
AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF BEIJING PUBLIC TRANSPORT
USERS’ SATISFACTION LEVEL
Hongmei Wang and Lingyu Jia
School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong Universtiy, Haidian district, Beijing, 100044, China
Keywords: Public transport, Users’ satisfaction, Matter element model, Coefficient of variation.
Abstract: Assessing the level of public transport users’ satisfaction is important not only to implication of public
transport priority policy, but also to improvement of public transport service level. In this paper, evaluation
index system of pubic transport passengers’ satisfaction is established according to basic requirement of
passengers. Then, based on matter element theory, evaluation model which uses coefficient of variation
method to calculate the weight of the evaluation indices is developed. Finally, the model is applied to
Beijing based on data surveyed by questionnare. The research indicates that public transport user
satisfaction degree in Beijing is ‘medium’.
1 INTRODUCTION
Along with the too rapid growth of motor vehicles,
congestion in Beijing has long been an increasingly
serious problem which brings negative effect to
urban development and daily life of residents.
Because of the limit in land resources, congestion in
Beijing can not be solved by increasing the area of
road substantially. As a result, transportation
demand management (TDM) emerged as a useful
tool. Improving public transport is one of the main
TDM measures. Preferential development of urban
public transport is an important measure to raise the
utilization rate of transport resources and reduce
traffic congestion. A convenient, fast and
comfortable public transport system can attract more
residents and thus improve the urban transport
structure. Whether residents choose public transport
mainly depends on its performance. The public
transport system should be improved according to
the requirements of the passengers. In that way
public transport can be more attractive to the
residents, so the congestion can be relieved effetely.
Assessing the level of public transport user
satisfaction is not only important to the implication
of public transport priority policy, but also of great
significance to the improvement of the public
transport service level. For the above reasons, this
paper focuses on the evaluation of public transport
user satisfaction.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Evaluation of public transport is worldwidely
academic concerned due to practical significance.
Foreign scholars have a preference for
questionnaire-based survey and statistics to analyze
factors affected to public transport user satisfaction.
Based on data of SP survey, Hensher & Stopher
(2003) did a research on 13 factors’ influence on
passengers’ satisfaction; the 13 factors include bus
travel time, seat availability on bus, driver attitude
and general cleanliness on board etc. Tyrinopoulos&
Antonio (2008) and Olio et al (2010) did similar
analyses on influencial factors.
Some scholars focus on evaluating methods of
public transport performance. Yeh et al (2000)
developed a fuzzy multicriteria analysis model to
assess the performance of bus companies; the model
was then applied to evaluate ten bus companies’
perfrmance in Taiwan. Cheng & Wang (2009)
established an evaluation system based on
government, transit operators and passengers, city of
Zhengzhou was selected for the empirical study.
Some scholars assessed public transport
performance by grey theory method. Li & Hu (2006)
presents 23 evaluation indices involve infrastructure,
384
Wang H. and Jia L..
AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF BEIJING PUBLIC TRANSPORT USERS’ SATISFACTION LEVEL.
DOI: 10.5220/0003586003840388
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (SSSCM-2011), pages 384-388
ISBN: 978-989-8425-54-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

service and benefit; and the city of Qingdao was
studied by means of grey clustering method. Chen &
Zhang (2009), Li & Sun (2010) did similar research
on Lanzhou and Jinan. Shao et al (2009) established
a comprehensive evaluation system based on
analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and grey relational
analysis in evaluation of public transport of
Yinchuan. Based on questionaire surveyed data,
Yang & Chen (2005) analyzed the influence degree
of attributes like road density, average speed,
departure intervals and accident rate on users’
satisfaction.
In the model built by Shao (2005), indices
involved five aspects including public transport
infrastructure, investment of bus companies, public
transit capacity and service quality. After the indices
are weighted by means of analytic hierarchy process
(AHP), evaluation was realized by an improved BP
neural network model.
Overview of literature above indicates that
evaluation criteria established in most of the recent
research mainly used data related to public transport
system instead of passengers’ subjective feeling.
Furthermore, fuzzy multicriteria analysis, grey
theory method and BP neural network model is
widely used to evaluate the service quality of public
transport. However, fuzzy multicriteria analysis and
grey theory method is often criticized for the
definition of membership function and
whitenization
function is arbitrary. BP neural
network model is
only effective when mass typical data is available.
So, in this paper, the authors will promote public
transport users’ satisfaction evaluation criteria from
the perspective of passengers. In addition,
comprehensive evaluation model is established
based on the theory of matter element.
3 EVALUATION MODEL OF
PUBLIC TRANSPORT USERS’
SATISFACTION LEVEL
Matter element analysis is an appropriate tool in
solving complex and incompatible problems.
Multicriteria evaluation model is established based
on matter element theory and it can be applied to
evaluate the public transport user satisfaction.
A set of n indices
12
,,
n
CC C",
are chosen to
evaluate public transport user satisfaction and the
corresponding numerical values of indices
are
12
,,
n
X
XX",
. The public transport user
satisfaction can be expressed as a matter-element:
()
nn
XC
XCN
XCNR
##
11
,, ==
j
R represents matter-element of classic domain
while
j
N is the jth grade of satisfaction and
,
j
ijiji
x
ab
⎡
⎤
=
⎣
⎦
is the value range of jth grade of
satisfaction on the ith index.
P
R
is matter-element
of section domain while P is whole grades of
satisfaction and
[
]
,
Pi Pi Pi
x
ab=
represents the
value range of
i
C
.
[
]
[]
[]
jnjn
jj
jjj
j
baC
baC
baCN
R
,
,
,
3
222
111
##
=
[
]
[]
[]
111
222
,
,
,
PP
PP
P
nPnPn
PC ab
Cab
R
Cab
=
##
Correlation degree is defined as the membership
between the index and the grade. In extenics,
correlation degree can be calculated by the
correlation function bellow:
()
(
)
()
()()
0
0
,
,
,,
iji
ji
ji
iji
ipi iji
xx
x
x
x
kx
xx
x
x
xx xx
ρ
ρ
ρρ
⎧
⎪
−∈
⎪
⎪
=
⎨
⎪
∉
⎪
−
⎪
⎩
where
()
22
,
jijijiji
ijii
abba
xxx
−
−
+
−=
ρ
,
jijiji
bax −=
and
(
)
j
i
kx
is the correlation degree
between the ith index and the jth grade. The
correlation degree of the evaluation object
matter-element and the jth grade can be calculated
as:
() ()()
ii
n
i
jj
xwxkxL
∑
=
=
1
where
(
)
i
wx is the weight of the ith criterion.
4 EVALUATION SYSTEM OF
MUNICIPAL PUBLIC
TRANSPORT USERS’
SATISFACTION
The evaluation index system is established follow
the principles of systematicity, multi-levels,
AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF BEIJING PUBLIC TRANSPORT USERS' SATISFACTION LEVEL
385
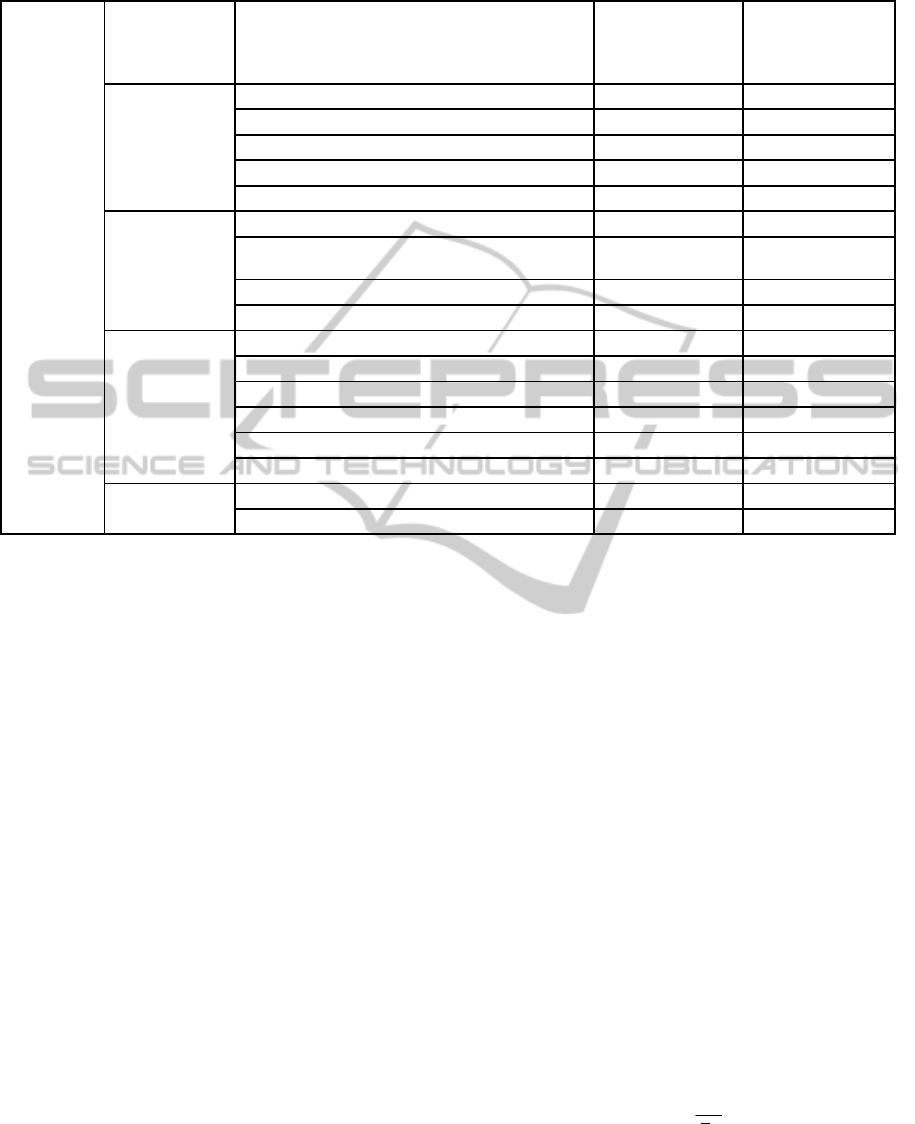
Table 1: Evaluation indices, values and weights of Beijing public transport users’ satisfaction level.
Satisfaction
level
Criteria Sub-criteria and their Weights Mean value of Indices
Weights of Indices
Efficiency 0.283
Waiting time at offpeak hours 0.156 7.41 0.044
Waiting time at peak hours 0.166 7.07 0.047
Transfer time 0.158 7.37 0.045
Travel time 0.275 3.74 0.078
Traffic information 0.245 4.57 0.070
Convenience
0.263
Transfer times 0.220 5.96 0.058
Walking time from station to destination 0.396
4.58 0.105
Station information by broadcast 0.174 6.23 0.046
Convenience during transferring 0.209 5.79 0.055
Comfort
0.361
Waiting order 0.169 5.12 0.061
Vehicle cleanliness 0.112 5.87 0.040
Vehicle temperature and air condition 0.148 5.15 0.053
Degree of crowding in the vehicle 0.241 3.23 0.086
Running stability of vehicle 0.200 4.77 0.072
Seat comfort 0.130 5.95 0.046
Service quality
0.093
Staff friendliness 0.486 5.85 0.045
Offerin
g
seats to o
t
her
p
erson 0.514
6.28 0.048
scientificity and feasibility. Finally, a three-level
evaluation index system was established. In this
system, municipal public transport user satisfaction
is the evaluation objective; five attributes including
efficiency, convenience, comfort and service are
considered as criteria; 17 sub-criteria are selected in
the third level (see table 1).
5 EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF
BEIJING PUBLIC TRANSPORT
USERS’ SATISFACTION
In this part, we will evaluate the satisfactory level of
Beijing public transport users based on the above
questionaire surveyed data.
5.1 The Questionaire Survey
A questionnaire survey was conducted at bus station,
urban rail and subway station, public transit hub,
shopping center, parks and schools etc. in Beijing in
January 2010 to obtain data of indices. The
questionnaire was designed based on the evaluation
index system. Indices were translated into questions
according to the actual situation to get information
from the passengers. We sent out 700 questionnaires
and 527 of them were collected. Of the 527
correspondents, 252 persons are female while 257 of
them are male; 182 (34.5%) correspondents’ families
have at least one private car; as to age structure, 443
(84%) of them are 18-45 years old, while senior
persons (elder than 60 years old) only occupied
0.9%.
Passenger’s judgment about public transport is
described as five grades, ‘very poor’, ‘poor’, ‘fair’,
‘good’ and ‘very good’ and the corresponding
numerical values are 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9 when recording
the data. The statistical data is presented in Table 1
(see column ‘mean value of the indices’).
5.2 Weights of Indices
Coefficient of variation method can be used to
calculate the weighs of indices objectively. It is
adopted in this paper to avoid the defect of
subjective methods such as AHP and Delphi method.
The weight can be calculated as follows:
j
j
j
x
D
=
δ
(1)
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
386

Table 2: Relational degrees in Beijing public transport
evaluation system.
Relational
degree
Ve r y
good
Good Medium Poor
Very
poor
Grade
Efficiency -0.4276 0.021 -0.159 -0.313 -0.571 Good
Convenience -0.435 -0.108 0.128 -0.294 -0.509 Medium
Comfort -0.489 -0.247 0.163 -0.105 -0.448 Medium
Service
quality
-0.396 0.050 -0.011 -0.414 -0.582 Good
Synthetically
relational
degree
-0.449 -0.119 0.046 -0.242 -0.511 Medium
∑
=
=
n
j
j
j
j
w
1
δ
δ
(2)
Where
j
x
is the mean value of jth index,
j
D
is
the standard deviation of the jth index,
j
δ
is the
coefficient of variation and
j
w
is the weight of the
jth index.
Weights calculated by means of coefficient of
variation method are presented in Table 1 (see
column ‘weights of indices’).
5.3 Evaluation of Public Transport
users Satisfaction Level
Mean value of the satisfaction degree obtained by
the survey is taken as the value of corresponding
index. Public transport user satisfaction degree can
be described as five grades, ‘very good’ (the value
range is 8-9), ‘good’ (6-8), ‘medium’ (4-6), ‘poor’
(2-4) and ‘very poor’ (1-2). According to the model
built in part 2, matter-element of evaluation object,
matter-element of classic domain and matter-element
of section domain can be defined and relational
degree between the indices and five grades can be
calculated. Synthetically relational degree between
public transport user satisfaction and five grades is
obtained by weight sum. According to the definition
of relational degree, the grade of public transport
user satisfaction is given by
)(
,...2,1
max x
j
L
nj
j
k
=
=
. The
relational degrees are presented in Table 2.
Data in Table 2 indicates that public transport
passenger satisfaction degree in Beijing is ‘medium’.
Furthermore, synthetically relational degree about
‘good’ is larger than it of ‘poor’. According to the
definition of relational degree in extenics, it is more
likely to translate into grade of ‘good’ from
‘medium’.
6 CONCLUSIONS
By improving public transport service quality to
satisfy passengers, more residents will be appealed
to use public transport instead, so that the congestion
could be relieved. In order to evaluate the public
transport user satisfaction, this paper proposed an
evaluation model based on matter-element analysis
theory. Based on the data obtained by questionnaire
survey, the public transport user satisfaction is
assessed from the perspective of passengers.
Coefficient of variation method is adopted to
calculate the weights of indices to overcome the
shortcoming of subjective methods used in previous
research. The research indicates that public transport
user satisfaction degree in Beijing is ‘medium’ and
close to ‘good’. Poor user satisfaction about
convenience and comfort affect the overall
satisfaction of public transport service. While
striving to construct public transport infrastructure,
the government should pay more attention to
improve the service quality of public transport to
make public transport more attractive.
*Supported by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the
Central Universities (Appraisal of TDM Measures in
Occurring Urban Congestion)” and “National Nature
Science Fund of China (Research of residents’ Selective
Mechanism in Public Transport)”.
REFERENCES
Chen Han, Zhang Xiaoyuan. Comprehensive evaluation of
the operation level of urban public transportation
based on the travel requirement of residents [J].
Technology & Economy in Areas of Communications,
2009, 6: 8-11.
Cheng Xi, Wang Wei, Ren Gang et al. A study on
comprehensive evaluation of metropolitan public
transit with fuzzy evaluation and analytic hierarchy
process [J].
Urban Public Transport, 2009, 2: 25-29.
Hensher D., Stopher P., Bullock P., Service
quality-developing a service quality index in the
provision of commercial bus contracts [J].
Transportation Research (Part A), 2003, 37: 499-517.
Li Yinghong, Sun Huijuan. Evaluation and research of
BRT service level[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong
University (Natural Science)
, 2010, 29(2): 285-289,
AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF BEIJING PUBLIC TRANSPORT USERS' SATISFACTION LEVEL
387

290.
Li Yuhua, Hu Yunquan. Gray clustering method applied to
evaluation of urban public transport development level
[J].
Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2006, 32(6):
125-132.
Olio L, Ibeas A, Cecín P. Modeling user perception of bus
transit quality [J]. Transport Policy, 2010, 17:
388-397.
Shao Fei, Deng Wei, Yi Fujun et al. Comprehensive
evaluation method of metropolitan public
transportation system based on analysis hierarchical
process and grey theory[J]. Journal of PLA University
of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition)
,
2009, 10(6): 536-541.
Shao Zufeng. Evaluation model of urban public traffic
service quality based on neutral network [J]. Municipal
Administration & Technology,
2005, 4: 178-180.
TyrinopoulosY, Antoniou C. Public transit user satisfaction:
Variability and policy implications [J]. Transport
Policy,
2008, 15: 260-272.
Yang Jun, Chen Rongqiu, Guo Congmin. Assessing
service quality of city public transport via grey
relational theory [J]. Industrial Engineering and
Management,
2005, 10(4): 89-92.
Yeh C, Deng H, Chang Y. Fuzzy multicriteria analysis for
performance evaluation of bus companies [J].
European Journal of Operational Research, 2000,
3(126): 459-473.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
388
