
A New Fully Auditable Proposal for an Internet Voting System
with Secure Individual Verification and Complaining Capabilities
Maider Huarte, Iñaki Goirizelaia, Juan José Unzilla, Jon Matías and Juan J. Igarza
Dept. of Communication Engineering, University of the Basque Country,
Urkixo Zumarkalea, Bilbao, Basque Country, Spain
Keywords: Cryptography, Distributed Systems, e-Voting Systems, Fault Tolerance.
Abstract: This paper introduces a new Internet voting (i-voting) system based on an analysis of the related literature,
oriented to democratic election principles (universality, equality, freedom and secrecy). The foundations
compiled from that analysis include both technical and social aspects because achieving voter confidence is
as important as creating “perfectly secure” systems when talking about democracy. The issues especially
addressed in the new system are: full audit-capability, secure individual verification and vote-complaining,
and N-Version Programming based robustness and transparency. Currently, this new i-voting system is
being tested for performance and usability in our lab.
1 INTRODUCTION
Principles for democratic elections were stated in
1966 by United Nations (UN, 1966) and revisited for
e-voting by the Council of Europe (CE, 2004).
According to them, eligible voters should be able to
participate in equivalent conditions (universality),
only one vote per voter is tallied (equality), each
vote should be cast free of coercion and reflect voter
opinion (freedom) and it must be impossible to
know how any particular voter voted (secrecy).
This paper deals with i-voting, in the sense of e-
voting platforms which use Internet to store votes in
server machines as they are cast and allow voting
from anywhere Internet is accessible (all other e-
voting platforms are not considered).
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2
resumes our analysis on i-voting literature; then, the
core of the paper explains in Section 3 the
foundations for i-voting outlined on that analysis,
and describes our new i-voting system in Section 4;
finally, conclusions are given in Section 5.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Our i-voting research began by performing a
thorough analysis of the related literature, which is
summarized in Figure 1. The analysis outlined
important information worth mentioning, which is
compiled in the following paragraphs.
Historically, i-voting systems have been designed
to support certain properties established as goals,
driving system specifications. Many property
definitions have arisen in i-voting literature, not all of
them totally concise. Sometimes, same notion was
renamed as a different property; in other cases,
overlapping characteristics were included in various
definitions. Thus, stating the desired properties for a
new system is not as simple as compiling a list from all
researched proposals.
Computer communication needs and democratic
election principles influenced cryptographic protocols
into becoming central elements in i-voting systems.
Although message exchange can be secured with basic
public/secret key encryption, advanced cryptography is
required to create the contents. The most commonly
used advance cryptographies in i-voting have been
blind signature (Chaum, 1983) and homomorphism
(Benaloh, 1987).
Nevertheless, it was found that even though the
achievable properties depend on the cryptographic
protocol scheme used (blind signature based or
homomorphic), it is not enough to ensure their
complete fulfillment. Thus, apart from a secure
cryptographic protocol, other elements are needed to
accomplish the properties which are not totally
addressed by the protocol itself.
The main result of this literature analysis was the
compilation of foundations for i-voting system design,
which set up the basis for our own proposal.
395
Huarte M., Goirizelaia I., José Unzilla J., Matías J. and J. Igarza J..
A New Fully Auditable Proposal for an Internet Voting System with Secure Individual Verification and Complaining Capabilities.
DOI: 10.5220/0004529803950402
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT-2013), pages 395-402
ISBN: 978-989-8565-73-0
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
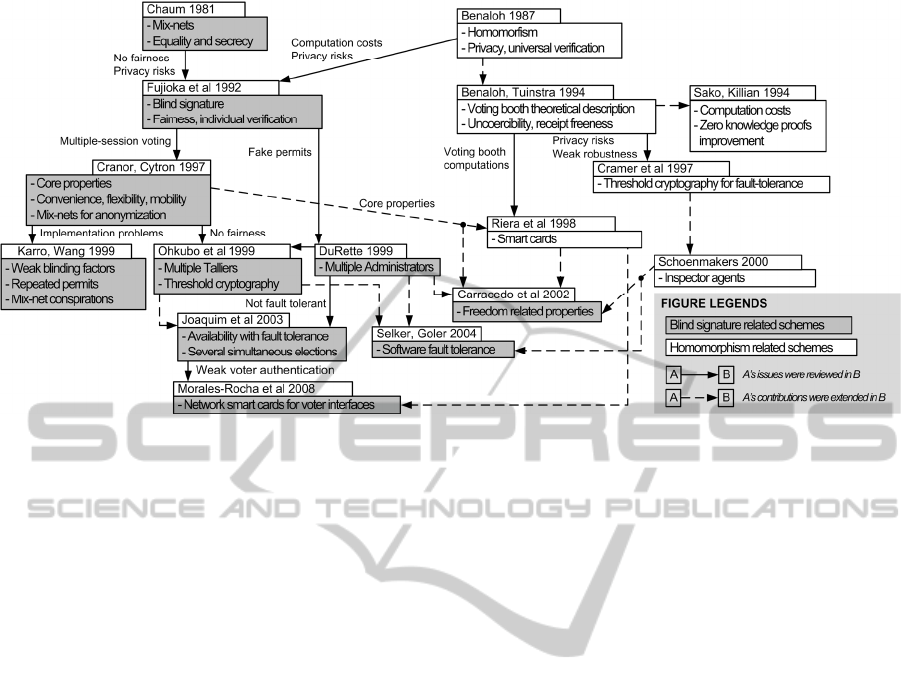
Figure 1: Summary of i-voting literature review.
3 FOUNDATIONS FOR A NEW
i-VOTING SYSTEM
3.1 Desired Properties
Table 1 introduces the properties decided for our i-
voting system, depicting the relationships between i-
voting properties, democratic election principles and
cryptographic protocol schemes. Stating these
properties as design goals, forces us to base our i-
voting system on the foundations described in the
following subsections.
3.2 Deciding the Cryptographic
Protocol Scheme: Blind Signature
vs. Homomorphism
As shown in Table 1, simplicity is nowadays
independent from the voting protocol, since single-
session voting was achieved for blind signature
based voting schemes (Ohkubo et al., 1999).
Although, it depends on how voter interfaces are
designed so as to be user-friendly for all voter types.
Both protocol schemes allow mobility too, but it
strongly affects privacy in remote i-voting, where
voting takes place outside the polling station, like in
traditional postal voting, making it voter interface
dependant as well.
Invulnerability and accuracy are both possible
with either protocol technique, as they rely on
public/secret key cryptography to send confidential
and certifiable messages to every system part.
The principle of freedom is the most conflicting one
for homomorphic protocols. Fairness is the only
property that can be accomplished with both
techniques. Flexibility cannot be achieved in
homomorphic schemes, as ballots have to fit a
certain format so as to be tallied; thus, no write-in
ballots can be implemented, and to our knowledge,
preferential tallying methods (e.g. used in Ireland or
Australia) are impossible to perform. However,
those are quite trivial for blind signature protocols.
Flexible systems can be adapted to different election
complexity (i.e., they can be used for simple
referenda too). Verifiability is difficult for
homomorphic protocols too, as individual
verifiability is not possible in order to preserve
privacy, and auditing fails to ensure that votes will
never be decrypted by colluding talliers (especially
after elections). Universal verifiability is nowadays
perfectly obtainable in blind signature based i-
voting; individual verification and auditing can also
be done exhaustively, if totally anonymous
communication channels are used for vote casting.
Finally, reliability is not totally accomplished with
homomorphic protocols either, because of
transparency problems. Observation cannot ensure
privacy will never be broken, and due to the extreme
mathematical complexity, homomorphic protocols
seem quite hard to understand. It can be argued that
blind signature is not easily understandable either,
but this shortcoming can be made up for because of
individual verification and secure vote-complaining
for incorrectly tallied votes.
Properties of the secrecy principle can be
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
396
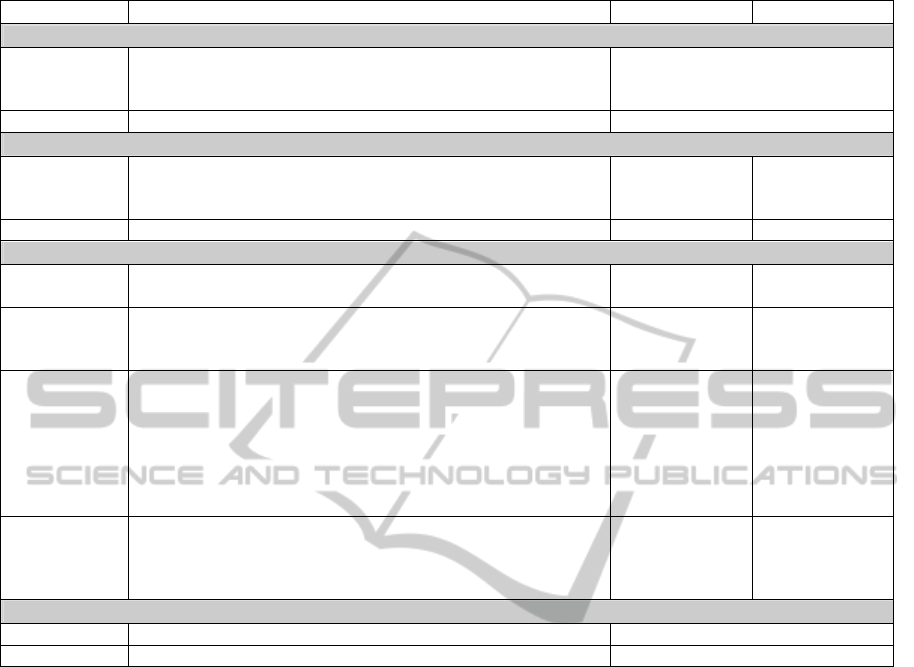
Table 1: Democratic election principles, i-voting properties and cryptographic protocol schemes.
PROPERTY DEFINITION Blind Signature Homomorphic
UNIVERSALITY PRINCIPLE
Simplicity
“Ease of use” characteristics:
Convenience.
Disability adaptation.
Same accomplishment level
Mobility
Both polling station and remote voters are admitted. Same accomplishment level
EQUALITY PRINCIPLE
Invulnerability
Considerations for legal votes (Cranor et al, 1997):
Only authenticated and eligible voters can vote.
Only one vote per voter is tallied.
YES YES
Accuracy
Only certified legal votes are tallied, which cannot be altered. YES YES
FREEDOM PRINCIPLE
Fairness
No intermediate results can be obtained while vote casting is
admitted.
YES YES
Flexibility
Ballot formats should not be limited for technical reasons, so as
to allow voters to express their opinion as accurately as possible.
Thus, any ballot format and tallying method should be admitted.
YES NO
Verifiability
Capability to check the functioning of the system:
Universal verifiability: Anyone can verify that the outcome was
obtained from legal votes.
Individual verifiability: each voter can verify that her vote was
correctly tallied.
Audit-capability: anyone can verify the correct functioning of
each part of the system in every electoral stage.
Accomplishable
(using totally
anonymous
communication
channels for vote
casting)
Universal only
Reliability
An i-voting system is trustworthy as result of its:
Robustness: it is technically able to survive attacks.
Transparency: it is understandable or, at least, observable.
Capability for secure vote-complaining.
Accomplishable Robustness only
SECRECY PRINCIPLE
Privacy
No vote can be related to the voter who cast it. Same accomplishment level
Uncoercibility
No voter can prove her choice to any third party. Same accomplishment level
satisfied by both protocol types to an extent. At this
time, well designed protocols can maintain privacy
and uncoercibility in message transport and system
procedures, but if the voter interface cannot ensure a
private environment with the user, all efforts are
worthless. Note that we did not include receipt-
freeness as a desired property (quite an outstanding
property among homomorphic schemes) because we
think that uncoercibility includes the basic notion of
receipt-freeness and the problem is not the existence
of a voting receipt itself, but rather its content. In
fact, providing a receipt is quite extended in blind
signature schemes as a means to perform individual
verification and vote-complaining.
Therefore, as it is outlined by the analysis in
previous paragraphs and the summary in Table 1,
nowadays, blind signature strategy seems more
suitable to accomplish democratic election
principles.
In the following points, we summarize the
characteristics on blind signature based schemes,
gathered from i-voting literature (see Figure 1), so as
to underscore some concepts that will be mentioned
in the following sections:
Blind signature is used to perform so called
anonymous channel voting schemes, where voters
have to communicate at least twice with the
system in order to vote.
The first communication, usually called permit
request, is to be done via a public channel (i.e.,
proving voter identity) to certain system agents
usually called Administrators or Validators. As a
result, the voter obtains a blindly signed value
from them, which she converts into a voting
permit that anyone can cryptographically verify to
be signed by the Validators without any possible
relation to her identity.
The second communication is for vote casting,
sending the permit and a cryptographycally closed
vote to Collectors or Talliers. It is essential that
the message is sent via an anonymous channel, so
that no one can relate the vote to the voter.
ANewFullyAuditableProposalforanInternetVotingSystemwithSecureIndividualVerificationandComplaining
Capabilities
397

3.3 Assisting the Cryptographic
Protocol Scheme: Network
Smartcards, Voter Interfaces,
Inspector Agents and Secure
Receipts
As outlined in previous Section 2 and looking at
Table 1, it is clear that even a blind signature based
protocol is not enough to achieve all desired
properties for i-voting by itself, so it has to be
supported by other elements. The following
paragraphs describe our proposals.
Smartcards are secure execution devices, suitable
for i-voting software. Currently, due to higher
memory capabilities they can store all the files
needed for universal user-friendliness (e.g., audio
files) and it is accepted that its tamper-resistance
protects voting operations from virus attacks. With
blind signature protocols, network smartcards should
be used (Morales-Rocha, 2008). These can create
their own IP packages, so that it could be managed
to use different unrelated IP source addresses for
permit request and vote casting, thus getting
complete (not only application level) anonymous
channels. The rest of the voter interface elements
should afford a private environment with the user, so
as to create a universal portable booth. In 2008 we
published a first proposal from a study of different
user capabilities (handicapped voters) and the need
of isolation for privacy (although multiple-casting
technique BSI-CC-PP-0097, 2008, can be adopted as
a first approach as well).
Equality principle needs multiple Validators to
independently sign permit requests (DuRette, 1999);
similarly, fairness and reliability need multiple
Collector-Tallier agents in a (t, n) threshold
cryptosystem (Ohkubo et al, 1999). This agent
multiplication requirement can be used to bring
software fault tolerance to i-voting systems,
operating as N-Version Programming or NVP
elements (see Selker, Goler, 2004, as NVP usage in
i-voting). To make the most of this, each multiplied
agent should be programmed and controlled by a
different inspection group, which have opposite
interests in the election outcome. This way, diversity
(needed in NVP) is easily achieved and the
observation concept (Schoenmakers, 2000) is added
too, gaining transparency and audit-capability.
Finally, secure vote-receipts are needed to
implement individual verification and complaining,
both for total verifiability and reliability
achievement. Vote-receipts have been a major point
of discussion and of great concern in i-voting. In
fact, receipt-freeness has been considered an
important property mainly in homomorphic
schemes. In contrast, blind signature protocols have
traditionally proposed receipt usage, firstly for
tallying (Fujioka et al, 1993; Cramer et al, 1996) but
as it was identified as a threat for vote secrecy, they
were redefined for partial individual verification
(only that the vote was tallied, but not if it was
tallied as cast). David Chaum himself proposed
secure paper receipts for e-voting in the Scantegrity
optical scan e-voting system (out of our scope),
which could be applied in polling station i-voting.
We consider that the threat for secrecy (mainly
addressed by homomorphic scheme supporters) is
not an issue because of the existence of a receipt
itself, but because of its lack of protection and its
contents. The receipt should meet two goals on
behalf of the voter; as response to vote casting, it
should certify to the voter that her vote was stored in
the system, so as to consider the voting process as
properly finished; also, after results are published, it
should serve to verify the correct tallying of the vote
and to complain in case of error. For the first goal,
considering the multiple Collectors to be used, the
receipt should contain a signature from every
Collector who accepted to store the vote. For the
second one, signatures should be related to the
closed vote stored and should contain some kind of
uniqueness (so as to be identifiable among all
published votes); moreover, relating the signatures
to the hash of the closed vote, instead of the closed
vote itself, makes the complaining process determine
that the tallied vote is different from the cast one,
without revealing its actual value. Individual
verification and claiming operations (e.g., every
receipt usage), should be audited too, that is, by
specific Complaint inspector agents.
All of these requirements can be met with a
proper receipt definition and treatment, that
transforms it into a so called vote-proof, which
enforces the collaboration (and thus, auditing) of the
majority of the inspector groups in individual
verifications and complaining processes.
As shown in Figure 2, the vote casting process
ends up with the voter creating the vote-proof,
derived from the correct receipt received. This vote-
proof should stay securely stored in the network
smartcard until it is used to perform individual
verification, vote complaining or the voter decides to
delete it. Note that for individual verification, only
the protected key shares are needed to be sent to the
inspectors (Ohkubo et al., 1999).
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
398
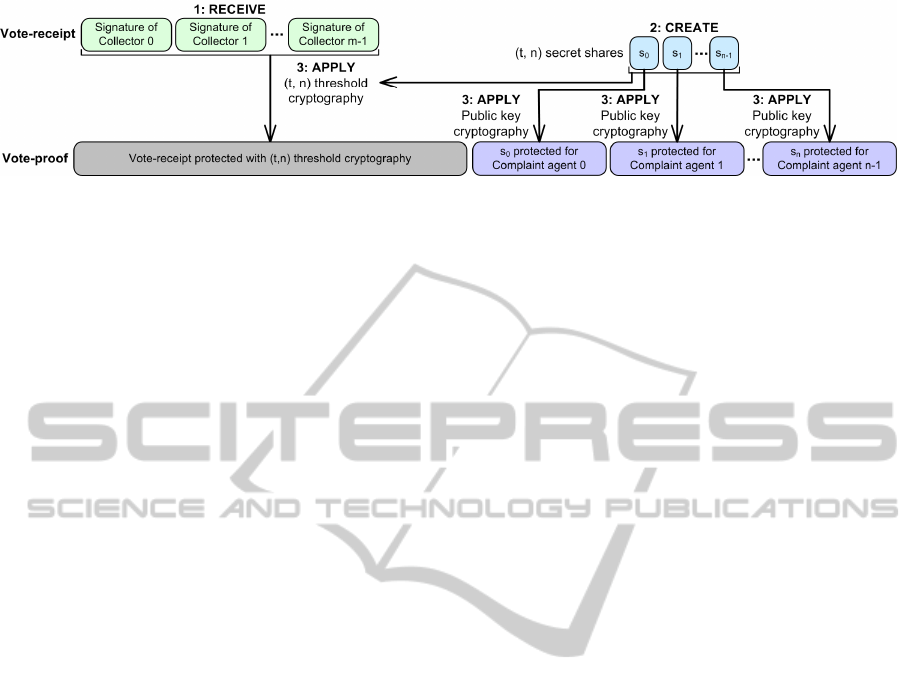
Figure 2: i-Voting receipt and vote proof generation in voter’s network smartcard.
3.4 One Step beyond: Validation
I-voting proposals should be validated. Two
complimentary validations can be performed.
Functional Validation: Both the Council of Europe
(CE, 2004) and Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der
Informationstechnik (BSI-CC-PP-0037, 2008)
have published security objective catalogues for
Common Criteria like evaluations. Their
objectives are derived from system operational
capabilities and thus, constitute useful guidelines
to check the functional completeness of i-voting
proposals. The first document is intended for
every e-voting system, so i-voting proposals
should consider it too. The second one is specific
for remote i-voting to be used in non-political
elections, as it sets the protection of vote choosing
as an assumption (not a system requirement).
Cryptographic Protocol Validation: Previous
catalogues assume cryptographic communication
protocols are correct; thus, a specific validation is
to be done so as to ensure it. As stated in Kremer
et al, 2005, it cannot be left as a secondary check,
as major flaws have been discovered in sound
protocols after years of usage. Model checking
tools such as ProVerif (Blanchet, B.) can validate
security protocols against i-voting properties. The
validations should be done in scenarios where the
attacker could even act as a legitimate agent (a
voter or a system agent) or where the protocol
itself is instrumented to demonstrate that some
property-attacking executions are not possible
(e.g. eligibility proof in Kremer et al., 2005).
4 NEW i-VOTING SYSTEM
APPROACH
Following the foundations introduced in Section 3,
we designed the system described in Figure 3.
The i-voting system has several Virtual Polling
Stations, made up of a Validation and a Storage
subsystem. Each of those subsystems follows the
“inspector agents” foundation, and is formed of an
electoral principal agent working as an NVP
controller over several inspector agents (addressed
in Figure 3 as NVP configuration). The same
configuration is followed in the Final Tallying and
Complaint subsystems too.
4.1 System Description
In this i-voting proposal, voters will interact with the
system through a network smartcard, called VC
(Voting Card); this card is to be distributed in a way
that even the authority cannot determine which card
will be used by each voter (e.g., in randomly
addressed envelopes). This is very important, in
order to create complete anonymous channels for
vote casting. On the other hand, as using an
anonymous channel protocol scheme, first voter-
system communication needs to ensure voter
identity. Our solution uses a second smartcard,
called CC (Citizen Card), both to sign the permit
request and help the VC to determine that its user is
the corresponding citizen in each usage session (in
each vote casting if multiple castings are performed,
in individual verification and in complaining). The
CC is a spare identity smartcard, supplied for any
identity-based e-administration application. Previous
to permit request, a personalization process is to be
run by the citizen in the VC, which secures it to her.
Thus, stealing personalized VCs in order to vote is
useless; also, our system detects if a voter has
personalized different cards and tries to get voting
permits with them, not allowing so.
Figure 4 shows the voting protocol designed. As
in Figure 2, the colored rectangles in the messages,
depict a different cryptographic operation, such as
public key encryption, signatures and hashes (i.e., a
Closed Vote is a plain text Vote.xml file encrypted
with the voting public key).
On voting phase (Figure 4), each voter sends her
permit request to a Validation subsystem and gets a
blind signature on it from the principal (V) and each
one of its inspectors (VIs), related to the polls in
which she is eligible. That permit request is sent by
ANewFullyAuditableProposalforanInternetVotingSystemwithSecureIndividualVerificationandComplaining
Capabilities
399
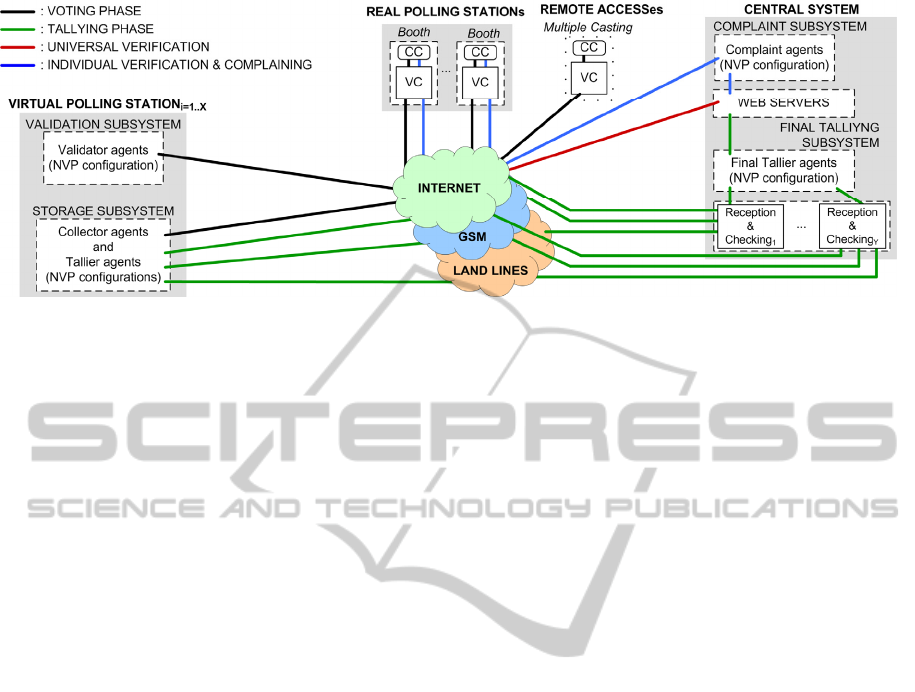
Figure 3: i-Voting proposal.
the VC but signed by the Citizen Card, so as to
ensure voter identity; the core of this message is a
unique vID cryptographically blinded (which
ensures permit uniqueness and avoids rejection of
legal votes from different eligible voters; see Karro,
Wang, 1999). Eligible voters can send as many
permit requests as they need to deal with situations
in which the corresponding response is not received.
Each permit request from the same voter will have a
different sequence number, which will be checked
by the Validators along with voter’s identity and
blinded vID (to ensure that it comes from the same
Voting Card). The blind signatures performed by the
Validators are called blind component permits and
altogether form the blind permit. Validators sign the
citizen identity and sequence number too, to ensure
the originality of the response. Unblinding the blind
component permits received from the Validation
principal, VC obtains the permit, that should contain
a majority of Validation agent signatures over its
vID so as to be valid. Although a voter can send
multiple requests, she will always receive the same
blind permit, so it can just be used to vote once.
Once a valid permit is obtained and a vote is
chosen by the voter, VC sends a vote casting
message to the Storage subsystem through an
anonymous channel (without voter’s identity and
with a different IP address from the one used when
permit requesting). This message contains the
permit, the poll code and the closed vote. The
Storage subsystem is structured as the Validation
one, but with Collector principal (C) and inspectors
(CIs). Their task is to check the validity of the
permit, the poll and the message signature, store the
closed vote in their databases if so, and create their
component receipts. In our protocol, a component
receipt is basically the signature of a Collector agent
on the vID, the poll code and a hash of the closed
vote. This signature is actually a private key
encryption, with uniqueness ensured by the vID-poll
combination. Once a valid receipt is received,
voter’s VC generates the corresponding vote-proof
as in Figure 2. Our system allows multiple casting
(BSI-CC-PP-0037, 2008), not just to deal with lost
responses but to face voter coercion in remote i-
voting. Each new cast is checked for having a
correct sequence number too and the new closed
vote replaces the stored one if so.
As for the tallying phase, Collector agents are
turned off and Talliers run in their same servers
(Figure 3), accessing the same databases. Note that
closed votes must be opened with a secret key (the
voting private key) accessible only by the Talliers;
this is a simple way to ensure fairness in anonymous
channel schemes. Talliers compute partial results
from the correct votes. As in traditional elections,
each such partial result is generated from the
collaboration of authority and inspector groups,
whose roles are played by the corresponding Tallier
computer agents. Partial result files are then sent by
each Storage subsystem to the Central System,
which will be in charge of generating final results
and providing the services of the publication
electoral phase. This file sending is done using
different networks, thus bringing NVP diversity to
secure partial results transport. Final results are then
calculated by the Final Tallier agents.
Finally, in the publication phase, Central System
web servers publish final results with all the
information needed to perform verifications:
Universal Verification: Anyone can verify that the
results were generated from valid votes, as they
are published along with the permit and receipt
generated. A receipt related “acceptance value” is
published as well, which reflects the percentage of
inspectors that accepted to tally the vote.
Acceptance values are visualized for every tally
level, supporting each of the partial results and
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
400
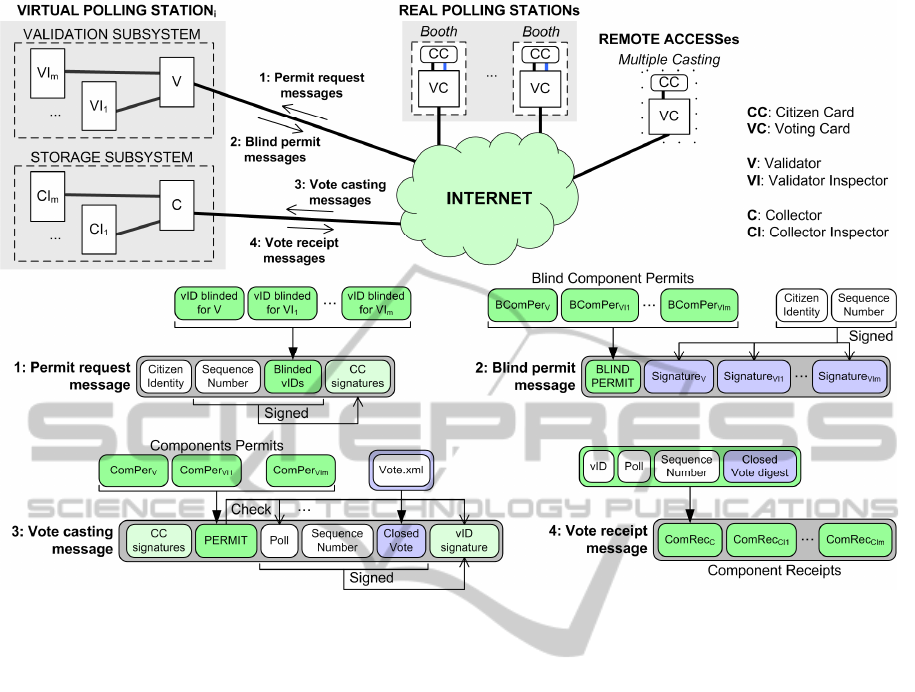
Figure 4: Voting protocol: permits and vote-receipts.
helping independent universal verifications.
Individual Verification and Complaining: These
two operations are to be performed via secure
anonymous channels, as with vote casting.
Because a multiple casting like solution is not
feasible for them, they are to be executed in real
voting booths at real Polling Stations. Of course,
both operations are completely voluntary and
special care has to be taken to protect privacy.
All operations are recorded in log files both in
principal and inspector agents, which can be used for
public audit.
4.2 System Validation
Complete system validation is a matter important
enough to comprise the main topic of a whole new
paper. Still, we would like to highlight that the two
validation types explained as system foundations in
previous Section 3.4 have been performed on our
system design, as a first approach to continue ahead
with real implementation and performance.
Functional Validation: One by one, all security
objectives from both documents (CE, 2004) and
(BSI-CC-PP-0037, 2008) were checked for this
validation. Foundations such as simplicity
(expressed as simple voting operation with voting
process stop and resume or vote correction),
eligibility, accuracy, fairness and privacy
properties, audit-capability characteristic (included
in our verifiability property, Table 1), multiple
casting and inspector agents, were found to
address many of the security objectives required.
Cryptographic Protocol Validation: ProVerif
model checker was used to perform this
validation, which required us to express the
protocol in Spi Calculus description language. The
same fairness and invulnerability (eligibility) tests
as Kremer and Ryan (Kremer et al, 2005) were
run, as are to be the same for all blind signature
based schemes; privacy property can be proved as
described there too. Additionally, new tests were
designed and run to check verifiability and
accuracy, as well as the secure vote-complaining
feature.
5 CONCLUSIONS
i-Voting systems have nearly 30 years of wide
research history. There have been many interesting
proposals throughout this time, but few practical
ANewFullyAuditableProposalforanInternetVotingSystemwithSecureIndividualVerificationandComplaining
Capabilities
401

implementations, due to different reasons that
mainly involve security, scalability and social
acceptance. Currently, it can be said that computer
system design and cryptographic protocol techniques
are becoming mature enough to create secure
systems that can exploit all i-voting potential.
This paper describes our new i-voting system
proposal designed to fulfill democratic election
principles. To this end, the system uses a blind
signature based anonymous channel protocol
together with certain reinforcing elements, such as
network smartcards and adapted interfaces for
voters, NVP inspector agents at server side and vote-
proof protection for secure receipt usage.
The i-voting system employs two smartcards to
protect voter privacy, supports multiple permit
requesting and vote casting, tallies votes in
collaboration with inspection groups, and allows
universal and individual verifications, full audit and
secure vote-complaining.
After functional and cryptographic validations,
we believe that our design includes all desired
features for a secure i-voting system, providing
voters with even better capabilities than in
traditional voting, as verifications (both universal
and individual) and complaining can be easily
performed. Thus, like in other Internet based
services, the big problem is reduced to Denial of
Service attacks, which can be countered by proper
usage of the several Virtual Polling Station facilities.
REFERENCES
United Nations, 1966. International Covenant on Civil
and Political Rights, art. 25 sect. B. Available from:
http://www.hrweb.org/legal/cpr.html. [5 March 2013].
Council of Europe 2004. Recommendation, Rec(2004)11.
Available from: https://wcd.coe.int/ViewDoc.jsp?
id=778189. [5 March 2013].
Chaum, D., 1981. Untraceable electronic mail, return
addresses, and digital pseudonyms. In Communica-
tions of the ACM, vol. 24, n. 2, pp. 84-90.
Benaloh, J., 1987. Verifiable secret-ballot election. Yale
University USA, PhD. Thesis.
Fujioka, A., Okamoto, T., Ohta, K., 1993. A Practical
Secret Voting Scheme for Large Scale Elections. In:
AUSCRYPT’92, vol. 718, pp. 244-251.
Benaloh, J., Tuinstra, D., 1994. Receipt-Free Secret-Ballot
Elections (Extended Abstract). In: Proceedings of the
twenty-sixth annual ACM symposium on Theory of
computing, pp. 544-553.
Sako, K., Kilian, J., 1994. Secure Voting Using Partially
Compatible Homomorphisms. In: Proceedings of the
14th Annual International Cryptology Conference on
Advances in Cryptology, vol. 839, pp. 411-424.
Cranor, L. F., Cytron, R. K., 1997. Sensus: A Security-
Conscious Electronic Polling System for the Internet.
In: Proceedings of the Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences, pp. 561-571.
Cramer R., Franklin, M., Schoemakers B., Yung, M.,
1996. Multi-authority secret ballot elections with
linear work. In: Advances in Cryptology –
EUROCRYPT’96, vol. 1070, pp. 72-83.
Riera, A., Borrell, J., Rifá, J., 1998. An uncoercible
verifiable electronic voting protocol. In: Proceedings
of the IFIP TC11 14th International Conference on
Information Security SEC'98, pp. 349-362.
Karro, J., Wang, J., 1999. Towards a Practical, Secure, and
Very Large Scale Online Election. In: Proceedings of
the 15th ACSAC, pp. 161-169.
DuRette, B. W., 1999. Multiple Administrators for
Electronic Voting. MIT USA. Bachelor’s thesis.
Available from: http://groups.csail.mit.edu/
cis/theses/DuRette-bachelors.pdf. [5 March 2013].
Ohkubo, M., Miura, F., Abe, M., Fujioka, A., Okamoto,
T., 1999. An Improvement on a Practical Secret
Voting Scheme. In: Proceedings of the Second
International Workshop on Information Security, pp.
225-234.
Schoenmakers, B., 2000. Fully Auditable Electronic
Secret-Ballot Elections. Available from: http://
www.xootic.nl/magazine/jul-2000/schoenmakers.pdf.
[5 March 2013].
Carracedo, J., Gómez, A., Moreno, J., Pérez E., 2002.
Votación electrónica basada en criptografía avanzada
(Proyecto VOTESCRYPT). Available from: http://
vototelematico.diatel.upm.es/articulos/articulo_venezu
ela_revisado.pdf. [5 March 2013].
Joaquim, R., Zúquete, A., Ferreira, P., 2003. REVS- A
Robust Electronic Voting System. In: Proceedings of
IADIS International Conference e-Society, pp. 95-103.
Selker, T., Goler, J., 2004. The SAVE system – secure
architecture for voting electronically. BT Technology
Journal, vol. 22, iss. 4, pp. 89-95.
Morales-Rocha, V., Soriano, M., Martínez-Peláez, R.,
Rico, F., 2008. New multi-channel voting scheme:
towards remote e-voting over the internet.
International Journal of Electronic Governance, vol. 1
n. 2, pp. 155-173.
Chaum, D., 1983. Blind Signatures for untraceable
payments. In: Advances in Cryptology - Crypto '82,
pp. 199-203.
Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik,
2008. Common Criteria Protection Profile for Basic
set of security requirements for Online Voting
Products; BSI-CC-PP-0037, v1.0, 18, Bonn.
Kremer, S., Ryan, M., 2005. Analysis of an Electronic
Voting Protocol in the Applied Pi Calculus. In: Proc.
14th European Symposium On Programming
(ESOP’05), pp. 186-200.
Blanchet, B. ProVerif. Available from: http://
proverif.inria.fr/.[5 March 2013].
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
402
