Wi-City
Living, Deciding and Planning using Mobiles in Intelligent Cities
Alfio Costanzo, Alberto Faro and Daniela Giordano
Department of Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering, University of Catania, Catania, Italy
Keywords: Mobile Computing, Location Intelligence, Decision Support Systems, Smart Cities, Intelligent Cities.
Abstract: The current GPS navigational systems are mainly developed with a proprietary approach based on
incomplete information and behave as general purpose information systems based on average traffic data.
On the contrary, effective location based services should be based on real time traffic information and
should take into account all the databases available at urban scale to help decision making and planning of
the mobile users. This paper aims at illustrating how a prototypical distributed information system, called
Wi-City, may help people in living, deciding and planning in cities where collective and cooperative
intelligence systems will be more and more adopted by the citizens. Indeed, Wi-City is an ubiquitous
information system available over an open/interoperable platform to support mobile user decisions taking
advantage from real time data and information available on the different databases at urban scale, including
the ones stored on the user mobiles.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper aims at illustrating how a prototypical
mobility information system, called Wi-City, may
help people in living, deciding and planning in cities
where collective and cooperative intelligence
systems are adopted by the citizens (Berthon et al.,
2011).
Wi-City is an ubiquitous information system
implemented following the Model-View-Controller
(MVC) paradigm to favor the implementation per
use cases that, as demonstrated in the literature, e.g.,
(Costanzo et al., 2012a) and (Dubberly, 2011), is
able to support effectively context aware
applications.
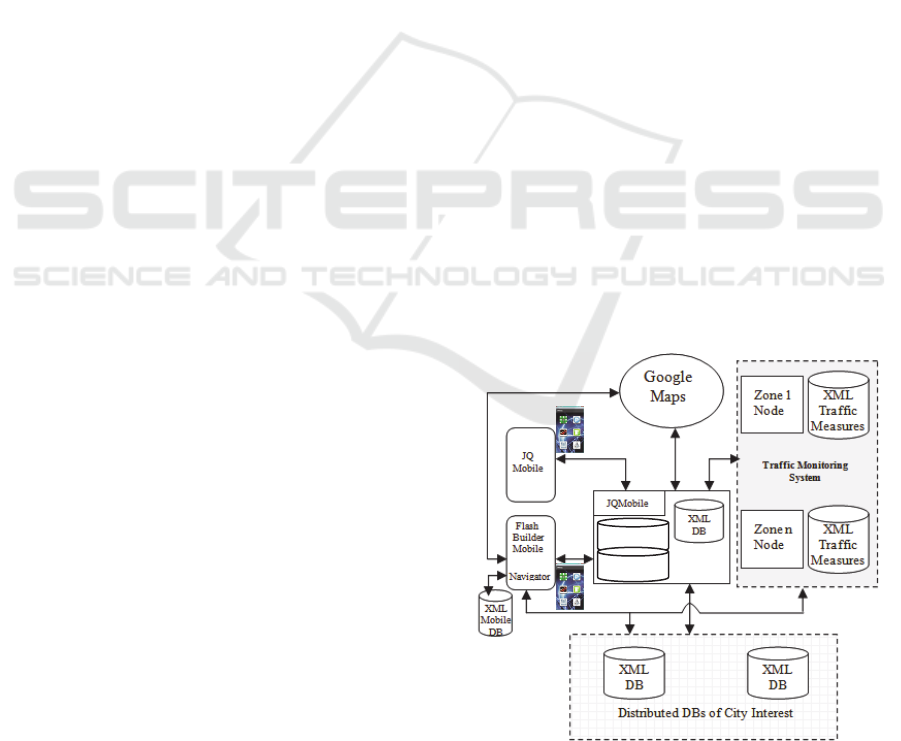
Fig.1 shows the Wi-City architecture, widely
discussed in (Costanzo et al., 2012b). All the data
required to help the mobile users are collected by the
MVC based server, i.e., Ruby on Rails (RoR) (Hartl,
2001), into an XML database. Such data deal with
the real time measurements on the traffic conditions,
and with the slowly changing information belonging
to the databases of interest of the citizens to carry
out e-government and e-commerce activities.
Personal and social data are used to support the
user decisions. The former information may reside
on either the mobile or the server, the latter one
deals with user preferences collected by a suitable
RoR program from social networks and resides on
the server.
Figure 1: Wi-City functional architecture.
Two types of user interface have been
developed: a) in the former the mobiles receive the
JQMobile scripts (David, 2011) from the RoR server
to display the relevant Google Maps based views, b)
in the latter, the users are provided with mobiles able
to display the Google Maps based views created by a
suitable Flash Builder program (Corlan, 2009)
resident on the mobiles to save the server CPU time.
The main functions of the Wi-City architecture
RoR
Se
r
ver
Preferences
Personal
Data
Personal
Data
98
Costanzo A., Faro A. and Giordano D..
Wi-City - Living, Deciding and Planning using Mobiles in Intelligent Cities.
DOI: 10.5220/0004340500980103
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Pervasive Embedded Computing and Communication Systems (PECCS-2013), pages 98-103
ISBN: 978-989-8565-43-3
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
are: a) a software layer that uses a suitable urban
vocabulary (ontology) for data integration of
distributed/federated databases as outlined in the
literature, e.g., (Zhai et al., 2008); such integration is
based on an XML/RDF approach inspired by the
semantic web paradigm (Quilits and
Leser, 2008), b)
a minimum path finder algorithm based on a
programming logic approach, and c) a fuzzy logic
engine that behaves as a Decision Support System
(DSS) to help user decisions.
The adopted solutions are described in previous
authors works: i) how building an urban ontology to
integrate the datasets available at urban scale,
usually coded in different proprietary formats, is
pointed out in (Faro et al., 2011a), where it is also
illustrated how computing the minimum paths to
destination and logistic cycles using programming
logic clauses, and ii) how a fuzzy engine manages
data on car traffic, weather conditions and personal
data (e.g., the user age or health status) to support
decisions is discussed in (Costanzo et al., 2012b).
In this paper we show how Wi-City may help the
user decisions by taking into account both crisp and
statistical processes. Also, we demonstrate by
examples the main services offered to users provided
with mobiles that may host the Flash Builder
version, e.g., iPhone and Samsung Galaxy Notes.
2 A FUZZY DSS BASED
ON CRISP AND STATISTICAL
DATA
How a fuzzy system computing with words (Wang,
2001) may support the user decisions using fuzzy
rules dealing with crisp and statistical data is
illustrated in this section by an example in which our
DSS should help a mobile user to find a restaurant or
a pharmacy. Let us assume that the DSS solves the
problem first by finding the maximum distance of
the service from the current user position, and then
identifying the most suitable service within such
distance. Also, we assume that the DSS is provided
with some rules to find the maximum distance, e.g.,
a) rule R1 concerns a person wanting to take a taxi
to reach the destination: if the person is a young
man, s/he does not like to pay a high cost for the
taxi, then the service should be at short/medium
distance, and b) rule R2 concerns a person wanting
to reach the destination by walking: if the person is
a young man and the weather is good, then the
service may be at a medium distance, otherwise it
should be very close.
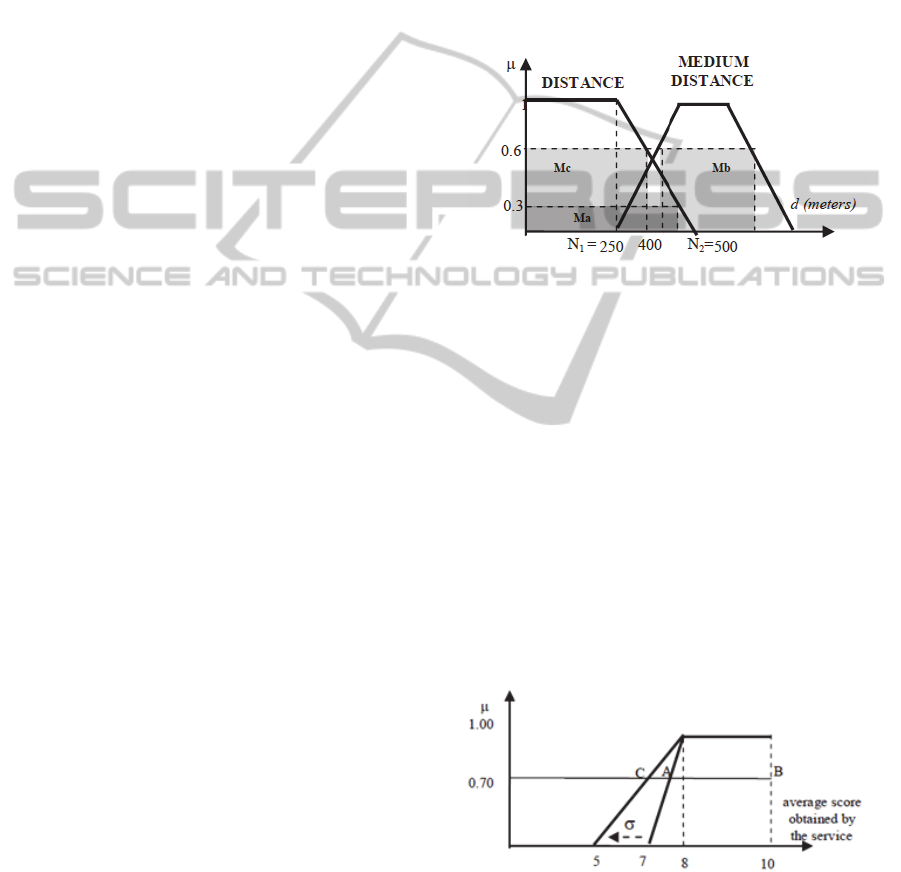
Under these assumptions, if the fuzzy sets
representing short and medium distance are the ones
in fig.2, and the evidence
y
that the user is young is
0.6, then the DSS will find by the rule R1 that the
maximum distance to reach the destination by taxi
would be the barycenter of the masses Mb and Mc
of fig.2, whereas if
y
= 0,6 and the evidence that the
weather is good is
w
= 0.7, then the DSS will
suggests, according to rule R2, that the maximum
distance to reach the destination by walking is the
barycenter of the masses Ma and Mb.
Figure 2: Fuzzy sets representing the words short-distance
and medium-distance.
After having delimited the area in which the
service should be located, the other problem is to
choose the most suitable service within this area. If
we assume that: a person usually chooses the
services preferred by persons of the same age, then
the most suitable services are ones that have
received a good score from the persons of the same
age of the user. Therefore, if
y
= 0,7, we should cut
the fuzzy set representing a good service depending
on the scores given by young people (see fig.3) with
the line at = 0.7, thus finding that the minimum
average score below which the services are not
recommended is the one related to the midpoint of
the segment AB.
Figure 3: Fuzzy set dealing with the word good-service
expressed by young people to evaluate a service. The
minimum value of this fuzzy set is 7 if = 0, otherwise it
decreases depending on .
However, the scores follow a statistical law, e.g.,
SHORT
GOOD SERVICE
Wi-City-Living,DecidingandPlanningusingMobilesinIntelligentCities
99
a Gaussian law. Thus, the above fuzzy set should be
enlarged by moving the oblique sides of a quantity
equal to the Gaussian standard deviation as shown
in fig.3. This will produce a small decrease of the
minimum acceptable average score below which the
service is not recommended to the user, i.e., the
score related to the midpoint of segment CB.
3 THE MAIN USE CASES
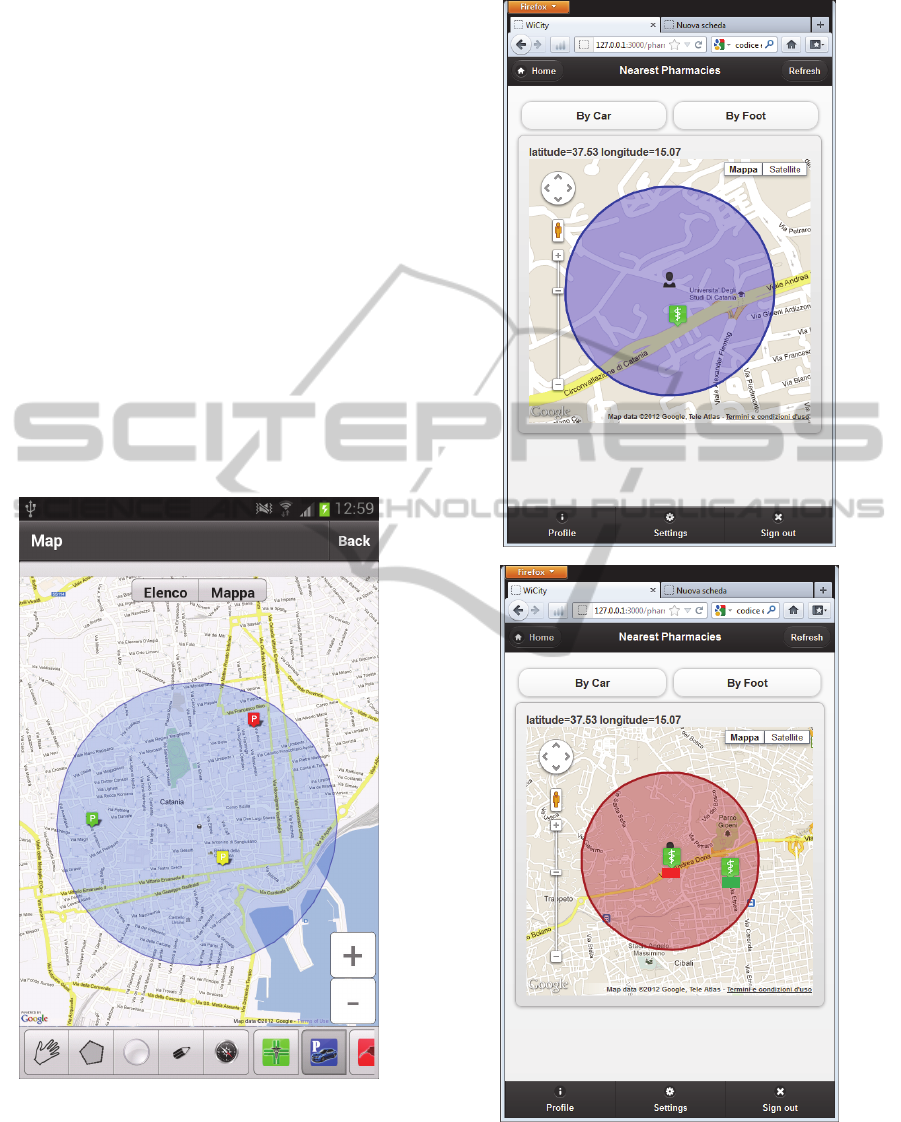
The first use case deals with an user searching a
park in an area defined by enlarging, using the
finger, a circle around the current user position or
the destination point of user interest. This function
has been implemented in Flash Builder so that it
may be linked easily to the mentioned fuzzy engine.
The parks with vacancies within the chosen area are
colour coded depending on the scores received from
the users (fig.3).
Figure 4: Screenshot illustrating the first use case:
searching a park with a query by sketch.
In the second use case, the fuzzy engine finds
the pharmacy nearest to the user position. The
available pharmacies are represented by colour
coded icons within a circle whose radius around
Figure 5: Screenshots illustrating the second use case:
searching a pharmacy nearest to the position of a walking
(a) or driving user (b). Pharm icons are colour coded
depending on the pharm scores.
(a)
(b)
PECCS2013-InternationalConferenceonPervasiveandEmbeddedComputingandCommunicationSystems
100
the user position depends on several rules, i.e., on if
the user is walking (fig.3a) or driving (fig.3b), and
on the user age and current weather conditions.
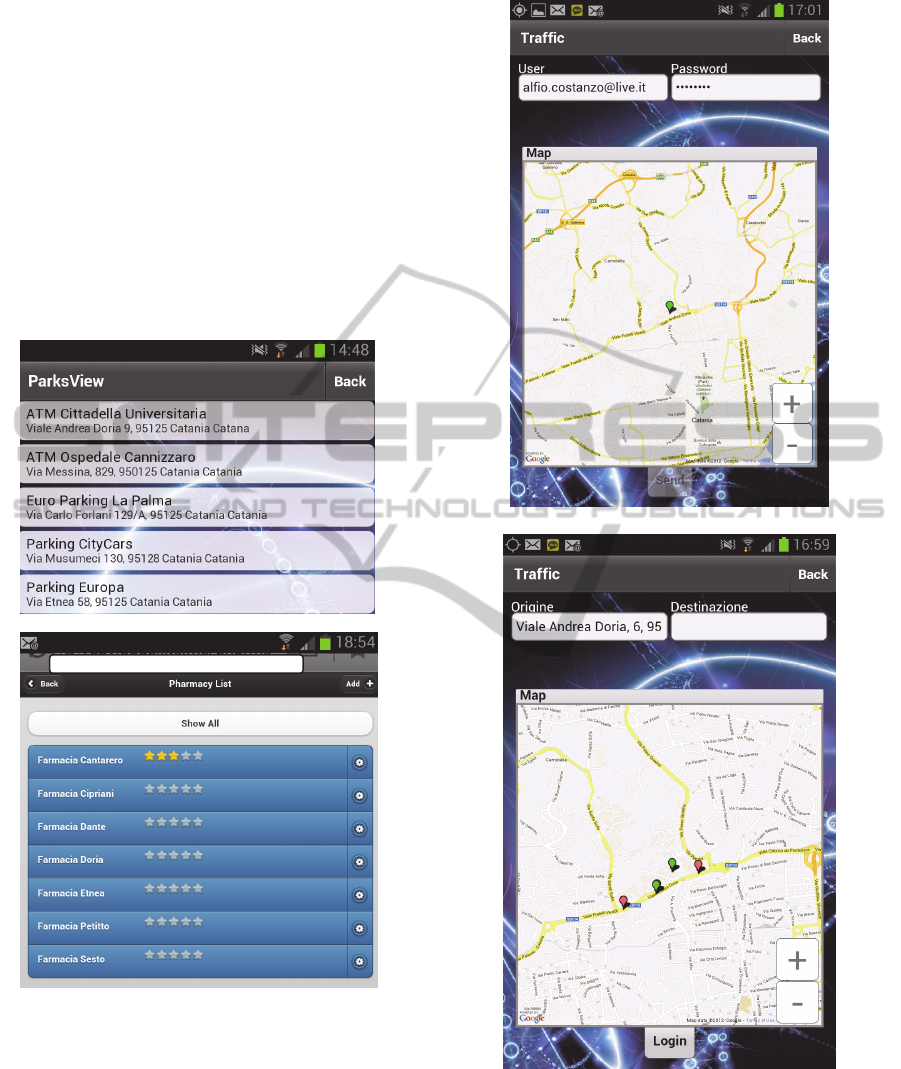
In the third use case, the users are interested in
receiving the list of the services of their interest
available in a certain urban zone. Fig.6a shows the
park list derived by the Flash Builder program from
the archives belonging to different associations.
Fig.6b shows the list of pharms and their scores; it is
built by the RoR server and sent to the mobiles as
JQMobile scripts. The users may insert their scores,
thus contributing to modify the average score. Both
these lists are built by an XML/RDF based
functionality executed by the mobile or the server.
Figure 6: Screenshots illustrating the third use case: list of
all the parks (a) and pharms (b) available at urban scale (or
within an urban zone).
After having decided the service, the user typically
needs to know the best path to the destination.
Therefore, it is necessary to identify the user and
destination positions with respect the urban
graph, i.e., the graph consisting of all the relevant
intersections. The fourth case, drawn in fig.7,
illustrates how the position of the user is identified
Figure 7: Screenshots illustrating the fourth use case: in
fig.7a the user is in a private area and cannot be localized,
whereas in fig.7b the user is into the Wi-City graph, and
then Wi-City may find quickly the road segment in which
the user is located using the signals sent from the user
GPS.
in the Wi-City urban graph superimposed to the
(a)
(b)
(a)
(b)
Wi-City-Living,DecidingandPlanningusingMobilesinIntelligentCities
101

Google Maps using the mobile GPS. The destination
is identified analogously, but using its address.
Therefore, Wi-City gives the responses on a
familiar Google Maps interface, but it executes the
travel time computations by modelling the car flows
in the urban graph according to a macroscopic traffic
model based on road travel times and waiting times
at the traffic lights derived from videos taken by
cameras (Faro et al., 2011b); (Crisafi et al., 2008),
data taken by in situ technologies (Leduc et al.,
2008) or people perceptions (Faro et al., 2008). Fig.8
shows two different paths to the same destination
computed by Wi-City depending on the current
Figure 8: Screenshots illustrating the fourth use case: best
paths from the current position to the same destination
depending on the current traffic flows.
traffic conditions. They may differ from the ones
computed by Google which uses average traffic
conditions.
The fifth use case shows how Wi-City may
support m-gov activities, i.e., e-government
activities carried out by mobile users. In particular,
fig.9a shows how Wi-City supports mobile users to
request an official certificate, whereas fig.9c shows
how it allows the users to fill out an auto-
certification according to an official format. The
certificates are sent as pdf files from the server to the
mobiles, where they may be visualized (fig.9b) and
possibly sent to the public or private office indicated
by the user.
Figure 9: Screenshots illustrating the fifth use case: the
users may request an official certification (fig.9a) or fill
out an auto-certification (fig.9c) while they are walking.
The response is a pdf file that may be visualized on the
mobile, e.g., fig.9b, and sent to the destination office
specified by the user.
4 CONCLUDING REMARKS
The paper pointed out, by some examples, an
ubiquitous information system called Wi-City that
(b)
(a)
(c)
PECCS2013-InternationalConferenceonPervasiveandEmbeddedComputingandCommunicationSystems
102

outperforms both the main commercially available
GPS navigators, such as Garmin and Tom Tom, and
"similar" available systems, e.g., (Joseph, 2007). The
main strengths of Wi-City are:
Wi-City limits at maximum the use of Google
Maps APIs, thus depending very few on Google,
although it gives the responses on a familiar Google
Maps interface;
Wi-City services are offered through an open
platform able to integrate distributed databases
coded in different formats to inform the users
effectively;
the Wi-City DSS engine is based on context
aware techniques. Fuzzy logic is adopted to avoid
that probabilistic recommendations may cause
unsafe situations;
user mobiles may host user data to be integrated
with other information to find the most suitable
services, thus playing an active role;
the Flash Builder solution, to be implemented on
suitable mobiles, e.g., Samsung Galaxy or iPhone,
offers the same services provided by the RoR server
at the same performance but involving the server
very little.
Currently, we are testing the implementation to
verify if and how it supports effectively users in: a)
deciding the most suitable services for their current
needs depending on real time constraints, and b)
planning their daily activities taking into account
traffic and weather forecasts. In both cases Wi City
recommendations consider the collective data issued
by the users, e.g., service scores or information on
road repairs not signalled by the public departments.
Also, how Wi-City supports typical e-government
tasks carried out by the citizens will be evaluated to
improve the outlined mobile government services.
Other future developments deal with the
implementation of video surveillance services for
public events and of emergency procedures, such as
people evacuation from either buildings or
dangerous areas using computer vision
methodologies, e.g., (Di Salvo et al., 2012).
REFERENCES
Berthon B., et al., Building and Managing an Intelligent
City, online, 2011.
Corlan M., Adobe Flash Platform, Adobe, 2009.
Costanzo A., Faro A., Giordano D., Spampinato C.,
Context Aware Services for Mobile Users: JQMobile
vs Flash Builder Implementations, IEEE Proc. of the
Federated Conference on Computer Science and
Information Systems, Fedcsis, Wroclaw, 2012.
Costanzo A., Faro A., Giordano D., Venticinque M., Wi-
City: A federated architecture of metropolitan
databases to support mobile users in real time, Int.
Conf. on Computer and Information Science, ICCIS
2012, A Conference of World Engineering, Science
and Technology Congress, ESTCON 2012, Kuala
Lumpur, 2012.
Costanzo A., Faro A., Spampinato C., Location
Intelligence Services for Mobiles using Ruby on Rails
and JQueryMobile, Proc. of the 8th Int. Conf. on Web
Information Systems and Technology (WEBIST),
INSTICC, 2012.
Crisafi A., Giordano D., Spampinato C., Griplab 1.0 : Grid
image processing laboratory for distributed machine
vision applications, Proceedings of the Workshop on
Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for
Collaborative Enterprises, WETICE, 188-191, 2008
David M., Developing Websites with jQuery Mobile,
Focal, 2011
Di Salvo R., Faro A., Giordano D., Spampinato C., People
flow control using cellular automata and computer
vision technologies, Advances in Intelligent and Soft
Computing, Volume 159 AISC, Issue1, 2012, Pages
95-104, Future Computer and Control Systems, FCCS,
2012
Dubberly Design Office, The Model-View-Controller
Pattern in a Rails-Based Web Server,
http://www.dubberly.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/
04/ DDO_Article _MVC_ Pattern.pdf, 2011
Quilits B., Leser U., Querying distributed RDF data
sources with SPARQL, Proc. of the 5th European
semantic web Conf. on the semantic web, 2008
Faro A., Giordano D., Spampinato C., Integrating
Location Tracking, Traffic Monitoring and Semantics
in a Layered ITS Architecture. Intelligent Transport
Systems, IET, vol.5(3), 197-206, 2011
Faro A., Giordano D. Spampinato C., Adaptive
background modelling integrated with luminosity
sensors and occlusion processing for reliable vehicle
detection. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent
Transportation Systems. Vol.12(4), 1398-1412, 2011
Faro A., Giordano D., Spampinato C.: Evaluation of the
Traffic Parameters in a Metropolitan Area by Fusing
Visual Perceptions and CNN Processing of Webcam
Images, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Vol.
19 (6), 1108-1129, 2008.
Hartl M., Ruby on Rails 3, Addison Wesley, 2011
Joseph A.D., (ed.), Urban Computing and Mobile Devices.
IEEE Pervasive Computing, Vol.6 (3), 2007
Leduc, G., Road Traffic Data: Collection Methods and
Applications, Working Papers on Energy, Transport
and Climate Change, N.1, JRC European
Commission, 47967, 2008
Wang P. P., 2001. Computing with words. Wiley
Inderscience, 2001
Zhai, J., Jiang, J., Yu, Y. and Li, J.: Ontology-based
Integrated Information Platform for Digital City, IEEE
Proc. of Wireless Communications, Networking and
Mobile Comp., WiCOM '08, 2008.
Wi-City-Living,DecidingandPlanningusingMobilesinIntelligentCities
103
