
Managing Data and Knowledge for the InmunoFlu Research Project
G. Lopez-Campos
1
, Enrique de Andres
2
, R. Almansa
3
, I. Martin-Loeches
4
, V. Lopez-Alonso
5
,
J. F. Bermejo-Martin
3
and F. Martin-Sanchez
1
1
Health and Biomedical Informatics Research Unit, University of Melbourne, 202 Berkeley Street, VIC, Australia
2
Applied and Industrial Maths Lab & Artificial Intelligence Center, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
3
Infection and Immunity Medical Research Unit (IMI), Hospital Clínico Universitario de Valladolid-IECSCYL,
Valladolid, Spain
4
Critical Care Centre Parc Tauli, Sabadell University Hospital, Sabadell, Spain
5
Bioinformatics Unit, Institute of Health Carlos III, Majadahonda, Spain
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Influenza Virus, Collaborative Research, Database, Biomedical Information
Systems.
Abstract: The InmunoFlu project was funded during 2009-2011 by the Government of Spain (Biomedical Research
Fund-FIS) for the study of the H1N1
pdm
influenza. It was an integrative project where clinicians from
intensive care units (ICUs) across Spain came together with fundamental researchers to analyse at the
molecular level the H1N1 infection. The multidisciplinary and geographical dispersion of the participants
required the development of data and knowledge management tools. The InmunoFlu database was
developed as a tool for the storage of all clinical data from patients associated with the ICUs and for the
subsequent clinical annotation of the samples used in the molecular analysis of the infection and host
response. The dispersion of participants in different centres fostered the development of InmunoFlu Web
portal, a collaborative web portal using web 2.0 technologies, which served as a knowledge management
tool for the project community. The web portal enabled among other characteristics document sharing as
well as other collaborative tools such as chat, wiki, etc... The use of both tools played a central role in the
success of this complex project.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pandemic influenza outbreak in 2009 caused by the
influenza virus H1N1
pdm
posed a significant series of
challenges for both health and research systems. In
those moments society was facing emergence of a
viral threat originated in a virus that resembled that
one 1918 pandemia which caused 20-50 million
deaths (Taubenberger et al., 2001). Under these
circumstances there was an obvious need to mobilize
resources seeking for a response against the risks
posed by the new virus. Those responses tried to
address different issues such as patient care and
disease prevention or development of vaccines.
Other studies were aimed at understanding the
biology of the virus by means of immunological and
virological research. Research also included trying
to develop new diagnostic tools. Finally several
integrative approaches, where healthcare and
fundamental factors were combined, contributed to a
better understanding of the interactions between
virus and patients and how those could explained the
final clinical outcomes. In the literature it is possible
to find thousands of papers published presenting the
results of the different approaches followed, a
PubMed search using the terms “pandemic influenza
H1N1 2009” results in more than 3500 research
papers in different areas (excluding reviews) (Cheng
et al., 2012)
Clinical data collection is a very important
procedure and it is a routine in epidemiological
studies. In many cases this process can be done
electronically extracting data from patient’s
electronical clinical record, (Kersun et al., 2010) or
other ad-hoc existing systems (Bertolini et al., 2011)
but in other cases data are still stored in paper. When
fundamental and clinical research are combined the
results of those analyses are extremely affected by
the quality on the clinical annotation of the samples
181
Lopez Campos G., de Andres E., Almansa R., Martin-Loeches I., Lopez-Alonso V., Bermejo-Martin J. and Martin-Sanchez F..
Managing Data and Knowledge for the InmunoFlu Research Project.
DOI: 10.5220/0004227701810186
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2013), pages 181-186
ISBN: 978-989-8565-37-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

used. The source of clinical annotation may come
either from automatic data retrieval from electronic
health records from patients or, in those cases where
electronic medical records are not available, it is
necessary to develop tools to store in an organised,
easily accessible and electronic format those data of
interest. It is also very important for the success of
those projects, which usually involve groups located
in remote places and with different scientific
backgrounds to have access to collaborative tools
that enable data and document exchange among the
project teams.
The work presented hereby represents the
development of tools for data and knowledge
management in the context of a multidisciplinary
and multinational project (InmunoFlu), combining
fundamental biology researchers with clinicians,
analysing the molecular aspects of infection by
H1N1
pdm
in patients at different intensive care units
across Spain during H1N1pdm outbreak in years
2009 and 2010. Due to the lack of a unified system
for data access at the different ICUs it was necessary
to develop an “in-house” built database to collect the
most relevant clinical data. They were then used for
clinical annotation of samples further processed in
the molecular analyses. The integration of molecular
data from different sources with the clinical
annotation enabled the analyses using clinical
phenotypes and clinical outcomes. (Bermejo-Martin
et al., 2010); (Almansa et al., 2011).
A pivotal aspect in interdisciplinary and
multicenter projects is knowledge management.
Knowledge management has been defined in
multiple ways (Chen at al., 2001); (Montani et al.,
2002); (Steels, 1993), and it is related with the
capture, representation, sharing and use of
knowledge within a community or an organization
so it can be effectively exploited.
Based on our previous experience with web-
based knowledge management tools, such as
BIKMAS, A Biomedical Knowledge Management
System (De Andrés-Galiana et al., 2009), we
developed InmunoFlu Web Portal, a knowledge
management tool designed using Web 2.0
technologies. The purpose of InmunoFlu web portal
was to provide the community with a tool accessible
to all members for enhanced collaboration and
exploitation of the knowledge generated in project.
2 METHODS
2.1 Database - InmunoFlu Database
For the design of the tools used in this project it was
necessary to take into account the characteristics of
the members involved on it and their specific
requirements. Data and sample collection at the
eight participating ICUs was performed in a high
demand environment where the professionals were
extremely busy and therefore required very simple
tools, with an easy to use interface, for that reason
we chose Microsoft Access as the Data Base
Management System, since it is a tool that all the
participants were already familiarised with and
because it was available at all data collection points.
Visual Basic was used on database forms.
2.2 Knowledge Management Tool -
InmunoFlu Web Portal
The knowledge management tool was developed
using open source software tools providing thus
reliability, stability and flexibility, among others.
One of the aims of this tool was to provide Web 2.0
based collaborative tools; for that reason for the
development of the portal we used Java technology
based on the Model-View-Controller.
We used the
portal manager Liferay (www.liferay.com), running
under Glassfish (http://glassfish.java.net/) as
application server, and MySql (www.mysql.com) as
the database management system.
Liferay has also the ability to run on any
application server, servlets container, database and
operating system, providing the possibility of
developing complex portlets (a portlet is a small
piece of functionality that is completely portable and
scalable) and supporting any portlet that is based in
the JSR-268 standard, so it is possible to add any
portlet developed with any technology as long as the
portlet is based on this standard.3 Results
3 RESULTS
3.1 InmunoFlu Database
3.1.1 Database Structure
In many of the hospitals involved in the study there
were not accessible electronic health records. For
this reason it was not possible to organise a system
based on an automatic data collection and
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
182

centralization process. Under those circumstances, a
set of different replicates of the database were
installed at each of the participant teams, so they
would collect data, and finally all collected data was
finally centralised and curated by a single project
group. A paper form for data collection was initially
developed and agreed by the clinicians participating
in the project comprising 7 pages. This original
questionnaire was later modified in the electronic
version including some additional data.
The database comprised a set of 18 tables
covering more than 80 clinically relevant related
fields that were organised into two different
categories:
Main tables. 15 tables containing the majority of
the relevant clinical data.
Auxiliary tables. 3 tables designed to contain
data used in combo-boxes or drop-boxes for data
entry in different forms.
This design including some auxiliary data, and the
development of data entry forms using drop-boxes
and limiting the entries to certain value types
avoided many inconsistencies in user data input. It
was also important to set a unified environment for
the different groups that had to work with the
database.
Database contents were structured in eight
relevant areas around the central element of patient
demographics. The surrounding areas contained
information related with:
1. Symptoms during illness. Data related with the
symptoms presented by the patient during
admission.
2. Co-presenting illness. Information about other
illnesses that were present during admission.
3. Co-morbidities. Other previously known diseases
affecting the patient during their acceptance in the
study.
4. Medication at admission
5. Time course and outcomes. These data covered
the dates for the initial symptoms, date of hospital
admission, date of ICU admission, date of other
procedures such as ventilation assistance, date of
UCI discharge and cause, or hospital discharge.
6. Treatments provided during ICU hospitalization
7. Microbiological test results. Describing the test
used, the date of the test and the results.
8. Analytical measurements. The data stored under
this area included a broad variety of clinical data
associated with the evolution of the patient in the
ICU such as organ dysfunction data, ventilation data,
haemograms and other.
An important aspect that was taken into account in
the design of the database and the forms for data
entry was that the purpose of the database was to
store data in a longitudinal study, and therefore a
single patient may have multiple records associated
with those events occurring along the time until ICU
discharge. This caused that entries should be
editable along a period of time and it had to be
considered as an important parameter in the design
of forms making it simple and transparent to the
users. For this reason and as a mean to avoid that
during the addition of data associated with a new
data point could lead to rewriting of a previous
record, warning messages were set in case a
previously recorded data was about to be edited.
3.1.2 Database Interface
In order to simplify the use of the application, an
interface consisting on only two different forms was
used. The first form consisted on a welcome form
including the three major patient management
options, adding a new patient, editing or adding new
data to a patient or deleting a patient and all the
associated data. Figure 1.
Figure 1: Screenshot of the first screen seen by the users
entering the database. The three buttons represent the
options Add New patient/Edit patient/Delete Patient.
A second form was used for data entry and
included the eight areas of data stored in the
application. This form included a set of subforms
sequentially accessible allowing the introduction of
data from the first initial data, required when a
patient was included in the study and their data were
captured into the database, to those forms related
with the temporal parameters measured along the
study. Figure 2.
The use of auxiliary tables altogether with the
use of drop-lists and combo boxes whenever was
possible was preferred in order to reduce the amount
of inconsistencies in the database due to typing
errors or the use of synonyms by the different user in
the different research groups.
ManagingDataandKnowledgefortheInmunoFluResearchProject
183

Figure 2: Screenshot of the second form used for data
entry. The left part of the screen represents the
demographical data.
3.2 InmunoFlu Collaborative Web
Portal
The knowledge management tool was embedded in a
collaborative web portal where all members of the
consortium (clinical groups, ICUs and fundamental
biology researchers performing the genomic
analyses) had access to the platform.
This knowledge management tool was designed
to store and track the knowledge generated within
the project (in the form of documents or data and
capturing other knowledge sources with the WIKI or
the forum) as well as providing information captured
from other web 2.0 resources on the internet.
The portal had a common shared area for all the
members of the community and from there each
member had access to a private area.
In the public shared area, the collaborative portal
was designed in such a way that each of the
members of the consortium had access to a common
public shared area and also their own private pages
where they could store and work on different
documents before making them public and sharing
them with the rest of the community.
The home page of the portal was common for all
the members of the community and it included a
common calendar where important dates for events
such as consortium meetings or deadlines were
published and accessible for all members. Figure 3.
The home page also allowed the users to access
their accounts where they were able to set their
public profile within the community and include
some additional contact data, such as their websites,
e-mail addresses.
The system was designed to provide some
collaborative tools as well. A WIKI and a Forum
were included and made accessible from the home
page of the portal for the users so they were able to
edit documents and keep open discussions.
A chat tool was included in the portal as another
way to communicate among the online members of
the community.
Figure 3: Screenshot of the home page InmunoFlu web
portal where it is possible to see the calendar, the chat tool
(lower right) and tabs for the different options (Forum and
WIKI)
The InmunoFlu Web Portal was designed to take
advantage of the opportunities available thanks to
the use of WEB 2.0. For instance, this allowed the
portal to include a widget created by the CDC
(Center for Disease Control) that captured the news
generated by the CDC related with the H1N1pdm
virus.
Within the private area there were four pages.
Three of them are devoted to RSS feeds coming
from selected sources and covering topics of interest
for the community, and one of them used as the
home page for the private area retrieving general
medical RSS information such as those news coming
from medical journals. The other two pages were
specifically devoted to the project aims. The first
page covered RSS feeds specifically related with the
H1N1pdm virus while the second page is linked to a
broader definition around respiratory diseases.
Figure 4.
A very important element for the web portal was
the inclusion of a “Document Library”. The
“Document Library” plays a key role since it serves
as the major file repository for all the documents and
files generated during the project.
This collaborative element allowed the
consortium members to upload and share in different
ways a diverse kind of files in a series of folders.
The folder structure in the “Document Library” was
divided into two major categories, the “Public
Folders” and the “Private Folders”. Documents
stored in the “Document Library” are shared within
the community and depending on their location in
the folder structure different users may have
different privilege of access to them.
All members of the community have access and
privileges to modify the “Public Folder” structure
adding new subfolders and having full privileges
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
184
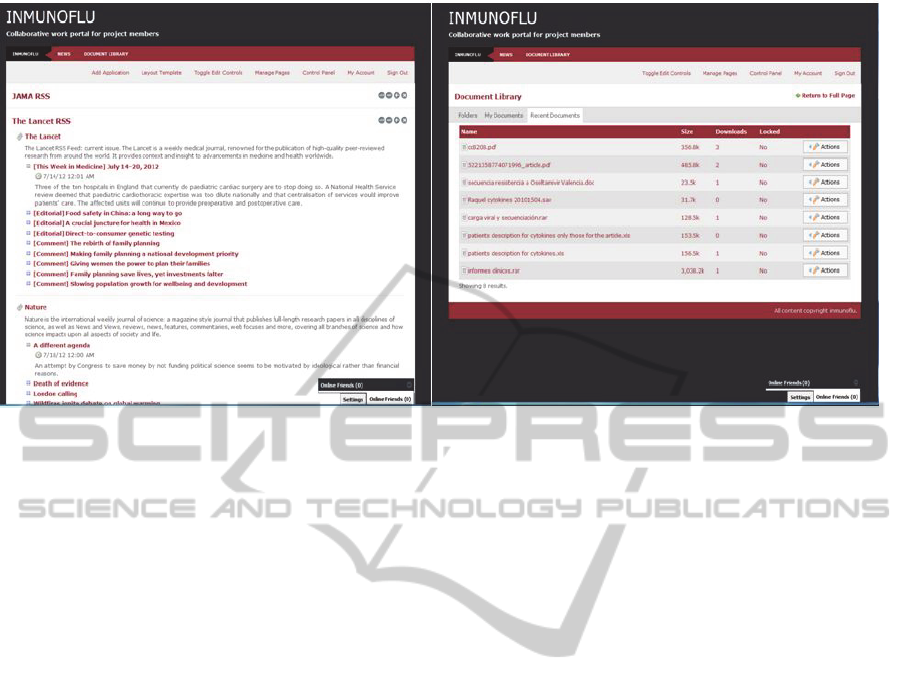
Figure 4: Screenshot representing the different areas of the private pages of the web portal the RSS feed from “News”
section and the “Document Library”.
over any document stored there. On the other hand
the “private folders” are under control of each of the
member of the community and has rights to upload
and set the privileges for the other members to just
access or edit the documents uploaded on their
folders.
One of the main characteristics of the
“Document library” is that it allows the community
to perform a series of actions on the elements stored
in the library. The actions available are
“View/Edit/Delete”.
“View” Under this option it is possible to
download the documents in the library as well as to
view some characteristics of the document such as
their use (number of downloads), version number,
size or document type. Every element in the library
can be viewed by any member of the community at
any time.
“Edit” option is limited to those documents that
are not “locked” by the owner and it allows the
download and substitution of the original document
by the “edited” one. An important aspect of the
system is that “tracks” the changes and the editing
events undergone by the elements of the document
library, showing the number of the latest version
available.
“Delete” option is just limited to the owner of the
document or the system administrator.
Another interesting collaborative tool
implemented within the ‘Document Library” was the
possibility of adding a discussion thread on the
documents using the comments option available.
Comments could be introduced using through the
“view” action on the document. Comments were
open on all documents for all members of the
community, who where therefore to add comments
even in those documents blocked for edition by their
owners. As it is common in other community tools,
“Comments” could be replied or voted as positive or
negative, showing the number of votes one received
and keeping track on how many of them were
positive or negative.
4 CONCLUSIONS
During the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemia there
was a need for the development of integrative
projects for the integration of biological and clinical
data associated with the infection. Inmunoflu project
was a Spanish initiative for the analysis of data from
patients from the ICU across the country; the lack of
electronic clinical records in some of the ICU
required the development of an electronic database
(InmunoFlu Database) for the storage of the clinical
data that was going to be analysed and associated
with the molecular biology data in the study.
Database structure was based on a previously
designed paper form agreed by ICU clinicians
participating in the project. The use of an electronic
format for the storage for the associated data
simplified and accelerated data retrieval for the
project and fostered the research and the
publications associated related with the project.
The development of a knowledge management
tool was a consequence of the multidisciplinarity of
ManagingDataandKnowledgefortheInmunoFluResearchProject
185

the project, constituted by a community of
researchers and clinicians with different
backgrounds and experiences, as well as a
consequence of the dispersion of the members across
different geographic regions and institutions. The
development of a collaborative web portal
(InmunoFlu Web Portal) was a consequence of the
dispersion of the InmunoFLu project members and it
was designed with the aim of providing the
community with a collaborative environment where
every member could interact with the others and
where the documentation related with the project,
either administrative, associated with research such
as paper drafts, or research data, and it was shared in
an accessible and editable way. The portal enabled a
simplified access to shared documents and
community discussions.
Although originally designed for this particular
project, InmunoFlu Web Portal could be easily
exported for other similar projects requiring a
collaborative environment. On the other hand
InmunoFlu database could be of use in other similar
projects for respiratory diseases of interest at ICUs.
The development of biomedical informatics tools
within the context of this integrative project
facilitated the success of the project enhancing the
collaboration and data availability for the project
goals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the Spanish ministry of
Health under the call “Convocatoria de
Investigación Comisionada en Gripe GR09/0021
(INMUNOFLU)”.
REFERENCES
Taubenberger J. K., Reid A. H., Janczewski T. A.,
Fanning T. G., 2001. Integrating historical, clinical
and molecular genetic data in order to explain the
origin and virulence of the 1918 Spanish influenza
virus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
29;356(1416):1829-39
Cheng V. C., To K. K., Tse H., Hung I. F., Yuen K. Y.,
2012. Two years after pandemic influenza
A/2009/H1N1: what have we learned?. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 25(2):223-63.
Kersun L. S., Coffin S. E., Leckerman K. H., Ingram M.,
Reilly A. F., 2010. Community Acquired Influenza
requiring Hospitalization:Vaccine Status Is Unrelated
to Morbidity in Children With Cancer. Pediatr Blood
Cancer. 54(1):79-82.
Bertolini G., Rossi C., Crespi D., Finazzi S., Morandotti
M., Rossi S., Peta M., Langer M., Poole D., 2011. Is
influenza A(H1N1) pneumonia more severe than other
community-acquired pneumonias? Results of the
GiViTI survey of 155 Italian ICUs Intensive Care
Med. 37(11):1746-55. Epub 2011 Aug 17
Bermejo-Martin J. F., Martin-Loeches I., Rello J., Antón
A., Almansa R., Xu L., Lopez-Campos G., Pumarola
T., Ran L., Ramirez P., Banner D., Ng D. C., Socias
L., Loza A., Andaluz D., Maravi E., Gómez-Sánchez
M. J., Gordón M., Gallegos M. C., Fernandez V.,
Aldunate S., León C., Merino P., Blanco J., Martin-
Sanchez F., Rico L., Varillas D., Iglesias V., Marcos
M. Á., Gandía F., Bobillo F., Nogueira B., Rojo S.,
Resino S., Castro C., Ortiz de Lejarazu R., Kelvin D.,
2010. Host adaptive immunity deficiency in severe
pandemic influenza. Crit. Care. 14(5):R167.
Almansa R., Anton A., Ramirez P., Martin-Loeches I.,
Banner D., Pumarola T, Xu L, Blanco J., Ran L.,
Lopez-Campos G., Martin-Sanchez F., Socias L., Loza
A., Andaluz D., Maravi E., Gordón M., Gallegos M.
C., Fernandez V., León C., Merino P, Marcos M. A.,
Gandía F., Bobillo F., Resino S., Eiros J. M., Castro
C., Mateo P., Gonzalez-Rivera M, Rello J., de
Lejarazu R.. O., Kelvin D. J., Bermejo-Martin J. F.,
2011. Direct association between pharyngeal viral
secretion and host cytokine response in severe
pandemic influenza.. BMC Infect Dis 31;11:232
Chen H., 2001. Knowledge management systems: A text
mining perspective. The university of Arizona.
Montani S., Bellazzi R., 2002. Supporting decisions in
medical applications: the knowledge management
perspective. Int J Med Inform. 18;68(1-3):79-90
Steels L., Corporate knowledge management, 1993.
Proceedings of ISMICK ‘93, Compiegne, France, pp.
9–30.
De Andres Galiana E., Lopez-Alonso V., Salamanca
Rodriguez L., Hermosilla Gimeno I., Martin-Sanchez
F., 2009. BIKMAS 2.0: A BIomedical Knowledge
Management Antenna System. Proceedings Medcine
2.0. 2009 Toronto.
HEALTHINF2013-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
186
