
Towards Virtualization of Rich Applications for Distribution under a
SaaS Model
D. A. Rodríguez-Silva, L. Adkinson-Orellana,V. Fernández-Díaz and F. J. González-Castaño
Gradiant, Network and applications Area, Ed. Citexvi, 36310 Campus, Vigo, Spain
Keywords: Virtualization, Saas, Desktop Applications, Cloud Storage, Remote Desktop, Streaming.
Abstract: Current mobile devices (smartphones, tablets, netbooks…), widely used nowadays, can run potent native
applications, but they cannot support typical desktop applications from any operating system. Since modern
devices support recent web standards as HTML5, it is possible to develop a solution based on a thin web
client to grant remote access to desktop applications offered under a SaaS model. This paper proposes the
development of an innovative remote desktop system able to detect application content and encode it
efficiently in real-time, to support an optimal visualization on clients, combining both remote desktop and
streaming protocols. The system is hosted by a cloud infrastructure that ensures scalability, and it follows a
pay-per-use model. Application providers can include their software in a dynamic cloud repository, from
where it is launched remotely to meet final user demands.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the use of mobile devices is increasing to
the point that, according to some forecasts,
smartphones and tablets will displace PCs in the
near future (Want, 2009). Although some mobile
devices do not seem constrained in terms of
computing performance or even display size, the
relationship between computational power and
battery capacity, the input interface or the maximum
number of concurrent applications are also limiting
factors.
Consequently, for some reason or another,
heavy, highly demanding rich applications are not
appropriate for simple user devices, and in most
cases applications functionalities need to be adapted
or reduced to show up in these devices. Cloud-
oriented remote visualization technologies which
allow running an application on a remote high-
performance server and exporting its graphic user
interface to a low-end terminal can be of help. They
also free end-users from the burden of software
maintenance and protection against malicious
attacks.
Remote desktops are well-known visualization
technologies (VNC, RDP, NX…). They usually
perform well with static graphic outputs, as they just
transmit screens differences. However, current
remote desktop technologies present drawbacks, as
the lack of efficient audio support or the poor
visualization of dynamic contents (i.e. video). On
the other hand, even though streaming may offer an
appropriate solution in that case, it results inefficient
when only a small part of the transmitted content is
changing.
In this paper we describe a virtualization cloud
platform that provides optimal remote access to rich
interactive applications through a thin web client,
supported by several recent mobile devices. The
platform relies on a cloud infrastructure that will
also host an application market, following a pay-per-
use business model. Section 2 explains the proposed
architecture and section 3 discusses related work.
Finally, section 4 concludes the paper.
2 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
The platform we pursue will allow the execution of
any application in a remote powerful virtual machine
through any client device, without installing any
local software. This will be completely transparent
to the user, regardless of the device capabilities.
The client side will be developed entirely using
standard web technologies, to achieve complete OS
independence. The server side will deploy ready-to-
370
Rodriguez-Silva D., Adkinson-Orellana L., Fernandez-Diaz V. and Gonzalez-Castaño F..
Towards Virtualization of Rich Applications for Distribution under a SaaS Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0004375503700373
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2013), pages 370-373
ISBN: 978-989-8565-52-5
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
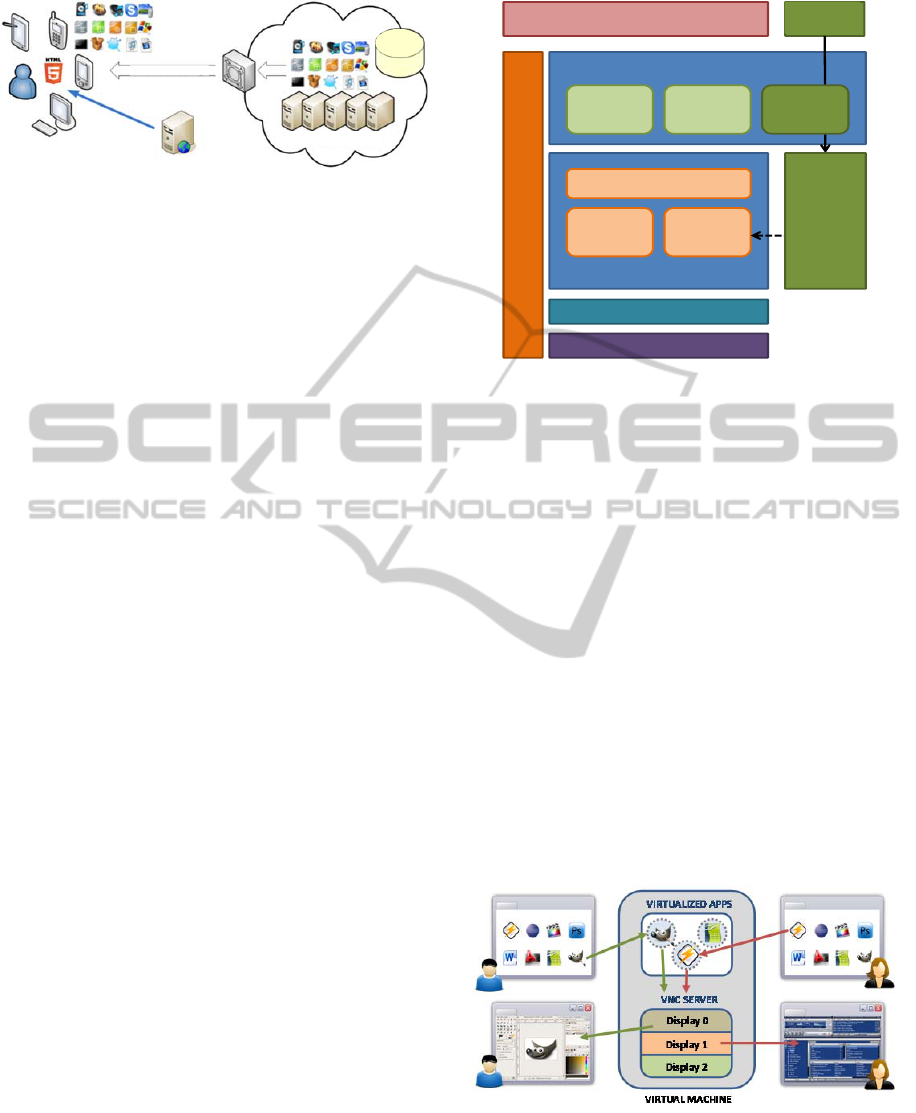
Figure 1: General architecture of the proposed system.
use applications and will detect motion in screen
content, in order to code any necessary information
intelligently to send it to the client in real-time using
the most appropriate protocol (RFB or streaming) in
each case. To enhance scalability, a cloud
infrastructure will be used. The general architecture
of the system is shown in Figure 1.
2.1 Cloud Infrastructure
The proposed architecture is composed of four
different layers: IaaS, hypervisors, a virtual resource
layer and the SaaS platform. The infrastructure level
provides the upper layers with the physical resources
necessary to run the applications. As the server side
will rely on a virtual machine, a cloud broker is
necessary to manage the cloud infrastructure, in
order to create virtual machines on demand.
As different users share the same virtual
environment, additional security measures are
required to guarantee data isolation. This is achieved
by keeping the user data that the applications access
in a cloud storage instead of in the virtual machine.
How this storage is implemented is open, as it can be
an internal component of the solution or it can be
provided by an external cloud storage service (e.g.
Dropbox). In both cases, the virtualized applications
will manage user files remotely and encryption
techniques will be applied to enhance the cloud
storage mechanism, so user data will remain safe
during the whole process.
Figure 2 shows the cloud architecture, where the
cloud broker is in charge of the virtual resource layer
that provides virtualized applications to the SaaS
platform. Applications will be available through a
repository, in which application providers will be
allowed to upload their software, to be delivered
according to a pay-per-use model. When an
application is uploaded, the repository manager
creates and configures a template for the virtualized
application following the OCCI standard
(http://occi-wg.org). This template is stored in the
application repository, enabling the corresponding
application for user access.
Figure 2: Cloud architecture.
2.2 Remote Visualization
Our virtual machines currently support either
Windows or Linux OS templates, although the
proposed scheme could be extended to other
operating systems.
In addition to the virtualized applications, each
virtual machine includes a RFB server to allow users
to access their applications remotely. The protocol
chosen for RFB communication is VNC (VNC,
1999), one of the most popular ones. This protocol is
conveniently combined with HTTP streaming (see
section 2.3) to improve the user experience at client
side. Each virtual machine can support different
remote desktop user sessions simultaneously through
different displays managed by different VNC servers
in the same machine. Thus, each user working with a
virtualized application will belong to a different OS
session with its own display (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Application virtualization architecture.
In Linux, this application virtualization relies on
Xvfb (http://www.xfree86.org/4.0.1/Xvfb.1.html),
an X window virtual frame buffer, which
Application
Manager
Users
Manager
Hypervisor
IaaS
SaaS Platform
VirtualResource Layer
CloudBroker
Cloud
Storage
Virtual
Applications
Application
Provider
Monitoring &Security
End Users
Repository
Manager
Application
Repository
Cloud applications
Cloud infrastructure
Cloud
storage
Web server
(HTML5 viewer)
Client with
HTML5 browser
Cloud
broker
RFB + streamin
g
TowardsVirtualizationofRichApplicationsforDistributionunderaSaaSModel
371

implements a virtual X server as a frame buffer in
which different graphical outputs can be dumped,
using several virtual displays, without overlaps. In
Windows there are no virtual graphic devices such
as Xvfb, so each application needs to be virtualized
in a separated virtual machine that contains its own
VNC server.
2.3 Motion Content Detection
The VNC server has three functions:
Screen delivery of low-motion content
through the VNC protocol.
HTTP video streaming of high-motion content
Intelligent switching between VNC and HTTP
streaming protocols depending on the content.
In order to detect whether the screen content is
static or dynamic, the raw images available at the
VNC server are analyzed as follows:
while(true)
fork=0 to N-1 begin
fb
k
= getFramebuffer(k);
for x = 0 to blocks(fb
k
)-1
w = 32; h = 32;
b
k,x
= getBlock(fb
k
,w,h);
changed =compare(b
k,x
,b
k-1,x
);
if (changed == true)
block_changes
x
+= 1;
end for
end for
for i=0 to size(block_changes)-1
if (block_changes
i
> thredshold)
block_changed
i
= 1;
else block_changed
i
= 0;
end
end if
detectMotionArea(block_changed);
end for
sleep(t);
end while
The frame buffer content is gathered ‘N’ times in
a loop, grouping the raw pixels in 32×32 blocks. The
blocks are compared with their instances in the
previous iteration and, if at least a pixel differs, the
entire block is marked as a change; on the other
hand, if all the pixels are the same, the block
remains unchanged.
When the comparison loop ends, the number of
changes occurred in each block is checked. If it
exceeds a predefined threshold, the pixels of the
block are set to ‘1’; otherwise, the block is set to ‘0’.
Finally, an array of binary values is obtained,
showing the position of the dynamic blocks in the
screen. Figure 4 shows an example of a VLC player
playing a video inside an Ubuntu desktop and its
corresponding representation as an array with the
motion detected areas marked with ‘1’.
Figure 4: Motion detection process.
Due to the high computational load required to
compare all the pixels of the frame buffer, only a
representative subset is checked. We decided to look
only at those pixels in block diagonals, simplifying
the complexity of the problem from order n
2
to 2n,
where n is the block width in pixels (assuming a
square block). Nevertheless, the accuracy of the
detection is preserved due to the proximity of the
pixels in a 32×32 block, compared with a typical
1024×720 desktop size. In addition, a hysteresis
criterion is followed to prevent false positives,
improving reliability. Once the motion area is
detected, the VNC server stops sending the RFB
images of that area. Then the stream is generated
and the client receives the URL to play the video in
the corresponding rectangle over the VNC content.
2.4 Web Client
A major concern regarding the visualization of
remote applications is the necessity of a specific
client for each device and platform. To cope with
this we propose the development of a thin client
based on common technologies supported by most
of devices (typically Web over HTTP), following
the latest standards as HTML5. Thus, the web client
may be accessible everywhere through compatible
web browsers.
This client combines and displays contents
received by VNC and HTTP streaming protocols
seamlessly, by using canvas and video tags. Hence,
users will have a web portal containing a catalogue
of the available applications and the client to access
them. The platform has an open-community
orientation, so that users will be able to demand and
CLOSER2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonCloudComputingandServicesScience
372

evaluate applications and software providers will
distribute their applications easily.
3 RELATED WORK
The fact that thin clients improve power efficiency
has been demonstrated previously (Vereecken et al.,
2010). However, a comprehensive study over a wide
range of well-known thin client protocols
(Deboosere et al., 2007) has proved that additional
functionality is required for a satisfying multimedia
experience. In this case streaming is a feasible
mature option, though it may consume lots of
unnecessary bandwidth in case the user interface is
quite static. Several studies have combined remote
desktop and streaming technologies like Simoens,
Praet, Vankeirsbilck, De Watcher and Deboosere
(2008) and Tan, Gong, Wu, Chang and Li (2010).
However, these solutions are not scalable at all, and
they severely limit the number of users that can
access the system. To solve this, some authors have
proposed the use of cloud computing to support
scalable remote visualization through optimized
protocols for mobile devices, although there are still
many open issues (Simoens et al., 2008). In (Zhong
et al., 2010), an approach named vSaas for providing
software as a service from the cloud was described.
Nevertheless, this solution does not offer a smoothly
remote visualization of applications. Shi, Lu, Li and
Engelsma (2010) have present the SHARC solution
for enabling scalable support of real-time 3D
applications in the cloud, delivering content to
clients through a streaming server. However, this
proposal requires installing a specific client or a
Flash browser to visualize the 3D contents.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper focuses on the development of a
virtualization platform that will provide optimal
remote access to rich interactive applications
through a thin HTML5 web client supported by
many recent mobile devices. For this to become
possible, it was necessary to apply mechanisms and
algorithms at the server side to automatically detect
changes in the screen content of the applications and
code the dynamic areas in real-time when necessary,
combining optimal protocols to display the screens
at the client side in a efficient way. In addition, the
solution, which is supported by a cloud
infrastructure, includes a repository with
applications that will be delivered as SaaS.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported by Spanish
projects VIMAIN (grant IPT-2011-1224-430000),
funded by MINECO, SECANI (grant
10SEC001CT), funded by Xunta de Galicia, and
partially by CloudMeUp (grant IDI-20101357),
funded by CDTI.
REFERENCES
Deboosere, L., De Wachter, J., Simoens, P., De Turck, F.,
Dhoedt, B., et al. (2007). Thin Client Computing
Solutions in Low- and High-Motion Scenarios. In
Proc. IEEE Third International Conference on
Networking and Services, p. 38-43.
Shi, W., Lu, Y., Li, Z. and Engelsma, J. (2010). Scalable
Support for 3D Graphics Applications in Cloud. In
CLOUD’10, Proc. of IEEE 3rd International
Conference on Cloud Computing.
Simoens, P., Praet, P., Vankeirsbilck, B., De Watcher, J.,
Deboosere, L., De Turk F., et al (2008). Design and
implementation of a hybrid remote display protocol to
optimize multimedia experience on thin client devices.
ATNAC’08, Telecommunication Networks and
Applications Conference.
Tan, K. J., Gong, J. W., Wu, B. T., Chang, D. C., Li, H.
Y., Hsiao Y. M. et al. (2010). A remote thin client
system for real time multimedia streaming over VNC.
In ICME, Proc. of the IEEE International Conference
on Multimedia and Expo.
Vereecken, W., Deboosere, L., Simoens, P., Vermeulen,
B., Colle, D.,Develder, C., et al. (2010). Power
efficiency of thin clients. European Transactions on
Telecommunications, vol. 21, pp. 479-490.
VNC (1999). Virtual Network Computing website.
Retrieved December 4, 2012, from
http://www.hep.phy.cam.ac.uk/vnc_docs/index.html
Want, R. (2009). When cell phones become computers.
IEEE Pervasive Computing, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 2-5.
Zhong, L., Wo, T., Li, J. and Li, B. (2010). A
Virtualization-Based SaaS Enabling Architecture for
Cloud Computing. In ICAS’10, Proc. of Sixth
International Conference on Autonomic and
Autonomous Systems, Cancun, Mexico.
TowardsVirtualizationofRichApplicationsforDistributionunderaSaaSModel
373
