
SUPPORTING BUSINESS MODELING
USING MULTIPLE NOTATIONS
A Case Study
Moshiur Bhuiyan
School of Computing and Mathematics, Charles Sturt University, Study Centre, Darlinghurst, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Sohel Rana, Kamrul Hasan
OptInfra Systems, Sydney, Australia
Keywords: Agent Oriented Conceptual Modelling (AOCM), Requirement Engineering, i*, BPMN, Process Modeling.
Abstract: In this paper, we present a case study that illustrate the use of an approach that facilitates and supports the
combined use of i* and BPMN for performing business modeling in a synergistic fashion on a complex
project for a large government agency in Australia. We used a constrained development methodology to
facilitate this modeling practice. The purpose of this case study is to further demonstrate the applicability of
our proposed methodology in a real time, big scale industrial project.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many notations have been developed for the task of
modeling business processes, and each have their
own focus of application and appropriate audience
(Bider et al, 2002) (Katzenstein et al, 2000) (Kavakli
et al, 1999) (Yu, 1995). In particular, high-level
conceptual models provide an understanding of an
organization from an intentional and social
perspective for reasoning support during redesign
(Yu, 1995). In comparison, lower-level technical
models are especially suited for applications in the
description, execution and simulation of business
processes (Yu, 1995b).
We argue the analysts need to base business
process development on principled high-level
models of the enterprise and the business context.
Commonly, processes are formulated in an ad-hoc
fashion without reference to these high-level models.
Some of the most prominent modeling notations
enlisted are primarily focused towards technically-
oriented data, and process modeling notations such
as ER, Data-Flow, Systems Flowcharting and UML
and workflow modeling (Davies et. al. 2004).
In this paper we present a case study on a large
scale project in a government agency in Australia.
This case study illustrates how the business
modeling phase of the project was implemented with
the support of multiple modeling notations and a
constrained development methodology proposed at
(Ghose et al, 2006) (Koliadis et al, 2006a) (Koliadis
et al, 2006b).
The following section starts with background
information about the project. We then describe the
business modeling strategy that was followed along
with a brief discussion on the notations used. We
then provide an illustration of the methodology,
techniques and templates. Finally we have a
discussion section about the project and some
concluding remarks.
2 PROJECT BACKGROUND
This case study is based on a large public
department in Australia. The organization structure
is a complex array of directorates and business units
with varying needs. It required an enterprise
software solution, which can accommodate its strict
security requirements while supporting standardized
and decentralized processes for time tracking,
project management, resource management,
financial management and reporting. The
department chose to configure the CA Clarity™
301
Bhuiyan M., Rana S. and Hasan K..
SUPPORTING BUSINESS MODELING USING MULTIPLE NOTATIONS - A Case Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0003510703010306
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 301-306
ISBN: 978-989-8425-55-3
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Project system (CA Clarity™, 2010) since its ability
to provide the solutions to the organization’s above-
referenced requirements under the terms of strict
tender.
The department’s highest priority at the time of
the project was “client success”. This was to be
accelerated by improving corporate capabilities to
ensure the success of initiatives introduced for this
purpose. The project was a result of the department’s
need for a long-term project governance solution
that will also be used to manage a variety of critical
variables such as resource management, project
portfolios, and demand for services in a number of
major programs.
3 MODELING NOTATIONS
BACKGROUND
3.1 i* Modeling
It has been argued that notations such as i* help
answer questions such as what goals exist, how key
actors depend on each other and what alternatives
must be considered. Furthermore, i* has been
acknowledged as illustrating the key social/strategic
inter-relationships between actors (Katzenstein et al,
2000) (Yu, 1995) required for effective business
process redesign. This is achieved via support for
reasoning about organizational activities and their
assignment to various organizational agents
(Loucopoulos et al, 1995) in respect to: the ability,
workability, viability, and believability of their
routines; and, level of commitment (Yu, 1995).
The i* framework consists of two modeling
components (Yu, 1995): Strategic Dependency (SD)
Models and Strategic Rationale (SR) Models. The
SD model consists of a set of nodes and links. Each
node represents an actor, and each link between the
two actors indicates that one actor depends on the
other for something (i.e. goals, task, resource, and
soft-goal) in order that the former may attain some
goal. The depending actor is known as depender,
while the actor depended upon is known as the
dependee. The object around which the dependency
relationship centers is called the dependum. The SR
mode further represents internal motivations and
capabilities (i.e. processes or routines) accessible to
specific actors that ensure dependencies can be met.
3.2 Business Process Modeling with
BPMN
Many existing Business Process Modeling notations
primarily focus on technical process aspects
including the flow of activity execution/information
and/or resource usage/consumption (Loucopoulos et
al, 1995). This perspective is aimed at describing
the sequence of activities, events and decisions that
are made during process execution, however social
and intentional components lack representation. The
technical focus of these notations is especially suited
for applications in the description, execution and
simulation of business processes but is lacking in
support for process redesign and improvement (Yu,
1995).
One such notation is the Business Process
Modeling Notation (BPMN), developed by the
Business Process Management Initiative
(BPMI.org). BPMN can be seen as primarily a
technically-oriented notation that is augmented with
an ability to assign activity execution control to
entities (e.g. roles) within an organization with
‘swim-lanes’. This effectively provides a view of
the responsibilities and required communications
between classes of process participants, but does not
provide a view of other social and intentional
characteristics including the goals of participants
and their inter-dependencies.
Since its initial publication BPMN has been
accepted by the greater Business Process
Management community (Becker et al, 2005) (Smith
et al, 2003), due to its expressiveness and ability to
map directly to executable process languages
including XPDL (Fischer, 2005) and BPEL (White,
2004) (Ouyang et al, 2006). The wide uptake of the
notation by most BPM2 tool vendors is also a sign
of its longevity (Hall et al, 2005). Some
practitioners have hailed BPMN as supplying a rich
representation that allows Business Process
Management Systems (BPMS) the ability to control
the required interactions with humans and 3rd party
applications (Miers, 2004). Furthermore, an analysis
of BPMN (Becker et al., 2005) also stated its high
maturity in representing concepts required for
modeling business process, apart from some
limitations in terms of representing state, and the
possible ambiguity of the swim-lane concept.
4 BUSINESS MODELING
STRATEGY
The project management team decided to conduct
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
302
detailed business modeling in order to configure the
Clarity Systems based on requirements of the
stakeholders. The project team put special emphasis
to make sure the individual directorate and business
units’ requirements were addressed. There were few
challenges; the department was very large with
complex organizational structure making it harder to
implement the software solutions by eliciting and
analysing requirements from every directorates and
business units. Also changes at the organization
level as well as the operational level were very
common; so there was a need for a methodology that
could track these changes both at organizational and
operational level so that the changes to the software
can be supported comfortably without losing
consistency at these levels. On the other hand, CA
Clarity (Clarity™ Project) itself is an extensive
project and program management tool covering
variety of organizational requirements with its own
configuration complexity. The idea was to perform
business modeling exercise using two different
notations i* and BPMN with the help of a
constrained development methodology mentioned at
(Ghose et al., 2006) (Koliadis et al., 2006a)
(Koliadis et al., 2006b).
The business modelling strategy examined the
requirements for developing and maintaining one or
more business models within the project,
recommended the most appropriate approach and
defined the techniques, standards, roles and
responsibilities for developing and maintaining the
required models during the course of the project.
The business modeling strategy informed the Project
Plan, the Stage Plans, the Project Quality Plan and
required Business Models.
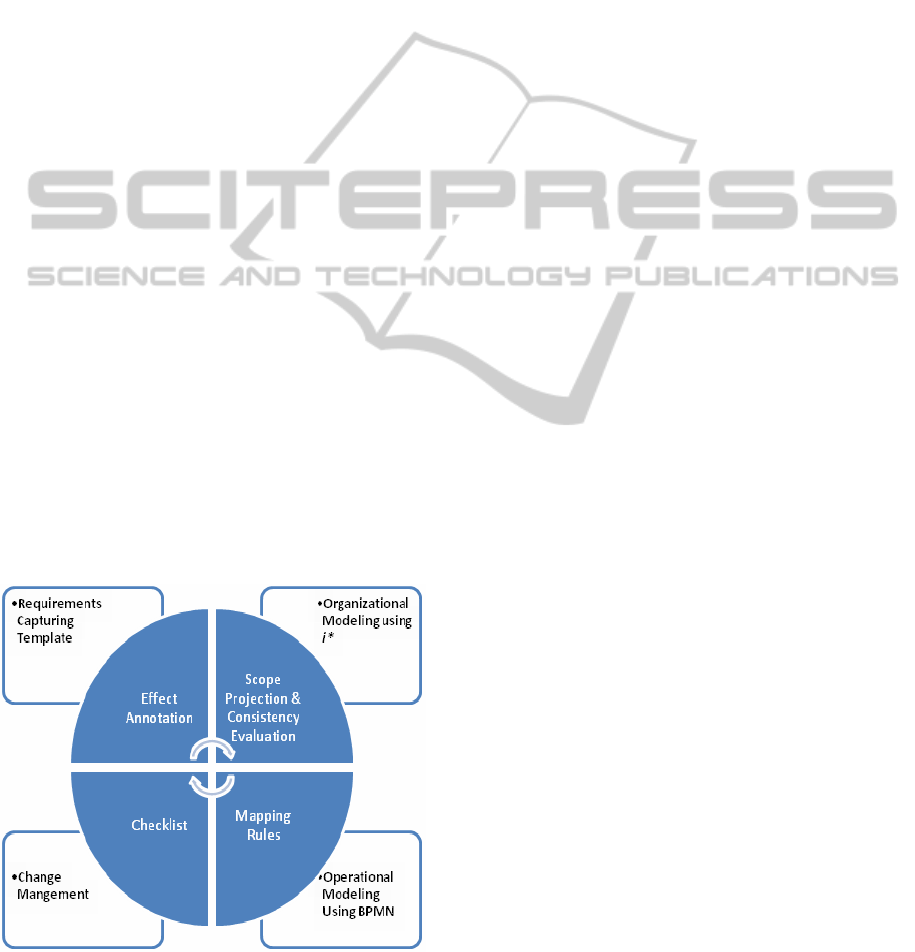
Figure 1: Proposed Modeling Strategy.
As mentioned earlier, proposed products of
business modeling were: High Level Organizational
Model (in i* organizational modeling notation),
Operational Business Process Model (in BPMN).
Given the organizational size and complexity of the
department it is quite normal to have a varied and
large range of business requirements models. The
large scope of the business units leads to greater
complexity. It was decided that a combination of
notations will be used in order to facilitate the
maintenance of the models in lieu of changes in the
context of their usage over the course of their
lifecycle.
For initial requirements engineering exercise i*
organizational modeling technique was used. These
models represented the scope, organizational
actors/roles and their dependencies and intentional
rationale. We then mapped the i* organizational
models into operational BPMN models and vice
versa (when required) using our constrained
development methodology.
5 MODELING APPROACH AND
METHODOLOGY
Early-phase RE activities have traditionally been
done informally (Yu, 1995), beginning with
stakeholder interviews and discussions on the
existing systems and rationales. Initial requirements
are often ambiguous, incomplete, inconsistent, and
usually expressed informally. We added some
structure to this informal consultation process via the
use of Requirements Capture Templates (RCTs).
In effect, these were forms that the modeller
seeks to fill out in the course of a stakeholder
consultation session and that were eventually signed
off by both the modeller and the stakeholder. The
process of filling out these forms provided structure
to stakeholder interview sessions. In addition, these
forms were designed to seek information specific to
the need of the underlying agent-oriented conceptual
model (i*) that the modeller seeks to build. As we
will show below these templates were designed in a
manner that makes it easy to systematically
transform them into SD and SR models.
Stakeholders were thus able to provide focused
input to the conceptual modeling task, while being
shielded from the complexity of understanding and
using the conceptual modeling language.
SUPPORTING BUSINESS MODELING USING MULTIPLE NOTATIONS - A Case Study
303
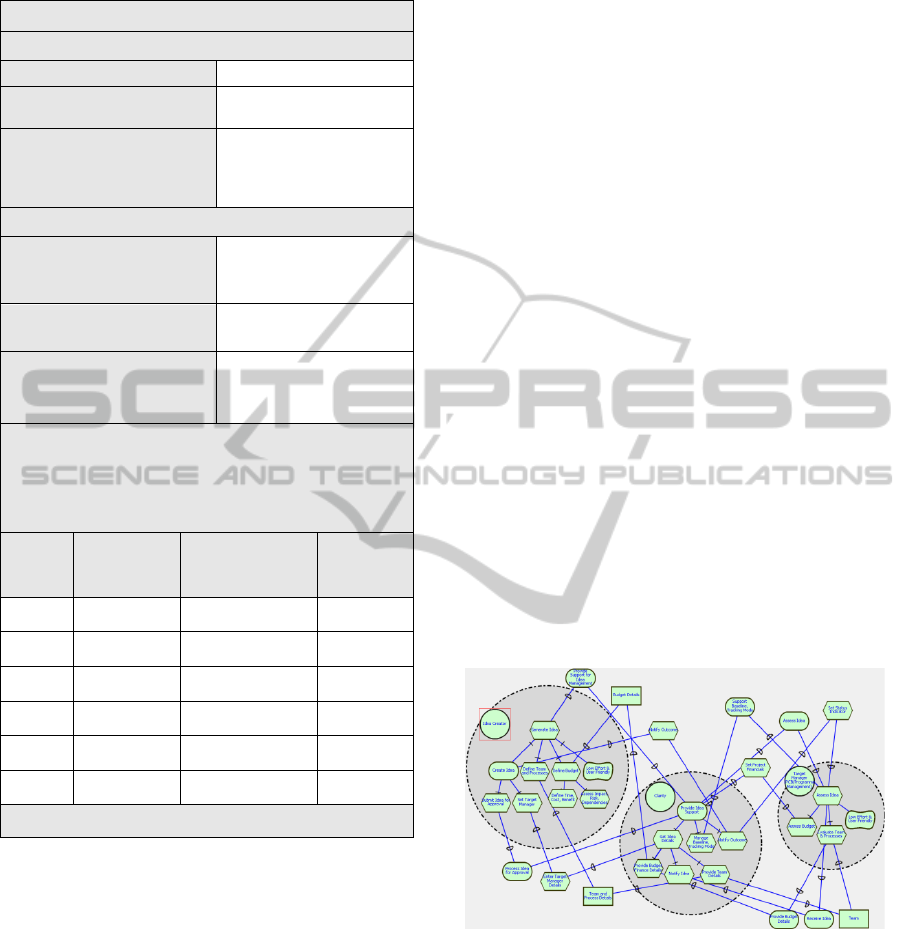
Table 1: Requirements Capture Template.
Requirements Capture Template
Function Elaboration for the department
Department Name
Function Name (Use separate
sheet for each function)
Function Rationales (Use
separate sheet for each function)
Activity Details for the Function
Activity Name and Description
(Use separate sheet for each
activity under the function)
Activity Rationales
Responsible Actor(s) involved in
the activity (Unique list of
Actor(s))
Relationship / dependencies between responsible actor(s) to
achieve / satisfy the above activity
(Relationship is described as the dependency from source actor on to
target actor, use separate row for each relationship And dependency)
Source
Actor
Relationship /
Dependency
Target Actor
Additional
information
Modeller Signature Stakeholder Signature
Once the templates were finalised and the i*
models were developed, we applied constrained
development methodologies proposed at (Ghose et
al., 2006) (Koliadis et al., 2006) (Koliadis et al.,
2006) to guide the derivation or maintenance of one
type of model given the availability of the other.
Figure 2 illustrate a sample SR model that was
developed for Demand Management modeling.
The development was supported with the
introduction of two concepts: fulfilment conditions
and effect annotations (i.e. as described in (Fuxman,
Liu, Mylopoulos, Pistore, Riveri and Traverso,
2004). An effect is broadly defined as the result (i.e.
product or outcome) of an activity being executed by
some cause or agent. An effect annotation is a
specific statement relating to the outcome of an
activity, associated to a state altering construct in a
given model. During BPM, effects are annotated to
atomic tasks/activities or sub processes within an
actor’s lane. The execution of a number of activities
in succession results in a cumulative effect that
includes the specific effects of each activity in the
sequence. We also note the fact that certain effects
can undo prior effects (i.e. in the case of
compensatory activities). Effect annotations may
possibly be formalized using the formal layers of
some currently well-developed Goal-Oriented
Requirements Engineering (GORE) methodologies
(Fuxman et al., 2004) (Lamsweerde, 2001),
however, we only state their applicability in this
work.
Fulfilment conditions were annotated to tasks
and goals assigned to actors in an SR diagram, and
dependencies (i.e. not including soft-goals as these
are used during assessment of alternatives and
describe non-functional properties to be addressed)
in an i* model. A fulfilment condition (Fuxman et
al., 2004) is a statement specifying the required
conditions realized upon the completion of a given
task, goal or dependency. Fulfilment conditions
recognize the required effects on a business process
model.
The application of the methodology was divided
into phases. Phases were annotating the i*
organization model, scope projection & consistency
evaluation, mapping rules.
Figure 2: SR Model of Demand Management.
All through the business modelings exercise, the
following criteria were followed:
• Reference models are aligned with the
Project Approach
• Modeling approach and technique meets
the modeling requirements in the most
efficient and cost-effective way
• Cost of tools and training provided are kept
to a minimum
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
304
• Models are easy to maintain and lend
themselves to an iterative approach
• Models require minimum specialist skills or
training to be interpreted by the project
team members
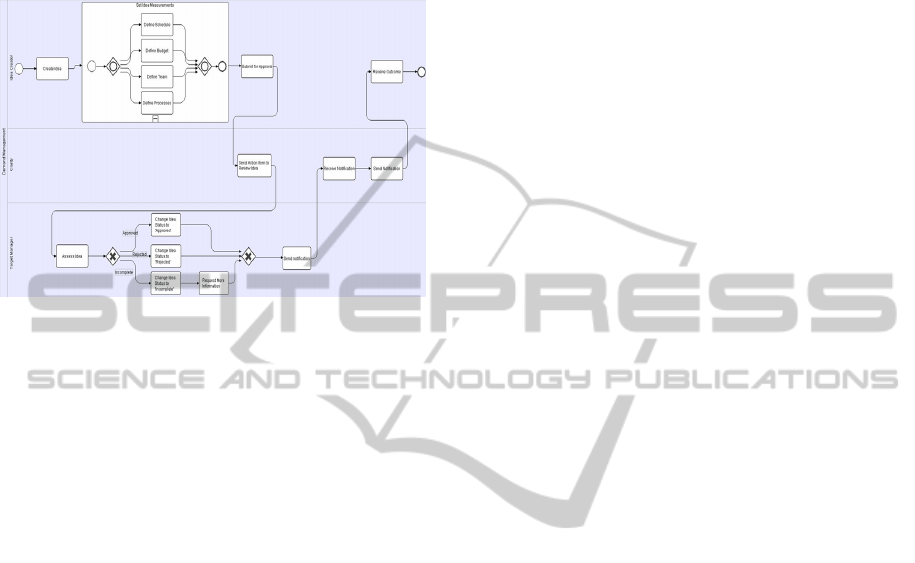
Figure 3: Represents a sample BPMN model derived from
the Demand Management SR model using the constrained
development methodology.
6 DISCUSSIONS AND LESSONS
LEARNT
Combined business modeling helped the project in
the following ways:
It helped the project to define its scope, identify
associated roles, their dependencies, represent the
processes embedded in the projects and clarify the
developers to design the test cases and implement
the configuration of the system.
Combined models acted as a common language
for communication for varied stakeholders’ goals,
policy implications, and/or operational constraints
by creating a contextual environment.
It helped to increase the department’s
organizational and operational management
capability by representing ‘what business process
exists’, and ‘what business process is required to
exist’.
The constrained development methodology used
in this exercise helped the modellers in two ways.
Firstly, it made the model transformation (i* to
BPMN and also BPMN to i* when required) smooth
and consistent. Secondly, in model management
when a change was required. This methodology
supported to tracing and managing changes in
organizational models and process models. We plan
to discuss this part in details in a separate work at a
later stage.
The RCTs presented here can ease the
requirements elicitation process. However, these
templates serve other useful functions as well. They
can provide a structured repository and record of
stakeholder interviews that can be revisited when
requirements must re-negotiated or revised (for
instance, when changes are made to models, or when
inconsistencies are detected). The detailed rationale
recorded in these templates can also be of value in
business process re-engineering. To anticipate and
support future business process re-engineering
efforts in the context of the department, we are also
detailing alternative solution scenarios by
completing additional RCTs that answer “how else”
questions (while the primary RCTs represent the “as
is” scenarios).
We do not claim this modeling effort was
successfully completed without any problems. We
did continue to get feedback from all parties
involved on the use of this methodology and
modeling exercise. Some of the concerns that rose
from the analysts are:
Firstly, model management is an important
issue/challenge perceived by many academics,
practitioner and vendors (Indulska, Recker,
Rosemann and Green, 2009). Hence, it is not
surprising to see that some of the analysts believe
that the implementation and management of two
business process models simultaneously might be a
quite difficult asks for many organizations.
Secondly, planning to integrate these
methodologies would bring various management-
related challenges such as change management and
resource commitment. This initiative would require
clear planning and goal setting which must be
accepted by the executives of the organization.
Without this and the commitment to the
methodology the initiative is unlikely to succeed.
Organisations with little or no expertise in the
process modeling area will likely to hire consultants/
modeling experts. While external consultants might
bring expertise and specialist knowledge into the
organisation, ROI need to be carefully examined.
Thirdly, according to Indulska et al (2009),
business process model’s ease of use is another
attribute that is highly regarded by many credential
practitioners, vendors and academics. Some of our
analysts believe that individuals without relevant
knowledge and expertise in the BPM area might find
this methodology quite challenging. This process
model should be fully understood otherwise it could
cause legitimate problems.
We believe the modeling implementation and
management implementation needs to be sustained.
The responsibility for this usually lies with
SUPPORTING BUSINESS MODELING USING MULTIPLE NOTATIONS - A Case Study
305

modellers, quality group, auditors or even the senior
project managers to ensure the methodology lives
long past it implementers and original sponsors. We
argue the implementation of this business modeling
is a long term goal. Once the exercise is complete
the aim is to keep them available and ensure the
benefits are realised full potential.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this work we have presented an industrial case
study that discussed the business modeling phase of
a project. We have illustrated the modeling strategy
and modelling approach. We have also discussed
how we used the constrained development
methodology and the requirements capture
templates. In our future work, we plan to elaborate
more details on the management of the multiple
models produced. We also plan to illustrate the fact
of how it was possible for us to implement the
transition to the “to be world” from the “as is
world”.
REFERENCES
Ghose, A., Koliadis, G., Bhuiyan, M., 2006. Correlating
Business Process and Organizational Models to
Manage Change, Australasian Conference on
Information System (ACIS2006).
Becker, J., Indulska, M., Rosemann, M., Green, P., 2005.
“Do Process Modelling Techniques Get Better? A
Comparative Ontological Analysis of BPMN,” in
Campbell, Bruce and Underwood, Jim and Bunker,
Deborah, Eds. Proceedings 16th Australasian
Conference on Information Systems, Sydney,
Australia.
Bider, I., Johannesson, P., 2002. “Tutorial on: Modeling
Dynamics of Business Processes – Key for Building
Next Generation of Business Information Systems,” in
The 21st International Conference on Conceptual
Modeling (ER2002), Tampere, FL, October 7-11,
2002.
CA Clarity™ Project system at http://www.ca.com/us/,
Accessed: 02/07/2010.
Fischer, L., 2005. Workflow Handbook, Workflow
Management Coalition, (WfMC).
Fuxman, A., Liu, L., Mylopoulos, J., Pistore, M., Roveri,
M., Traverso, P., 2004. Specifying and analyzing early
requirements in Tropos. In: Requirements
Engineering, Springer London, 9(2) 132–150
Koliadis, G., Vranesevic, A., Bhuiyan, M., Krishna, A.,
and Ghose, A., 2006a. Combining i* and BPMN for
Business Process Model Lifecycle Management. In the
Proceedings of the BPM-2006 Workshop on Grid and
Peer-to-Peer based Workflows, Lecture Notes in
Computer Science Series, ISBN 978-3-540-38444-1,
416-427, Springer Verlag.
Hall, C., Harmon, P., 2005. The 2005 Enterprise
Architecture, Process Modeling & Simulation Tools
Report, Technical Report, bptends.com.
Indulska, M., Recker, C., Rosemann, M., and Green, P.,
2009. Business process modeling : current issues and
future challenges. In: 21st International Conference
on Advanced Information Systems, 8-12 June 2009,
Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Katzenstein, G., Lerch, J., 2000. Beneath the surface of
organizational processes: a social representation
framework for business process redesign. ACM
Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS), 18(4),
(pp. 383-422).
Kavakli, V., and Loucopoulos, P., 1999. “Goal-Driven
Business Process Analysis - Application in Electricity
Deregulation,” Information Systems, Vol 24, No3, pp.
187-207, 1999.
Koliadis, G., Vranesevic, A., Bhuiyan, M., Krishna, A.,
and Ghose, A., 2006b. A combined approach for
supporting the business process model lifecycle.
Proceedings of the Asia-PacificConference on
Information System
Lamsweerde, A., 2001. Goal-Oriented Requirements
Engineering: A Guided Tour. In: The 5th International
Symp. In Requirements Engineering (RE’01), Aug.
Loucopoulos, P., and Kavakli, E., 1995. “Enterprise
Modeling and the Teleological Approach to
Requirements Engineering,” International Journal of
Intelligent and Cooperative Information Systems, Vol
4, No1, pp. 45-79.
Miers, D., 2004. “The Split Personality of BPM,”
Business Process Trends, bptrends.com.
White, S., 2004. Business Process Modeling Notation
(BPMN), Version 1.0, Business Process Management
Initiative (OMG.org).
Yu, E., 1995. Modeling Strategic Relationships for
Process Reengineering. PhD Thesis, Graduate
department of Computer Science, University of
Toronto, Toronto, Canada, pp. 124.
Yu, E., 1995b. “Models for Supporting the Redesign of
Organizational Work,” Proceedings, Conf. on
Organizational Computing Systems (COOCS'95)
August 13-16, Milpitas, California, USA. pp. 225-236.
Smith, H., Fingar, P., 2003. Business Process Management
– The Third Wave, Tampa, FL: Meghan-Kiffer Press.
Ouyang, C., van der Aalst, P., Dumas, M., and ter
Hofstede, M., 2006. “Translating BPMN to BPEL,”
BPM Center Report BPM-06-02, BPMcenter.org,
2006.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
306
