
Ontology for Simulation
of Ambient Assisted Living Environments
Juan B. Mocholí, Pilar Sala, Juan C. Naranjo
Vicente Traver and Carlos Fernández-Llatas
TSB-ITACA, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Valencia, Spain
Abstract. This paper describes the ontologies developed in the framework of
the European project VAALID. They are a set of OWL ontologies that are used
to define Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) solutions, providing the semantics to
model services, the actors involved in the service, AAL environments and their
spaces, devices and furniture. The ontologies also include concepts to model
the interaction among all the parts of the AAL solution, which mainly define
requirements and restrictions. The model of interaction is based on the Com-
mon Access Profile.
1 Introduction
Ambient Assisted Living services (AAL), as other ambient intelligence solutions do,
need to model the context in which the user is involved, being this one of their main
goals. Among current definitions and references about context definition, Dey, Salber
and Abowd give in [1] the following definition of what context is: “Any information
that can be used to characterize the situation of an entity, where an entity is a person,
place, or object that is considered relevant to the interaction between a user and its
application, including the user and the application themselves. Context is typically
the location, identity and state of people, groups and computational and physical
objects.” Therefore, information managed by context is sometimes related to the envi-
ronment, to the user and to the devices, plus a description of available services, in
which both static and dynamic information is managed regarding all these concepts:
- User: concerning his/her profile (anthropologic, demographic, preferences), social
relationships, activity (all types: sports, hobbies, etc.), etc.
- Environment: concerning its users, devices, software, localization (geographical
or abstract, global or local), environmental conditions (lighting, humidity, noise,
temperature, etc.), etc.
- Devices: regarding potential users, network connections, CPU, display features,
type of device, whether it describes a specialized device like a sensor or not, the type
and value of the signal measured, etc.
- Services: dealing with the description of their functionalities, the flow, the para-
meters, type of invocation, etc.
Mocholí J., Sala P., Naranjo J., Traver V. and Fernández-Llatas C..
Ontology for Simulation of Ambient Assisted Living Environments .
DOI: 10.5220/0003352800880097
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Semantic Interoperability (IWSI-2011), pages 88-97
ISBN: 978-989-8425-43-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

This information allows defining flexible AAL services with a high level of detail
(or the amount of detail needed) by describing both the potential users who will con-
sume the applications and services offered and the localization, the activity of the
users, their preferences, the time stamp, etc.
All the effort and time invested in describing the context hasn’t been in vain, since
it will allow increasing the personalization capabilities of the application and services.
It will also allow increasing the automation of everyday activities by means of count-
ing on accurate data retrieved from the environment, etc. As a result, the user satisfac-
tion when making use of these services has been increased.
The ontologies described in this paper have been developed in the framework of
the European project VAALID [17]. The VAALID project aims at creating an open
and descriptive formal model to define “the users”, “the environments” and their
“interactions” of AAL services and solutions [18]. VAALID project intends to devel-
op tools in order to assess that AAL products and services fulfill the accessibility and
usability requirements and restrictions for this new combination of interaction mod-
alities when used in a service design.
1.1 User
The information regarding the user must be more specific. In addition to define the
profile and activities of the user, it must identify the skills, abilities, impairments and
diseases (only with informative purpose), because all this information characterizes
how the user will interact with the whole system. These concepts can be divided in
psychological, social, and physiological/biological. Moreover, the description of how
these characteristics change with the ageing process has also been added. The Interna-
tional Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) [2] was chosen as
the classification to be used.
ICF aims to be the standard language for the description of users. ICF is divided
in different domains, which are described from the body, the individual and the socie-
ty perspectives, distinguishing two parts:
- Part 1 is related to functioning and disability, and consists of 'body functions and
structures' and 'activities and participation';
- Part 2 is related to contextual factors and consists of environmental factors and
personal factors.
As ICF classification addresses a very broad range of concepts, we need to focus on a
subset of concepts that are relevant for the design of AAL Solutions.
The selection of concepts from the ICF body of knowledge has been based on the
“Design for All” guidelines for ICT products and services provided by the ETSI [3],
in particular, the desired attributes of the users to be taken into account when design-
ing ICT products that are:
- Sensory abilities such as seeing, hearing, touch, taste, smell and balance.
- Physical abilities such as speech, dexterity, manipulation, mobility, strength and
endurance.
- Cognitive abilities such as intellect, memory, language and literacy.
89

1.2 Environment
Concerning environments, the most frequent environments in which AAL services
are deployed are “enclosed” spaces as residences, hospitals or houses, although there
are other services intended for being deployed in more “open” spaces like train sta-
tions, metro stations, etc. Here it seems clear that a distinction between indoor spaces
and outdoor spaces will be needed:
- Outdoor spaces can be seen as those spaces that are typically represented in 2D
defining a geographic space like a region or an area, even a building (in fact building
can have 3D representation), which can be located by means of using an absolute
reference system like the latitude-longitude-altitude or the Universal Transverse Mer-
cator (UTM), or can be located by using relative references like landmarks or points
of interest.
- Indoor spaces are those spaces which are more conceptual; they are typically
represented in 3D and can use absolute or relative reference systems.
Several classifications about this matter are available being particularly interesting the
one proposed by Hightower and Borriella; in [4] they propose a taxonomy of location
systems for mobile-computing applications.
Together with the environment, we need to have the information about the devices
contained in and that provide the functionality to the AAL Service.
In addition to all that, the most important goal for modelling the elements partici-
pating in an AAL service is to evaluate the interaction between them in terms of the
accessibility facets, consequently a very important need to cover with the models is
the information related to the interaction capabilities and its accessibility.
2 Review of Current Approaches
From the huge variety of approaches that can be consulted in the literature related to
context modelling, we have reviewed the ones from the following list: Amigo EU
project [5], Soprano EU project [6], DomoML project [7][8], DogOnt project [9],
CODAMOS project [10], SOUPA ontology for pervasive computing [11], CONON
ontology [12] and COMANTO ontology [13][14].
Most of these solutions provide OWL ontologies. Some of the ontologies re-
viewed explicitly say that they reuse other ontologies, for example Soupa or Amigo.
The ontologies DomoML, DogOnt have some parts based on standards. Apart from
defining concepts related with the requirements pointed out in the introduction chap-
ter, some ontologies also provide concepts to define the quality of service (Amigo), or
are oriented to domotic systems (DomoML and DogOnt).
Concerning how they manage the user information, the ontologies DomoML and
DogOnt don’t hold information related to users, perhaps because they could rely on
reusing other existing ontologies for user modelling. The rest of them hold informa-
tion about demographic data (Name, address, nationality, etc.). However, only some
of them also maintain anthropological data, but this information is limited to hold
Gender, Height and Weight. About concepts for defining skills, limitations and im-
90

pairments, the ontologies here reviewed were not intended for modelling this area:
Amigo provides concepts to hold information about skills and personality behaviour,
but they are “upper” concepts; the same occurs with Codamos, it provides concepts to
hold mood and role but not further information about skills or impairments. The
Amigo ontology allows defining the user context for a lot of concepts, including
personality and psychological features, or preferences about devices and foods. Soupa
defines the class Agent that could be thought as an “alter ego” that acts in behalf of
the user.
Information related to environment is present is some of the ontologies, the ontol-
ogies Amigo, DomoML and Codamos the environment can be located, but it doesn’t
have dimensions, only Soupa provides both location and dimensions. However, Sou-
pa doesn’t provide any environmental condition whereas Amigo, DogOnt, Codamos
define environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, etc. The ontologies de-
veloped in Amigo, DomoML, DogOnt, and Soupa allow defining a lot of different
types of environments. Moreover, Amigo, DomoML also allow to define a lot of
types of object and devices and Codamos defines the classes Hardware and IODevice.
Services are described only in some of the approaches reviewed; Amigo and Co-
damos offer services by describing them as OWL-S. Amigo also provides the class
Activity in order to define the activities of the user, whereas Codamos offers the
classes Task and Activity. DomoML describes actions and services by defining se-
quences of operations, DomoML allows defining events and actions, but they are not
part of the ontology. Finally Soupa doesn’t provide real services, only classes Even
and Action
3 Ontology Developed
After reviewing the projects and ontologies described in the chapter 2, none of them
addressed the concept of the user in the way that was required , consequently a new
ontology that were able to express the characteristics of the user in terms of abilities
and capabilities to interact with other elements was needed. Other requirement is to
define the properties that characterize the interaction between the elements and that
could provide information about the degree of accessibility of this interaction. This
approach resulted quite new and was not included in any of the reviewed ontologies,
hence it was decided to create it new and adapted to these needs.
The ontology covers concepts related to model the context in which the user is in-
volved, being this one of their main goals. Information regarding context is related to
environment, users, devices, descriptions of the available services and the interaction
among them.
According to the needs presented in chapter 1 and the results of the ontologies
benchmarking presented in chapter 2, the following models have been defined:
- User Model
: collect concepts related to profile (anthropologic, demographic),
abilities, preferences etc. It is a new developed model as no previous work has been
found to cover all requirements for this model.
- Environment Model
: collect concepts related to elements present, devices, dimen-
sions, environmental conditions (lighting, humidity, noise, temperature, etc.), etc.
91

Some device’s taxonomies have been used from the ontologies reviewed in Chapter 2
and adapted to the needs of the project.
- AAL Services
: collect concepts dealing with the description of their functionalities,
the flow, the parameters, type of invocation, etc. It is also a new developed model,
specifically tailored to requirements identified.
- Interaction Model
: collect the concepts that describe the capabilities of each ele-
ment present in the interaction and the accessibility aspects of this interaction. It is a
new developed model that has been based on the new ISO/IEC 24756:2009 [15],
which defines a framework for specifying a common access profile (CAP) of needs
and capabilities of users, computing systems, and their environments, providing a
basis for identifying and dealing with accessibility issues in a standardized manner
across multiple platforms
3.1 User Model
This model is used to describe the relevant characteristics of the user or group of
users that will interact with the AAL solution. These include physical and sensory
attributes, habits, preferences and accessibility capabilities.
With this model the designer can define as many user interaction profiles as
needed to address the whole range of requirements from target populations.
The user model is based on the ICF [2]. This standard offers a balance between a
purely medical and a purely social approach of describing the limitations of people.
This mixed approach allows grouping of limitations that are not only due to impair-
ments but produce an equivalent result in the interaction with the proposed system
As the project focus on the evaluation of the interaction between the user and the
AAL Service, out of the whole range of concepts that ICF offers to describe a person,
the project has selected those having direct impact on successful use of ICT product
and services, following the recommendations of the ETSI EG 202 116 [3]:
- Sensory
abilities are Seeing (Visual Field, Visual Acuity and Quality of Vision),
Hearing (Sound and Speech discrimination), Balance and Touch (Temperature, Vi-
bration and Pressure).
- Physical
abilities are Endurance, Manipulation (Lifting, Carrying or Putting down
objects), Speech (Production of sounds and Production of Speech sounds), Strength,
Dexterity (Pulling, Catching, Pushing, …) and Mobility (Voluntary and Involuntary
Movements).
- Cognitive
abilities are Intellect functions, Attention (Sustaining, Shifting or Shar-
ing), Orientation (Time, Place and Person), Language (Reception and Expression of
language) and Memory (Short and Long term).
The previous concepts where grouped in a higher concept call Ability as root of a
taxonomy to define abilities, disabilities and impairments of the user.
As summary, an overview of the main concepts used in characterizing the user is
depicted by the Figure 1. Users are defined by using the Person concept. A Person
has a Gender, can be located in a Space, have a Contact Profile and a Profile. The
Profile is used to define the Preferences, Abilities and Habits. Abilities have been
92
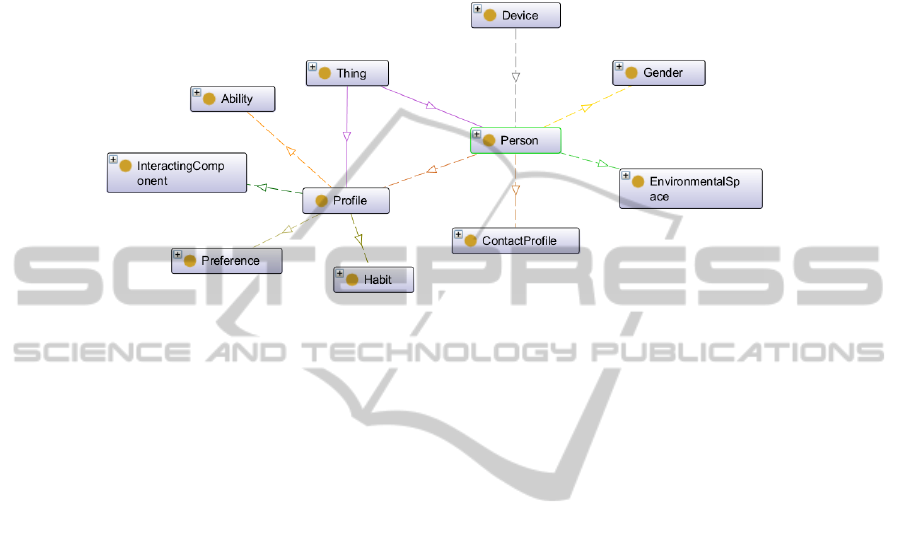
described in the previous paragraphs. Concept Habit is used to describe the habits of
the person, normally in relation to their needs for support in the AAL domain, i.e.
cooking, eating, sleeping or taking medication. For these concepts is collected infor-
mation about the usual time when are performed and for some concepts it is collected
also the usual duration.
Fig. 1. Concepts and properties for person.
3.2 Environment Model
This model defines the concepts involved in the description of the pervasive technol-
ogy within a real physical ambient. It includes description of physical spaces as well
as sensors, actuators and any interaction device available to the beneficiary.
This model is particularly complex because in the case of environment and devic-
es is needed to handle two types of behaviour, on one side the one that will be graphi-
cally represented in virtual reality during the simulation, for instance the movement of
an opening door; and on the other side the one that will result in a interaction with the
beneficiary, for instance a presence sensor that will send a message when activated.
The first one is done out of IDE developed within the project and it is part of a 3D
scene file. The second one is done using workflows, defining the possible states of
the object, the inputs that will change its state and the outputs it will provide to the
system. The model has been defined in such a way to provide the links between these
two behaviours in order to assure the consistency across the solution.
The Figure 2 shows the taxonomy and some object properties of the main con-
cepts involved when defining an environment and the spaces attached to it. The Envi-
ronments are defined as entities that can be placed at several Floor levels; each Floor
level can be composed by several Spaces, each one of these Spaces can be catego-
rized as Rooms, Stairs or Ramps. Spaces have Dimensions, have Environmental Con-
ditions (temperature, humidity, …) and can be bounded by a Polygon. Spaces can
contain several objects that are defined by the concept EnvironmentalElement, which
define all kind of devices. EnvironmentalElements are categorized as Controllable or
Uncontrollable. Controllable elements can define States, Services (functionality) and
Communicate events. Some of the concepts covered by the taxonomy of Controllable
are: Appliances (White and Brown goods), Devices (Sensors and Actuators), and
93
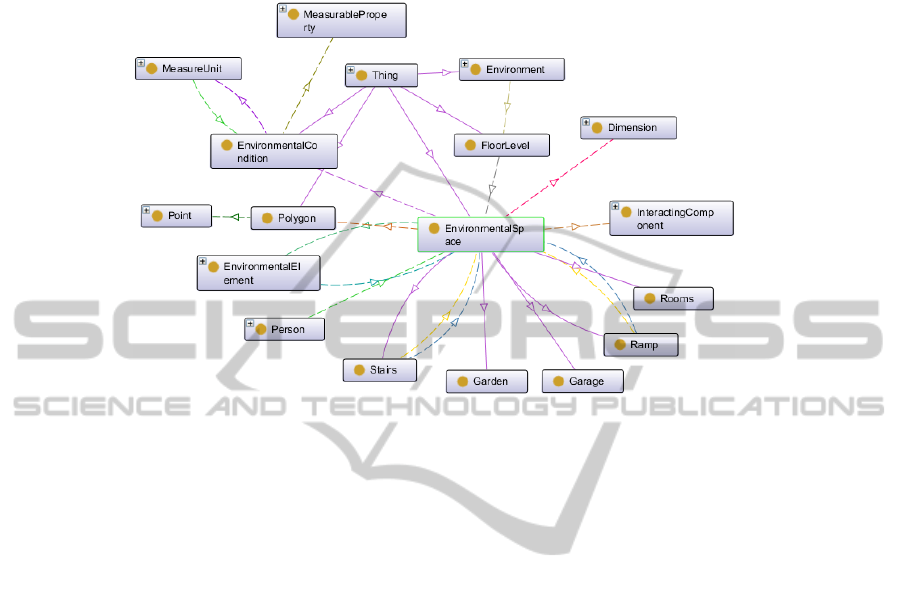
Lighting. Uncontrollable elements have been categorized as Junctions (Doors and
Windows) and Furniture (Beds, Tables, Closets,…).
Fig. 2. Main concepts and object properties of the Environment model.
3.3 AAL Service Model
The AAL Service model is very simple, because it relies on the description of the
dynamic between devices and user in the environment done by workflow, therefore
only a set of properties mainly used for classification and general description of AAL
services has been included in the model.
When defining an AAL Service it is provided the Context of use, a Description,
the link to the Workflow that implements the behavior of the service, the Type of
Service and the Actors involved.
3.4 Interaction Model
On the topic of defining interaction and accessibility, and in order to deal with the
description of all the possible features of a user and the functionalities provided by
devices and systems in terms of accessibility constraints, Fourney in [16] presented
the Common Accessibility Profile (CAP); Fourney defines CAP “as a framework for
identifying the accessibility issues of individual users with particular systems configu-
rations, defining and describing the needs and capabilities of systems, devices and
users to communicate among them”. CAP has been taken as basis of the standard
ISO/IEC 24756:2009 [15], although in this standard CAP is defined as Common
Access Profile. CAP can be used to evaluate the accessibility of systems, services or
solutions deployed in an environment for a specific user.
94
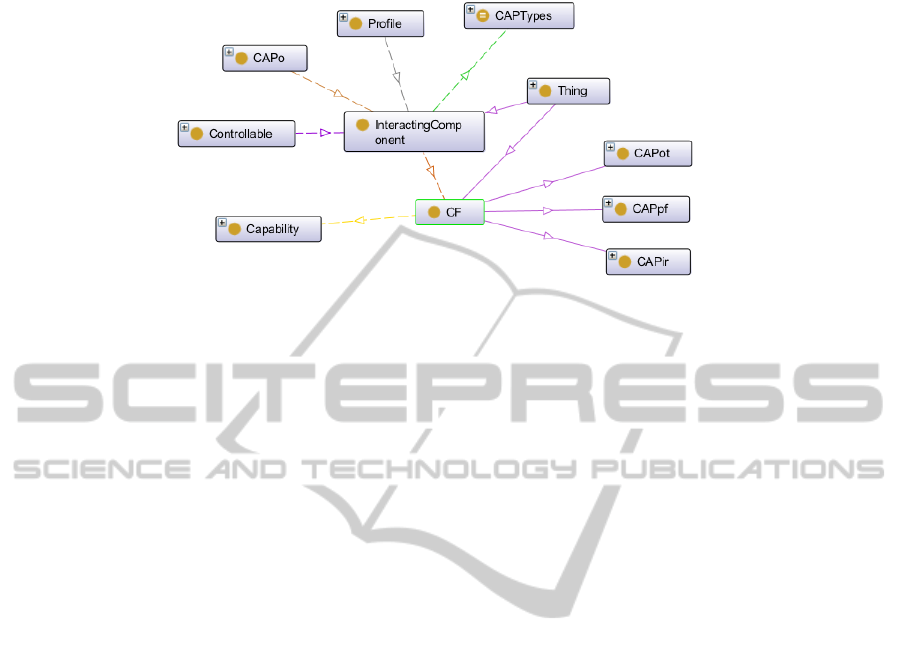
Fig. 3. Main concepts of the Interaction model.
In the context of an AAL project, this model is used in the Simulation Environ-
ment to perform the accessibility constraints verification; this functionality is used
during the design and implementation phase and it allows the designer to automatical-
ly detect accessibility issues derived from matching accessibility profiles of the users
with the different elements included in the simulation: environment and objects. It
can be seen as the equivalent for AAL solutions of a tool for automated web accessi-
bility evaluation.
The Figure 3 depicts the main concepts present in the Interaction Model: The CAP
Overall of the AAL service to be modelled and used during the above-mentioned
check is composed by the union of the CAP of the user (CAPuse), the CAP of the
devices (CAPsys and CAPat) and the CAP of the environment (CAPenv).
By following this approach, the CAPuse is used to model the capabilities of inte-
raction of a user; this CAPuse is aligned (partially automatically aligned) with the
description done using the ICF descriptors. In the same way CAPsys and CAPenv
describe the capabilities of the devices and the environment involved.
Each CAP is specified by means of its set of Interacting Components (IC), which
can express a set of capabilities related to Input Receptor (IR), Output Transmitter
(OT) or the Processing Functions (PF) that transform IR to OT. The definition of the
IC and its properties permits to perform matching and checking of constraints auto-
matically by creating an easy set of rules.
An easy example of how it works can be the following: a designer is developing
an AAL service with an auditory alarm (fills the CAP of the system, the CAP of the
devices, …), and selects a user with auditory problems (described with the ICF de-
scriptors and his CAP); then, when the accessibility constraints verification is run, a
warning will be thrown. In the same way the designer can test the solution with a vast
variety of users (with different CAPs) and check how it adapts to the necessities of
each user.
4 Conclusions
In this paper a set of OWL ontologies to model AAL solutions has been presented. It
95

has also been presented the main concepts that compose them and also a review of the
relevant solutions available on the field of describing AAL solutions.
In summary the ontologies described in this paper collect concepts to model the
context, the environment, the devices, the user involved, the services deployed, and
especially the concepts related to model interactions and allows the designer of AAL
solutions to model and characterize the actors (the end beneficiary and other second-
ary actors, like relatives, formal caregivers, etc.) involved in the AAL service, define
their abilities by using ICF descriptors. When defining an entire AAL solution using
the VAALID ontologies, the restrictions set by the model can be checked by the
VAALID Authoring Tool and the concepts collected by them can be also simulated
by using the VAALID Simulation Environment.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the European Commission for the project funding and the
VAALID consortium for their support.
References
1. Dey, A. K., Salber, D., and Abowd, G. D. A conceptual framework and a toolkit for sup-
porting the rapid prototyping of context-aware applications. Human-Computer Interaction
2001, 16(2-3)
2. World Health Organization (2001), International Classification of Functioning, Disability,
and Health (ICF) at http://www.who.int/classiffications/icf/en/.
3. ETSI, EG 202 116 v1.2.1 (2002-09): Human Factors (HF); Guidelines for ICT products
and services; “Design for All” at http://www.etsi.org.
4. Hightower J., Borriella G. Location Systems for Ubiquitous Computing. IEEE Computer
2001, vol. 34, pp. 57-66.
5. AMIGO project website, http://www.hitech-projects.com/euprojects/amigo/ last access
October 2010.
6. SOPRANO project website, http://www.soprano-ip.org last access October 2010.
7. L. Sommaruga, A., Perri, F., Furfari: "DomoML-env: an ontology for Human Home Inte-
raction" In Proceedings of SWAP 2005, the 2nd Italian Semantic Web Workshop, Trento,
Italy, December 14-16, 2005, CEUR Workshop Proceedings.
8. F., Furfari, L. Sommaruga, C., Soria, R., Fresco, “DomoML: the definition of a standard
markup for interoperability of Human Home Interactions”, Proceedings of the 2nd Euro-
pean Union Symposium on Ambient intelligence (EUSAI 2004), November 8-10, Eindho-
ven, The Netherlands.
9. Dario Bonino and Fulvio Corno, DogOnt - Ontology Modeling for Intelligent Domotic
Environments, Proceedings of 7th International Semantic Web Conference, October 26-30,
2008. Karlsruhe, Germany. Ed. Springer-Verlag, Lecture Notes on Computer Science, pp.
790-803.
10. Preuveneers D., Van Den Bergh J., Wagelaar D., et al. Towards an extensible context
ontology for Ambient Intelligence. Proceedings of the Second European Symposium,
EUSAI 2004. Ambient Intelligence. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3295, pp.
148-159. Springer.
96

11. Harry Chen, Filip Perich, Tim Finin, and Anupam Joshi. SOUPA: Standard Ontology for
Ubiquitous and Pervasive Applications. In Proceedings of the First Annual International
Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking and Services. Boston, MA:
Mobiquitous 2004, 2004.
12. Wang, X. H., Zhang, D. Q., Gu, T., Pung, H. K.: Ontology based context modeling and
reasoning using owl. In: Proceedings of PERCOMW 2004. (2004).
13. Roussaki, I., Strimpakou, M., Pils, C., Kalatzis, N., Anagnostou, M. Hybrid context model-
ling: A location-based scheme using ontologies. 4th Annual IEEE International Conference
on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PERCOMW’06). 2006.
14. M. Strimpakou, I. Roussaki, and M. E. Anagnostou. A context ontology for pervasive
service provision. In 20th Int. Conf. on Advanced Information Networking and Applica-
tions, pages 775–779, 2006.
15 ISO/IEC 24756:2009, Information technology - Framework for specifying a common
access profile (CAP) of needs and capabilities of users, systems, and their environments at
http://www.iso.org/.
16. Fourney D., (2007) Using a common accessibility profile to improve accessibility. Master
Thesis submitted to the College of Graduate Studies and Research, University of Saskat-
chewan, Saskatoon, Canada.
17. Consortium VAALID. VAALID Project: Accessibility and Usability Validation Frame-
work for AAL Interaction Design Process. http://www.vaalid-project.org 2008-2010.
18. Naranjo J. C., Fernández C., Sala P et al. (2009) A modelling framework for Ambient
Assisted Living validation. Universal Access in HCI, Part II, HCII 2009, LNCS 5615:228-
237.
97
