
Using Fact-orientation for Educational Design
Peter Bollen
Department of Organization and Strategy,
Faculty of Economics and Business Administration
University of Maastricht, 6200 MD Maastricht, The Netherlands
Abstract. In this paper we will show how fact-orientation can be used as a
knowledge structuring approach for verbalizable knowledge domains, e.g.
knowledge that is contained in articles, text books and instruction manuals
further to be referred to as ‘subject matter’. We will also show that the fact-
oriented modeling constructs allow us to structure knowledge on the first five
levels of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives and we will show how
the fact-oriented approach complies to the 4C/ID model for educational design.
Moreover, we will derive a ‘knowledge structure metrics’ model that can be
empirically estimated and that can be used to estimate the complexity metric of
a subject matter.
1 Introduction
In the body of literature on fact-oriented conceptual modeling, a number of
publications define a hierarchy in knowledge elements for a specific knowledge
domain [7, 8, 9]. This research has generalized the fact-oriented modeling constructs
and CSDP into a knowledge reference model for subject matters, thereby applying
fact-orientation on a much larger playing field than the field of schema design for
relational databases.
In this paper we will illustrate the applicability of fact-orientation for the objective
of structuring knowledge, by showing that a fact-oriented knowledge reference model
(KRM) can also be used for determining the complexity of a given subject domain
and subsequently for the educational design of a course on a such a subject. We will
illustrate this with examples in the field of university education on two generally
accepted sub-domains within the business administration subject: operations
management and marketing. Earlier work that discussed the application of a
predecessor to this KRM on the field of logistics can be found in [4]. In that paper the
following knowledge classes are distinguished: sentence instances, sentence types
(including associated constraints) and derivation rules.
A subject matter has its own intrinsic structure [9]. Educational programs on a
subject matter therefore, need to enable students to access such a structure or
‘conceptual schema’. Unfortunately, in many available descriptions of a subject
matter, e.g. text books, lecture notes, manuals, the intrinsic structure is (at best)
hidden among non-structural descriptions of such a subject matter. In analogy with
the Conceptual Schema Design Procedure [5: 58-60] for application domains, that
Bollen P..
Using Fact-orientation for Educational Design.
DOI: 10.5220/0004539800140023
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Interaction Design in Educational Environments (IDEE-2013), pages 14-23
ISBN: 978-989-8565-65-5
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

serves as a ‘knowledge extractor’ by structuring the explicit and eliciting the implicit
knowledge of domain experts in a user-analyst dialogue, we can define a knowledge
extracting procedure (KEP) [3] that can be applied on explicit subject knowledge that
is documented in a web-document, a text book or an instruction manual.
2 Deriving the Intrinsic Structure of a Subject Domain
In most, if not all cases, a verbalizable knowledge source is a document that often is
incomplete, informal, ambiguous, possibly redundant and possibly inconsistent. As a
result of applying the fact-oriented knowledge extracting procedure (KEP) [3, 8], we
will yield a document that only contains structured knowledge or a knowledge
grammar which structures verbalizable knowledge into the following elements
(knowledge reference model(KRM)):
1. Knowledge domain sentences
2. Definitions and naming conventions for concepts used in domain sentences
3. Knowledge domain fact types including sentence group templates
4. Population state (transition) constraints for the knowledge domain
5. Derivation rules that specify how specific domain sentences can be derived
from other domain sentences.
6. Rules that specify what fact instances can be inserted, updated or deleted.
7. Event rules that specify when a fact is derived from other facts or when a fact
must be inserted , updated or deleted.
A KRM of a complete text book would contain hundreds, possibly thousands of
concept definitions, naming conventions, fact types, population constraints, derivation
rules and event rules. The knowledge extracting procedure (KEP) specifies how we
can transform an informal, mostly incomplete, mostly undetermined, possibly
redundant and possibly inconsistent description of domain knowledge into the
following classes: informal comment, non-verbalizable knowledge and verbalizable
knowledge to be classified into types 1 through 7 of the KRM. In section 3 we will
give a sample of the results of applying the knowledge extracting procedure on an
operations management text book and a marketing text book.
3 Application of the KEP on the Business Subject Matter
In this section we will show the KRMs, which are a result of the application of the
fact-oriented KEP on the content of textbooks on the operations management and
marketing subjects of business administration. Because of space limitations in this
article we haven chosen to select a very small subset of concepts contained in these
subjects.
15

3.1 The Operations Management Subject of the Economic Order Quantity
We have selected a widely-used text book on the field of operations and process man-
agement: Ritzman, Krajewski and Malhotra: Operations Management: Processes and
Value Chains, 8
th
edition, Pearson/Prentice-Hall, 2007 [11]. We will now provide a
self-contained sample of the KRM for this text book (see the list of definitions for op-
erations management and the diagrammatic part of KRM elements 3, 4 and 5 ex-
pressed as a knowledge structure diagram in ORM-1 notation in figure 1).
Partial List of Definitions for Operations man. Subject: Economic Order Quantity EOQ
Item An individual product that has an identifying item code and is
held in inventory somewhere along the value chain (p.524
1
)
Synonym: Stock Keeping Unit
Item Code An item code is a unique signification for an [Item] that enables
us to identify a specific [Item] within the set of all [Item]s within
the context of a business organization
Lot A lot is a quantity of [Item]s that are processed together.(p.350)
Cost A sacrifice or expenditure
Ordering Cost The [Cost] of preparing a purchase order for a supplier or a pro-
duction order for the shop. (p. 464)
Synonym: Set Up cost (p.472)
Inventory Holding Cost The sum of the [Cost] of capital and the variable [Cost]s of keep-
ing [Item]s on hand, such as storage and handling, taxes, insur-
ance and shrinking (p.463)
Fig. 1. Knowledge structure diagram in ORM-(1) notation for EOQ from [12].
3.2 The Marketing Subject of Branding
We have chosen the following text book on the field of marketing: David Jobber,
Principles and Practice of Marketing, 4
th
edition, McGraw-Hill, 2004 [6]. We will
now provide a KRM for a sample from this text book in the list of definitions for
marketing management and the diagrammatic part of KRM elements 3 and 4 (ex-
pressed as a knowledge structure diagram in ORM-1 notation) in figure 2.
1
The referenced pages in the list of definitions refer to [12].
16
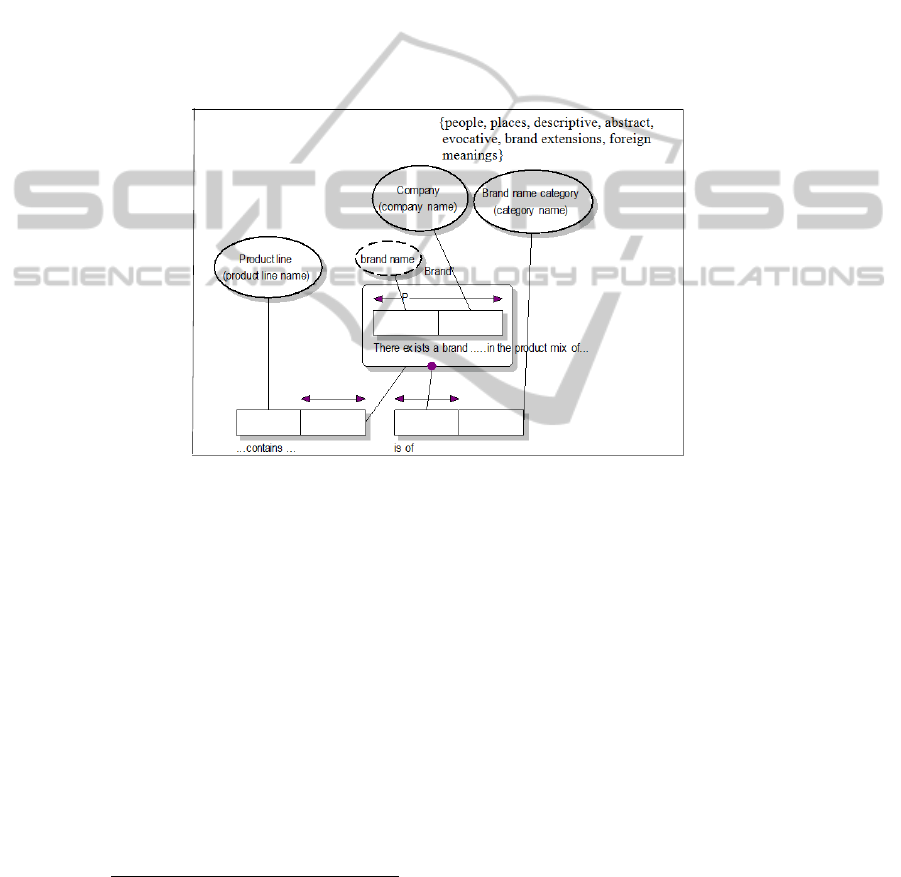
Partial List of Definitions for Marketing Management Subject: Branding
Product Anything that is capable of satisfying customer needs (p. 260
2
).
Brand A distinctive name, packaging and design for a [Product]
(p.261)
Brand name A brand name is a unique signification for an [Brand] that enables
us to identify a specific [Brand] within the set of all [Brand]s
within the context of a specific company.
Product line A group of [Brand]s of a Company that are closely related in
terms of their function and the benefits they provide (p.262)
Product line name A product line name is a unique signification for a [Product Line]
that enables us to identify a specific [Product Line] within the set
of all [Product Line]s within a specific company.
Fig. 2. Knowledge structure diagram in ORM-(1) notation for Branding from [6].
4 Using Fact-orientation to Compare Subject Matters
When the relative amount of informal comment and non-verbalizable knowledge in
such a knowledge field is large we can consider the knowledge field to be of the
‘phenomenological’ type. This normally points at knowledge fields that are beginning
to develop and in which no clearly agreed upon relevant concepts and their definitions
exist. When the relative amount of informal comment and non-verbalizable
knowledge of the subject matter, on the other hand, is small, the knowledge domain
can be considered relatively structured, this means that basic domain concepts are
agreed upon and their definitions are known. Furthermore, semantic relationships be-
tween those concepts exist and are known to the extent that they can be verbalized. In
the latter types of knowledge domains, it is possible that more complex rules, laws,
derivation rules and event rules can be defined. The former analysis naturally applies,
2
The referenced pages in the list of definitions refer to [7].
17

in those situations in which a text book is well-written from an educational point of
view. In some cases the actual quality of writing can be insufficient, which can lead to
a ‘phenomenological’ text book for a very well-structured knowledge domain or a
text book in which the order of comprehension for the introduction and definition of
concepts is practically random. In the next section we will postulate a model that can
be used to estimate the size and complexity of a subject matter.
5 Using the Building Blocks of Fact-orientation as Size
and Complexity Metrics
As was illustrated in section 3 of this paper, for the text books on marketing and oper-
ations management, it is possible to apply the KRM and its accompanying KEP on the
field of business administration. In many situations, educational programs at colleges
and (professional) universities are built up around acknowledged subjects or topics.
The study load for such a subject or topic is mostly determined by the number of con-
tact hours and the quantity of literature that must be read and studied. In our view, this
practice does not acknowledge the differences between knowledge fields in terms of
the building blocks of the KRM. We will restrict the fields of knowledge of interest to
‘structurally relevant verbalizable’ knowledge domains. We will furthermore divide
the fourth element of the Knowledge Reference Model: population state (transition)
constraints (see section 2) into a discrete number of pre-defined constraint types and
general constraints.
We will now give a linear model (see equation (1)) that can be used for deter-
mining the size and complexity of a subject domain and determining the study load
and the educational design for a course on the subject matter.
SL=(a*DEF)+(b*FT)+(Σ(c
j
*PSC
j
))+(d*PTC)+(e*GC) + (f*DR) + (g*ER) . (1)
Where SL is the study load (in hours) of a knowledge field or a ‘size and complexity’
metric that can be easily transformed into a study load equivalent and where a, b, c
j
,
d, e, f, g, respectively are weight factors for the number of definitions in the list of
definitions, the number of fact types, the number of population constraints of type
PSC
j
, the number of state transition constraints, the number of general population
constraints, the number of derivation rules , the number of event rules in the applica-
tion knowledge structure (diagram). Finally, DEF, FT, PSC
j
, PTC, GC, DR and ER
are the total number of definitions, the total number of fact types, the total number of
constraints, the total number of state transition constraints, the total number of gen-
eral population constraints, the total number of derivation rules and the total number
of event rules, respectively in the application knowledge structure.
This model can be empirically determined by estimating the weight factors: a, b, c
j
,
d, e, f, g after a large number of samples of knowledge fields (e.g. text books, instruc-
tion manuals) have been analyzed in terms of the knowledge reference model. For this
future empirical research we need to define standardized test that enable us to deter-
18

mine to what extent students have sufficient knowledge of the relevant parts of the
text book.
When we compare the two knowledge reference models for the operations man-
agement and the marketing management examples, we see that relative extent of con-
cept definitions is about equal for both example fields, the number of constraints is
bigger for the operations management example. The operations management example
contains a derivation rule whereas the marketing management KRM does not have a
derivation rule (see table 1).
Table 1. Sample data for Linear Model.
Variable\subject EOQ (operations man.) Branding (marketing)
DEF 10 12
FT 4 2
PSC
1 (uniqueness)
4 1
PSC
2 (mandatory role)
0 1
PSC
2 (value)
0 1
DR 1 0
6 Application of Fact-orientation in Educational Design
In this section we will show how the fact-oriented analysis and abstraction of (a) sub-
ject matter(s) in combination with the determined weight factors from our study load
estimation model in section 5 can be used for educational design. The total study load
can be determined using the linear model in section 5. The next decision that has to be
made is to design the tasks, exercises, assignments, chapters to study and so forth in a
way that optimizes the productivity of teachers and instructors and that also optimizes
the required time for a student to fully understand the subject. The fact-oriented
knowledge reference model (KRM), provides the blue-print for the creation of educa-
tional material and its accompanying educational design and test-design. In [8] this is
called knowledge driven educational design which contains (amongst others) the step
‘didactizing’ which can lead to the following instance of an educational design:
1) In educational design, the existing knowledge network of the prospective
students will (partly) determine the sequence in which concepts should be in-
troduced and it will determine the way in which competencies should be
trained [8, 10]. In some cases available representations of subject matter, e.g.
manuals, text-books do not provide the explicit structure to do this at all
times [12: 633]. Fact-orientation can help structuring the subject matter by
creating a list of definitions that can be anchored in the student’s existing
knowledge network and it can be sequenced in order of comprehension. Fur-
thermore, a knowledge structure diagram that contains fact types, population
constraints and derivation- and event-rules can be added (see figures 1and 2
and the accompanying lists of definitions).
2) Let the students prepare a number of pages of the text book (preferably in the
fact-oriented KRM format) that contain α concept definitions and β fact types
19

and the accompanying population constraints, derivation rules and event
rules.
3) Design an educational session in which the comprehension of the concepts,
fact types and constraints is tested by providing ‘sentence instances’ or
scaled down ‘real-life’ examples in such a way that in the beginning in each
example, one rule is confirmed or violated (see figure 3a), leading to exercis-
es in which multiple constraints are violated/confirmed at the same time (see
figure 3b).
4) A final set of exercises can be constructed in such a way that the comprehen-
sion of the concepts, fact types, constraints and derivation rules is tested by
providing students with instances of fact types and values for parameters that
are contained in one or more derivation rules. The students will subsequently
be asked to apply the derivation and/or event rules (see figure 3c).
5) On a program level it is recommended to provide integrated exercises that
cover subject matter that has been covered in earlier courses on a specific
subject.
Item ordering cost
ab105 $ 43,--
ab106 $ 56,--
ab105 $ 66.--
Company Brand Brand category
Masterfoods Mars people
Masterfoods Whiskas --
Masterfoods Mars brand extension
Question: is this an allowed
example of
communication ?
Question: calculate the EOQ for item a345
Question: is this an allowed
example of
communication ?
(A)
(B)
(C)
The company Ajaxfan, produces all kinds of accessories for the Amsterdam football team Ajax
ranging from shawls to coffee cups. For the stock keeping unit with item code a345 the annual
demand is estimated at 12 000 units. There is a fairly constant demand throughout the year.
The ordering cost with the chinese supplier for this item is Euro 234.--. The unit holding cost
for this SKU at Ajaxfan is Euro 1.25/unit/year.
Fig. 3. Examples of exercises to be used for instruction.
In addition we can use the same underlying KRM to design exams and test questions
that can range from problems on an application instance level to problems on a meta
level. The design of course evaluations, exams or tests goes hand in hand with the
aforementioned educational design. The test will exactly reflect the level of instruc-
tion, since the underlying test objectives have been clearly laid down in the KRM of
the subject matter.
20

6.1 The Fact-oriented KRM and Bloom’s Taxonomy
In educational sciences, Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives [2] is an accept-
ed framework to divide objectives in the cognitive domain. Bloom’s taxonomy can be
considered a pyramid, in which every next-higher level includes the lower level as a
subset. Level 1 in Bloom’s taxonomy: knowledge, is defined as the remembering or
recall of previous learned material. Level 2: comprehension is defined as the under-
standing of the material or the ability to interpret the material. Level 3 of Bloom’s
taxonomy: application refers to the ability to use the learning material in new situa-
tions. Bloom’s level 4 of educational objectives refers to the ability to break down
material into component parts. Level 5 in Bloom’s taxonomy: synthesis, refers to the
ability to put parts together.
We will now match the levels and elements from the KRM with the levels in
Bloom’s taxonomy. The availability of domain sentences without an accompanying
list of definitions for the concepts can be considered to refer to the knowledge level 1.
If we add the (relevant) concept definitions and naming conventions we will be able
to communicate ‘knowingly’ about a subject domain (level 2 of Bloom’s taxonomy).
For polytechnic and university level educations, we require the content of the courses
to be on at least level 3 of Bloom’s framework which implies that students must at
least be able to apply derivation rules to derive new sentences if ‘knowledgeable’ in-
gredient sentences (including a list of definitions) is provided in a practical case set-
ting. Bloom’s level 4 of educational objectives refers to the meta-level of the KRM.
This basically is the same KRM, albeit applied on a specific UoD, namely the UoD of
creating a knowledge reference model [7, 8]. Level 5 refers to the ability to put parts
together. Our claim is that this involves multi-disciplinary knowledge and therefore
can only be achieved when knowledge for different domains is integrated and there-
fore, level 5 (and this implies level 6) can in general not be achieved by the educa-
tional objectives laid down in a single text book. Level 5, however can be achieved by
integrating multiple relevant subjects. If we would consider the synthesis of two sub-
jects that we have given in this article, we could for example derive the knowledge
that the manufacturing of more brands would lead to more production set ups. Level 6
in Bloom’s taxonomy: evaluation, is a level that is normally achieved after students
have had experience in a specific field for a number of years, and thereby have
achieved the ability to evaluate their way of working in the field.
6.2 The Fact-oriented KRM and the 4C/ID-Model for Educational Design
In this section we will show that the application of the fact-oriented approach for edu-
cational design complies to the interrelated components of van Merriënboer’s four-
component educational design model (the 4C/ID-model) for competence based educa-
tion [13].
The first component of the 4C/ID model is learning tasks. In [1] task classes are
given in which simple-to-complex categories of learning tasks are defined. In this sec-
tion it was already illustrated how this can be done in the fact-oriented KRM.
The second component of the 4C/ID model is supportive information. This compo-
nent deals with the availability of additional information that is coupled to tasks clas-
ses that may contain general knowledge and concrete cases that exemplify the ‘theo-
21

retical’ knowledge [1]. In terms of the fact-oriented approach it means, that the exam-
ple information on a UoD is provided, that allow learners to abstract from tangible
examples and to test the presence/absence of constraints by inspecting the supplied
case information in the taks.
The third component of the 4C/ID model is Just-In-Time information which refers
to the specification of routines that are identical for many learning tasks [1]. In terms
of fact-orientation we can consider the different steps in the ‘knowledge extracting
procedure’ (KEP), to be the most important example(s) of this. This means that stu-
dents must acquire these skills in order to be able to ‘grasp’ the content of the course
in the fact-oriented format, but most of all acquiring these skills will allow the stu-
dents to handle every future situation in which knowledge must be absorbed and ap-
plied.
The fourth component of the 4C/ID model is part-task practice. In this component
provisions are made for additional learning of particular routine aspects that need a
high degree of automaticity [1]. In the application of the fact-oriented approach on the
field of educational design, this part-task practice can be directed at meta-level cogni-
tive skills (applying (parts of the) KEP) or on application-level skills (the application
of derivation rules, e.g. a calculation of a EOQ).
We now have shown how the fact-oriented KRM enables us to fulfill educational
objectives up to level 5 of Bloom’s taxonomy and how the fact-oriented approach
complies to the 4C/ID model for educational design.
In the past 20 years, a large number of students on a polytechnical level in the
field of computer science, business administration and law have been [8] trained using
educational material expressed in a knowledge reference model format based upon
standard text books on the subject matter. The time investment needed for the stu-
dents in such an ‘accelerated’ learning program turned out to be substantially lower
than in a ‘conventional’ educational setting [10:434-435].
7 Concluding Remarks
The fact-oriented approach has its roots in the conceptual modeling school for infor-
mation systems development and database schema design. In this paper we have ex-
tended the ‘playing field’ of this approach as a knowledge structuring approach, illus-
trated by two samples of subjects within the academic field of business
administration. Moreover, we have given a (linear) model that can be used for deter-
mining and predicting the size and complexity of a subject matter. The size and com-
plexity of the implicit structure of a subject can range from structures that can be fully
modeled by a small number of definitions, via models of implicit structures that con-
tain a large number of definitions and fact types, to ‘complex’ knowledge reference
models in which a large variety of population state (transition) constraints exist even-
tually having derivation rules, and event rules.
The conclusion and implications for the educational practice of the fact-oriented
KRM are threefold. Firstly, the KRM for a text book will give us insights into the
context of the knowledge domain in terms of relevant structural knowledge. Secondly,
the fact-oriented KRM will allow us to estimate the study-load and contact hours for a
specific course having a given text book/domain knowledge by using the complexity
22

model that was given in section 5. Thirdly, the fact oriented approach can be applied
as a methodology for educational design that complies to Bloom’s taxonomy of edu-
cational objectives and the 4C/ID model for educational design.
Our belief is that the ‘quantification’ of knowledge that is proposed in this article
will lead to a more productive and effective ‘engineering’ of educational systems in a
broad sense and will provide a solid foundation for claims as ‘better learn one rule
than 20 facts’.
References
1. Bastiaens, T., van Merriënboer, J and Hoogveld, B.:A design methodology for Complex
(E)-learning. Innovative session 2. AHRD conference, Honolulu Hawai (2002)
2. Bloom, B. and Krathwohl, D.: Taxonomy of educational objecti ves: the classification of
educational goals- handbook I: cognitive domain, McKay, New-York (1956)
3. Bollen, P.: The Natural Language Modeling Procedure’, In: Fifth Workshop on Next Gen-
eration Information Technologies and Systems (NGITS’2002), Lecture Notes in Comput-
er Science 2382, Springer-Verlag, (2002) 123-146.
4. Bollen, P. and Nijssen, G.: Universal Learning as a tool for educational transformation and
process control systems in problem-based programs’, in: W,Gijselaers, D. Tempelaar, P.
Keizer, J. Blommaert, E. Bernard & H. Kasper (eds.), Educational innovation in economics
and business administration: the case of problem-based learning, (1995) 436- 443.
5. Halpin, T.: Information Modeling and Relational Data bases, Morgan Kaufmann (2001)
6. Jobber, D.: Principles and practice of marketing, 4
th
edition, McGraw-Hill (2004).
7. Nijssen, G.: Kenniskunde 1A, PNA Publishing, Heerlen, Netherlands (in dutch) (2001)
8. Nijssen, G. and Bijlsma, R.: Kennis-gebaseerd onderwijs ontwerpen” (Knowledge Driven
Educational Design), OnderwijsInnovatie (Educational Innovation) Nr 3, Open Universiteit
Nederland, September (2005) pp. 17-26. (in dutch)
9. Nijssen, G. and Bijlsma, R.: A Conceptual Structure of Knowledge as a Basis for Educa-
tional Designs. The 6th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technolo-
gies, Theme: Advanced Technologies for Life-LongLearning”, ICALT,(2006)
10. Nijssen, G. and Bollen, P.: Universal Learning: A science and methodology for education
and training’, in: W,Gijselaers, D. Tempelaar, P. Keizer, J. Blommaert, E. Bernard & H.
Kasper (eds.), Educational innovation in economics and business administration: the case
of problem-based learning, (1995) 428- 435
11. Ritzman, L., Krajewski, L. and Malhotra, M.: Operations Management: Processes and Val-
ue Chains, 8
th
edition, Pearson/Prentice-Hall. (2007).
12. Thomson, J., Greer, J. and Cooke, J.: Automatic generation of educational hypermedia with
APHID. Interacting with Computers 13 (2001) 631-654.
13. Van Merriënboer, J.: Training complex cognitive skills: A four- component educational
design model for technical training. Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1997)
23
