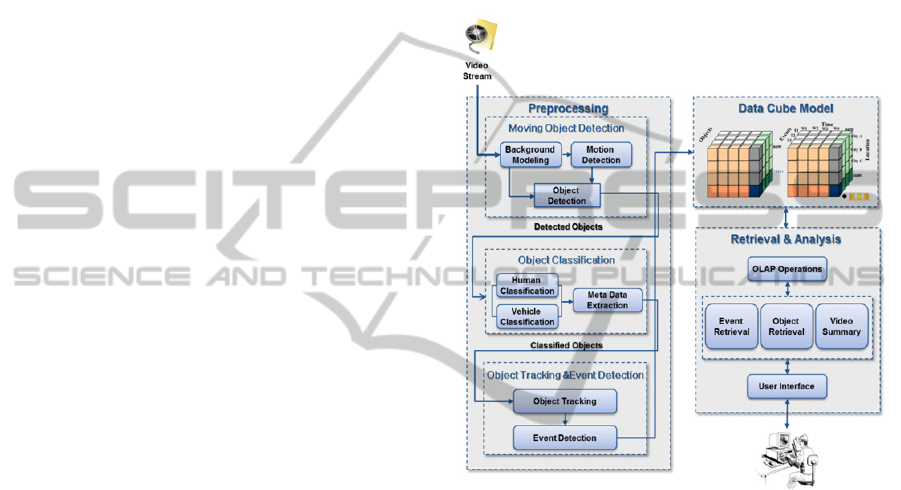
retrieved. Figure 1 illustrates the overall architecture
of SurvCube which consists of the pre-processing
module, data cube model and retrieval/analysis
module.
Figure 1: Overall architecture of SurvCube.
2.1 Pre-processing
The pre-processing step for constructing the data
cube of surveillance videos is basically based on the
video analytics. It consists of three main steps:
moving object detection, object classification and
object tracking/event detection.
The first step of pre-processing is the moving
object detection which consists of three components:
background modelling, motion detection, object
detection. While the background modelling can be
used for the static cameras, it cannot be used for the
pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) cameras. In case of PTZ
cameras, the background modelling can be omitted.
Because the CCTV cameras are generally installed
outdoors, the background should be dynamically
updated to avoid the effect of environment such as
shadow, illumination, weather, etc.
Once moving objects are detected, each object is
classified into one of human and vehicle classes or it
is discarded otherwise because the interesting
SIGMAP2013-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
164

objects are only human and vehicle for surveillance
purpose. After classification of human and vehicle,
the meta-data is extracted from human or vehicle
objects. For example, the dominant colour of cloths,
facial feature (if a face is detected) are extracted
from human objects and a sort of vehicle (sedan, bus,
truck etc.), the dominant colour of vehicle, the
register number (if plate number is detected) are
extracted from vehicle objects. The CCTV cameras
have one of field of views: wide field of view
(WFOV) and near field of view (NFOV). In NFOV,
the face and plate number can be detected and
recognised. In general, we fail to detect face and
plate number in WFOV. The example of WFOV and
NFOV is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Example of WFOV and NFOV.
The last step of pre-processing is the object tracking
and event detection. The classified objects are
tracked automatically and the pre-defined events are
detected using trajectories of objects and inter-
relations between objects. Under some circumstance,
the size of object become larger or smaller very
quickly as the object is moving. It is difficult to track
the moving object with changing of object size. The
tracking algorithm should be robust to occlusion,
illumination and changes of object size.
Once pre-processing steps are finished, the
multi-dimensional data cube is constructed using the
information of detected events, detected objects with
meta-data, time stamp and locations of each video
clip recoded.
2.2 Multi-dimensional Data Cube
Model
The multi-dimensional data model is a core
component of data warehouse and OLAP tools and it
views data in the form of a data cube. A data cube
model allows data to be modelled and viewed in
multiple dimensions and defined by fact and
dimensions (Han et al., 2007). In general,
dimensions are the point of view or entities, which a
user is interested in and wants to analyse. Each
dimension is defined as a dimension table with
attributes that describe dimension. The fact table
consists of the measurements (called facts) which
are subjects to be analysed and keys to the
associated dimension tables.
To model the SurvCube, we defined four
dimensions: time, location, event and object. These
dimensions define the relationships between several
correlated pieces of footage captured by a plurality
of cameras at different locations. We also used the
indices of surveillance video clip unit number as
measurements in a fact table. The proposed
SurvCube consists of four dimension tables and one
fact table. If a new viewpoint for analysis is required,
the dimension in the data cube can be easily added.
In this paper, we use a star schema for describing the
multi-dimensional data cube model. This is most
widely used for representing the data cube. Figure 3
shows the star schema for the SurvCube.
Figure 3:
SurvCube
star schema.
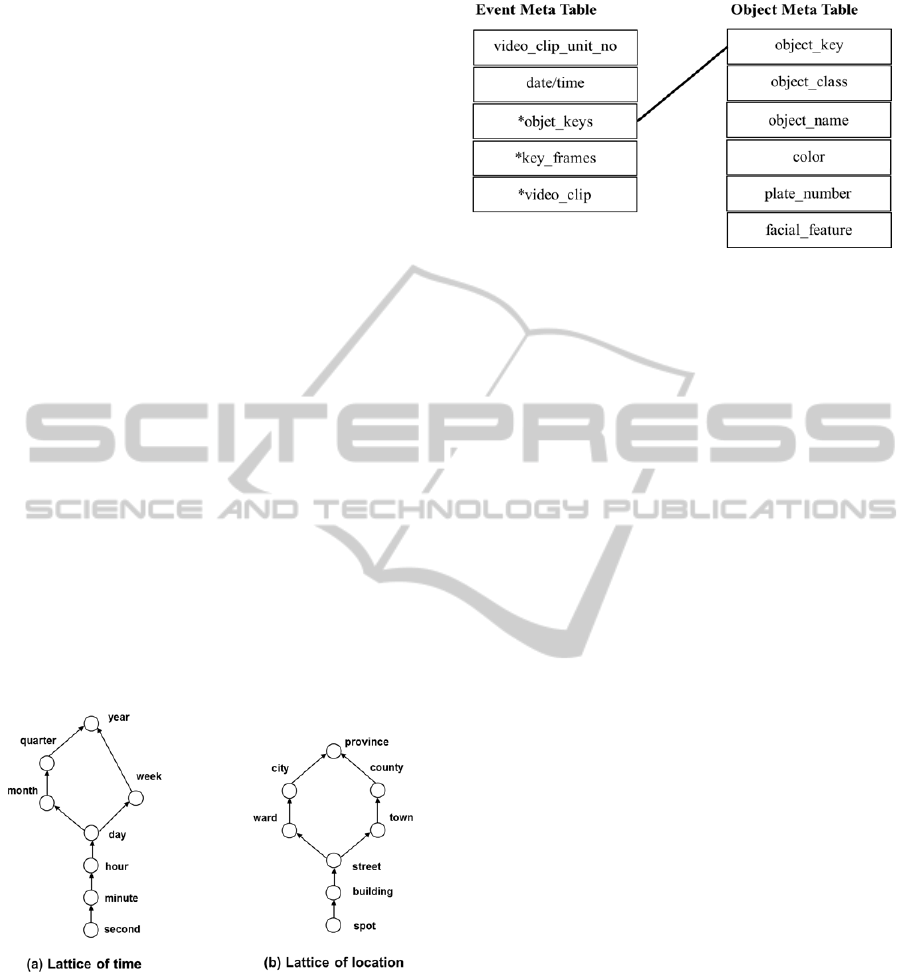
The object dimension table consists of the three
attributes: object_key, object_class and object_name.
The value of the object_class will be one of two
classes: human or vehicle. The event dimension
table is presented by the attributes event_key and
event_name. An attribute event_name has one of
pre-defined events which are provided by event
detector in the pre-processing step. For example,
loitering, tampering, intruding, abandonment, etc.
The time dimension table is describe by the 9
attributes: time_key, second, minute, hour, day,
week, month, quarter and year. The location
dimension table has 9 attributes: location_key, spot,
building, street, town, ward, county, city and
province.
ADataCubeModelforSurveillanceVideoIndexingandRetrieval
165
The data cube has been designed and proposed
for analysing a huge volume of numeric data in a
data warehouse. Therefore, the measurements of a
traditional data cube model are numerical data and
the numerical functions are employed as the
aggregation function. However, in the SurvCube,
measurement is the indices of surveillance video clip
unit number, video_clip_unit_no, which is unique
sequence number with respect to the recoding order
and location. The attribute video_clip_unit_no
represents the event itself and including objects. It is
also used in a meta-data table as a primary key. We
define the aggregation function as a list of the events
that is a set of values in video_clip_unit_no.
A concept hierarchy defines a sequence of
mappings from a set of low-level concepts to higher-
level and more general concepts (Han et al., 2007).
It allows data to be handled with varying levels of
abstraction. The attributes of an object dimension
are organised in a total order forming a concept
hierarchy as "object_name < object_class". Since the
event dimension has only one concept, the concept
hierarchy does not exist. The attributes of a time
dimension are organised in a partial order, forming a
lattice. The partial order for the time dimension is
"second < minute < hour < day < {month < quarter;
week} < year" as shown in Figure 4(a). Figure 4(b)
shows the lattice of the location dimension, which is
defined as “spot < building < street < {town <
county; ward < city} < province”.
Figure 4: A concept hierarchies of SurvCube.
The surveillance videos are the multimedia data
which contains a lot of useful information. As the
results of the pre-processing step, we extract the
additional information which describes the events
and the objects in detail. We employ more rich data
structure, meta-data table, for storing the
descriptions of events and objects such as recording
date/time, objects, key-frames, and location of video
clip. Figure 5 shows the example scheme of meta-
data tables.
Figure 5: Example of the meta-data tables.
3 OLAP OPERATIONS
AND EXAMPE SCENARIOS
Here, we discuss the basic OLAP operations applied
to the SurvCube and example scenarios. In a data
cube model, each dimension contains multiple levels
of abstraction defined by concept hierarchies, which
provides users with the functionality to view data
from different perspectives. There are a number of
OLAP operations for materialising these different
views. It allows interactive querying and analysis of
the data (Han et al., 2007). The basic OLAP
operations such as roll-up, drill-down, slice and dice
are used to retrieve useful information from the data
cube of surveillance videos.
The roll-up operation performs aggregation on a
data cube by climbing up a concept hierarchy for a
dimension or by dimension reduction. The drill-
down operation is the reverse of roll-up operation,
which step down a concept hierarchy for a
dimension or by introducing additional dimension.
By applying the roll-up and drill-down operation,
the user can retrieve the objects and events at a
different level of abstraction. For example, the
following operations retrieve the human objects in
the loitering events. Figure 6 is example of a
loitering event.
Drill-down on Object (from all to object class),
event = “Loitering” AND object = “Human”
The slice operation selects one dimension of the
given cube and this result in a sub-cube. A two-
dimensional view can be obtained. This operation is
able to trace the object trajectories across the
cameras. For instance, the following operations
retrieve all video clips across the camera including
sedan car.
SIGMAP2013-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
166

Figure 6: Example of a loitering event.
Drill-down on Object (from all to object name)
AND Time (from all to day),
Slice for time = “March 3, 2013”,
object = “sedan car”
Figure 7: Example of a swoon event.
The dice operation defines a sub-cube by
selecting two or more dimensions of the given data
cube. This operation reduces the search space of
events and objects. It can provide the summarization
of surveillance video with respect to interesting
objects (and/or event) and abstract level of time and
locations. The example operations for retrieving
swoon events on March 3, 2013 in Seoul are given
bellow and example of a swoon event is shown in
Figure 7.
Drill-down on Time (from all to day) AND
Location (from all to city),
Dice for Time = “March 3, 2013” AND
Location = “Seoul”,
event = “swoon”
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed a novel data cube model
for a framework of surveillance video analysis, viz.,
SurvCube, which is able to analyse the surveillance
videos according to chronological view, objects,
events and region (or location). It provides users
with various facilities on the surveillance videos
such as 1) retrieval of objects and events at a
different level of abstraction, i.e., coarse to fine
grained retrieval; 2) providing the tracing of
interesting object trajectories across the cameras; 3)
providing the summarization of surveillance video
with respect to interesting objects and abstract level
of time and locations.
For the future work, we will apply the proposed
framework to the real-world applications and
concern the video data mining of the surveillance
videos.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the IT R&D program of
MOTIE/KEIT. [10039149, Development of Basic
Technology of Human Identification and Retrieval
at a Distance for Active Video Surveillance Service
with Real-time Awareness of Safety Threats].
REFERENCES
Su, Y., Qian, R., Ji, Z., 2009. Surveillance Video
Swquence Segmentation Based on Moving Object
Detection. In Proc. Int. Workshop on Computer
Science and Engineering, pp. 534-537.
Le, T., Boucher, A., Thonnat, M., Bremond, F., 2010.
Surveillance Video Retrieval: What we have already
done?. In proc. Int. Conf. on Communications and
Electronics.
Yang, Y., Lovell, B., Dadgostar, F., 2009. Content-Based
Video Retrieval (CBVR) System for CCTV
Surveillance Videos. In Proc. Digital Image
Computing: Techniques and Applications, pp. 183-187.
Le, T., Thonnat, M., Boucher, A., Bremond, F., 2009.
Surveillance Video Indexing and Retrieval using
Object Features and Semantic Events. Int. Journal of
Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 23(7),
pp. 1439-1476.
Zhang, C., Chen, X., Zhou, L., Chen, W., 2009. Semantic
Retrieval of Events from Indoor Surveillance Video
Databases. Pattern Recognition Letter, 30, pp. 1067-
1076.
Lin, C., Ding, B., Han, J., Zhu, F., Zhao, B., 2008. Text
Cube: Computing IR Measures for Multidimensional
ADataCubeModelforSurveillanceVideoIndexingandRetrieval
167

Text Database Analysis. In Proc. of Int. Conf. on Data
Mining.
Zhang, D., Zhai, C., Han, J., 2009. Topic Cube: Topic
Modeling for OLAP on Multidimensional Text
Databases. In Proc. of Int. Conf. on Data Mining.
Gonzalez, H., Han, J., Li, X., 2006. FlowCube:
Constructing RFID FlowCubes for Multi-Dimensional
Analysis of Commodity Flows. In Proc. of Int. Conf.
on Very Large Data Bases, pp. 834-845.
Tian, Y., Hankins, R., Patel, J., 2008. Efficient
Aggregation for Graph Summarization. In Proc. of
SIGMOD, pp. 567-580.
Arigon, A., Miquel, M., Tchounikine, A., 2007.
Multimedia Data Warehouses: a Multiversion Model
and a Medical Application. Multimed Tools Appl, 35,
pp. 91-108.
Lee, H., 2008. A Data Cube System for the Semantic
Analysis of News Video. Ph.D. Dissertation, Korea
University. Seoul, Korea.
Lee, H., Yu, J., Jung, H., Im, Y., Park, D., 2009. A New
Data Cube System for the Multi-dimensional Analysis
of News Videos. In Proc. of Int. Conf. on Emerging
Databases.
Han, J., Kamber, M., 2007. Data Mining: Concepts and
Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. 2nd
edition.
SIGMAP2013-InternationalConferenceonSignalProcessingandMultimediaApplications
168
