
ACHIEVING MODEL COMPLETENESS FOR HIERARCHALLY
STRUCTURED ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIFE
Usman Naeem, Abdel-Rahman H. Tawil, Rabih Bashroush and Ameer Al-Nemrat
School of Architecture, Computing & Engineering, University of East London
Docklands Campus, University Way, London, U.K.
Keywords: Hierarchal Activities of Daily Life, Alzheimer’s Disease, Task Sequences, Decision Trees, ID3 Algorithm,
Object Usage.
Abstract: Being able to recognise everyday activities of daily life provides the opportunity of tracking functional
decline among elderly people who suffer from Alzheimer’s disease. This paper describes an approach that
has been developed for recognising activities of daily life based on a hierarchal structure of plans. While it
is logical to envisage that the most common activities will be modelled within a library of plans, it can be
impossible to imagine that the library contains plans for every possible hierarchal activity. In order to
generalise the activity recognition capability outside the framework of the core activities constructed to
support recognition, decision trees are constructed using a well-known induction algorithm during a train
period. The motivation of this work is to allow people with Alzheimer’s disease to have additional years of
independent living before the disease reaches a stage where it becomes incurable.
1 INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive disease that
gradually destroys an elderly person’s memory and
their capability to learn, communicate and carry out
everyday activities. Managing people with this
disease incurs high costs for the government, as well
as the people associated with person who has the
disease. The total cost of dementia for the UK in
2006 was an estimated £17 billion, which then
escalated to an approximate £23 billion in 2010
(Alzheimer’s Research Trust, 2010).
In order to provide any form of assistance or to
find out if the elderly person is safe, it is important
to recognise what Activity of Daily Life (ADL) they
are carrying out. Depending on the memory
condition of an elderly people with Alzheimer’s
disease, their brain sometimes does not permit them
to remember what activity they were carrying out.
Usually in these cases, the sufferers are often
prescribed a set of daily activities by visiting carers
in order to deal with forgetfulness as well as giving
the elderly stimulation and a framework for an
independent life (The Alzheimer’s Association,
2005). Nevertheless, there can be still many
instances where the elderly person can forget what
activity they were conducting, which can lead to
anxiety (Feretti et al., 2001) and frustration as they
become aware that they are slowly losing their
independence. Hence, the recognition of activities
not only provides useful information about what
activity the sufferer is carrying out, but it also has
the capability of providing information about what
activity the sufferer is meant to be doing next and
provide assistance accordingly.
This paper describes a hierarchal approach that
has been developed for carrying ADL recognition,
which utilises more knowledge about the structure of
ADLs rather than solely relying on data gathered
from the extensive monitoring.
2 RELATED WORK
Activity recognition in the home can be conducted
in many ways, however the work in this paper
focuses on carrying out activity recognition with
object usage data, as opposed to data generated by
visual based systems. In order to make this possible,
a popular technique has been adopted, which is
known as ‘Dense Sensing’ (Buettner et al., 2009);
(Philipose et al., 2004). This is based around
numerous individual objects such as toasters and
kettles being tagged with wireless battery-free
51
Naeem U., H. Tawil A., Bashroush R. and Al-Nemrat A..
ACHIEVING MODEL COMPLETENESS FOR HIERARCHALLY STRUCTURED ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIFE.
DOI: 10.5220/0003802200510057
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Pervasive Embedded Computing and Communication Systems (PECCS-2012), pages 51-57
ISBN: 978-989-8565-00-6
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
transponders that transmit information to a computer
via an Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) reader
(Kalimeri et al., 2010); (Philipose et al., 2005) when
the object is used or touched. Wearable sensors such
as accelerometers can be seen as more intrusive then
RFID tags, however they are very practical for
capturing data that is concerned with human body
movements, as they provide accurate recognition of
movement (Wang et al., 2007).
Many computational models have been
constructed for recognising activities, typical
examples include Hidden Markov Models (HMM)
and Bayesian Models, whether it is simply
determining the likely sequence of an activity given
the objects (Wilson et al., 2005); (Patterson et al.,
2005) or being used as temporal smoother for
specific classifiers, and classifying likelihoods
(Lester et al., 2005). Dynamic Bayesian Networks
(DBN) have been used to capture relationships
between state variables of interest (Petney et al.,
2006), for example, in the common sense based joint
training approach (Wang et al., 2007), the DBN is
able to represent the state of a system in time slices.
The work in this paper is performing much the
same function of activity recognition via object
usage data. However rather than having complete
dependency on the object data for activity
recognition, we have developed a approach that is
based on hierarchal structured plans (representing
ADLs) where knowledge at different levels of
abstraction is used to determine which activity is
being carried out.
3 HIERARCHAL ACTIVITIES OF
DAILY LIFE
For the work in this paper, ADLs have been
represented in a hierarchal structure, where the
ADLs can correspond from a simple action such as
“switching the kettle on”, to a more complex activity
such as “making breakfast”. In order to
accommodate the different range of activities the
ADLs are modelled as plans. The plans are made up
of sub-plans. Where a plan cannot be decomposed
any further it is then recognised as a task. Task
recognition is based on analysing sensor event data
that is based on the usage of objects that have been
used to perform the activity. While ADL recognition
is based recognising constituent tasks that belong to
a particular ADL (Naeem and Bigham, 2009).
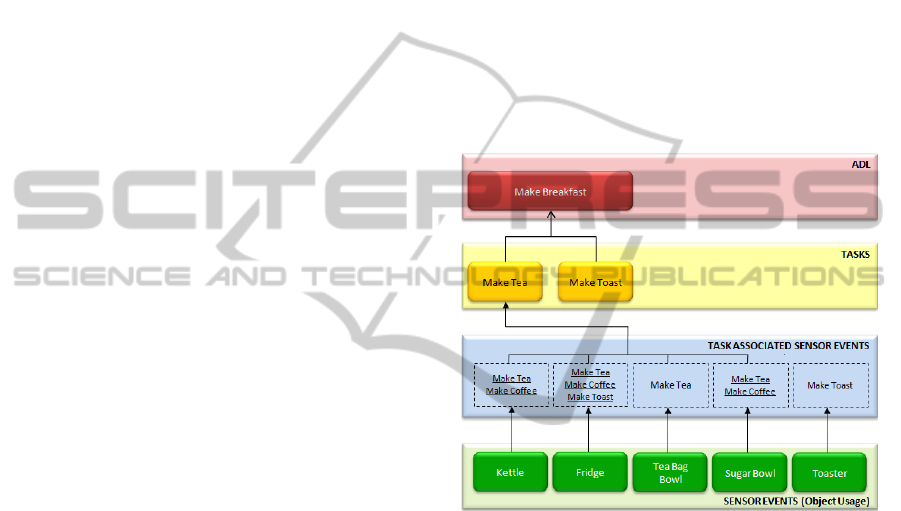
Figure 1 illustrates a structure of a Hierarchal
ADL (HADL), which depicts the ADL “Make
Breakfast”. This ADL contains a simple sequence of
tasks such as “Make Tea” and “Make Toast”. The
lowest tier of this hierarchal structure deals with the
incoming sensor events that have been detected.
These sensor events are then associated with the
tasks. For example in figure 1, kettle sensor event
can be associated with “Make Tea” or “Make
Coffee”. Once the sensor events have been mapped
into the associated tasks, an algorithm is then
applied in order to segment the tasks efficiently. For
the task recognition tier an approach has been
developed, which is responsible for generating a set
of different tasks sequences from a stream of object
usage data that is based on the conjunction of the
disjunction of task possibilities for each sensor
event. This approach is called Generating
Alternative Task Sequences (GATS).
Figure 1: Example of a hierarchal ADL (HADL).
For the higher tier, the number of levels above
the task identification level depends on the
complexity of the task. For example, an ADL may
have a series of nested sub-activities above the
actual task recognition level. Also there is a series of
possibilities that need to be considered when
modeling/ representing ADLs, such as:
Some ADLs may occur in parallel with other
ADLs.
ADLs may also have temporal constraints.
Not all sub- activities need to be executed.
Taking the above into consideration, ADLs have
been represented using a knowledge representation
language called Asbru. This is a task-specific and
intention-oriented plan representation language
which was initially designed to model clinical
guidelines (Fuchsberger et al, 2005). This plan
representation feature allows the capability of being
able to represent ADL and sub-activities within an
PECCS 2012 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
52

ADL, for example, “Prepare Lunch” is and ADL,
and a sub-activity of this ADL is to “enter kitchen”.
An ADL 3recognition component for the higher tier
has been developed, which manages the output from
the task recognition component (lower tier) to
determine which activity is going to be conducted
and determine the current and future intentions of
the elderly person. Future intentions are established
by predicting what ADL the subject might conduct
next.
In order to generalise the activity and intention
recognition capability outside the framework of the
core ADLs constructed to support recognition,
decision trees are constructed using a well-known
induction algorithm during a training period. Once
the tree has been developed the trees are used as a
support tool for determining if a correct task or ADL
has been recognised at the current iteration of the
recognition process.
3.1 Task Recognition – Lower Tier
Tasks are considered to be short activities,
essentially atomic. The stream of sensor events from
the different objects will be small, and so an
enumeration based approach is feasible as long as
the combinations are explored in an ordered manner.
Hence the lower tier allows enumeration of the
possibilities, which can be useful when testing the
learning and feedback approaches at the higher tier
of the HADL. An enumeration-based approach is
also necessary for carrying out task segmentation in
this type of task identification. The entire sensor
event stream is segmented into appropriate task
segments. The segmented tasks are then used to
determine which ADL is currently active. There is
range of techniques that can be applied to the task
associated sensor events for segmenting them into
appropriate tasks. However the difference between
the GATS approach and other statistical approaches
(Naeem and Bigham, 2007) is that the GATS
approach employs a simple algorithm that works out
all the possible combinations for each task given the
sensor event. This approach therefore mitigates the
chances of not being able to recognise tasks that
have been conducted via different variations (Naeem
and Bigham, 2009). The execution of this approach
may seem computationally expensive when
performed, however a best first identification in
synchronisation with the ADL recognition in the
higher tier could prove a simple but effective
approach, particularly as each task will not be
associated with a large number of distinct sensor
events.
3.2 ADL Recognition – Higher Tier
The higher tier of the hierarchal approach gives an
overview of the possible ADLs that can occur within
a specified time frame. Additionally, the higher tier
has the capability of taking into account any
overlapping ADLs, which can be useful when trying
to determine the ADL that is currently active from
the tasks that are discovered in the lower tier task
recognition. The input for the higher tier recognition
components are task sequences generated by the
lower tier, while the output is a list of alternative
ADL sets, which are sequences of the possible
ADLs that could occur given the tasks sequences
that have generated from the lower tier. Each of the
ADLs sets has an associated utility, which is based
on the cost of each segmented task sequence. Hence
it is imperative to recognise as many tasks as
possible within a window of events, which in return
will lead to accurate activity recognition. The
generated utilities for the ADL sets are based on
ADL schedules within a certain time frame (e.g.
10.00am to 10.15am). This allows a more
manageable and accurate recognition process, as it
eliminates any unlikely possibilities from the initial
stages of the recognition process. The inspiration for
ADL schedules that are used for the hierarchal
approach originates from real life prescribed
activities that have been constructed by the
Alzheimer’s Association. The ADL schedules are
developed for helping people suffering from
dementia by planning their day with a prescribed set
of ADLs (The Alzheimer’s Association, 2005).
These set of activities are based on an interval based
structure, where the activities are grouped according
to different time segments throughout the course of
the day. However, there is always the possibility that
a number of ADLs can occur at any given time, e.g.
a phone ringing leads to the activity ‘engaged in a
phone call’. In the proposed hierarchal approach
these ADLs are referred to as interruption ADLs and
therefore these are modelled within every ADL
schedule in the ADL library.
4 RECOGNITION OF ADLS
SUPPORTED BY DECISION
TREES
Given the nature of the prescribed activity schedules
for people suffering from dementia and the
hierarchal recognition approach, it can be logical to
envisage that the most frequent ADLs will be
ACHIEVING MODEL COMPLETENESS FOR HIERARCHALLY STRUCTURED ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIFE
53
modelled in the library of plans. However it can be
an audacious and near impossible task of making
sure that the library contains plans modelled for
every possible hierarchical ADL. Hence, extensive
use of decision trees has been made for constructing
trees using a well-known induction algorithm during
a training period that will support the recognition
capability outside the framework of the core ADLs.
The trees are used to support recognition of the ADL
at each iteration of the recognition process. For
example, every time a new task is recognised by the
lower task recognition tier, an ADL recognition
iteration is performed at the higher tier, which is also
used to predict the next ADL. This capability sits on
top of the hierarchal recognition process that finds
the best match in the kernel of ADLs. It is
instinctively obvious that if the ADL to be
recognised is in fact one of the core ADLs within the
library of plans, then recognition and prediction
could be fine tuned further.
For the recognition process, a decision tree is
generated for each ADL schedule, which is used to
classify the correct task/ADL that is being conducted
within the current ADL schedule given the current
instance and taking into account the training data.
The decision tree has to be learned during a training
phase. The data needed for this training phase can be
generated in two ways. In the first case, the data
generated can be based on subjects performing
ADLs from the core ADLs only, where the
information used is based on the tasks and sub-
activities actually undertaken by the subject. In the
second case, the subject may follow other plans, not
necessarily one of the core ADLs during training
and the information used in the training instance is
based on tasks actually observed and the best match
to ADLs in the core ADL library. Even though none
of the core plans are necessarily being followed, the
system will find a nearest match to use in the
training instance. In both cases the training is done
using information taken from the core ADLs.
A learning instance is created when each task is
labelled during training. The objective of the
decision tree is to act as a classifier that is used to
predict the class label for all labelled instances. In
order to determine an outcome for an instance a
decision tree needs to find an appropriate node to
split in order to form the branches and leaves of the
tree, which will lead to a predicted outcome.
Information theory is used to split the sets of training
instances associated with each node in the tree,
which leads to small and consistent nodes being
generated. The algorithm used is ID3.
4.1 Information Gain Split Decision
Trees
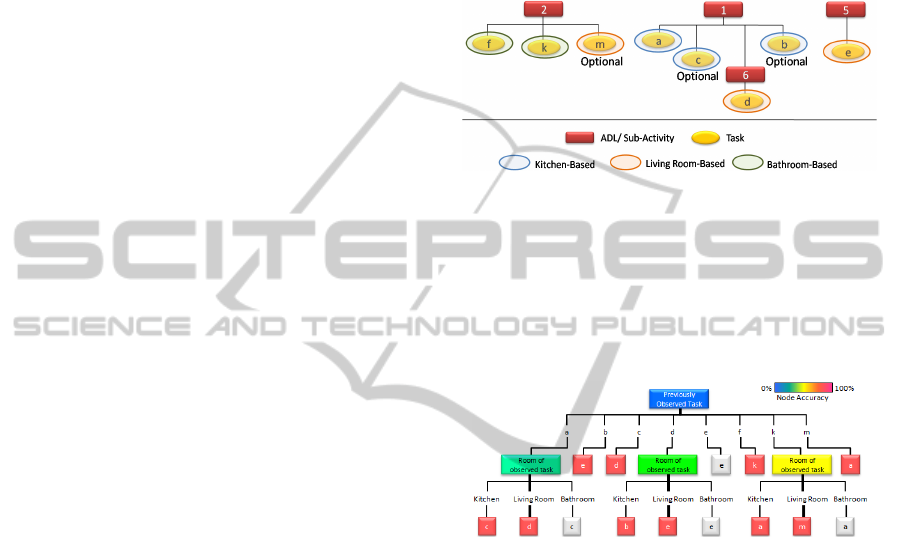
Figure 2 shows an ADL schedule modelled for the
time interval 9.00- 10.00. This ADL schedule also
incorporates the location of where each task is
conducted.
Figure 2: ADL schedule 1 modelled for decision trees.
When a task is recognised in the lower tier, the
location of where the task was conducted does get
recognised, however we make full use of this
information when constructing a decision tree based
on the ADLs within the ADL schedule that this task
belongs to.
Figure 3: Decision tree (ID3 Splitting) based on ADL
schedule 1.
Typically the decision tree learning algorithm
computes the quality of each possible split that can
be produced by each attribute and chooses the
attribute that has the highest utility based on the
quality of the split. The ID3 algorithm has been
adopted and illustrated in figure 3.
The entropy formula (1) is an idea formulated in
information theory that is used to measure the
amount of information in an attribute. Given a
collection S (entire sample set) of m outcomes:
m
i
ii
ppSEntropy
1
log)(
(1)
where
i
p
is the proportion of S belonging to class i,
while ∑ is over the m labels. Note that a entropy
formula normally uses log base 2, however on this
occasion we use log base 10 as we are simply
looking to get to a classification point where the
lowest entropy, rather than an absolute value.
PECCS 2012 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
54

This is then followed by computing the expected
entropy for each attribute to see which attribute has
the highest gain so that it can be used as a split to
build the tree further. The gain for each attribute is
determined is a follows (2):
)_()_()( setschildSsetcurrentSAGain
(2)
The gains for each of the attributes are shown in
table 1, which shows that attribute ‘Previous Task’
has the highest gain value, hence in figure 3 it is
chosen as the node which is split.
Table 1: Gains for all of the attributes to determine where
to split node.
Attributes Gain
Room 1.457
Time Frame 1.128
ADL 1.903
Previous Task 2.165
Previous ADL 1.276
This splitting process continues until a situation
is reached were the remaining entropy is equal to 0.
Given the following instance after a task has
been identified, we can identify by looking at the
decision tree (figure 3) that the task that has been
conducted is task ‘c’.
{Room of Observed Task = Kitchen, Time Frame
of Observed Task= 9.15-9.30, Parent ADL of the
Observed Task =1, Grandparent ADL of the
Observed Task = Root, Previously Observed
Task=a, ADL of Previously Observed Task=1}
We can see that information gain is good as a quality
measure for the decision trees that we have
constructed for correctly classifying a task within the
ADL schedule. However only one attribute is tested
at time for making a decision, therefore it cannot
take into consideration other future child nodes, as
its priority is to split the attribute it is currently at. In
addition it can also be computationally expensive
when classifying continuous data.
4.2 Gain Ratio Split Trees
Another method that can be used as splitting criteria
is gain ratio, which is a way of compensating for a
large number of attributes by normalising. This is
done by computing the information gain for an
attribute, which is then followed by dividing the gain
for the attribute by the information associated with
that attribute that is based only on the set of values
for that attribute. Figure 4 shows a tree constructed
based on the labelled data generated by figure 2.
Figure 4: Decision tree (Gain Ratio Splitting) based on
ADL schedule 1.
It can be seen that both of the trees generated via
two different splitting methods are different,
however both of the generated trees are correct in
terms of current training data that we have and we
already know. It is important to evaluate both sets of
trees to see which would be best suited for carrying
out classification if an unlabeled instance occurred.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
The objective of these experiments is to see which
splitting criteria is best suited to construct the
decision trees and to assess the potential of the
decision tree approach in predicting the next task or
ADL in a context where the performed activities do
not match any of the plans associated within the core
ADLs. Both of the splitting methods have been
tested with different combination ranges of labelled
and sample holdout instances.
The training instances for these experiments are
based on activities that have been carried out using a
wide range of objects (e.g. Kettle, Mug) that were
tagged with RFID transponders. Whenever these
objects were used or touched the object data was
captured by an RFID reader, which is a size of
matchbox and was worn on the finger of the subject
conducting the experiment. The subjects carried out
these experiments in a range of rooms such as
kitchen, bathroom and living room.
The activities carried out were based on two
ADL schedules, ‘Morning’ and ‘Afternoon’
activities. Both ADL schedules are similar to the
ADL schedule in figure 2, as they take into
consideration the location of where the tasks have
been conducted. For both of the schedules, two sets
of decision trees have been constructed from two
sets of training data, one is used to classify the
outcome of the next task, while the other tree is
classifying the parent ADL of the next task being
conducted. Both ADL schedules for morning and
ACHIEVING MODEL COMPLETENESS FOR HIERARCHALLY STRUCTURED ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIFE
55
afternoon will also incorporate Interruption ADLs,
such as a phone call, someone at the door or going to
the toilet. Each of the ADL Schedules used for these
experiments has different training data sets used to
build its decision tree. As well as having instances
which correspond to the different timings of the day
(e.g. morning and afternoon), each of these decision
trees built from the training data also have different
characteristics that imposed to validate different
types of schedules. For example, training data for
morning ADL schedule has incorporated instances
that have an outcome of an interruption ADL
differently to the way the instances are incorporated
in the training data for afternoon ADL schedule.
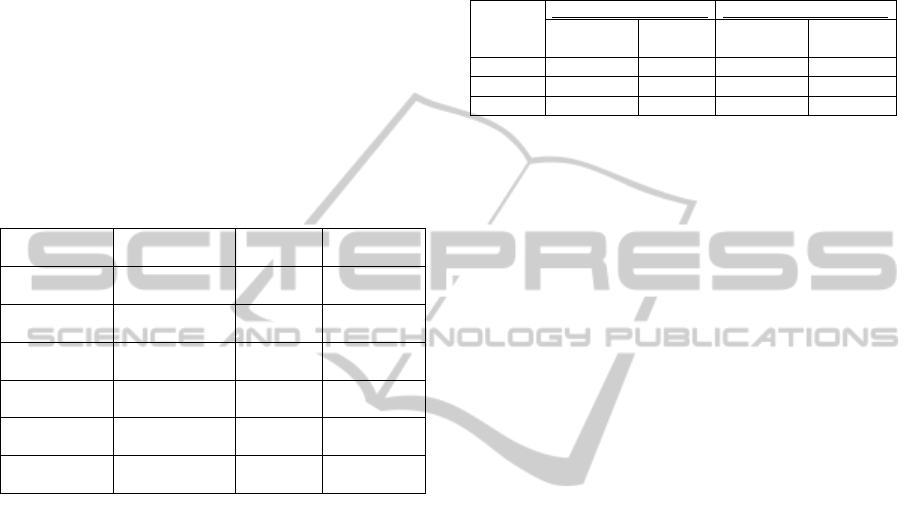
Table 2: Holdout samples for splitting criteria
experiments.
Holdout Sample
[%]
Training
Data
Holdout
Sample
Morning ADL
schedule
20 176 46
Morning ADL
schedule
50 111 111
Morning ADL
schedule
90 22 200
Afternoon ADL
schedule
20 162 40
Afternoon ADL
schedule
50 101 101
Afternoon ADL
schedule
90 20 182
Using different size variations of the labelled
data as holdout samples has been used to see how
well the splitting approaches work with different
sizes of holdout samples. Table 2 shows the
variations of holdout samples that were used for
these experiments. Three variations of holdout
sample have been used, these are 20%, 50% and
90% of the complete training data size, which is 222
instances for morning ADL schedule and 202
instances for afternoon ADL schedule.
The results in table 3 indicate that for both ADL
schedules, gain ratio was more efficient way of
splitting the attributes for constructing a decision
trees as it had higher percentage of classification
results for the holdout samples. One of the reasons
why gain ratio performed better as a splitting
approach than the ID3 is because in contrast to the
gain ratio splitting approach, the ID3 tends to learn
the training set too well when attributes have a large
number of distinct values, which can also be its
downfall when trying to classify instances that have
not occurred before.
In relation to the task being carried out, the
attribute with the highest gain might be the previous
task within the current ADL schedule, as this will
also be able to uniquely identify a task given the
previous task. However this is not always suitable,
as a tree that focuses its classification based on
previous tasks is unlikely to recognise a task that has
not been witnessed before.
Table 3: Results of holdout samples correctly classified.
Holdout
Sample
[%]
Morning ADL Schedule
Afternoon ADL Schedule
ID3
[%]
Gain Ratio
[%]
ID3
[%]
Gain Ratio
[%]
20 91 93 98 99
50 75 82 96 98
90 62 71 78 86
The results in table 3 reiterate the fact that the
gain ratio splitting is better at considering unknown
tasks or unlabelled instances, as gain ratio splitting
performed better with all holdout samples for the
morning ADL schedule, which consisted of tasks
from interrupted ADLs occurring at random
junctures within the constructed training data.
Another observation is that both of the splitting
methods classified the holdout samples better for the
afternoon ADL schedule than the morning ADL
schedule. This was expected as the morning ADL
schedule was intentionally constructed with
infrequent and inconsistent appearance of tasks with
no particular order. However, this does not imply
that training data constructed for the afternoon
schedule was simply easy for classification, as it was
constructed keeping in mind the general slower
pattern of how activities and tasks would normally
be conducted by Alzheimer’s patients.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The work described in this paper looked at how
decision trees can be utilised for generalising a
hierarchal approach for activity recognition. The
integration of decision trees gives the potential of
being able to carry out activity recognition, with the
intention of being able to learn and predict the
likelihood of what task within an activity may be
conducted next. Out of the two splitting methods
that were used for constructing the decision trees it
can be seen that the gain ratio method performed
better whilst trying to classify instances that have
not occurred before. However, the interaction of
these approaches is only successful when consistent
and cohesive training data is available.
Further work is being carried out that is
exploring ways of using the ADL recognition
process that has been described in this paper for
hygiene related activities that can help stop
PECCS 2012 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems
56

spreading of diseases amongst Alzheimer’s patients.
In addition, privacy is an area of prime importance,
as assistive technologies should not be needlessly
intrusive or the elderly community will simply
refuse to use them, despite their potential benefits.
Hence the work in this paper did not make use of
any visual surveillance equipment. Nevertheless
even RFID sensors can be intrusive to a certain
extent and once such approach that will be
investigated is the integration of privacy policies
into our current hierarchal approach. A person may
want to switch some or all of the sensors off from
time to time, or may opt for a programmed approach
where more sensors can be used at certain times of
the day, or if the system believes that the person is in
need of help. The question of accuracy is a difficult
one as increased detection usually means false
positives and a trade off between the two is
necessary. However policies for when more
information is needed could be used to mitigate this
problem.
REFERENCES
The Alzheimer’s Association, 2005. Activities at Home,
Planning the day for a person with dementia,
http://www.alz.org/national/documents/brochure_activ
ities.pdf
Alzheimer’s Research Trust., 2010. Dementia 2010, The
prevalence, economic cost and research funding of
dementia compared with other major diseases.
Executive summary, Health Economics Research
Centre, University of Oxford for Alzheimer’s
Research Trust. http://www.dementia2010.org/reports/
Dementia2010ExecSummary.pdf
Buettner, M., Prasad, R., Philipose, M., Wetherall, D.,
2009. Recognizing Daily Activities with RFID-Based
Sensors. In Proceedings of the 11
th
International
Conference on Ubiqitous Computing, Orlando
Ferretti, L., McCurry, S. M., Logsdon, R., Gibbons, L. E.,
Teri, L., 2001. Anxiety and Alzheimer’s Disease. In
Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, vol.
14, no. 1, pp.52-58
Fuchsberger, C., Hunter, J., McCue, P., 2005. Testing
Asbru Guidelines and Protocols for Neonatal Intensive
Care. In Proceedings of the Tenth European
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Aberdeen,
United Kingdom, pp.101-110
Kalimeri, K., Matic, A., Cappelletti, A., 2010. RFID:
Recognizing failures in dressing activity. In
Proceedings of the 4
th
International Conference on
Pervasive Computing Technlogies for Healthcare
(PervasiveHealth), Munich
Lester, J., Choudhury, T., Kern, N., Borriello, G.,
Hannaford, B., 2005. A Hybrid
Discriminative/Generative Approach for Modelling
Human Activities. In Proceedings of the 19
th
International Joint Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, pp. 766-772
Naeem, U., Bigham, J., Wang, J., 2007. Recognising
Activities of Daily Life Using Hierarchical Plans. In
Proceedings of the 2nd European Conference on
Smart Sensing and Context, LNCS 4793, Lake
District, UK, pp. 175-189
Naeem, U., Bigham, J., 2009. Activity Recognition in the
Home using a Hierarchal Framework with Object
Usage Data. In Journal of Ambient Intelligence and
Smart Environments, IOS Press
Patterson, D. J., Fox, D., Kautz, H., Philipose, M., 2005.
Fine-Grained Activity Recognition by Aggregating
Abstract Object Usage. In Proceedings of the 9
th
IEEE
International Symposium on Wearable Computers,
Osaka, Japan, pp.44-51
Petney, W., Popescu, A., Wang, S., Kautz, H., Philipose,
M., 2006. Sensor-Based Understanding of Daily Life
via Large-Scale Use of Common Sense. In
Proceedings of the 21
st
AAAI Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, Boston, USA
Philipose, M., Fishkin, K. P., Perkowitz, M., Patterson, D.
J., Kautz, H., Hahnel, D., 2004. Inferring Activities
from Interactions with Objects. In IEEE pervasive
Computing Magazine, vol.3, no.4, pp.50-57
Philipose, M., Smith, J. R., Jiang, B., Mamishev, A., Roy,
S., Sundara-Rajan, K., 2005. Battery-Free Wireless
Identification and Sensing. In: Pervasive Computing
IEEE Journal, vol. 4, no.1, pp.33-45
Wang, S., Petney, W., Popescu, A., Choudhury, T.,
Philipose, M., 2007. Common Sense Based Joint
Training of Human Activity Recognizers. In
Proceedings of the 20
th
International Joint Conference
on Artificial Intelligence, Hyderabad, India, pp.2237-
2243
Wilson, D. H., Long, A. C., Atkeson, C., 2005. A Context-
Aware Recognition Survey for Data Collection Using
Ubiquitous Sensors in the Home. In Proceeding of the
International Conference for Human-Computer
Interaction, Portland, Oregon, USA, pp.1865-1868
ACHIEVING MODEL COMPLETENESS FOR HIERARCHALLY STRUCTURED ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIFE
57
