
QUALITY OF TRANSFORMATIONS PROVIDING
INTEROPERABILITY IN SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
MODEL-DRIVEN DEVELOPMENT
Liliana Dobrica
Faculty of Automation and Computers, University Politehnica of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania
Keywords: Model-driven development, Model transformations, Quality, Software architecture.
Abstract: This paper defines the quality of model to model transformations based on a set of concerns addressed by an
user and a developer. The user is a software architect that benefits of this quality during the design and
evaluation of software architecture models. Then the paper performs an analysis of the quality on a recent
approach of interoperability of tools and languages in a model-driven development environment. The key
technique used to achieve interoperability stays in the alignment of various forms of metamodels. A special
focus of discussion is on several aspects, such as the model transformation correctness, the management of
the elements possibly lost while transforming or the back propagation of changes performed in the
generated model to the original model.
1 INTRODUCTION
While Model Driven Architecture (MDA) focuses
on the generation of software implementations from
models, the same technologies can be used for other
purposes, such as transforming software architecture
(SA) model into an analysis model of a quality
attribute (Dobrica, 2011). This approach applied in
SA development is motivated by the increased
complexity of today software systems that provide
the best quality for customer satisfaction. Although
quality attributes analysis methods and techniques
exists (Clements et al., 2002); (Lassing et al., 2009)
they are not widely used because they require heavy
modeling effort throughout the development
process. To ensure that these methods and
techniques are used, they must be made accessible,
integrated into the software development process
and supported with a proper interoperability in a
tools ecosystem. Research community has
demonstrated the viability of model-to-model
transformations for design and analysis models
interchange (Dobrica et. Al., 2011) (Moreno and
Smith, 2009) (Martens et al, 2010). Interoperability
is the ability of two or several tools to exchange
information and thus to use the exchanged
information. In SA development interoperability is
required in several scenarios: architecture
refinement, architecture recovery, round-trip
engineering, tool and architecture description
language (ADL) evolution to address backward
compatibility with previous versions and, for
instance, collaborative development. Using such a
model-driven interoperable environment, an
architect should know about the provided level of
quality of a transformation.
This paper defines and analyses the quality of
model transformations from the viewpoint of
software architecture development. The paper is
organized as following. The role of the next section
is to scope the research domain. The paper continues
with the definition of quality of model
transformations. This is the main contribution of the
paper because it gathers for the first time the main
concerns addressed by a software architect, as the
main user, and a developer in specific attributes and
properties. The last section is a discussion regarding
managing the properties of transformations such that
to guarantee the required quality. It refers to the
analysis of the main attributes of quality of
transformations on a concrete example.
2 MODEL TRANSFORMATION
Model transformation is an essential operation in
model-driven engineering (MDE). Model
transformations are always based on a metamodel. A
305
Dobrica L..
QUALITY OF TRANSFORMATIONS PROVIDING INTEROPERABILITY IN SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE MODEL-DRIVEN DEVELOPMENT.
DOI: 10.5220/0003613303050308
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Software and Database Technologies (ICSOFT-2011), pages 305-308
ISBN: 978-989-8425-77-5
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

model-to-model transformation creates another
model, which is typically based on a different
metamodel than source model (Czarneki and Helsen,
2006). Such transformations generally describe how
the constructs of the source metamodel are mapped
on the constructs of the target metamodel. Both the
source and target of a model transformation are a set
of models. The Query/View/Transformation (QVT)
specification (OMG, 2005) is the solution for model
transformations in the OMG modeling framework.
There are many other model transformation
languages emerging from industrial and academic
efforts (Didonet et al., 2006). As a consequence,
there is an increasing number of model
transformations that are being developed for
different applications domains and therefore
software modelers should be able to compare and
select the languages and tools for their particular
problem. It should be noticed that a model
transformation is also considered a model (Bezivin
et al., 2006). Just as a model can be created,
modified, and augmented through a transformation,
a transformation can be regarded as a model, and
therefore, it can itself be instanced or modified.
Higher order transformations (HOT) represent a
solution of obtaining automatically model-level
transformations by taking other transformations as
input and producing other transformations as output.
Series of model-to-model transformations that
enable information migration among models are
used to define a transformation system. Weaving
models form the logic that generates
transformations. A number of methods to specify
and construct weaving models are currently being
developed. Conceptually weaving models conform
to a given weaving metamodel and they can be
defined either manually or by scripting languages.
A number of interesting tools, most of them open
source are available today. These tools may be used
to automate model transformations. Many
technologies are emerging in the context of Eclipse
platform. Some of the most important are Eclipse
Modelling Framework (EMF) and Generative Model
Transformer (GMT). GMT is a container of projects
and AtlanMod Transformation Language (ATL) is
part of it. ATL is a model-to-model transformation
engine that has matured over the past several years
(Jouault and Kurtev, 2006
). ATL is QVT compliant.
An ATL transformation is specified as a set of
transformation rules. In ATL rule inheritance is a
mechanism that makes the transformation code more
compact and it shows clearly what is common and
what is specific in the transformation of similar
elements. ATL is part of the platform called
AtlanMod Model Management Architecture
(AMMA), which contains various tools for the
creation of domain specific languages. Among these
tools, AMW is the platform that manages weaving
models. A weaving model conforms to an extensible
weaving metamodel. The weaving models are
defined by the XML Metadata Interchange (XMI).
3 TRANSFORMATION QUALITY
The quality of a transformation is defined
considering various concerns addressed by an user
and a developer. In our view, the user is a software
architect that benefits of such a tools ecosystem
during design and evaluation of software
architecture models. The developer is another
stakeholder, who has a specific viewpoint regarding
a development process (Rozanski and Woods,
2005). Thus, the quality of a transformation is
defined as a complex of specific characteristics that
include the startup effort, transformation mainte-
nance, traceability, invertibility and correctness of a
transformation (Cortelessa et al., 2008). Futhermore,
when dealing with multiple transformations of
different models important is lost in translation
property. The startup effort represents the startup
time in using a transformation language tool. In
addition, with transformation languages it is
necessary to formally define and maintain source
and target metamodels. Transformation maintenance
concerns the evolution in time of a transformation.
This means that a transformation has to be
maintained by adding/removing/changing transfor-
mation rules. Traceability is the ability to trace back
elements of the target model to elements of the
source model. Invertibility is defined as the ability to
automatically build the inverse transformation.
Traceability and invertibility are the main attributes
of concern in round-trip engineering (RTE). Two
models are synchronized with respect to a
transformation if the relevant part of the target
model can be created by applying the transformation
to the source model. Another main issue regarding
transformation is to verify the correctness of a
transformation, in fact how to guarantee that the
output model is consistent with the source model.
This opens the possibility to build formal proofs of
transformation correctness (Bordin and. Vardanega ,
2007). Correctness of a transformation is divided
into syntactic correctness and semantic correctness.
Syntactic correctness should answer to the following
question: Given a well-formed source model, can be
guaranteed that the target model produced by the
ICSOFT 2011 - 6th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
306
transformation is well-formed? A guarantee of
syntactic correctness is the presence of mechanisms
to check if a model conforms to its metamodel.
Semantic correctness should answer the following
question: Does the produced target model have the
expected semantic properties? It can be exactly
defined by what kind of properties should be
satisfied through model transformation.
In multiple transformations of different models,
the models should be kept aligned and consistent.
One of the most important properties to preserve is
when changes made on the generated model must be
propagated back to the others. Various approaches
have been recently proposed in order to tackle this
problem. In (Hettel et al., 2008) the authors provide
a framework to compare current model
synchronization approaches, classifying them by the
nature of the involved transformations (i.e., whether
they are total or partial, bijective or injective, and if
the reverse transformations are given or not). All of
these approaches can be exploited depending on the
assumptions made on the transformations generated
from the weaving models. For example, assuming
that the generated transformations are total and
bijective, then the corresponding approach may be
used. This implies that an analysis of the generated
transformations should be performed and
assumptions on them should be considered. When
this solution is not possible to be applied (e.g.,
transformations with many manual ad hoc
refinements are hard to classify) a basic and generic
mechanism to keep models consistent is devised in
(Malavolta et al., 2010).
4 ANALYSIS OF QUALITY IN
MODEL TRANSFORMATIONS
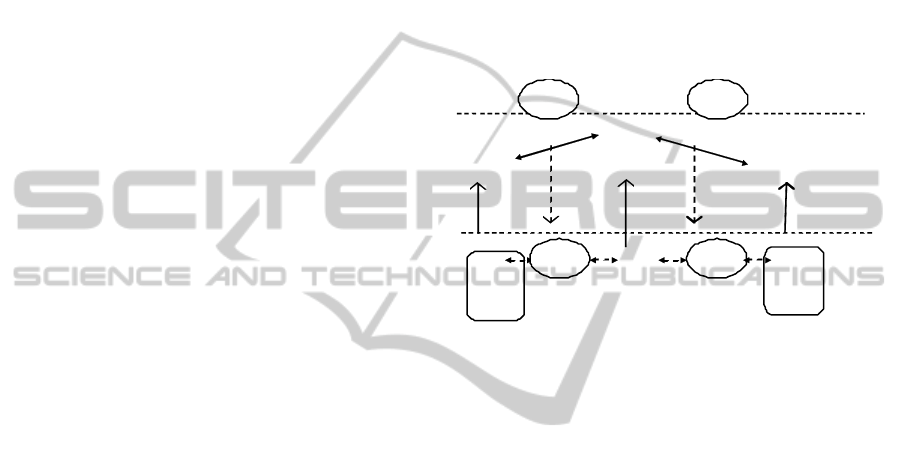
DUALLy is a framework to create interoperability
among ADLs based on a specific star topology
(Malavolta et al., 2010). In the centre of the star is
the semantic core set of modelling elements. The
transformation system is made of a series of low-
level model-to-model transformations that enable
information migration among model instances.
These transformations are constructed automatically
executing HOTs (Figure 1). From a technological
viewpoint DUALLy is engineered as an extension of
an open source platform that manages weaving
models. Extension consists of an editor, a weaving
metamodel and a set of HOTs. The main advantages
that DUALLy provides are compliance with OMG
standards and interoperability with other modelling
tools. DUALLy achieves independence from tools
used for modeling or analysing SAs. DUALLy
provides a good level of scalability since software
architects do not need to trace models while round-
tripping DUALLy-zed models. The correspondence
between model elements is identified by directly
referring to an identification attribute. The weaving
models form the logic that generates ATL
transformations. While the ATL transformations
generation phase can be the most crucial, the
framework makes it totally transparent to the
software architect that does not need any knowledge
about model transformations.
M1
A0
model
M2
A0
MM
MM 2
MM1
semantic mm
link
s
emantic mm
link
con forms to
conforms to
aut omatic
transf .
automatic
transf.
MM
Level
M
Level
m2m
transf.
m2m
transf .
MMM
Level
HOT
weaving
mm.
weaving
mm.
Tool 1
(Design
Tool)
Tool 2
(Analysis
Tool)
Figure 1: DUALLY Model Transformations.
The startup effort for DUALLY is high because
transformations are implemented in ATL and KM3
language, which is are young languages and
developers have poor experience in using them.
Transformation maintenance is simple because
DUALLY is implemented in ATL, which is a
transformation language supported by tools that
automatically manage many aspects of maintenance.
Traceability and invertibility are also satisfied
because of ATL language, which is formally defined
and openness the possibility to build formal proofs
of transformation correctness. Thus it raises in this
way the level of trustability of the transformation.
DUALLY provides and demonstrates the
correctness of transformations. It analysis corre-
ctness problems on bidirectional transformations and
identifies conditions that disambiguate a possible
non-determinism.
Lost in translation with DUALLy is handled with
a specific mechanism. This mechanism stores un-
matched elements in a model conforming to the lost-
in-translation metamodel in order to properly
redeploy them in the proper diagram, when moving
back to the originating technology. This mechanism
provides the means to automatically store and read
those lost elements when closing the round-trip
journey. The generated direct transformation is
instructed so that it returns as output a target model
QUALITY OF TRANSFORMATIONS PROVIDING INTEROPERABILITY IN SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
MODEL-DRIVEN DEVELOPMENT
307

and an additional model containing the lost-in-
translation elements. Reverse transformation takes
as input the changed generated model and a
previously created lost-in-translation model and
reads its elements to the originating model. When
executing a HOT, kinds of transformations are
possible. Among these, it can be mentioned not
instructed, when the model transformation does not
take into consideration the lost-in-translation
mechanism and instructed, when the transformation
creates the additional lost-in-translation model and
adds its elements to a target model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has defined the concept of quality of
model-to-model transformations based on a set of
concerns addressed by an user and a developer.
Because model-driven environment is the current
trend in software architecture design and analysis, a
key user, who is the principal beneficiary of such a
tools ecosystem, is the software architect. The
developer is also an important stakeholder
addressing various concerns regarding quality during
development and evolution of such an approach.
Then the paper has performed an analysis of the
quality on a recent approach of interoperability of
tools and languages in a model-driven development
environment. The description of this approach has
revealed that the key technique used to achieve
interoperability stayed in the alignment of various
forms of metamodels. A special focus of discussion
was on several properties, such as the model
transformation correctness, the management of the
elements possibly lost while transforming or the
back propagation of changes performed in the
generated model to the original model.
Because this paper has described work in
progress, much remains to be done to refine the
definition given here. This definition will be used in
other evaluations and we’ll try to develop metrics
for analysing quantitatively this quality of model-to-
model transformations. The final goal of the future
work is an ontological definition to be integrated in a
knowledge management system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Romanian research
grant CNCSIS –UEFISCSU, project number PNII –
IDEI 1238/2008.
REFERENCES
Bezivin J., F. Buttner, M. Gogolla, F. Jouault, I. Kurtev,
A. Lindow, 2006. Model Transformations?
Transformation Models!, Model Driven Eng.
Languages and Systems, pp. 440-453, LNCS 4199.
Bordin M., T. Vardanega, 2007. Correctness by
Construction for High-Integrity Real-Time Systems: A
Metamodel- Driven Approach, Proc. of Ada-Europe
2007, LNCS 4498, pp. 114-127.
Clements, Kazman, Klein, 2002. Evaluating Software
Architectures: Methods and Case Studies, Addison-
Wesley.
Cortelessa V., S. Di Gregorio, A. Di Marco,2008. Using
ATL for Transformations in Software Performance
Engineering: A step ahead of Java based
transformations?, WOSP’08, Princeton, New Jersey, p.
127-131.
Czarnecki K., S. Helsen, 2006. Feature-based survey of
model transformation approaches, IBM Systems
Journal, 45(3).
Dobrica L., 2011. Exploring Approaches of Integration
Software Architecture Modeling with Quality Analysis
Models, 2011, Ninth Working Conference on
Software Architecture (WICSA 2011), (in press).
Dobrica L., Ionita A. D., Pietraru R., Olteanu A., 2011.
Automatic Transformation of Software Architecture
Models, U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Series C, 2011 (in press).
Didonet Del Fabro M., J. Bezivin, P. Valduriez. 2006.
Weaving Models with the Eclipse AMW plugin, in
Procs. of the Eclipse Summit Europe.
Hettel T., M. Lawley, K. Raymond, 2008. Model
Synchronisation: Definitions for Round-Trip
Engineering, Proc. Int’l Conf. Model Transformation.
ISO/IEC 9126-1:2001, Software Engineering - Product
Quality, Part 1: quality model, June 2001.
Jouault F., I. Kurtev. 2006 Transforming models with
ATL, in Satellite events at the Models 2005
Conference, LNCS 3844/2006, p. 128–138.
Lassing, N., et al., 2002. Experiences with ALMA: Archi-
tecture-Level Modifiability Analysis, Journal of
Systems and Software, Elsevier, pp. 47-57.
Malavolta I., H. Muccini, P. Pelliccione, D. A. Tamburri,
2010. Providing Architectural Languages and Tools
Interoperability through Model Transformation
Technologies, IEEE Transactions on Software
Engineering, 36(1), pg. 119- 140.
Martens A., Koziolek H., Becker S, Reussner R., 2010.
Automatically Improve Software Architecture Models
for Performance, Reliability, and Cost, WOSP/SIPEW
2010.
Moreno G. A., C. U. Smith, 2009. Performance analysis of
real-time component architectures: An enhanced
model interchange approach, Performance Evaluation
Journal.
OMG, 2005. Object Management Group, MOF QVT spe-
cification, Final Adopted Specification (ptc/05-11-01).
Rozanski N., E. Woods, 2005. Software Systems
Architecture, Pearson Education.
ICSOFT 2011 - 6th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
308
