
A BUSINESS-FOCUSED IT SERVICE MODEL FOR CLOUD
David Miller and Mark Woodman
School of Engineering and Information Sciences, Middlesex University, Hendon, London, NW4 4BT, U.K.
Keywords: Business-focused IT, Alignment, IT governance, Service assessment, Service measurement, Service per-
formance, Service quality, Services science, Skills profiling, Experience based assessment, Assessment
framework, Service excellence, Cloud computing, Total business experience.
Abstract: The hitherto limited interpretation of service as deployed in IT value creation and solutions implementation
is perhaps a reason why so few IT projects are seen to have successful business outcomes. There are strong
indications that the commonly used measures of quality and performance have never been adequate for
complex services such as IT. As cloud-based technology changes the business and IT landscape it is impor-
tant to consider how IT services will evolve and can be managed to become more business-focused. A ser-
vices-based model for IT is described which has been developed from evidence gathered from business and
IT and ideas from other sectors. Validated in the field, it is designed around the high value touch-points be-
tween business and IT and uses needs-based and experience-based measures for business alignment and
service excellence. It is the first time that services have been identified formally as being necessary for
business and IT alignment. This is of critical importance to businesses using cloud-based solutions and con-
sistent with the service science notion of the co-creation of value.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing (‘cloud’ for short) is a significant
development in the delivery of IT services. Much of
the cloud discussion is currently of a technical na-
ture but the implications of cloud will be even more
profound for those buying, using and managing IT
services. The dominant worldview for IT service
provision is moving from one in which IT resources
are constrained by available capital, to a cloud-
influenced one where apparent commoditisation
means that resources are available as needed and
paid for on a utility basis: in budgetary terms we are
moving from capital expenditure for facilities (‘cap-
ex’) to operational expenditure (‘op-ex’).
Cloud is bringing about changes to both the IT
industry structure model and to business models.
Enterprises may choose to maintain a ‘cap-ex’ ap-
proach by installing managing their own private
cloud-based infrastructure to create internal services
e.g. the UK Government “G-Cloud” project (HMG
2010). Alternatively externally managed, ‘op-ex’
services can be obtained such as Software as a Ser-
vice, Platform as a Service, and Infrastructure as a
Service. (Whether these are truly ‘services’ is dis-
cussed below.) The range of services is increasing,
old competitive (vendor) advantages are being
eroded, and new ‘big brand’ entrants are now evi-
dent, e.g. Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Sales-
force.com, etc. The attendant new business models
are typically concerned with flexibility to do with
varying scale, dynamic facilities requirements and
operational efficiency; new opportunities are emerg-
ing in terms of how business might interact with
technology – i.e. by becoming both a consumer and
a configurator (Sharif 2010).
Arguably the beneficiaries of the changes will be
the consumers of what we might term commoditised
IT services across all parts of the business ecosys-
tem, from supplier to end user – hereafter collec-
tively referred to as ‘the business’. However, (as
discussed further below) primary and secondary
evidence shows that IT services are not delivering
business value. Hence, for cloud services a resolute
and diligent business focus is needed to be sure of
realizing business value from these services. The
challenge to the cloud-oriented IT services industry
will be whether it can meet the many needs of the
business, which is after all, the most important cloud
entity and the principle quality driver (Vouk 2008).
Cloud technology is still maturing, so there is
considerable uncertainty and much to be done to
309
Miller D. and Woodman M..
A BUSINESS-FOCUSED IT SERVICE MODEL FOR CLOUD.
DOI: 10.5220/0003389203090318
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER-2011), pages 309-318
ISBN: 978-989-8425-52-2
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

create a true utility (Buyya et al. 2008), but some
clear trends are emerging. Firstly there is heavy in-
vestment by the IT services industry in cloud tech-
nology which is attempting to commoditize IT
through product homogenization e.g. platform virtu-
alization, unit cost reduction, and ease of access.
Secondly there is a gradual ‘convergence’ of busi-
ness and IT:
• business people who are IT literate;
• businesses sometimes operate as the configu-
rators when purchasing cloud services;
• businesses are behaving as process engineers
using tools such as BPM;
• service concepts are transferring from the
business world to the IT world.
As IT is becoming more business-focused, prob-
lematically, the established IT service management
methods are grounded on the use of IT resources and
production processes (OTGI&OGC 2008); in a
cloud-based environment the business may have no
knowledge of these. The emergence of cloud com-
puting is an opportunity for businesses and IT ser-
vice providers to not merely improve current stan-
dards of IT service delivery but to adapt to the
changes now taking place within the industry so that
this improvement can be maintained.
This paper discusses the changing relationship
between business and IT. It considers new service
models and measures of performance and quality
that are more appropriate to a cloud environment
and which will impact on the way cloud facilities are
packaged, either as commoditised products or value-
enhancing services.
The paper is structured as follows. Section 2 out-
lines the research programme and the data from
which concepts used later have emerged. Section 3
discusses the nature of an IT service, how this can be
made to be totally business-focused, and describes a
service model and related concepts. Section 4 re-
views developments over recent years for measuring
services in IT and other sectors – going in some
depth into ideas from other disciplines to make the
point that metrics other than the traditionally techni-
cal need to be considered for cloud services. Sec-
tion 5 defines an assessment framework that meets
our definition of IT services and which is suitable
for cloud. Section 6 is the summary.
2 BUSINESS PROBLEMS WITH
IT/CLOUD SERVICES
The approach to cloud service provision is based on
output from a research programme that is looking to
maximize the business impact of IT.
The research approach is practice-based. It has
two parallel aspects - empirical (Miller 2008) and
grounded theory (Corbin and Strauss 2008). The
data for the grounded theory consists of 100 inter-
views with different people in several large interna-
tional enterprises from business (consumers of ser-
vices) and IT (suppliers of services). Each conversa-
tion is focused upon IT service improvement. So far,
100 codes or concepts have been identified from
almost 2000 coded segments of text. Five major
themes (or categories) have emerged to define the
complexity of the relationships between business
and IT, which must be managed if the business im-
pact is to be maximised. The central theme is the
total business experience of the service and its po-
tential as a measure for improvement; this will be
discussed. Space does not permit a full exposition of
the data and it’s coding; instead, interview fragments
from three of the companies, denoted ORG1, ORG2
and ORG3, will be quoted to provide a flavour of the
evidence.
Among the research aims is a better understand-
ing of the opportunities for value creation and the
role and nature of the service relationship between
the business and IT against the background of the
changes taking place within the IT industry such as
the emergence of cloud.
There are many facets to the problems if IT ser-
vices that affect cloud. Since businesses are con-
cerned with value, it is appropriate to start with that
concept. For example, a senior IT operations man-
ager from ORG1 said that
“Customers are probably
satisfied with the service from operations but would like
systems to respond more quickly to providing new or
additionalcapabilities... IT isnowmorewilling toprovide
value‐add services.”
Cloud makes this possible and
introduces an agility for provisioning that was not
available previously, although
“combined with the
other IT constraints of security, global standardization
etc. can mean long delays and frustration for the user.
Toomuchofadelayandthereisariskthattheywillstop
asking for help, a risk that they may go elsewhere and
sourcesolutionsoutsideoftheIT
domain.”
Cloud makes the combination of facilities tech-
nically easier too. However, the technology was not
the concern in either of the just quoted cases: there is
a need to manage the business experience such that
business value is added by IT services (of whatever
kind) and corporate controls are maintained. What
the IT manager of ORG1 has implicitly recognized
is that regardless of any current measure of service
quality, businesses operate on at least perceptions of
utility and value. As a senior IT applications man-
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
310

ager from ORG1 put it:
“[IThas]majorconcernsabout
managing expectation and delivering a service to meet
the business needs.”
The same organization’s quality
manager put the dangers more bluntly:
“End users
consider themselves the best and expect the best. Don’t
knowwhattheythinkofusbutitmaynotbegood.”
That fear is well founded. A board member of
ORG2 stated:
“…ITinvestmentprioritymustbegivento
initiatives which improve the design and delivery proc‐
esses.InITterms,[we]mustcontinuetostoplocalinitia‐
tives.When making investment decisions we must be
vigilanttoensurethattherearebenefitsandthatweare
notjustinvestingtomake
peoplehappy.”
A senior group manager in ORG3 said:
“The
whole business needsa betteruser experience.I expect
this to be achieved technically using portal and small
footprint devices to aprivate cloud.”
She also went on
to say that the problem went beyond simply engi-
neering the right technical solution. Because there
may be no direct control IT will need to be managed
differently; we have to think about what constitutes
the business experience and how this matches the
business need and the service specification. These
considerations are at the heart of the research re-
ported here: establishing the principles for services
in general so as to maximize the value returned by
utilizing cloud services
3 MAKING IT SERVICES
BUSINESS-FOCUSED
A significant confusion in practice is concerned with
the notions of service and product – not necessarily
about their definitions but about their role. For ex-
ample, the senior IT operations manager for ORG1
opined that IT
“could be offering a greater prod‐
uct/servicerange”.
Hence to start to address the busi-
ness challenges with the provision of cloud facilities,
a.k.a. services, a brief discussion of terminology is
useful.
Traditionally products and services have been
contrasted by describing ‘products’ as capable of
being manufactured and held in stock prior to pur-
chase (transfer of ownership). By contrast, the key
characteristics of ‘services’ are frequently referred to
as being their intangibility (e.g. consultancy), in-
separability (i.e. delivery and consumption happen
simultaneously), variability (i.e. each instance of the
delivery will vary depending on the subject busi-
ness) and perishability (i.e. service capacity not con-
sumed is lost forever).
IT has adapted, extended and even distorted
these ideas through firstly the standardization of
process and then the introduction of automation –
making them essentially products. Thus a business
service becomes an information service orchestrated
by a software product – e.g. using a web ‘service’ or
service oriented architecture. The existence of a
product in the delivery of a service also changes the
nature of the service required to support it; thus
though management has tended to focus on the
product element the product/service mix is what has
to be managed. By invoking measures of product
performance to assess the whole the critical act of
the co-creation of value becomes neglected. If the
same mistake is made with cloud-based services
major business opportunities may be missed.
A distinguishing attribute is the potential for
ownership: the consumer of a product can acquire
ownership, whereas the consumer of a service can-
not. This also has a significant effect on how a busi-
ness perceives the value and utility it might need
from a product or service such as cloud.
Ultimately, a full debate on the appropriate ter-
minology is probably needed. For brevity in this
paper we will generally assume a consensus on their
meanings. In the context of cloud-based IT our posi-
tion is that if the value is inherent in a product and is
realized by its consumption then we have a product-
orientated supply chain. If the value is co-created by
the supplier of the service and its customer – who
implicitly enter a mutually dependent relationship –
then we have a service-orientated supply chain. Ac-
cordingly, we see services as people-dependant ac-
tivities, which may be exploiting product within the
mix.
By definition hardware and software product and
information services such as web based applications
or requests for shared resources (e.g. from a cloud)
are perhaps firstly an output from a value creation
service and secondly potential inputs to other people
services where it has been recognised that there is
value in their consumption. The business, however,
may see both the people-related services and the
information-based services as integral and will judge
the IT services provider accordingly. For instance, a
director of ORG2 stated:
“IT must adequately equip
Company2toworkwithcustomers,partners,andsuppli‐
ers as a virtual team.”
This is a crucially important
point when designing cloud-based services: business
assumes that people are part of a service (in which
value is co-created) and judge the service according
to how well it meets their needs. Technology may
enable a service to be provided in the first place, and
automated to minimize people dependency, but the
technology options, the service specification, the
delivery, the discussions about service improvement
A BUSINESS-FOCUSED IT SERVICE MODEL FOR CLOUD
311
opportunities, etc. come from people. Thus the busi-
ness will look to IT to not just deliver good product
but also to contribute to value creation – achieved by
matching the service to the business need.
If an enterprise is to maximise its opportunities
to gain business value from cloud, it must reflect
these principles in the technical and management
models it adopts. In other words, while the technical
developments of cloud computing progress (and are
sometimes packaged as ‘services’), deep service
ideas that connect to business needs and the realisa-
tion of value must also be progressed. Our experi-
ence shows that there are significant beneficial con-
sequences associated with maintaining a business
focus. As an engineer in ORG2 said,
“Improvements
willprobably comethrough a moreintegrated effortand
amoreintegratedteam,i.e.businessandITpeoplework‐
ing together.”
, and “ORG2 must have a more homoge‐
nous technical environment that improves the connec‐
tivitybetweenORG2,Corporate ,restofthegroup,part‐
nerandclientorganisations.”
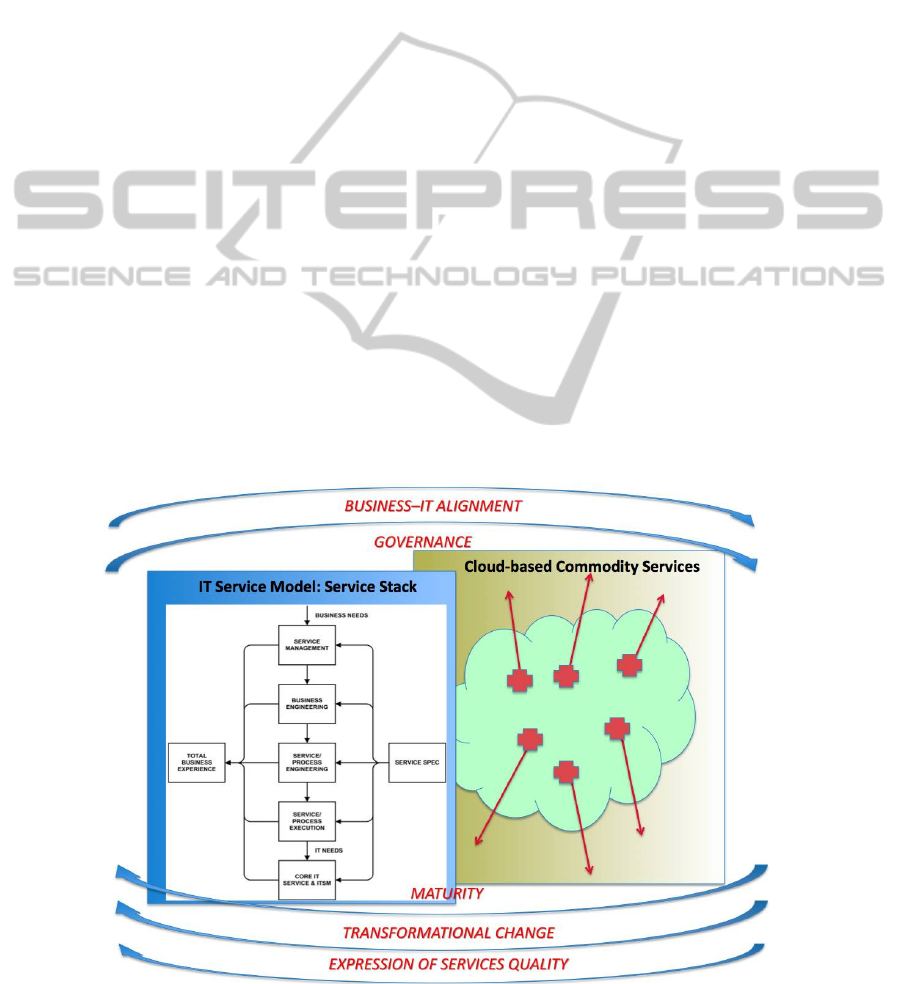
Figure 1 shows the layers of a particular tried-
and-tested IT service model (Miller 2009) and iden-
tifies the related concepts that have had to be rede-
fined not just for a business-focused service model
but also in a cloud context:
• The expression of service quality
• Business–IT alignment
• Governance
• Maturity
• Transformational change.
Miller’s IT service model shows that business
needs, the total business experience and a service
specification are interrelated through a five-layer
‘service stack’: (1) service management, (2) business
engineering, (3) service/process engineering, (4)
service execution and (5) Core services and Opera-
tional IT service management.
This is an important shift from the past focus on
the IT requirements specification which embodies
only the bottom layer of the five service categories
described by the service stack. We argue that this
has contributed to the persistently low success rates
in terms of the business outcomes of IT projects over
the last forty years, e.g. (Standish 2009) and others;
see (Miller and Woodman 2010) for that discussion.
The consequences for maximizing business value
from cloud services are that mere IT requirements
specifications are not enough.
Our evidence shows a ‘perception gap’ between
business and IT. This perception gap arises not just
because of the poor success rates just mentioned but
also because IT typically uses a product orientation
to measure IT service performance, according to the
IT requirements specification and the service
specification or service level agreement, whilst the
business is asking itself whether the total business
experience of using the service meets their needs –
an assessment of satisfaction with a broad range of
services, not products. Hence the business
Figure 1: Expanding the management model.
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
312

inclination is to measure and assess services, while
the IT inclination is to measure a assess product.
This product orientation by IT has limited the nature
of discussions with the business, limited business
expectations of IT and limited IT’s ability to add
value. There is a question as to whether the manner
in which IT services are currently measured has ever
been adequate for something as complex as IT,
never mind cloud. Add to this the necessity to deal
with the complexities of modern businesses: the
business ecosystems and service supplier and solu-
tion relationships make the co-creation of value a
more significant opportunity.
Arguably the existing IT management methods
are even less helpful in the context of cloud if they
rely on controlling the IT resources and processes.
Those management methods are of diminishing
value in an environment in which cloud has an in-
creasing influence, except perhaps where it is possi-
ble for an informed cloud user to have total visibility
of, if not control over, the IT resources and proc-
esses used by the cloud service provider. For these
reasons the way all IT services, including cloud ser-
vices, are managed must now include a measure of
which reflect the business experience of the service.
ORG2’s director reflected a common business
stance on the consequences of ignoring this:
“The
culture of the group is such that if IT does not listen or
failstorespondtodemand,thenotherswilldotheirown
thing.”
An IT service model suitable for cloud such as
that described provides the means of bringing about
this change. It tells us which activities need to be
embraced and we now have to ask if current metrics
and expressions of business value are all that is
needed for service management and service
improvement purposes.
4 RELATED WORK
This section reviews work related to the points
raised. It considers developments pertaining to the
measurement of service performance and service
quality not just in IT but in other sectors and other
management disciplines. Due to space limitations
and to highlight how a non-IT view of service qual-
ity can be relevant, this brief review somewhat over-
emphasises the concepts from other disciplines.
As business has moved from the industrial era to
the services era (Grant 2000) performance manage-
ment systems have had to adapt. Quantitative service
performance measurement has been the main means
of monitoring and improving performance in deliv-
ering services. IT too has adopted this approach by
managing the production processes that have been
developed to automate the information services. The
receiver of cloud services does not control the pro-
duction process and so to improve services to busi-
ness involving cloud a greater emphasis must be
placed on analysing and measuring the experience
received. The business experience of general service
consumption can be always assessed regardless of
who delivers it and how it is delivered – provided
we can agree on the measurement method. Business-
focused measurement of IT services (i.e. of the kind
relevant to business people) is not yet widely used
but we can expect it to include service performance,
service quality and other measures that are ulti-
mately connected to cloud computing including
what is already available to us.
Service quality measurement has been under de-
velopment by marketing professionals for the busi-
ness-to-consumer sector since the 1980s as a means
of understanding customer expectation and satisfac-
tion. This has given rise to the concept of ‘discon-
firmation’ (Zeithaml et al. 1988) as described within
a service quality model. Disconfirmation uses the
pre-consumption expectation as a reference point for
a comparative judgment that is made following the
actual delivery of a service. Service quality is as-
sessed using what is referred to as the attitudinal
headings of: tangibles, reliability, responsiveness,
assurance, knowing the customer, and access. Ser-
vice quality has been controversial not least because
of its relative subjectivity. Some would argue that
measures of service performance are all that is
needed (Cronin. and Taylor 1992). However, be-
cause much of this debate was in a business-to-
consumer context there was little concern for the co-
creation of value.
Customers generally expect more than they get;
so there is a risk associated with trying to improve
customer perceptions if the assessment is made from
a single viewpoint (Rosen et al. 2003). Be that as it
may, when businesses (as the consumers of cloud
services) perceive the cause of service failure to be
within the control of the service provider, and so
likely to occur again, they will be more dissatisfied
than when the opposite conditions hold (Bitner
1990). We conclude that to eliminate the most likely
causes of failure we must understand them, especial-
ly those that may occur again.
Methods of assessing IT solutions focus on
measuring value, which is also close to the service
performance viewpoint. Where possible, and more
precisely, these assessment methods measure the
price-value comparison of systems from the perspec-
A BUSINESS-FOCUSED IT SERVICE MODEL FOR CLOUD
313

tive of value for money. Value-based software engi-
neering (Boehm 2003) introduces seven key ele-
ments that provide the foundations: benefits realisa-
tion analysis, stakeholder value proposition elicita-
tion and reconciliation, business case analysis, con-
tinuous risk and opportunity management, concur-
rent system and software engineering, value based
monitoring and control, and change as opportunity.
A value perspective also implicitly requires a focus
on outcomes.
By contrast, COBIT (ISACA) and ITIL (OGC
2010) are IT-focused methods for auditing the de-
ployment of IT resources and the production proc-
esses that are constantly being updated to keep pace
with changes in technology. Their focus is opera-
tional systems.
These and as many as twenty other frameworks,
methods and standards (each typically with their
own operational focus) are used in combination by
many but have they been criticised because there has
been little attempt at internal standardisation or
process definition (Galup et al. 2007).
Another problem relevant to cloud services is the
confusion between notions such as IT service man-
agement (ITSM), business services management
(BSM), and IT governance (Winniford et al. 2009).
Some suggest a closer alignment with business.
(Velitchkov 2008) points to the vast array of devel-
opment/management methods and the generally ac-
cepted view that IT is failing to meet business ex-
pectations. He suggests that the fault lies in the lack
of business and IT alignment, problems with IT
strategy and inadequate control mechanisms. As a
solution he advocates extending the architectural
approach (Zachman 1987; Zachman 1978) by com-
bining the objects within the domains of enterprise
architecture and IT strategy. Others also focus on
enterprise architecture and advocate its use as a cor-
porate planning tool by the inclusion of business
model components like goals, products, markets, or
competitors (Winter and Schelp 2008). Such archi-
tectural developments have been the basis of many
automated tools and they will become more impor-
tant but there is a risk that reliance on approaches
such as this underestimate the dynamics between the
IT service provider and the business required for the
co-creation of value.
If we are to rise to the challenge of maximising
the value business experiences with cloud comput-
ing, we must progress the theory of service value
creation, or co-creation, (Chesborough and Spohrer
2006). To achieve that we must look beyond the
traditional IT boundaries and recognise that the ser-
vice science is becoming multi-disciplinary
(Glushko 2008). As an example, (Pinhanez 2008)
describes the benefits of applying services science
principles to the design of on-line service applica-
tions. Worldwide there is an interest in innovation
in the services industry and (Feldman et al. 2006)
describe the importance they attach to business de-
sign and implementation, business optimisation and
management, and service delivery. Two key themes
here are the component business model and virtual-
isation, combining different disciplines in creative
ways to make this successful. Many of us are locked
into a manufacturing/production paradigm” (Spohrer
and Maglio 2008) and as the nature of the relation-
ship between the business and the IT service pro-
vider changes, driven in some part by cloud-based
technologies, we must consider how that relationship
needs to be managed in the future.
In a converged world where a business is able to
utilize commoditised IT services from cloud, we
should model and assess those services using a wide
range of management skills (including IT). Recog-
nising the importance of the more intangible proper-
ties of service in the context of marketing profes-
sional services, (Kotler et al. 2002) developed the
concept of brand equity. Here it is used to describe a
brand’s overall strength as a function of its image,
the price-value relationship it offers, and customer
loyalty. They explain that all three factors influence
each other though in the case of IT services the dura-
tion of a business-supplier relationship can often be
the result of product inertia or lock-in rather than
service loyalty. Lock-in will arise in cloud as a con-
sequence of a lack of standardisation (Buyya et al.
2008). When applied to something as complex as IT
services the work suggests that a wide range of qual-
ity and performance measure are appropriate..
A number of strategic frameworks for managing
organisational performance were developed in the
1980s and 1990s to overcome the obvious dangers
of simply relying on financial information. These are
the Malcolm Baldridge National Quality Award
(MBNQA), European Foundation for Quality
Management(EFQM)and the Balanced Scorecard.
The limitations of each have been identified (Dror
2008). These models were not designed for anything
as complex as today’s businesses in which a de-
pendency on complex IT is embedded and it can be
safely assumed that they are not contenders for
measuring IT services in any context including
cloud.
The added complexities of outsourced services
cannot be omitted from this discussion as it is an-
other area where the IT resources and IT processes
may be obscured from the business. The work of
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
314
(Vandaele et al. 2007) describes the management
relationships between consuming organizations and
service suppliers and usefully separates the concepts
of contractual governance and relationship govern-
ance. Both are treated equally but the relationship
between them is not further defined. Contractual
governance in the context of cloud is important and
may break new ground where it is necessary to seek
guarantees, e.g. that data storage or processing must
only be undertaken within countries with adequate
data protection legislation.
In some parts of the services sector organizations
seek to manage customer experiences and to use this
to design service delivery systems (Zomerdijk and
Voss 2009). Although their work was limited in
scope and complexity they advocated designing ser-
vices around the key touch-points. This applies to IT
and cloud services in particular and the service stack
is such a service model.
IT must embrace a wider range of measures that
more reasonably reflect the complexities of the rela-
tionship between the business customer and IT and
that this is likely to lead to a heightened awareness
of the opportunities to add value.
5 DETERMINING THE TOTAL
BUSINESS EXPERIENCE
As services become dominant in many economies,
and as cloud is adopted for IT service provision,
there need to be consequential changes to business
models and to the IT industry, especially in the way
service quality is expressed. Some way of measuring
performance is needed which enables us to improve
the quality of those services to the business cus-
tomer, including value creation, success rates, and
hastening the onset of maturity, in a way that hasn’t
been achieved before.
The proposed method has been used during suc-
cessful consultancy assignments for improving IT
services and should be seen in the context of a Ser-
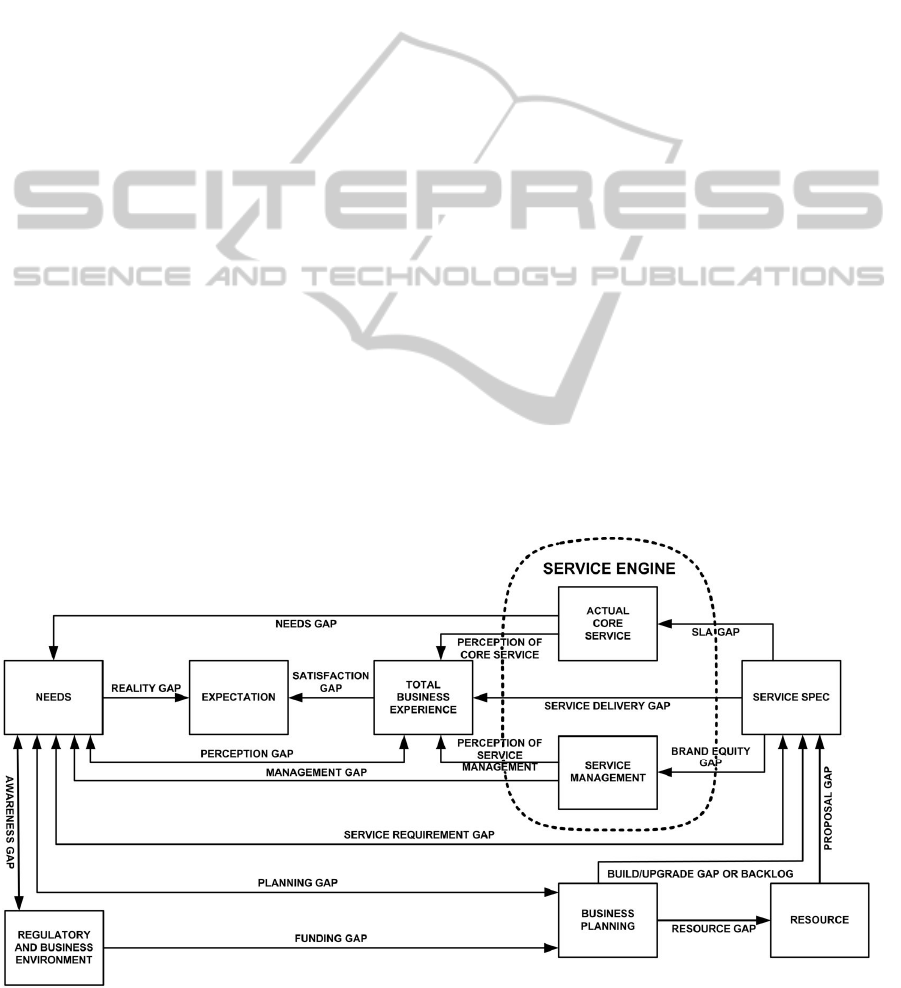
vice Excellence Model (SEM) (Miller 2008, Fig. 2.2
p28). The model is a business-to-business extension
of the business-to-consumer service quality model
(Parasuraman et al. 1985). The SEM as depicted in
Figure 2 is used for establishing service excellence
by checking for the existence and nature of any ser-
vice gaps. These can either be gaps in service plan-
ning or service delivery. Cloud should have benefi-
cial implications for many aspects of service plan-
ning, e.g. Funding Gap and Resource Gap, and so
improve expectation. Whereas the consumer model
used in marketing is based on the perception of ser-
vice and the buy/no buy decision, the SEM is based
on the total business experience for the purpose of
service improvement. For cloud computing the focal
point of the SEM is the service engine at the heart of
the model, which is circled in Figure 2, and its out-
put, the Total Business Experience (TBE). The ser-
vice engine encompasses the functions provided by
the core service(s) actually supplied and service
management. (These are explained later.) By being
able to comprehensively assess the TBE against the
Figure 2. Service Excellence Model, adapted from (Miller, 2008).
A BUSINESS-FOCUSED IT SERVICE MODEL FOR CLOUD
315
business need the service engine can be improved
and thus the TBE provides a measure of alignment
Consider for example the different cloud experi-
ences from software as a service, platform as a ser-
vice, and infrastructure as a service in the supply
mix of the service engine. Will the business express
its preferences for cloud facilities as ‘true’ services
rather than as rented products?
By applying the work of Kotler et al. to IT ser-
vices we could argue that the TBE is a function of
the price-value relationship of the core service and
the brand value created by its externally facing ac-
tivities. In order to make this useable in an IT and
cloud context we have substituted the term ‘core
services’ (C) for ‘price-value relationship’ and ‘ser-
vice management’ (M) for the ‘brand value’ of the
externally facing activities. This can be expressed as
follows:
Total Business Experience (TBE) = ƒ(C, M)
Picking up on the multi-disciplinary nature of
value creation in the preceding section, this relation-
ship has been developed further by considering the
properties of the business experience that contribute
to delivering core services and service management
respectively in the context of IT and how a value for
the TBE can be derived from these properties; this is
covered in more detail in the next section.
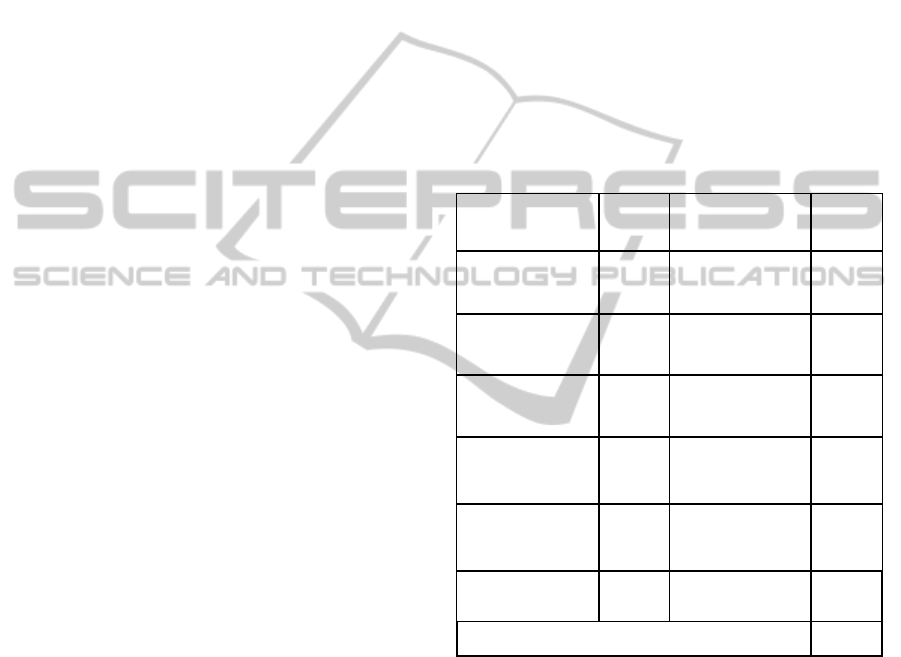
Miller (2008) has devised a framework for un-
derstanding TBE. Table 1 illustrates the approach
for profiling the properties that the business experi-
ences when consuming a service. It is based upon
elements from the review in Section 4 used in com-
bination with the SEM. Together they identify and
address issues of:
• Commonality (common causes of concern)
• Cause and effect
• Supply and demand.
The table represents a summary of an assessment
of the properties of a given IT service. The resulting
profile is typically based upon multiple perspectives
and constitutes a consensus view or one held as true
by the key stakeholders (Becker and Bjorn 2007). It
expresses the extent to which these different proper-
ties of the service meet the ideal needs of the busi-
ness. Comparisons with other suppliers or with con-
ventional maturity models are not introduced into
the assessment unless these are relevant to any of the
stakeholders or the business case thus avoiding any
risk of the over-engineering of the services.
The properties are generic to any service but here
are modelled on IT service provision in a business-
to-business context. Each property is broken down
into some detailed dimensions and measured using
appropriate criteria incorporating the standard quan-
titative and qualitative measures. If we compare the
scope of this approach with existing practice in IT,
the service performance metrics used with the many
IT methods are principally confined to the properties
concerning the definition and the delivery of the
products and services of Table 1. This can be seen,
for example, in the work of the SFIA Foundation
(SFIA 2003). Thus existing investment in these
methods is not wasted but that investment may be
insufficient. Service quality data used in IT is simi-
larly restricted to assessments of the people and the
culture. Thus, current IT-related methods only par-
tially address 3 of the 10 properties within the scope
of this new framework.
Table 1: Assessing the service experience.
PROPERTY SCORE PROPERTY SCORE
Definition of prod-
ucts and services
85 Business and sector
awareness
65
Delivery of prod-
ucts and services
85 Marketing and
communications
60
Bought-in products
and services
75 Sales and value
creation
50
Security 80 Commercial, finan-
cial, compliance, &
admin
80
Technology 75 People, organisa-
tion and culture
65
Core services score
(C)
80 Service Mgt score
(M)
64
Total Business Experience (TBE) 51
The table identifies the key elements of the as-
sessment arranged in two pairs of columns; the first
pair contains the five properties representing the
core service/product with a score (out of 100) for
each, the second pair contains the five properties that
influence service management and their scores. The
whole constitutes what the business experiences as a
result of receiving the service. Each score represents
the extent to which those properties meet the ideals
required by that business. The scores represent the
consensus view resulting from a 360 degree assess-
ment by business people, representatives from the IT
service provider, and other key stakeholders across
the ecosystem. The improvement and developmental
ideas resulting from the gap analysis are subjected to
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
316

importance/performance assessments.
Overall, the core service activities have more
quantitative performance measures than the service
management activities where qualitative judgments
are more prevalent.
The average score for the core services (C) and
the service management (M) are the statistical mean
of the properties of which they are comprised. The
Total Business Experience (TBE) is calculated as the
product of the score for the core service and the ser-
vice management and expressed as a percentage of
the ideal, i.e.
C = (85 + 85 + 75 + 80 + 75) / 5 = 80%
M= (65 + 60 + 50 + 80 + 65) / 5 = 64%
TBE = (80
x 64) / 100 = 51%
The empirical evidence from several commercial
case studies suggests that poor service management
reduces the impact of the core service and that this
formula yields the closest expression of the func-
tional relationship between the core services, service
management, and the TBE. The scores for the TBE
contrast markedly with those from typical customer
satisfaction surveys which are often treated as public
relations exercises and where much higher scores
have come to be expected. From a business im-
provement perspective the output from an assess-
ment and discussion of the TBE is likely to yield
many more improvement opportunities for attaining
service excellence.
Subjectivity is minimised but not eliminated by
the detailed breakdown of the properties into their
dimensions and by the assessment methods used
such that there has never been any dispute about the
results of the analysis amongst stakeholders. The
model is also frequently used in workshop sessions
following minimal explanation with good results.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Current IT-focused methods of managing IT ser-
vices have not, on their own, been totally successful
as far as business is concerned; arguably they will be
less relevant where there is no knowledge of the
resources or production processes used, e.g. cloud-
based technologies.
The emergent service based method of assess-
ment and alignment with business builds on a key
concept of service science, that of the co-creation of
value. This is believed to be the first time that ser-
vices have been identified as formally being neces-
sary for business and IT alignment.
The hitherto limited interpretation of services
deployed in IT value creation and solutions imple-
mentation is perhaps another reason why so few IT
projects are seen to have successful business out-
comes. By contrast a study based on these ideas for a
global financial services organisation generated
around a hundred service improvement initiatives
across ten work streams.
By taking ideas from sectors where the concepts
of product and service are easier to comprehend, we
have shown that IT management, including where
services are in the cloud, can be redefined to become
more business-focused using new service models:
• The Service Stack: designed around the high
value touch-points between business and IT
• The Service Excellence Model using gap
analysis as an indicator of service quality
• Total Business Experience: framework for
assessing and aligning service needs.
REFERENCES
Becker, J. and Niehaves B. 2007. "Epistemological
perspectives on IS research: a framework for analysing
and systematizing epistemological assumptions."
Information Systems Journal 17:197-214.
Bitner, M.J. 1990. "Measuring Service Quality: A
Reexamination and Extension." Journal of Marketing
54(April 1990):15.
Boehm, B. 2003. "Value-Based Software Engineering."
ACM Software Engineering Notes 28(2):12.
Buyya, R., Yeo, C.S., Venugopal, S., Broberg, J., and
Brandic, I., 2008. "Cloud Computing and Emerging IT
Platforms: Vision, Hype, and Reality for Delivering
Computing as the 5th Utility." In
CloudITPlatforms2008.
Chesborough, H. and Spohrer, J., 2006. "A Research
Manifesto for Services Science." Communications of
the ACM 49(7):8.
Corbin, J., and Strauss, A., 2008. Basics of Qualitative
Research. third edition Edition: Sage.
Cronin., J. J., and Taylor, S.A., 1992. "Measuring Service
Quality: A Reexamination and Extension." Journal of
Marketing 56(July 1992):15.
Dror, S., 2008. "The Balanced Scorecard versus quality
award models as strategic frameworks." Total Quality
Management 19(6, June 2008):12.
Feldman, S. I., Nathan, K.S. , Li, T., Hidaka, K., and
Schulze, C., 2006. "The Clarion Call for Modern
Services: China, Japan, urope, and the U.S."
Communications of ACM 49(7):4.
Galup, S., Dattero, R., Quan, J.J., and Conger, S., 2007.
"Information Technology Service Management: An
Emerging Area for Academic Research and
Pedagogical Development." In SIGMIS CPR'07. St.
Louis..
Glushko, R J. 2008. "Designing a service science
discipline with discipline." IBM Systems Journal
47(1):13.
A BUSINESS-FOCUSED IT SERVICE MODEL FOR CLOUD
317

Grant, R. M. 2000. "Shifts in the world economy: The
drivers of knowledge management." In Knowledge
horizons: The present and the promise of knowledge
management, ed. C. Despres and D. Chauvel:
Butterworth-Heinemann.
HMG. 2010. HM Government ICT Strategy January 2010.
ed. Cabinet Office. London: HMSO.
ISACA. COBIT, Available from: http://www.isaca.org/
Knowledge-Center/COBIT.
Kotler, P., Hayes, T., and Bloom, P., 2002. Marketing
Professional Services. 2 Edition.
Miller, D. 2008. Business-Focused IT and Service
Excellence. 2
nd
edn.. British Computer Society,
London.
Miller, D., and Woodman, M., 2010. "Software
Engineering Systems as Services Using a Business-
Focused Service Framework." In 5th Intl. Conference
on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software
Engineering. Athens, Greece.
OGC. 2010. ITIL. OGC, Available from
http://www.ogc.gov.uk/.
OTGI & OGC. 2008. “Aligning CobiT® 4.1, ITIL® V3
and ISO/IEC 27002 for Business Benefit”, The IT
Governance Institute.
Parasuraman, A., ZelthamI, V.A., and Berry, L.L., 1985.
"A Conceptual Model of Service Quality and Its
Implications for Future Research." Journal of
Marketing 49.
Pinhanez, C. 2008. "A Service Science Perspective for
Interfaces of Online Service Applications." In IHC
2008 – VIII Simpósio Sobre Fatores Humanos em
Sistemas Computacionais. Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil.
Rosen, L.D., Karwan K.R. and Scribner L.L., 2003.
"Service quality measurement and the disconfirmation
model: taking care in interpretation." Total Quality
Management 14(1):13.
SFIA. 2003. "Skills Frameowrk for the Information Age."
SFIA Foundation. Available from http://
www.sfia.org.uk/.
Sharif, A. 2010. "It’s written in the cloud: the hype and
promise of cloud computing." Journal of Enterprise
Information 123(2):4.
Spohrer, J and Maglio, P.P., 2008. "The Emergence of
Service Science: Toward systematic service
innovations to accelerate co-creation of value."
Standish. 2009. "CHAOS Summary 2009." Available
from:
www.standishgroup.com/newsroom/chaos_2009.
Vandaele, D., Rangarajan, D., Gemmel, P., and Lievens,
A., 2007. "How to govern business services
exchanges: Contractual and relational issues."
International Journal of Management Reviews 9(3):23.
Velitchkov, I. 2008. "Integration of IT Strategy and
Enterprise Architecture Models." In International
Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies -
CompSysTech'08.
Vouk, M.A., 2008. "Cloud Computing – Issues, Research
and Implementations." Journal of Computing and
Information Technology 16(4):12.
Winniford, Dr. M.A., Conger, S., and Erickson-Harris, L.,
2009. "Confusion in the Ranks: IT Service
Management Practice and Terminology." Information
Systems Management 26:12.
Winter, R. and Schelp, J., 2008. "Enterprise Architecture
Governance: A Need for a Business-to-IT Approach."
In SAC'08. Fortaleza, Ceari, Brazil: ACM.
Zachman, J. 1987. "A framework for information systems
architecture." IBM Systems Journal 26(3):17.
Zachman, J. A. 1978. "The Information Systems
Management System: A Framework For Planning."
Data Base Winter 1978:6.
Zeithaml, V. A., Berry, L.L., and Parasuraman, A., 1988.
"Communication and Control Processes in the
Delivery of Service Quality." Journal of Marketing
52(April 1988):15.
Zomerdijk, L. G. and Voss, C.A., 2009. "Service Design
for Experience-Centric Services." Journal of Service
Research 13(67):17.
CLOSER 2011 - International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
318
