
On the Use of an Ontology to Improve
the Interoperability and Accesibility
of the Electronical Health Records (EHR)
Belen Prados Suarez
1
, Carlos Molina
2
, Miguel Prados
3
and Carmen Peña
3
1
Software Engineering Department, University of Granada, Granada, Spain
2
Computer Science Department, University of Jaén, Jaén, Spain
3
University Hospital “San Cecilio”, Computing Department, Granada, Spain
Abstract. In this paper we present a proposal to conceptualize the EHR, based
on the semantic description of the information, according to the documentary
structures and the clinical aspects of the EHR contents. Our aim here is to per-
form a formalization with a double purpose: on one hand to enable the interope-
rability; on the other hand, to improve the accessibility to the EHR, according
to clinical or assistance contexts, provi-ding the clinical data retrieval system
with flexibility and operativity. To this purpose we propose the use of an On-
tology to represent this conceptualization, and include properties and relations
between the components of the EHR.
1 Introduction
Every day more the Electronic Health Record (EHR) is an extended reality in the
majority of the Hospitals, with different degrees of development. It has opened the
access to new uses of the EHR, optimized and with more benefits for the medical
acti-vity. However, new problems and perspectives have also arisen, related to the
management of the clinical information [1].
As the use of the EHR spreads over the different medical specialities and assis-
tance acts, it must integrate more documents and information items, from different
sources and types. It is unavoidable to think on the risk that the EHR runs of becom-
ing as unmanageable as the old health records in paper: with such a quantity of in-
formation and documents, the access to concrete data items required in relatively
simple situations can be really difficult.
Another main problem is the interoperability, with the aim is to communicate and
make possible the understanding between different models of EHR from different
hospitals and providers. The ISO 13606 [2] regulation establishes the basis and gen-
eral framework of the semantic interoperability model [3], to allow the univocal in-
terpretation of the information transmitted during the capture of the context where it
was generated. The ISO 13606 regulation proposes a dual model where the first
model is the reference model and the second one is the archetypes model. Both of
them will be commented later.
In addition to the above mentioned problems, there are also several important is
Prados Suárez B., Molina C., Prados M. and Peña C..
On the Use of an Ontology to Improve the Interoperability and Accesibility of the Electronical Health Records (EHR) .
DOI: 10.5220/0003352500730081
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Semantic Interoperability (IWSI-2011), pages 73-81
ISBN: 978-989-8425-43-0
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

sues that must also be addressed and solved, like:
• The Mobility: The use of mobile devices (tablet PC, PDAs, …) requires agile and
summarized navigation models on the EHR.
• The Contextualization: The contextual use of the information would provide the
doctor with information pertinent to the assistance act where he/she is involved.
• Access Focusing: The idea is to allow the navigation through the EHR directing
the search according to a semantic purpose.
• The personal access of the owner: Every day more the patients demand the access
to their clinical data since, as owner of them, they have the right to access them.
However, at this moment nor the systems are ready for this purpose nor the citizen
have the technical knowledge to use them.
The bibliography reviewed shows a great concern about these problems of the EHR
systems, specially the interoperability one. In particular about the use of Ontologies
as a means to represent models capable of understand and communicate to each other
[10]. However, though in the literature most of the proposals are mainly focused on
the interoperability and its tools, they do not propose explicitly applications towards
the accessibility, use and management of the EHR at a local level.
In this paper we offer a different point of view, more focused in this latter line,
offering different alternatives of use of the EHR for the doctors, making more
efficient the accessibility to the information needed. It is quite important since the
great volume of documents and information contained in the EHRs, is so extensive
that usually one of the main causes of complains from the users is related to the
difficulties to navigate through them.
It all have lead us to think that the EHR can be considered as a universe of know-
ledge that can be conceptualized in such a way that each individual information item
can be defined in a semantic family, according to its properties and relations with
other information items [6].
In addition, this paper provides with a novel point of view, applying the Ontology
based representation models to make easier the use and navigation.
It is specially interesting, since opens the possibility of performing semantic re-
trieval of information, through the construction of Agents that interpretate the queries
and allow the access to the pertinent data items.
Our proposal then, is an approach to the conceptualization of the universe of
clinical data contents of the EHR, through the use of an Ontology, based on our own
EHR model. Starting from this conceptual formalization and on the basis of the gen-
erated knowledge we can construct “agent procedures”. These procedures approach
the user to the information items that, due to their semantic value, can be more useful
according to the access model.
2 Background
Before presenting our proposal we are going to point some notes about the frame-
work from which we have started our research, specially the information system and
the legal framework.
74
2.1 System Used
To perform our proposal we have based on the system “ARCHINET”, the EHR sys-
tem developed and implemented in the Universitary Hospital San Cecilio of Granada
(Spain) [1]. This system was implemented 10 years ago, is continuously improved
and counts on around 1.000.000 of EHRs. It is organized according to the highest
level structures: “assistance episodes” and “pathological processes”.
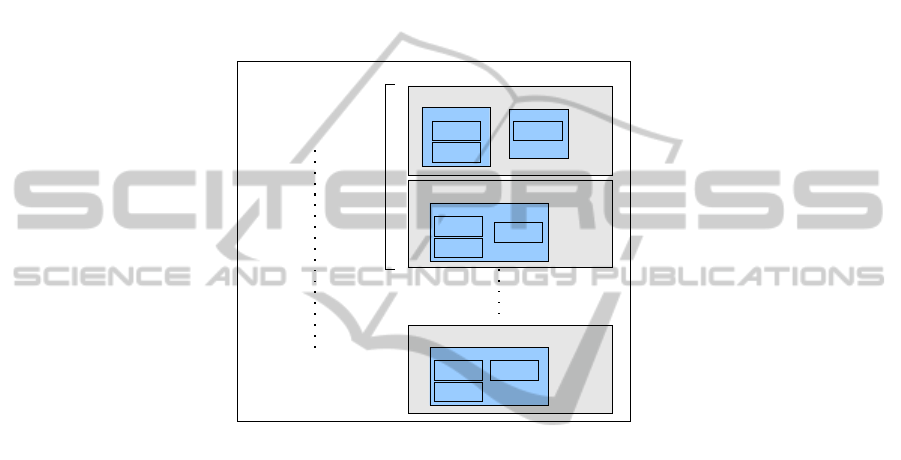
The EHR (Figure 1) is a set of documents (e.g. cardiograms, analytical tests, etc.),
and each of them may consist on a set of data groups (e.g. some variable in an ana-
lytical test, each of the images in a TAC, etc).
Health Record
Asistencial episode 1
Document 1
Data Group 1
Data Group 2
DATA
DATA
DATA
Document N
Data Group 1
DATA DATA
DATA
Document 2
Data Group 1
DATA
DATA
DATA
Fig. 1. Example of EHR structure.
In addition we have also made use of the “access base” that registers all the ac-
cesses to the system, information items acceded or modified and the assistance con-
text where the user was involved.
To define the Ontology’s structures, the Protégé tool has been used, allowing also
the operations of validation, representation and translation to descriptive languages.
2.2 Legal Framework
As mentioned above, the ISO 13606 regulation proposes a dual model where the first
model is the reference model and the second one is the archetypes model.
The reference model is used to represent the structure of the clinical data of a con-
crete model like, as an example, the model of a given hospital. It is based on a class
called “structure” that gives rise to the following hierarchy of members:
• Folder: It represents the divisions at the highest level inside the extracts of the
clinical history.
• Composition: It is the set of annotations related to a unique given clinical session
or document.
75

• Sections: They are groupings in a clinical session.
• Entry: Each one represents a clinical observation or a set of them.
• Cluster: It is used when the representation of a unique observation or action re-
quires a complex data structure, like a list, a table or a temporal series.
• Element: It contains a unique value that must be instance of some of the types
defined by it.
The second model sets the Archetypes [4], [5] as a way to define the clinical concepts
managed by the system. The archetypes are definitions of sets of clinical information
items, that have a concrete clinical meaning; and they are created using the compo-
nents defined in the ISO 13606.
However this regulation just sets the basis and general description on which eve-
rything is opened and must be concreted, which is what we do in this paper.
3 Ontology Proposed
To materialize the general models described in the previous section, we propose and
describe in this section an ontology.
3.1 General Description
The EHR structure’s design itself implies the existence of a categorization according
to the semantic classes of the documentary organization, and also to the assistance
part. As an example, the documents are classified by their types, and the data are
organized regarding their clinical orientation inside the document. In addition these
data items are organized according to assistance acts and medical specialities. Based
on it we make the formalization through the ontology.
To choose the components of the Ontology we have used two criteria. On one
hand, the documentary criteria, that gives rise to the classes that structure and define
the set of documents included in the EHR. On the other hand, we approach a clinical
criteria determinating the categories related to the clinical processes and concrete
pathologies, and even the assistance context on which the information is used.
Nevertheless, the semantic universe must be manageable and easily formalizable,
so we have avoided to define categories that are not clearly useful to reach our final
targets, previously indicated.
3.2 Semantic Categories in the Ontology
We have analyzed the semantic categories to define the Ontology. The main purpose
was double: on one hand, to categorize every kind of data that could be found in the
EHR, on the other hand to respect the information structures defined in our EHR
model. Whit it the classes defined in the Ontology are:
Structure Model (EHR-EXTRACT): This class corresponds to the structure defi-
76

ned in the ISO 13606, and has the members Folder, Composition, Section, Entry,
Cluster and Element.
Document: A document can be considered as any grouping of data with a common
purpose, nested regarding a clinical action or observation. The documents are hierar-
chized depending on whether they are “general”, “of process”, “of medical special-
ity”, “of nursery”, “surgical” or “logistical”. Hence, this class can be considered as
the fundamental logical grouping of the organization of the information in the EHR.
With this class the EHR can be organized according to assistance acts (admissions,
consultations, emergencies,…) or to pathological processes, always grouping docu-
ments. Each document may contain different sections of contents, and each section
has its own entries, clusters and elements as concrete data in the document.
Assistance Process: These processes define the clinical pathology environments,
previously set, on which sequences of clinical actions are pre-established. As an ex-
ample, we have the “diabetes process”, “cataract process”,… Here we have focused
on the pathologies with well defined processes, since not all the pathologies have
them. The members of this class represent the different pre-established actions for
each process.
Data Type: They can be considered as texts, encoded data, magnitudes that include
rations, intervals, lengths, durations, graphs, images, signals, dates and so on.
Observation Type: The aim of this class is to qualify the data item according to its
source: if it is a subjective observation, an objective result of an analysis, a protoco-
lyzed observation, a related fact or a chronological action, among others.
Assistance Procedure: It contains the references to the diagnosis methods, explora-
tions, sources of knowledge, technological support, and any other source of data. As
an example, we have electromedical explorations (electrocardiogram, electroencepha-
logram,…), radiological explorations (RMN, TAC, conventional radiology,…), and
direct observation, among others.
Clinical Context: It is related to the variety of situations or states of an assistance act,
like a revision consultation, a postsurgical consultation, an admission, an emergency
assistance or a ward checkup. These contexts are obviously classified according to the
medical speciality and, in some cases, to sub-speciality and process.
Assistance act: It determines the origin of the assistance procedure (admission, con-
sultation, emergency,…).
Agent: This class is used to define the kind of professional that is involved in the act,
locating him/her in the corresponding service and professional category (doctor,
nurse, assistant,…).
Archetype: We use the internally defined archetypes and those other defined by the
different research groups working on the interoperability of the EHR [7].
Application: This class captures the variety of functional applications from different
providers and the specific tools, that the clinical workstations entail and must be inte-
grated. These applications are complimented in the system ARCHINET by means of
its own and specific functionalities, with a logistical or departmental character. Some
examples are the application of medicine and unidosis management, the application
of analytical requests management, or the emergency monitoring. Some of these ap-
77
plications may derive clinical data towards the EHR.
ICD-10 Hierarchy: It reproduces the class structure in this international classifica-
tion [8]. We have chosen this classification since it is the most habitually used in the
Hospital for diagnosis encoding.
Data Model: It is a class of internal use for the procedures of computing agents. Its
aim is to reproduce the data model starting from its logical modelling and down to
reach the physical Data Base model of the EHR. This is how the tables stored in the
data base are described. The instances of this class are each of the individual data
(columns). The hierarchy of this class shows the typology of these structures: move-
ment tables, primary tables, history tables, etc.
3.3 Properties in the Ontology
Regarding the properties in the Ontology, their purpose is to create sets of restrictions
based on the taxonomical relation between classes, in such a way that each possible
entry in a EHR has a semantic map to contextualize its use, and hence its relations to
other elements in the EHR.
This way, as an example, the entry “anaesthesia type” belongs to the document
“anaesthesia sheet”, is a data type of restricted values, and is part of the context “in-
trasurgical information” and of the assistance procedure “Anaesthesia”. In addition,
it is characteristic of the assistance acts “admission”, “emergency” and “surgical day
hospital”. Its agent profile is “anaesthetist doctor” and it is considered as related to
the archetype “anaesthetic report”.
Fig. 2. OWL Based Relationships Between Classes and their Properties.
To allow the creation of these “semantic contextual maps” in the Ontology we ha-
Type of information
. . . .
Cluster
Controlled values
Document
. . . .
Elect. Document Pre-anaesthetic
Section Ventilation
Ventilation
Agent Æ . . . . Æ Anesthetist doctor
Process
. . . .
Surgical
General procedure
Procedure Æ . . . Æ Electro medical observation
Application
. . . .
Carmenes
Archinet
Specialist
. . . .
Anesthesiology
An
d
r
ea
ni
m
a
ti
o
n
Archetype
. . . .Complementary study
Pre-anaesthetic
study
78

ve defined complex relations between classes and their corresponding attributes and
restrictions.
The process to create these relations is quite complex. However, it is easier using
the information stored in the EHR Base and in the Access Base, and also referencing
the data model itself. Doing it most of them can even be automatically generated.
In the Ontology we have also included implicit properties for concrete classes like
the “character of a document” (confidential or open), or the “type of document”
(gene-ral, of speciality, of process, logistical,…).
Finally, we must remark that the definition of the Ontology is not a closed topic,
but a continuous process that, depending on the experiments, we widen or modify.
4 Results
The creation of the Ontology provides a Knowledge Base formalized with structures
that the computing procedures can use to answer the query processes performed on
the EHRs [9], and opens the possibility of using new accessibility models to the EHR.
Concretely, it makes possible the conceptual accessibility to the data in the EHR,
what opens the path towards the interoperability between EHR systems, since it pro-
vides the system with the capability to semantically interpretate the clinical data re-
trieval pro-cessess. In addition, it sets the basis for the next uses of the information
and the system:
Contextual Use: to allow the doctors to have the information really needed for the
assistance activity in which he/she is involved, acceding just to a determined context.
This way superfluous or not pertinent information items are avoided, as well as com-
plex accesses with the navigation systems.
Restricted Navigation: used in the cases where only some concrete information
items are needed, avoiding the unuseful navigation through acts, processes and
documents with no interest to the search purposes.
Limited Navigation for Mobile Devices: The navigation through the contents of the
EHR is quite difficult in mobile devices, since their screens set a very limited repre-
sentation capability, especially for complex menus. In this case, the information pre-
sented can be initially focused according to a given work environment, like the medi-
cal speciality, the assistance act to be performed, the process or the assistance proce-
dure. All of them set an environment to which the system can give a response depend-
ing on the information relevant to it.
Ontology Navigability: Traditionally there have been discrepancies regarding the
different ways to show the documental organization of the EHR. Some times it is
necessary to organize them according to assistance acts, whereas in other cases the
organization according to processes is preferred. In our case the user can choose, with
the scheme of classes that the Ontology provides, allowing him/her to design of
his/her own navigation model.
Interoperability: It is easier to reach with the Knowledge Base provided, making
possible the understanding with other formalized models, especially with the Refer-
ence and Archetypes models defined in the ISO 13606.
79

Access According to the Semantic Valuation: It makes possible the direct access to
elements contained in the EHR, using the terminology in the Ontology.
As a summary, the Ontology conceptualizes our model of EHR, opening the access to
a great variety of opportunities to develop computing procedures to make easier the
use, control and availability if the EHR.
To our best knowledge, there are some proposals of ontologies for contextualized
access in others fields (e.g. e-Goverment, business context [13]) but none for EHR
access so a comparison with our proposal is not possible.
5 Conclusions
In this paper we have made several proposals:
1. We have presented a semantic conceptualization model for an EHR system, that
offers a number of utilities towards three purposes: the interoperatibility, the accessi-
bility and the mobility.
2. We have proposed concrete accessibility models for the EHR, as a practical appli-
cation of the design proposed.
3. The proposed design can be generally and widely applied, independently of the
documentary structure, the technological support or the development degree.
4. The Ontology provides a formalized Knowledge Base that allows the
development of computing procedures with several purposes, from analytical to the
accessibility, opening the path to new alternatives to the traditional navigation and
access procedures to the EHRs.
However, we assume that this work is just the “starting point” for future develop-
ments and for the creation of computing procedures, more or less “intelligent”, to be
used as user interfaces for the EHR.
At this moment the work carried out has only been limited to the design and con-
struction of the Ontology, and must be continued with the production of the corre-
sponding computing agents.
Regarding this research line it is not finished, since it is just in an experimental
phase, and is opened to modifications in the Ontology design, depending of the re-
sults obtained. In the present phase, we are working on the development of computing
interfaces procedures and in the automation of the generation of classes and proper-
ties of the Ontology from the information stored in the system.
Finally, we must indicate that the experimental results obtained up to this moment
lead us to consider quite viable the implementation at a general level.
References
1. Prados M. and Peña M. C., Sistemas de Información hospitalarios. Organización y gestión
de Proyectos. EASP (Escuela Andaluza de Salud Pública), Granada, (2003).
80

2. UNE-EN 13606-1:2007. Informática sanitaria. Comunicación de la historia clínica electró-
nica. Parte 1: Modelo de referencia. UNE-EN 13606-2:2007. Informática sanitaria. Comu-
nicación de la historia clínica electrónica. Parte 2: Arquetipos. (2007)
3. Maldonado Segura J. A., Moner Cano, D., et al. Semantic Upgrade and Normalization of
Existing EHR Extracts. Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference EMBC,
pp. 1466-1469. ISBN: 978-1-4244-1815-2. ISSN: 1557-170X.
4. P. Serrano, D. Moner, T. Sebastian, J. A. Maldonado, R. Navalón, M. Robles
2
, Á. Gómez.
Representación De Estructuras De Datos Clínicos Mediante Arquetipos Y Terminologías.
Inforsald (2009).
5. V. Bicer, O. Kilic, A. Dogac, and G. B. Laleci. Archetype-Based Semantic Interoperability
of Web Service Messages in the Health Care Domain. Journal on Semantic Web & Infor-
mation Systems, 1 (4), 1-23. (2005).
6. C. Golbreich, O. Dameron, B. Gibaud, and A. Burgun. Web ontology language require-
ments w.r.t expressiveness of taxonomy and axioms in medicine. In 2nd International se-
mantic web conference, ISWC 2003, Sanibel Island, Florida, US, October 20, 2003 pro-
ceedings. Berlin: Springer. (2003).
7. Sundvall E, Qamar R, Nyström M, Mattias F, Hakan P, Ahlfeldt H, Rector AL. Integration
of Tools for Binding Archetypes to SNOMED CT. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision
Making. 8, S7 (2008).
8. World Health Organization; International Classification of Diseases (ICD):
http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/
9. J. Mei y E. P. Bontas. Reasoning Paradigms for SWRL-Enabled Ontologies. In Protégé
With Rules Workshop: 8th International Protégé Conference, Madrid, Spain, (2005).
10. Garde S, Knaup P, Hovenga E, Heard S. Towards semantic interoperability for electronic
health records. Methods Inf.Med. 46, 332-343 (2007).
11. JA. Maldonado, D. Moner, D. Boscá, C. Angulo, I. Abad, D. Pérez, P. Serrano, E. Reig, M.
Robles. LinkEHR-Ed: Una herramienta para la estandarización de la historia clínica
electrónica. Libro de comunicaciones del Inforsalud. Pag. 317-322 (2008).
12. M. O’Connor, H. Knublauch, S. Tu, B. Grosof, M. Dean, W. Grosso, y M. Musen. Sup-
porting Rule System Interoperability on the Semantic Web with SWRL. In Proceedings of
the 4th International
13. Hamdi Chaker, Max Chevalier, Chantal Soule-Dupuy, and Andre Tricot. Improving infor-
mation retrieval y modelling business context. In Advances in Human-Oriented and Perso-
nalized Mechanisms, Technologies and Services (CENTRIC), 2010 Third International
Conference on, pages 117 –122, 2010.
81
