
THE METHODOLOGY OF PARALLEL MEMETIC ALGORITHMS
DESIGNING
Wojciech Bo˙zejko
Wrocław University of Technology, Janiszewskiego 11-17, 50-372 Wrocław, Poland
Mieczysław Wodecki
University of Wrocław, Joliot-Curie 15, 50-383 Wrocław, Poland
Keywords:
Metaheuristics, Parallel computing, Evolutionary algorithm, Memetic algorithm.
Abstract:
The paper presents the methodology of parallel algorithm designing based on the memetic approach (Lamarck
and Baldwin evolution theory) making use of specific properties of the problem and distributed island model.
This approach is presented on the example of the single machine scheduling problem with earliness/tardiness
penalties.
1 INTRODUCTION
The memetic algorithm is an evolutionary approach
based on the process of natural evolution adhering to
the principles of natural selection, crossover and sur-
vival. The Lamarck’s model (Michalewicz, 1994) of
evolution is applied to intensify the optimization pro-
cess. In each generation a certain part of the popu-
lation is replaced by their local minima simulating a
learning effect which can be succeeded by the next
generation as a ’meme’. From the current popula-
tion some subset is drawn. Each individual of this
subset is a starting solution for the local optimization
algorithm. Thus, there are five essential steps of the
memetic algorithm:
1. selection – choosing some subset of individuals,
so-called parents,
2. crossover – combining parts from pairs of parents
to generate new ones,
3. mutation – transformation that creates a new indi-
vidual by small changes applied to an existing one
taken from the population,
4. learning – an individual is improved (e.g. by a
local optimization),
5. succession – determining the next generation’s
population.
New individuals created by crossover or mutation re-
place all or a part of the old population. The process
of evaluating fitness and creating a new population
generation is repeated until a termination criterion is
achieved.
Similar to the GA, following kinds of paralleliza-
tion are usually applied to memetic algorithms MAs:
• global parallelization,
• independent runs,
• island model,
• diffusion model,
with similar properties as applied to the classic GA.
Additionally, a local search procedure can be par-
allelized in MA. Such an approach is proposed by
(Berger and Barkaoui, 2002) and applied to the Vehi-
cle Routing Problem with Time Windows (VRPTW)
by using a master-slave parallel approach. The master
controls the memetic algorithm execution, synchro-
nizes and handles parent selection while the slaves ex-
ecute genetic operations together with local search in
parallel. Parallel memetic algorithm was also consid-
ered by (Bradwell and Brown, 1999) (asynchronous
MA) and (Tang et al., 2006) (MA based on popula-
tion entropy).
Implementation of algorithms which are based on
multithread multiple-walk searching of the solutions
space are usually coarse-grained application, i.e. they
require sparse communication and synchronization.
These type of algorithms are easy to be applied in
distributed calculation systems, as clusters which ex-
press beneficial efficiency-to-price ratio. Apart from
speeding up the calculations, it is possible to improve
643
Bo
˙
zejko W. and Wodecki M..
THE METHODOLOGY OF PARALLEL MEMETIC ALGORITHMS DESIGNING.
DOI: 10.5220/0003186006430648
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART-2011), pages 643-648
ISBN: 978-989-8425-40-9
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

quality of obtained results. Search processes can be
either independent or cooperative.
1.1 Independent Searching Threads
In this category we can distinguish two base ap-
proaches:
• Researching of the solution space by using multi-
ple trajectories, which begin from different start-
ing solutions (or different starting populations in
the case of using population-based approaches).
Searching threads can use either the same or dif-
ferent strategies, i.e. the same or different local
search algorithms, the same or different parame-
ters (tabu list length, population size, etc.). Trajec-
tories can cross themselves in one or more places
of the neighborhood graph.
• Parallel researching of subgraphs of a neighbor-
hood graph obtained by decomposition of the
problem into a few subproblems (for example fix-
ing of some variables). Subgraphs of the neigh-
borhood graph are searched concurrently without
crossing search trajectories. We obtain partition-
ing of the neighborhood graph into disjoint sub-
graphs.
The first parallel implementation of the tabu
search method based on multiple-walk searching of
the solution space was proposed by Taillard for the
quadric assignment problem (QAP) (Taillard, 1991)
and the job shop problem (Taillard, 1994). The
multiple-walk parallelization strategy based on inde-
pendent searching threads is easy in implementation
and one can obtain good values of the speedup un-
der condition of proper decomposition of the solution
space into searching threads (and their trajectories).
1.2 Cooperative Searching Threads
This model constitutes the most general and promis-
ing type of solution space searching strategy by using
parallel metaheuristics, however it requires knowl-
edge of solving problem specificity. ’Cooperative’
means here the interchange of information – experi-
ence of searching history up to now. Specific infor-
mation, which is characteristic for the problem and
the method (i.e. the best solution found so far, elite so-
lutions, the frequency of moves, tabu lists, backtrack-
jump list, subpopulations and their sizes, etc.) has to
be exchanged or broadcasted.
Information shared by search processes can be
stored as global variables kept in the shared memory
or as records in the local memory of the dedicated
central processor which communicates with all other
processors providing them with requested data. In the
model, in which information gathered during moving
along a trajectory is used to improve other trajecto-
ries, not only can one expect convergence of such a
parallel algorithm, but also founding in the same time
a better solution than the parallel algorithm without
communication can take place. In such a case we can
say that cooperative concurrent algorithms constitute
a new class of algorithms in deed.
The first heuristic algorithm of this type was asyn-
chronous parallel tabu search algorithm proposed by
Crainic, Toulouseand Gendreau (Crainic et al., 1995).
Packages such as ParSA (Kliewer et al., 1999) of-
fer ready implementations of parallel simulated an-
nealing algorithms based on cooperative searching
threads. The interaction strategy is also very efficient
in implementation of parallel genetic algorithms (in
the sense of obtained solutions). There are plenty of
ready libraries such as POOGAL (Bubak and Sowa,
1999). The majority of cooperative implementations
of parallel genetic algorithm is based on the migra-
tion island model. Each process has its own subpop-
ulation exchanging from time to time a number of
individuals (usually the best – elite) with other pro-
cesses (Bubak and Sowa (Bubak and Sowa, 1999),
Crainic and Toulouse (Crainic and Toulouse, 1998)).
Bo˙zejko (Bo˙zejko, 2010) proposed a parallel path-
relinking metaheuristics based on the parallel scatter
search algorithm.
1.3 The Problem
This paper aim is to present a parallel memetic ap-
proach on the instance of a strongly NP-hard schedul-
ing problem. We additionally assume that the con-
sidered problem has no idle constraint (TWET-no-idle
problem), which means that the machine works with-
out stops. The problem of scheduling with earliness
and tardiness (total weighted earliness/tardiness prob-
lem, TWET) is one of the most frequently consid-
ered in literature. In this problem each job from a
set J = {1, 2,...,n} has to be processed, without in-
terruption, on a machine, which can execute at most
one job in each moment. By p
i
we represent the exe-
cution time of a job i ∈ J , and by e
i
and d
i
we mean
an adequately demanded earliest and latest moment
of the finishing processing of a job. If scheduling of
jobs is established and C
i
is the moment of finishing
a job i, then we call E
i
= max{0, e
i
−C
i
} an earliness
and T
i
= max{0,C
i
− d
i
} a tardiness. The expression
u
i
E
i
+ w
i
T is the cost of job execution, where u
i
and
w
i
(i ∈ J ) are nonnegative coefficients of a goal func-
tion. The problem consists in minimizing a sum of
costs of jobs, that is to find a job sequence π
∗
∈ Φ
n
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
644

such that for the goal function
F(π) =
n
∑
i=1
(u
π(i)
E
π(i)
+ w
π(i)
T
π(i)
), π ∈ Φ
n
, (1)
we have
F(π
∗
) = min
π∈Φ
n
F(π). (2)
This problem is represented by 1||
∑
(u
i
E
i
+ w
i
T
i
) in
literature and it belongs to a strongly NP-hard class
(if we assume u
i
= 0, i = 1,2, ... ,n, we will ob-
tain a strongly NP-hard problem 1||
∑
w
i
T
i
- Lenstra
et al. (Lenstra et al., 1977)). Baker and Scudder
(Baker and Scudder, 1990) proved, that there can be
an idle time in an optimal solution (jobs need not
to be processed directly one after another), that is
C
π(i+1)
− p
π(i+1)
≥ C
π(i)
, i = 1,2,. .. ,n − 1. Solv-
ing the problem amounts to establishing a sequence
of jobs and its starting times. Hoogeven and van
de Velde (Hoogeveen and van de Velde, 1996) pro-
posed an algorithm based on the branch and bound
method. Because of exponentially growing computa-
tion time, this algorithm can be applied only to solve
instances where the number of jobs is not greater than
20. Therefore, in practice almost always approximate
algorithms are used. The best ones are based on artifi-
cial intelligence methods. Calculations are performed
in two stages.
• Determining the scheduling of jobs (with no idle
times).
• Establishing optimal starting times of jobs.
Bo˙zejko and Wodecki (Bo˙zejko and Wodecki, 2005)
proposed a parallel coevolutionary algorithm for the
considered problem.
1.3.1 Block Properties
For the TWET-no-idle problem, each schedule
of jobs can be represented by permutation π =
(π(1),π(2),..., π(n)) of elements of the set of jobs J .
Let Φ
n
denote the set of all such permutations. The to-
tal cost π ∈ Φ
n
is F(π) =
∑
n
i=1
f
π(i)
(C
π(i)
), whereC
π(i)
is completed time of the job π(i),C
π(i)
=
∑
i
j=1
p
π( j)
.
The job π(i) is considered early if it is completed be-
fore its earliest moment of finishing (C
π(i)
< e
π(i)
), on
time if e
π(i)
≤ C
π(i)
≤ d
π(i)
, and tardy if the job is com-
pleted after its due date (i.e. C
π(i)
> d
π(i)
).
Each permutation π ∈ Φ
n
is decomposed
into subpermutations (subsequences of jobs)
B = (B
1
,B
2
,. ..,B
v
) called blocks in π, where:
1. B
i
= (π(a
i
),π(a
i
+ 1),. .. ,π(b
i
− 1),π(b
i
)), and
a
i
= b
i−1
+ 1, 1 ≤ i ≤ v, a
0
= 0, b
v
= n.
2. All the jobs j ∈ B
i
satisfy the following condi-
tions:
e
j
> C
π(b
i
)
, (C1)
e
j
≤ C
π(b
i−1
)
+ p
j
and d
j
≥ C
π(b
i
)
, (C2)
d
j
< C
π(b
i−1
)
+ p
j
. (C3)
3. B
i
are maximal subsequences of π in which all the
jobs satisfy either Condition C1 or Condition C2
or Condition C3.
By definition, there exist three types of blocks implied
by either C1 or C2 or C3. To distinguish them, we will
use the E-block, O-block and T-block notions respec-
tively. For any block ϒ in a partition B of permutation
π ∈ Φ
n
, let
F
ϒ
(π) =
∑
i∈ϒ
(u
i
E
i
+ w
i
T
i
). (3)
Therefore, the value of a goal function
F(π) =
∑
n
i=1
(u
i
E
i
+ w
i
T
i
) =
∑
ϒ∈B
F
ϒ
(π). (4)
If ϒ is a T-block, then every job inside is early.
Therefore, an optimal sequence of the jobs within ϒ
of the permutation π (that is minimizing F
ϒ
(π)) can
be obtained, using the well-known Weighted Short-
est Processing Time (WSPT) rule, proposed by Smith
(Smith, 1956). The WSPT rule creates an optimal se-
quence of jobs in the non-increasing order of the ra-
tios w
j
/p
j
. Similarly, if ϒ is an E-block, than an op-
timal sequence of the jobs within can be obtained, us-
ing the Weighted Longest Processing Time (WLPT)
rule which creates a sequence of jobs in the non-
decreasing order of the ratios u
j
/p
j
. Partition B of
the permutation π is ordered, if there are jobs in the
WSPT sequence in any T-block, and if there are jobs
in the WLPT sequence in any E-block.
Theorem 1 ((Bo˙zejko et al., 2006)). Let ϒ be an or-
dered partition of a permutation π ∈ Φ
n
to blocks. If
β ∈ Φ
n
and F(β) < F(π), so at least one job of some
block of π was moved before the first or after the last
job of this block in the permutation β.
Note that Theorem 1 provides the necessary con-
dition to obtain a permutation β from π such, that
F(β) < F(π). Let B = (B
1
,B
2
,. ..,B
v
) be an ordered
partition of the permutation π ∈ Φ
n
to blocks. If a
job π( j) ∈ B
i
(B
i
∈ B), therefore moves which can
improving goal function value consists in reordering
a job π( j) before the first or after the last job of
this block. Let N
bf
j
and N
af
j
be sets of such moves
(N
bf
j
=
/
0 for j ∈ B
1
and N
af
j
=
/
0 for j ∈ B
v
). There-
fore, the neighborhood of the permutation π ∈ Φ
n
,
N(π) =
n
[
j=1
N
bf
j
∪
n
[
j=1
N
af
j
. (5)
As computational experiments show, the neighbor-
hood defined in (5) has a half smaller size than the
neighborhood of all the insert moves.
THE METHODOLOGY OF PARALLEL MEMETIC ALGORITHMS DESIGNING
645
2 MEMETIC ALGORITHM
All operations in a coevolutionary memetic algorithm
(selection, crossover, local optimization and succes-
sion) are executed locally, on some subsets of the cur-
rent population called islands. It is a strongly decen-
tralized model of an evolutionary algorithm. There
are independent evolution processes on each of the
islands, and communication takes place sporadically.
Exchanging individuals between islands secures di-
versity of populations and prevents fast imitating of
an individual with a local minimum as its goal func-
tion. On each island a hybrid algorithm is applied, in
which an evolutionary algorithm is used to determine
the starting solutions for the local search algorithm.
The outline of the standard memetic algorithm is pre-
sented on the Fig. 1.
Algorithm 1. Memetic algorithm
Number of iteration k :=0;
P
0
←initial population;
repeat
P
′
k
←Selection(P
k
);
P
′′
k
←Crossover(P
′
k
);
P
′′
k
←Mutation(P
′′
k
);
A ←RandomSubSet(P
′′
k
);
P
′′
k
← P
′′
k
∪LocalMinimumSet(A);
P
k+1
←Succession(P
k
, P
′′
k
)
k := k + 1;
until
some termination condition is satisfied;
Figure 1: Outline of the memetic algorithm.
3 PARALLEL MEMETIC
ALGORITHM
The parallel algorithms based on the island model di-
vide the population into a few subpopulations. Each
of them is assigned to a different processor which per-
forms a sequential memetic algorithm based on its
own subpopulation. The crossover involves only in-
dividuals within the same population. Occasionally,
the processor exchanges individuals through a migra-
tion operator. The main determinants of this model
are: (1) size of the subpopulations, (2) topology of
the connection network, (3) number of individuals to
be exchanged, (4) frequency of exchanging. The is-
land model of parallel memetic algorithm is charac-
terized by a significant reduction of the communica-
tion time, compared to the global model (with dis-
tributed computations of the fitness function only).
As shared memory is not required, this model is also
more flexible.
Below, a parallel memetic algorithm is proposed.
The algorithm is based on the island model of par-
allelism (see Bo˙zejko and Wodecki (Bo˙zejko and
Wodecki, 2006)). We have adapted the MSXF (Multi
– Step Crossover Fusion) operator which is used to
extend the process of researching for better solutions
of the problem. Originally, a MSXF has been de-
scribed by Reeves and Yamada (Reeves and Yamada,
1998). Its idea is based on local search, starting from
one of the parent solutions, to find a new good so-
lution where the other parent is used as a reference
point. Here we propose to use block properties de-
fined in the Section 1.3.1 to make the search pro-
cess more effective – preventchanges inside the block
(which are unprofitable from the fitness function’s
point of view). Such a proceeding is consistent with
an idea of not making unprofitable changes between
memes. In this way we design a MSXF+B (MSXF
with blocks) operator.
The neighborhood N (π) of the permutation (in-
dividual) π is defined as a set of new permutations
that can be achieved from π by exactly one adjacent
pairwise exchange operator which exchanges the po-
sitions of two adjacent jobs of a problem’s solution
connected with permutation π. The distance measure
d(π,σ) is defined as a number of adjacent pairwise ex-
changes needed to transform permutation π into per-
mutation σ. Such a measure is known as Kendall’s τ
measure. The outline of the procedure is presented on
the Fig. 2.
Algorithm 2. Multi-Step Crossover
Fusion with Blocks
Let π
1
, π
2
be parent solutions. Set x = q = π
1
;
repeat
Determine blocks in the solution π.
Determine restricted neighborhood N (π)
according to blocks;
For each member y
i
∈ N (π) calculate d(y
i
, π
2
);
Sort y
i
∈ N (π) in ascending order of d(y
i
, π
2
);
repeat
Select y
i
from N (π) with a probability
inversely proportional to the index i;
Calculate C
sum
(y
i
);
Accept y
i
with probability 1,
if C
sum
(y
i
) ≤ C
sum
(x), and with
probability P
T
(y
i
) = exp((C
sum
(x)−
−C
sum
(y
i
)) / T) otherwise
(T is temperature);
Change the index of y
i
from i to n and the
indices of y
k
, k = i+1,. ..,n from k to k−1;
until
y
i
is accepted;
x ← y
i
;
if
C
sum
(x) < C
sum
(q)
then
q ← x;
until
some termination condition is satisfied;
q is the offspring.
Figure 2: Outline of the Multi-Step Crossover Fusion with
Blocks procedure.
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
646
In the implementation proposed here Multi-Step
Crossover Fusion with Blocks (MSXF+B) is an inter-
island (i.e. inter–subpopulation) crossover operator
which constructs a new individual by making use
of the best individuals of different islands connected
with subpopulations on different processors. The con-
dition of termination consisted in exceeding 100 it-
erations by the MSXF+B function. The outline of
the whole parallel memetic algorithm is presented
on the Fig. 3.
Algorithm 3. Parallel memetic algorithm
parfor
j = 1,2,. .. , p { p - #processors }
i ← 0;
P
j
← random subpopulation connected
with processor j;
p
j
← number of individuals in
j-th subpopulation;
repeat
Selection(P
j
,P
′
j
);
Crossover(P
′
j
,P
′′
j
);
Mutation(P
′′
j
);
if
(k mod R = 0)
then
{every R iteration}
r := random(1, p);
MSXF+B(P
′
j
(1),P
r
(1));
end if
;
P
j
← P
′′
j
; i ← i + 1;
if
there is no improvement of the
average C
sum
then
{Partial restart}
r ← random(1,p);
Remove α = 90 percentage of individuals
in the subpopulation P
j.
;
Replenish P
j
by random individuals;
end if
;
if
(k mod S = 0)
then
{Migration}
r ← random(1,p);
Remove β = 20 percentage of individuals
in the subpopulation P
j
;
Replenish P
j
by the best individuals
from the subpopulation P
r
taken from processor r;
end if
;
until
Stop Condition;
end parfor
Figure 3: Outline of the parallel memetic algorithm.
4 COMPUTER SIMULATIONS
The algorithm was implemented in the Ada95
language and ran on the SGI Altix 3700 Bx2
supercomputer installed in Wrocław Center of
Networking and Supercomputing under the Novell
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server operating sys-
tem. Tests were based on 125 instances with
40,50 and 100 jobs taken from the OR-Library
APRD
number of jobs n
1 processor 4 processors
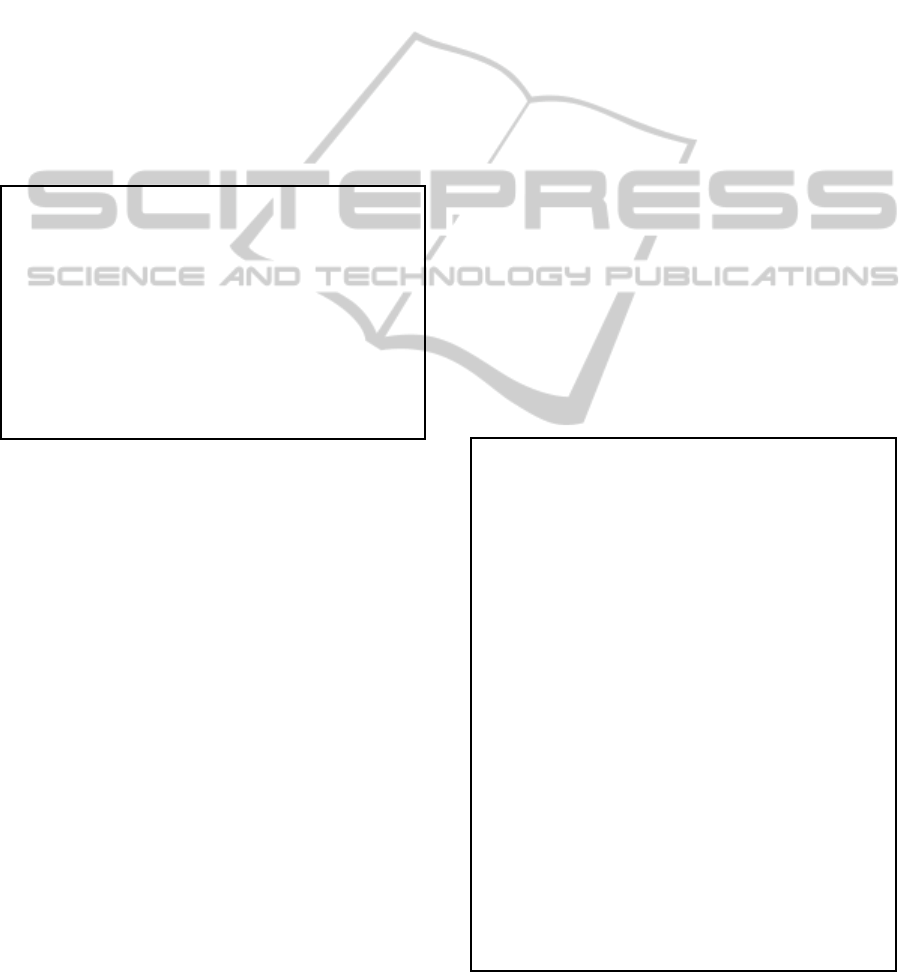
Figure 4: Average percentage relative deviations (APRD)
to the best known solutions for the sequence and parallel
memetic algorithms.
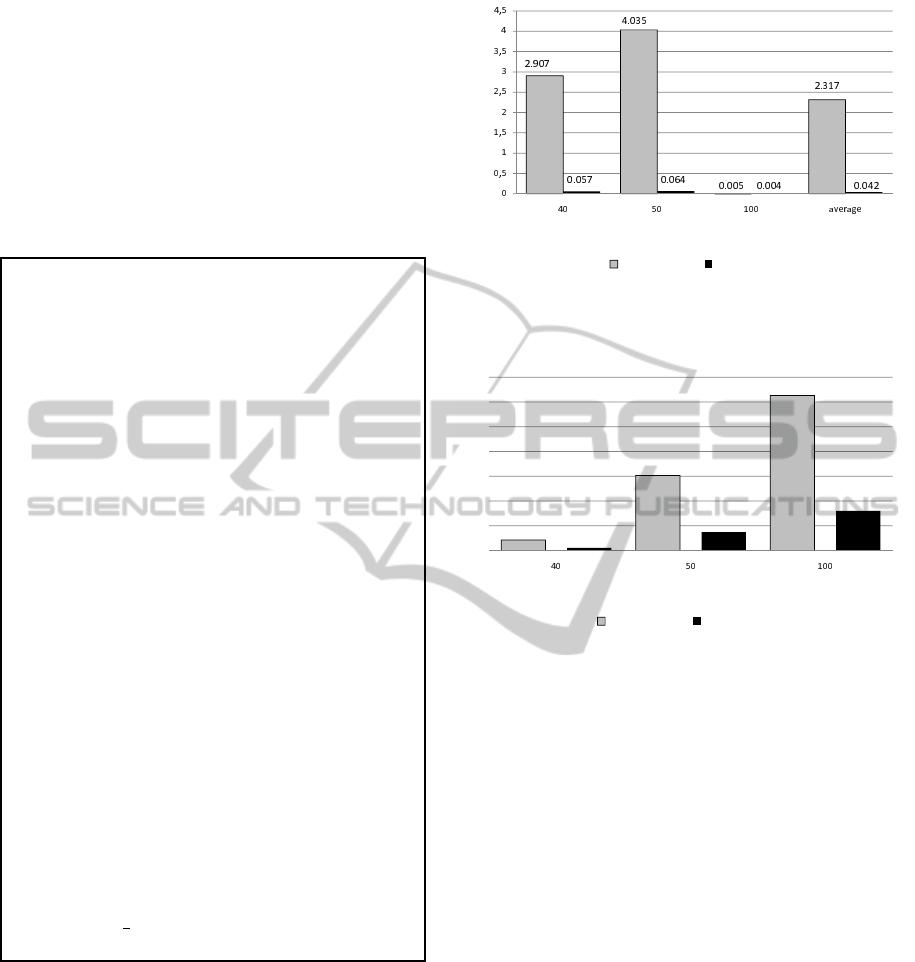
02:03:14
14:34:26
30:04:40
00:32:39
03:35:04
07:40:51
wall time (hours:min:sec)
number of jobs n
1 processor
4 processors
Figure 5: Computing times.
(http://people.brunel.ac.uk/∼mastjjb/jeb/info.html).
The results were compared to the best known, also
taken from OR-Library.
The computational results as well as computing
times are presented on Figures 4 and 5. The num-
ber of iterations was counted as a sum of iterations
on processors, and permanently set to 800. For exam-
ple, 4-processor implementations make 200 iterations
on each of the 4 processors, so we can obtain compa-
rable costs of computations. As we can observe, the
parallel versions of the algorithm achieve much better
results of the average and maximal relative deviation
from the optimal (or the best known) solutions, work-
ing (parallel) in a shorter time. Due to the small cost
of communication the speedup parameter of the par-
allel algorithms is almost linear.
5 REMARKS AND
CONCLUSIONS
The Lamarck evolution theory as well as memetic ap-
proach not only significantly extend traditional GA,
but offers more effective approach, too. It is well
THE METHODOLOGY OF PARALLEL MEMETIC ALGORITHMS DESIGNING
647

known, that the classic GA has a week search inten-
sification phase – genetic operators as well as a mu-
tation mainly diversify the search process. Addition-
ally, in the memetic approach it is possible to make
use of specific problem properties such as the new
MSXF+B operator with block properties. Embedding
special properties of the problem inside GA is usually
difficult. Further benefits are obtained by using an is-
land model with inter-island operator for the parallel
asynchronous coevolution.
As we observe MA is also able to improve conver-
gence time comparing to GA. Compared to a sequen-
tial algorithm, the parallelization of MA shortens the
computations time and improves quality of obtained
solutions. The proposed methodology of memetic al-
gorithms parallelization can be applied to solve con-
currently all scheduling problems with block proper-
ties, such as flow shop and job shop problems with
makespan criterion, single machine scheduling prob-
lems, etc., for which a solution is represented as a per-
mutation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was partially supported by the Polish Min-
istry of Science and Higher Education, grant No.
N N514 470439.
REFERENCES
Baker, K. and Scudder, G. (1990). Sequencing with ear-
liness and tardiness penalties: a review. Operations
Research, 38:22–36.
Berger, J. and Barkaoui, M. (2002). A memetic algorithm
for the vehicle routing problem with time windows.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Command
and Control Research and Technology Symposium,
http://www.dodccrp.org/events/7th ICCRTS/Tracks/
pdf/035.pdf.
Bo˙zejko, W. (2010). Parallel path relinking method for
the single machine total weighted tardiness problem
with sequence-dependent setups. Journal of Intelli-
gent Manufacturing, in press, doi: 10.1007/s10845-
009-0253-2.
Bo˙zejko, W., Grabowski, J., and Wodecki, M. (2006).
Block approach tabu search algorithm for single ma-
chine total weighted tardiness problem. Computers &
Industrial Engineering, 50:1–14.
Bo˙zejko, W. and Wodecki, M. (2005). Task realiation’s
optimization with earliness and tardiness penalties in
distributed computation systems. volume 2528 of
Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, pages 69–75.
Springer.
Bo˙zejko, W. and Wodecki, M. (2006). A new inter-island
genetic operator for optimization problems with block
properties. volume 4029 of Lecture Notes in Artificial
Intelligence, pages 324–333. Springer.
Bradwell, R. and Brown, K. (1999). Parallel asynchronous
memetic algorithms. In Cantu-Paz, E. and Punch, B.,
editors, Evolutionary Computation, pages 157–159.
Bubak, M. and Sowa, K. (1999). Objectoriented implemen-
tation of parallel genetic algorithms. In Buyya, R.,
editor, High Performance Cluster Computing: Pro-
gramming and Applications, volume 2, pages 331–
349. Prentice Hall.
Crainic, T. and Toulouse, M. (1998). Parallel metaheuris-
tics. In Crainic, T. and Laporte, G., editors, Fleet man-
agement and logistics, pages 205–251. Kluwer.
Crainic, T., Toulouse, M., and Gendreau, M. (1995). Par-
allel asynchronous tabu search in multicommodity lo-
cationallocation with balancing requirements. Annals
of Operations Research, 63:277–299.
Hoogeveen, J. and van de Velde, S. (1996). A branch
and bound algorithm for single-machine earliness-
tardiness scheduling with idle time. INFORMS Jour-
nal on Computing, 8:402–412.
Kliewer, G., Klohs, K., and Tschoke, S. (1999). Parallel
simulated annealing library: User manual. Technical
report, Computer Science Department, University of
Paderborn.
Lenstra, J., Kan, A. R., and Brucker, P. (1977). Complexity
of machine scheduling problems. Annals of Discrete
Mathematics, 1:343–362.
Michalewicz, Z. (1994). Genetic Algorithms + Data Struc-
tures = Evolution Programs. Springer Verlag.
Reeves, C. and Yamada, T. (1998). Genetic algorithms, path
relinking and the flowshop sequencing problem. Evo-
lutionary Computation, 6:45–60.
Smith, W. (1956). Various optimizers for single-stage pro-
duction. Naval Research Logistic Quart, 3:59–66.
Taillard, E. (1991). Robust taboo search for the quadratic
assignment problem. Parallel Computing, 17:443–
455.
Taillard, E. (1994). Parallel taboo search techniques for the
job shop scheduling problem. ORSA Journal on Com-
puting, 6:108–117.
Tang, J., Lim, M., and Ong, Y. (2006). Adaptation for paral-
lel memetic algorithm based on population entropy. In
Proceedings of the 8th Annual Conference on Genetic
and Evolutionary Computation (Seattle, Washington,
USA, July 08 - 12, 2006), GECCO ’06, pages 575–
582. ACM.
ICAART 2011 - 3rd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
648
