
OPTICAL DOMAIN MULTIUSER INTERFERENCE ESTIMATION
FOR SPECTRAL PHASE ENCODING OPTICAL FIBRE
CDMA SYSTEMS
Arash Yazdani
1,4
, Morteza Noshad
2
, Hojat Jaliloghli
3
,
Amirhossein Jaliloghli
3
and Mohammad Noshad
5
1
Islamic Azad University of Noor, Noor, Iran
2
Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran
3
Islamic Azad University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran
4
Telematics Department, Universidad Politecnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain
5
Electrical Engineering Department, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Optical fiber code division multiple access, Spectral phase encoding, Optical domain multiuser interference
detection, Temporal multiuser interference estimation, Nonlinear multiuser interference estimation.
Abstract:
In this paper, an effective technique for reducing the multi-user interference (MUI) in spectrally-phase-
encoded optical code division multiple access (SPE-OCDMA) systems has been proposed. In this method
the effect of MUI signal on the main user’s signal has been decreased using multiuser interference detection
(MID). Two structures have been introduced for accomplishing MID and degrading its destructive effect on
the decoded ultra-short light pulse; temporal multiuser interference estimation (TMIE) and nonlinear mul-
tiuser interference estimation (NMIE). Both of these methods utilize two photo-detectors for estimating the
MUI signal. In spite of simple structure of these two receivers, their performance analysis shows an improved
performances comparing to other receivers.
1 INTRODUCTION
A spectrally-phase-encoding optical fibre code divi-
sion multiple access (SPE-OFCDMA) system is a
system in which a phase encoding has been applied
on a coherent ultra-short light pulse with a rectangu-
lar spectral pattern (Salehi et al., 1990). Similar to
the other kind of optical fibre CDMA systems, the
MUI is the main limiting factor on the performance of
the SPE-OFCDMA systems (Salehi et al., 1990). The
MUI effect in these systems appear as an noise-like
signal distributed in the bit period in the vicinity of the
ultra-short optical pulse of main user. But because of
the slow response time of photo-detectors comparing
to the ultra-short pulse duration, a part of the noise-
like signals of other users is also gathered by the de-
tector and degrade the performance of the receiver.
Some solutions such as using time gating (Lee et al.,
2002), second harmonic generation (SHG) (Ni et al.,
2007), self phase modulation (SPM) (Ni et al., 2007),
and two photon absorption (TPA) detectors (Jamshidi
and Salehi, 2007), have been proposed for the fibre
OCMDA systems to alleviate the MUI problem.
Multi-user interference estimation has been pro-
posed for decreasing the undesired interference ef-
fect of the users in multiple access networks (Brandt-
Pearce and Aazhang, 1994). But because all of these
methods was in electrical domain, the estimation pro-
cess takes much time and limits the bit-rate of the sys-
tem. Also it needs to the information of the other
users. In this manuscript we investigate a novel
method for declining the MUI effect on the signal of
the desired user in SPE-OFCDMA systems. In this
approach a interference estimation in optical domain
has been used for this purpose. Actually two photo-
detectors with different integration times are used to
estimate and reduce the MUI destructive effect on de-
sired signal. In the both of the proposed structures for
MID the effect of interference is reduced after making
an estimation of it. In the TMIE structure, an estima-
tion of the interference is made using the temporal
distribution of the MUI signal. Then an estimation
of the interfering signal is made using the output of
second detector and subtracted from the output of the
146
Yazdani A., Noshad M., Jaliloghli H., Jaliloghli A. and Noshad M..
OPTICAL DOMAIN MULTIUSER INTERFERENCE ESTIMATION FOR SPECTRAL PHASE ENCODING OPTICAL FIBRE CDMA SYSTEMS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003526701460149
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Communication Networking and Optical Communication System (OPTICS-2011), pages
146-149
ISBN: 978-989-8425-69-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
first one. In the second structure, NMIE, the inter-
ference has been estimated from the decoded signal
and a nonlinear function of it. The simulation results
shows the performance of the proposed technique.
2 PRINCIPLES OF SPECTRAL
PHASE ENCODING SYSTEMS
In the SPE-OCDMA systems, the bandwidth of the
ultra-short optical pulse of each user has been divided
into N
0
spectral bins with identical bandwidth and
the phase of each bin has been altered according to
a specific code sequence of that user. So at the out-
put of the transmitters the optical pulse become as a
noise-like signal. At the detector the conjugate of the
desired transmitter’s code is applied on the received
signal. Thus all of the phase alternations removed
at the decoder and the ultra-short pulse has been re-
vealed. For the signals of the other users the phase
shifts rearranged at the decoder but aren’t removed.
So the signals of the interfering users remain spread
and noise-like. In this study it is considered that users
have equal power at the receiver and each bit stream
from each user is synchronized. It should be noted
that power equality and synchronization are not nec-
essary for the system although we have used them to
simplify the analysis and simulation.
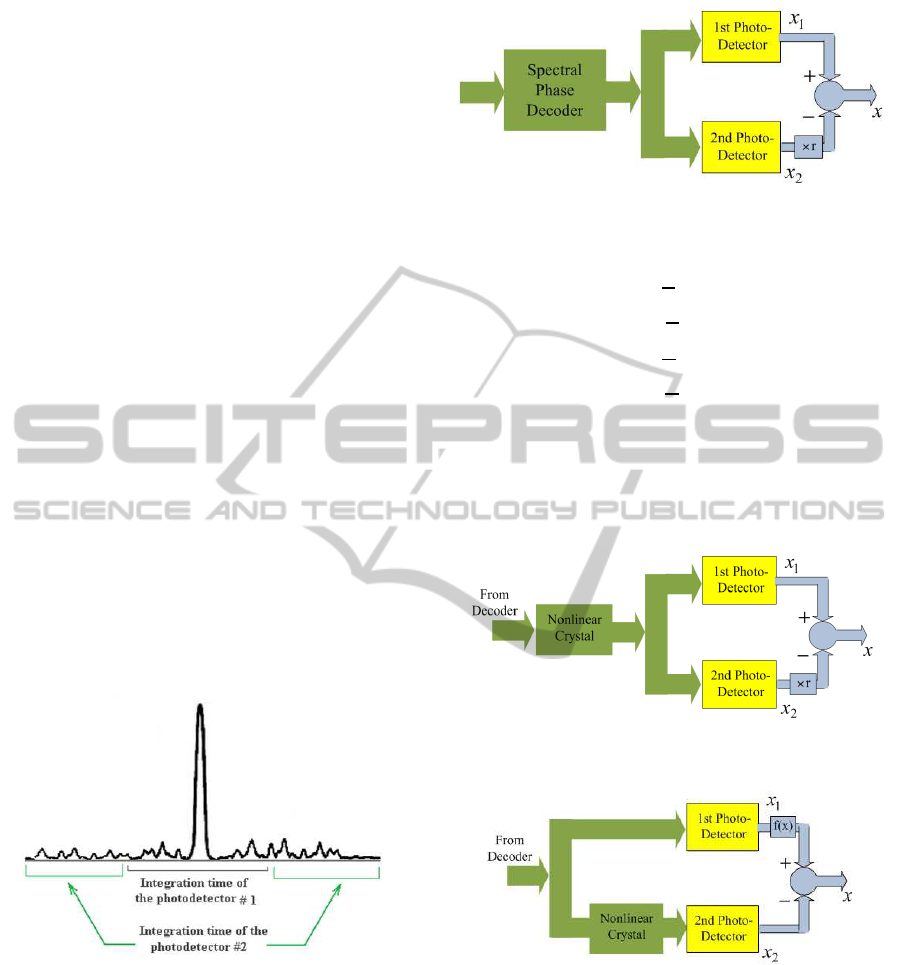
Figure 1: Integration times of the first and second photo-
detectors.
The MID receiver can be implemented in two
ways. In the first way is to use temporal multiuser
interference estimation (TMIE) to lower the MUI ef-
fect. This receiver consists of two photo-detectors,
one for collecting the main signal in the time duration
of T
1
and the other for gathering the interference sig-
nal due to the other users in the time duration of T
2
.
The two detectors can have an overlap in their inte-
gration time. The integration time of photo-detectors
is depicted in Figure 1. So the output signals of each
Figure 2: Structure of TIME receiver.
detector can be expressed as
X
1
=
Z
T
r
2
−
T
r
2
P
1
(t)dt (1)
X
2
=
Z
T
b
2
−
T
b
2
P
2
(t)dt (2)
We define a new output based on the outputs of
the two photo-detectors (Figure 2) as follows
X = X
1
− rX
2
. (3)
where r is defined as the ratio of integration times
Figure 3: TIME receiver after a nonlinear optical device.
Figure 4: Structure of NIME receiver.
of the first and second detectors, i.e. r = T
1
/T
2
. Re-
garding the autocorrelation function of the interfer-
ence signal in SPE-OCDMA systems (Salehi et al.,
1990), the mean of the MAI can be eliminated in X
but its variance will be increased. So the error proba-
bility will be declined.
The TMIE receiver can be used alongside the
other nonlinear approaches such as SHG and SPM as
illustrated in Figure 3. In this case the received signal
passes through a nonlinear media before the detection
OPTICAL DOMAIN MULTIUSER INTERFERENCE ESTIMATION FOR SPECTRAL PHASE ENCODING OPTICAL
FIBRE CDMA SYSTEMS
147
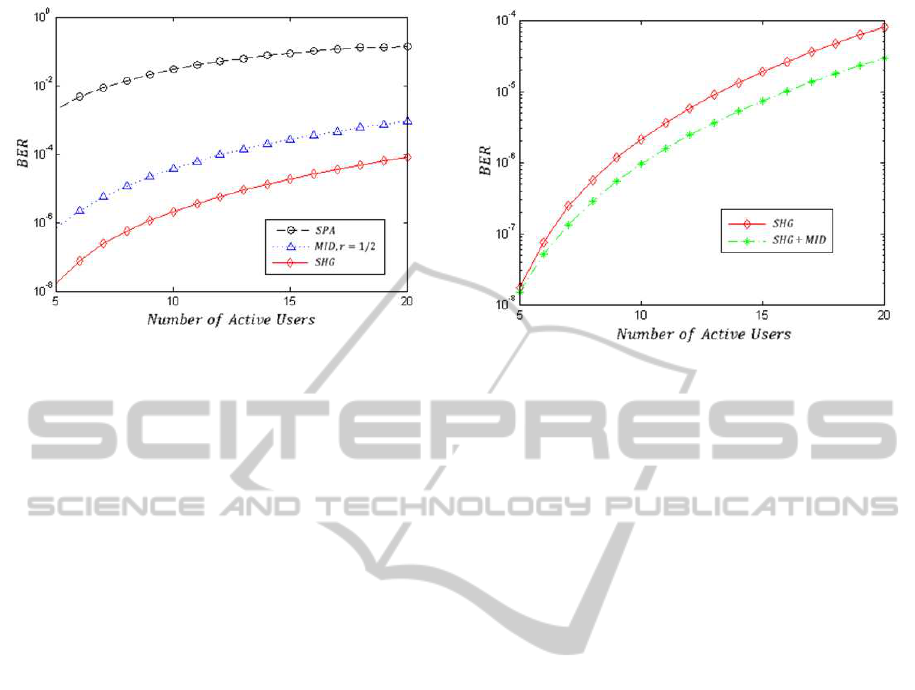
Figure 5: BER versus the number of active users for SPA,
MID and SHG receivers.
and then TMIE by two photodiodes is used for esti-
mating the Interference signal. Similar to the previ-
ous case the mean of the MAI signal can be removed
by selecting an appropriate value for the parameter r.
The other type of the MID receiver is Nonlin-
ear Multiuser Interference Estimation (NMIE) as de-
picted in Figure 4. In this kind of MID receiver two
photo-detectors are used for interference estimation
as before but with the same integration time. The dif-
ference between the photo-detectors is that the first
one integrates on the decoded signal but the second
one integrates on the decoded signal passed through
a nonlinear media. The output of the receiver in the
term of the first and second photo-detectors outputs
can be expressed as follows
X = f(X
1
) − X
2
. (4)
where f(x) is a function for canceling the mean of
the MUI signal at the output which depends on the
function of the nonlinear media. For example for the
receiver with SHG as nonlinear media f(x) is αx
2
,
where α is a proper coefficient.
3 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
In this section, performance analysis of the proposed
system will be made and compared with that of SHG
and Single Photon Absorption (SPA) codes. MAI has
been considered as the main performance degrading
factor of the SPE-OCDMA system and the shot noise
and thermal noises have been neglected. In our per-
formance analysis, 1Gbps bit rate and 20nm optical
bandwidth have been considered. Also, code-length
has been supposed to be 500. The results are for the
equal probable bit transmitting.
Figure 6: BER versus the number of active users for re-
ceivers using SHG and both SHG and MID.
The bit error rates for three different receivers,
MID, SHG and SPA, are depicted in Figure 5 versus
the number of active users for the 10mW optical peak
power for each user. As can be seen the SHG receiver
has the best performance comparing to the other re-
ceivers. But the interesting part of these results is the
performance of the MID receiver. In MID receiver we
are able to improve the system performance only by
using two photo-detectors and nothing else. Despite
the simple structure of the MID receiver, its BER is
only one order worse than the SHG receiver. Figure
6 shows the performance of a system when both SHG
and MID are used at the receiver. According to these
results the performance of the receiver with both SHG
and MID is a bit better than that of a receiver with
only SHG.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper a novel receiver for SPE-OCDMA sys-
tems has been introduced. The proposed system
works based on the estimation and reducing the inter-
ference signal of the other users. Two different struc-
tures, TMIE and NMIE, have been proposed. But of
these structures utilize two photo-detectors to make
estimation from the MUI signal. The TMIE receiver
has an acceptable performance comparing to the SHG
receiver regarding its uncomplicated structure.
REFERENCES
Brandt-Pearce, M. and Aazhang, B. (1994). Multiuser
detection for optical code division multiple access
OPTICS 2011 - International Conference on Optical Communication Systems
148

systems. IEEE Transaction on Communications,
42(2/3/4):1801–1810.
Jamshidi, K. and Salehi, J. A. (2007). Performance anal-
ysis of spectral-phase-encoded optical CDMA sys-
tem using two-photon-absorption receiver structure
for asynchronous and slot-level synchronous transmit-
ters. IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave Technology,
25(6):1638–1645.
Lee, J. H., The, P. C., Petropoulos, P., Ibsen, M., and
Richardson, D. J. (2002). A grating-based OCDMA
coding-decoding system incorporating a nonlinear op-
tical loop mirror for improved code recognition and
noise reduction. IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave
Technology, 20(1):36–46.
Ni, B., Lehnert, J. S., and Weiner, A. M. (2007). Per-
formance of nonlinear receivers in asynchronous
spectral-phase-encoding optical CDMA systems.
IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave Technology,
25(8):2069–2080.
Salehi, J. A., Weiner, A. M., and Heritage, J. P. (1990). Co-
herent ultrashort light pulse code division multiple ac-
cess communication systems. IEEE/OSA Journal of
Lightwave Technology, 8(3):478–491.
OPTICAL DOMAIN MULTIUSER INTERFERENCE ESTIMATION FOR SPECTRAL PHASE ENCODING OPTICAL
FIBRE CDMA SYSTEMS
149
