
A COLLABORATIVE OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR
STRATEGIC PERFORMANCE
Zhang Hao, Cui Li, Zhou Yong-sheng and He Ming-ke
School of Business, Beijing Technology and Business University, Beijing, China
zhhaozhhao@126.com
Keywords: Strategy, Performance, Collaborative optimization, Chaos optimization.
Abstract: The logical framework formed by enterprise strategic performance which designed from the dimensions of
structure, capability and the culture is what we used to refine the key points of strategic performance. To
construct a collaborative optimization model for strategic performance, it should be based on the overall
optimization framework of collaborative optimization technology with the chaotic optimization method.
The objective of system-level optimization is strategic performance optimization. The optimization goal of
the subsystem-level is to make the difference between the designed subsystems and the subsystems
provided by system-level optimization as little as possible. The numerical simulations show that the model
is scientific and feasible.
1 INTRODUCTION
The operation of the enterprise consumes a variety of
resources. Both the external resources and the
internal resources are factors that affect the
enterprise strategic objectives. Allocation of
resources is the key content of strategic
development, strategy implementation and strategic
control. It is in the process of being continuous
optimized. The optimization of strategic
performance can be achieved by allocating the
limited resources so as to maximize the performance,
and create cost-effective for companies, so that the
limited resources can get into the most lucrative
returns. How to effectively optimize the performance
of the strategy is an important task both in theory
and practice community. Based on the concept of
collaborative optimization, this paper forms the
strategic synergy mechanism operation framework
with the sub-systems coupling by structure,
capability and culture, and composes collaborative
optimization model for strategic performance
combined with chaos optimization method and
makes numerical simulation.
2 THE LOGICAL FRAMEWORK
OF THE FORMATION OF
ENTERPRISE STRATEGIC
PERFORMANCE
Strategy performance optimization is to
comprehensively and dynamically adjust the
input-output relations between the financial elements
and non-financial elements which will influence
strategy performance, so as to achieve the enterprise
overall strategy performance optimization. Strategic
system consists of the structure, capacity and cultural
composition, as shown in Figure 1. The three
dimensions are coupling with one another,
interrelated and mutually supporting. The strategic
system adjusts the relationship between the three
dimensions according to changes in the internal and
the external environment of the enterprise. It will
adjust the configuration of resources and the extent
of influence in order to make sure the strategic
performance optimization. Cooperating the sectors
of enterprises and the resource allocation, making
the strategy performance always maintain the
optimal status, adjusting the disharmony factors
between enterprise and its business environment, and
correcting deviations in time will help enterprise
adapt to the external environment better. After all the
strategic business units are aware of the stimulation
645
Hao Z., Li C., Yong-sheng Z. and Ming-ke H..
A COLLABORATIVE OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR STRATEGIC PERFORMANCE.
DOI: 10.5220/0003573306450649
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (MMLM-2011), pages 645-649
ISBN: 978-989-8425-56-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

from the external environment, they will achieve
information sharing by initially screening and
analyzing the information then communicating with
each other. Thus, the strategic business unit formed a
coupling relationship. However, the coupling
manner and extent are not determined by the
strategic business units. They pass the information to
the strategy system, and then the strategy system
calculates and balances the internal and external
environment status and the development trend
comprehensively. On one hand it will pass the
amended information to the strategic business units,
on the other hand it will export the strategic
collaborative performance. The strategic business
unit adjusts the coupling relationship between each
other according on the instruction passed by the
strategic layer, so that to achieve a dynamic
optimization strategy and to ensure that the
companies can adjust their strategies timely.
Figure 1: Logical Framework Which Strategy Performance
Formed.
3 PRINCIPLES OF
COLLABORATIVE
OPTIMIZATION FOR
STRATEGIC PERFORMANCE
This paper uses the idea of collaborative
optimization for reference to design the principles of
collaborative optimization for strategic performance.
Collaborative optimization is method proposed by
Braun which decomposing, coordinating and
integrated optimizing according to one discipline to
multidisciplinary designed optimization. Each
discipline’s calculations have a very good degree of
autonomy, without taking into the account of the
impact of other disciplines. The basic framework of
collaborative optimization consists of optimization
of system-level and subsystem level. In sub-system
optimization, design variables are only related to the
design parameters of the discipline involved with
and coupling variables of other related disciplines. If
it meets the requirement of the internal constraints of
the subsystems, the optimization objective is to make
the difference between the optimization solution of
the subsystem and system level as minimum as
possible. The task of system-level optimization is to
make the best overall objective of the system, and
coordinate activities of the various subsystems so
that the variance between each sub-system’s
optimization results will gradually decrease. Taking
strategic system as the system-level of optimization,
structure, capability, culture as a subsystem (which
can also be divided from other aspects), the coupling
relationship between subsystems will be determined
by the system level optimization.
Definition I. During the process of designing and
operating the enterprise strategy system,
collaborative optimization for enterprise strategic
performance must analyze the extent of the
interaction between subsystems, and adjust the
models and methods of enterprise system
optimization by taking advantage of these
interactions.
Definition II.
Co
i
SubsystemSystem
Δ+Δ=Δ
∑
)( (1)
In equation (1),
System
Δ means the overall
system performance,
∑
Δ
i
Subsystem
is the sum
performance of subsystem, and
Co
Δ
means the
increment calculated the interaction between the
various subsystems after collaborative
optimization.
Definition III. Subsystem: The basic module in
enterprise system which are independent in functions
but keeping mutual exchange of information and
material as well. Such as: sales department and
production department, finance department and sales
department.
Definition IV. Design variables: A group of
independent variables used to describe the
characteristics of the strategic system, and can be
controlled in the design process.
Definition V. State variables: A set of parameters
Strategy System
Framework
Capabilit
Culture
Strategy Performance
External environment
Stimulation
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
646
used to describe the function or characteristics of the
system or subsystems.
Definition VI. Constraints: The constraints needed
to be met during the operation of system or
subsystems.
Definition VII. System Collaborative Optimization:
In collaborative optimization for strategic
performance, the subsystems coordinate for their
common strategic goal - the best of the overall
enterprise systems. The relationship of each
subsystem is more cooperative. System layer is
responsible for planning, coordination and leading
the overall direction of optimization; subsystem is
responsible for the compatibility optimization, and
study the feasibility of the direction of optimization.
The mathematical description of collaborative
optimization for strategic performance as:
System layer:
)(min xf
..t
s
0)( =xC
i
Sub-system layer
: )(min
∗
xC
i
..t
s
)(xg
i
)()()(
∗∗∗∗
−−= xxxxxC
T
i
)()()( xxxxxC
T
i
−−=
∗∗∗
ni ,,3,2,1 "=
In the equation above:
x
is the system level
design variables,
)(xf
is the objective function,
)(xC
i
is the compatibility constraint of subsystem
i
,
∗
x
is the design variables of sub-system layer,
∗∗
x
is the design variables’ optimization results of
subsystem, )(
∗
xC
i
is the objective function for the
subsystem
i
,
n
is the number of the variables.
4 THE COLLABORATIVE
OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR
STRATEGIC PERFORMANCE
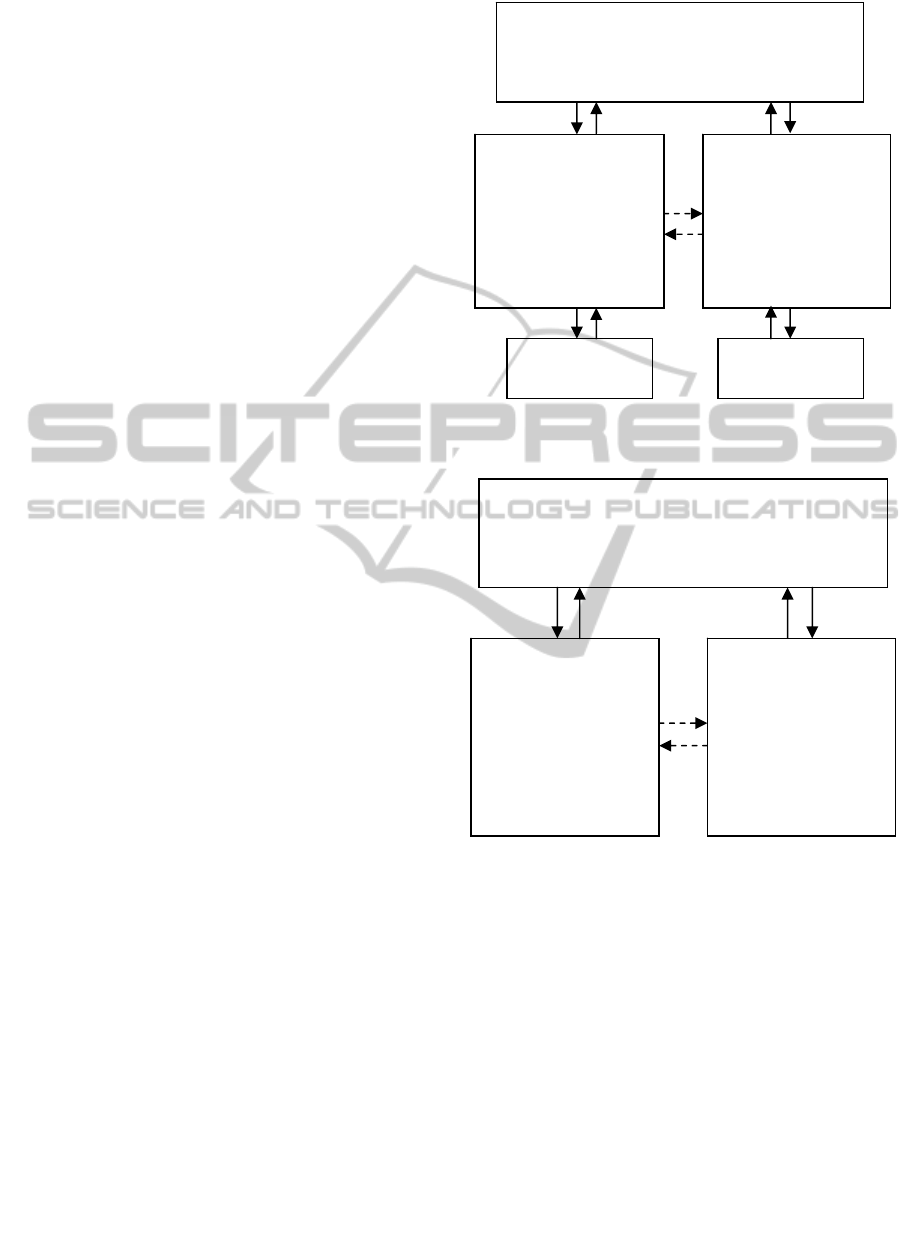
The structure of Collaborative optimization model
can be designed according to the logical framework
of strategic performance. It can be divided into two
levels: system level and subsystem level. System
layer is responsible for the overall strategic systems
optimization; the sub-system layer is responsible for
the optimization of the subsystem itself. The system
level and subsystem layer have got a close coupling
relationship. The subsystem-level’s optimization
goal is to make the difference between the designed
subsystems and the subsystems provided by
system-level optimization as little as possible.
Figure 2: Framework of Collaborative Optimization for
Strategic Performance.
Figure 3: Function for Collaborative Optimization for
Strategic Performance’s Framework.
The strategic elements of structure dimension
contain capital structure, product structure,
organizational structure and personnel structure. The
strategic elements of capacity dimension include
marketing capability, management capability,
innovation and decision-making capability. The
strategic elements of culture dimension consist of
values, cohesion, entrepreneurship, enterprise
learning. Standardized the value of the performance
elements of the strategy, making
i
x
represents the
performance value of the
i
strategic element,
)(xf
for the system level performance value,
1
f ,
2
f ,
3
f
for performance value corresponding to the
System level strategic optimization
Optimization:System objective
Constraint : The coupling variables
b
etwee
n
subsystems and shared variables are same
Optimization of subsystem
1
Optimization:
Collaboration
between
subsystems
Constraint:Constraint of
subsystem 1
Optimization of subsystem
n
Optimization:
Collaboration
between
subsystems
Constraint:Constraint of
subsystem 1
Analysis module of
subsystem 1
Analysis module of
subsystem
n
System level strategic optimization
)(min zf
..t
s
0))((),(
2
=−=
∑
∗∗
zxPzxJ
iii
Optimization of
subsystem 1
2
1
))((
)(min
zqx
xJ
ii
i
−
=
∑
..t
s
0)(
1
≤
id
xh
0)(
1
=
ie
xg
Optimization of
subsystem
n
2
))((
)(min
zqx
xJ
ii
in
−
=
∑
..t
s
0)( ≤
ind
xh
0)( =
ine
xg
A COLLABORATIVE OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR STRATEGIC PERFORMANCE
647

three subsystems respectively. As enterprise systems
with the feature of complexity, chaos and
collaboration, so combined the collaborative
optimization with chaos optimization, collaborative
optimization model for strategic performance is
shown below. In this model
∗
x
is the optimal
solution calculated by the system,
∗∗
x
is the
optimal solution returned by the subsystem,
α
is
for the weight. Strategic performance is the bigger
the better, therefore, in the design of system level,
we take
)(xf
as the reciprocal of the value of
strategic performance.
(1) System layer:
i
i
i
xxf
∑
=
=
12
1
/1)(min
α
(2)
..t
s
10 ≤≤
i
x
)12,,2,1( "=i
0)()(
)()()(
2
1212
2
1111
2
88
2
66
2
4
1
1
=−+−+
−+−+−=
∗∗∗∗
∗∗∗∗∗∗
=
∑
xxxx
xxxxxxf
i
i
i
0)()(
)()()(
2
1212
2
1010
2
22
2
11
2
8
5
2
=−+−+
−+−+−=
∗∗∗∗
∗∗∗∗∗∗
=
∑
xxxx
xxxxxxf
i
i
i
0)(
)()()(
2
77
2
66
2
33
2
12
9
3
=−+
−+−+−=
∗∗
∗∗∗∗∗∗
=
∑
xx
xxxxxxf
i
i
i
(2) Subsystem layer:
① Subsystem 1:
2
1212
2
1111
2
88
2
66
2
4
1
1
)()()(
)()(min
∗∗∗
∗∗
=
−+−+−+
−+−=
∑
xxxxxx
xxxxf
i
i
i
(3)
..t
s
9.05.0
1
≤≤ x
861
5.05.0 xxx +≥
95.0
3
≤x
12114
6.04.0 xxx +≥
②Subsystem 2:
2
1212
2
1010
2
22
2
11
2
8
5
2
)()()(
)()(min
∗∗∗
∗∗
=
−+−+−+
−+−=
∑
xxxxxx
xxxxf
i
i
i
(4)
..t
s
95.06.0
5
<
<
x
5102
5.05.0 xxx ≤+
1247
6.04.0 xxx +≥
6108
5.05.0 xxx +≥
③Subsystem 3:
2
77
2
66
2
33
2
12
9
3
)()(
)()(min
∗∗
∗∗
=
−+−+
−+−=
∑
xxxx
xxxxf
i
i
i
(5)
..t
s
9.0
9
≤x
4.0
10
≥x
10119
7.03.0 xxx ≤
+
5.0
11
≥x
10712
xxx ≤
If
i
x
generated by the chaotic sequence cannot
satisfied the constraints, then transformed
i
x
,take
1,
)(
+
+=
niiii
xdckx ,
i
c
is the lower limit for the
constraint,
i
d
is the absolute value of the
difference between the upper and lower limit
constraints.
5 MODEL SIMULATIONS
Standardize the performance evaluation of strategic
elements of the enterprise, each evaluation value is
somewhere in between
]1,0[
. The weight of each
index, initial value, final value, function values are
shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Simulation Data.
i
x
i
α
i
x
initial
value
i
x
final
value
)
(min xf
(min
x
f
∗∗
1
x
0.092 0.946 0.527
3.106 1.145
2
x
0.105 0.173 0.351
3
x
0.067 0.146 0.864
4
x
0.057 0.909 0.569
5
x
0.112 0.195 0.746
6
x
0.085 0.591 0.023
7
x
0.073 0.139 0.459
8
x
0.096 0.109 0.814
9
x
0.064 0.188 0.870
10
x
0.095 0.161 1.000
11
x
0.078 0.241 1.000
12
x
0.076 0.210 0.026
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
648

Figure 4: Alternation curve with
50=n
.
The value of each index of current enterprise’s
performance is the initial value. Through optimized,
each index can obtain its relative optimum value in
the strategic systems. When the time f alternation is
50, the optimization curve is what’s shown in Figure
4. When the initial function value is 3.106, the
corresponding value of the strategic performance is
0.322. After iterations, the optimal function value is
1.145, the corresponding optimal value is 0.873.
That’s optimal value is the theoretical value, the state
it corresponds to is ideal, which may have got some
difference with the reality. For example, the optimal
value which corresponds to the management ability
6
x and the corporate learning
12
x is too small. The
deviation with the actual situation is the result of the
constraint set. The relative optimal value is
theoretical. In practice, there may be a variety of
uncontrollable factors. In theory, if we can express
each influential factor by function scientifically and
reasonably, and set the corresponding constraints,
then the method can offer useful ideas for enterprise
strategy collaborative optimization.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper designs principle and structure about
strategic performance collaborative optimization the
bases on the concept of collaborative optimization,
composes operation collaborative optimization model
combined with chaos optimization method and makes
numerical simulation. Taking strategic system as the
optimization system-level, analyzing strategic
elements from dimensions of structure, capability and
cultural, the coupling relationship between
subsystems is determined by the system-level
optimization. Strategy system calculates and balances
the internal and external environment status and the
development trend comprehensively. On one hand it
will pass the amended information to the strategic
business units, on the other hand it will export the
strategic performance. The strategic business unit
adjusts the coupling relationship between each other
according on the instruction passed by the strategic
layer, so that to achieve a dynamic optimization
strategy, which reflects the consistency and
collaboration of the internal and external environment.
The model is feasible in theory proved by numerical
simulations, in practice, it still needs to set more
comprehensive and specific data conditions.
REFERENCES
Chen Qiu-lian, Li Tao-shen, Wu Heng, Zhou Dong.
Foundation excavation co-evolution based on particle
swarm optimization [J].
Journal of Computer
Applications
, 2007, 27 (7): 1780-1782.
Chung-Ming Lau, Daphne W. Yiu, Ping-Kwong Yeung,
Yuan Lu. Strategic orientation of high-technology
firms in a transitional economy [J].
Journal of
Business Research
, 2008,61 (7): 765-777.
Fan Hui, Li Weiji. An Efficient Method for
Reliability-based Multidisciplinary Design
Optimization [J].
Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,
2008, 21 (4): 335-340.
Han Ming-hong, Deng Jia-ti. Improvement of
Collaborative Optimization [J].
Chinese Journal of
Mechanical Engineering
, 2006, 42 (11):34-38.
Hong-Zhong Huang, Ye Tao, Yu Liu. Multidisciplinary
collaborative optimization using fuzzy satisfaction
degree and fuzzy sufficiency degree model [J].
Soft
Computing - A Fusion of Foundations, Methodologies
& Applications
,2008, 12 (10):995-1005.
José F. Rodríguez, John E. Renaud, Brett A. Wujek,
Ravindra V. Tappeta. Trust region model management
in multidisciplinary design optimization [J].
Journal of
Computational and Applied Mathematics
, 2000,124
(1-2): 139-154.
Mehrdad Baghai, Sven Smit, Patrick Viguerie. Is Your
Growth Strategy Flying Blind? [J].
Harvard Business
Review
, 2009,87(5): 86-96.
M. Iansiti, R. Levien. The Keystone Advantage: What the
New Dynamics of Business Ecosystems Mean for
Strategy, Innovation, and Sustainability [J].
Journal of
Engineering and Technology Management
, 2007, 24:
287-289.
Robert S Kaplan, David P Norton. How to Implement a
New Strategy Without Disrupting Your Organization
[J].
Harvard Business Review, 2006, 84 (3): 100-109.
Vassili Toropov, Alastair Wood. Metamodel-based
collaborative optimization framework [J].
Structural &
Multidisciplinary Optimization
,2009, 38 (2): 103-115.
Zhang Hao, Cui Li, Hou Han-po. Content of Corporate
Strategy Synergy Mechanism Based on Synergetics
[J].
Journal of Beijing Technology and Business
University(Social Science Edition)
, 2011, 26 (1):69-74.
Generation
A COLLABORATIVE OPTIMIZATION MODEL FOR STRATEGIC PERFORMANCE
649
