
A TRUST EVALUATION MODEL OF INTERNET
BANKING CUSTOMERS
Xiaoyan Wang
1,2
and Sulin Pang
1
1
Department of Accountancy & Institute of Finance Engineering
School of Management Jinan University, Guangzhou, China
2
Business Administration Department, Guangdong University of Finance, Guangzhou,China
Keywords: Internet banking, Trust, Trust degree, Trust evaluation model.
Abstract: It is a hot topics that how to measure the trust degree of the Internet banking customers. The major factors
on impacting the customers’ trust are their personal trust propensity and the recommendation trust before
the customer uses it. But the customer's own experience is the major factor after they have used it. In this
paper,we establish a two-stage Internet banking customer trust evaluation model. Using this model, the
bank managers can measure the trust degree of the customers in the different periods. We hope the model
can provide a strong support for the bank managers’ decision.
1 INTRODUCTION
The issue of trust has been paid all the while by
multidisciplinary such as psychology, sociology,
economics and other subjects concern. Psychologists
emphasize the internal nature of the trust ,and they
consider trust as inherent personality traits and a
kind of human expectations, beliefs, confidence,
varying with different individuals. Sociologists
stressed the externalities generated by trust that the
trust is a simplified mechanism as the product of
social mechanism and cultural norms. And trust is a
social phenomenon based on legal (laws and
regulations) or ethical (social and cultural norms)
and a kind of believe that other people can look
forward to cooperative behavior. While economists
argued that, trust is a result of the individual’s
rational choice when the benefit of trust is greater
than that of no confidence. Trust was discussed by
different disciplines from different perspectives, in
the resulting of different understanding, thus the
definition of trust has been unable to unify. Until
1995, Mayer et al (Mayer et al., 1995) advanced the
notion of trust currently widely accepted based on a
comprehensive understanding of various disciplines,
that one side always thought that the other part will
act in accordance with his manner regardless of his
monitoring and control abilities, thus he is willing to
put his own in the state of risk.
Along with the appearance of network
transaction methods, the issues network trust have
caused computer science concerns and made certain
achievements, especially in the area of trust model
research. Marsh (Marsh, 1994) (1994) was one of the
earliest scholars who carried out trust formalistic
research on the basis of sociology. He divided trust
into three types: basic trust, general trust and
situational trust, and proposed a calculable trust
model under the distributed artificial intelligence
environment. In the model, Marsh defined basic trust
as an individual tendency of trust dereferencing in
the interval [-1,1], and he stressed that the basic trust
varies with different individuals because of different
individual tendency. Beth (Beth et al, 1994) (1994)
introduced the concept of experience and used the
method to express the measure of the probability of
trust. Trust is defined in the interval [0,1]. The model
defines two kinds of trust relations: direct trust and
recommendation trust. Beth also gave the first
formula of recommendation trust worthiness: namely,
is the trust worthiness derived from a single path,
and the comprehensive recommendation trust
worthiness is simple average of these single-degree
recommendation trust worthiness. Abdul-Rahman et
al (Abdul-Rahman, 2000) (2000) considered no
practical significance about continuous quantitative
trust, they divided trust according to semantic
variables as fully trust, great trust, trust, a little trust,
not trust, not trust at all , and the discrete values
119
Wang X. and Pang S.
A TRUST EVALUATION MODEL OF INTERNET BANKING CUSTOMERS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003268601190124
In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Informatics and Semiotics in Organisations (ICISO 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-8425-26-3
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

are 4,3,2,1,0, -1. Tang et al (Wen and Zhong, 2003)
(2003) believe that trust is essentially a faith-based,
with subjective and ambiguous character, he draw
fuzzy set theory into trust management studies and
used the grade of membership to describe the
ambiguity of trust. They defined the trust vectors as
measurement mechanism of trust, and adopted
method of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation to
measure trust. But the model denied the random of
trust, and considered the ambiguity as the unique
characteristics of trust. Song et al (Song and Hwang,
2005) (2005), proposed the dynamic trust model
based on fuzzy logic under network environment in
account with the dynamic nature of trust. In their
model, they not only took into account the evidence
production of dynamic trust value, but also took into
account historical factors, and got the final trust
value through these two weighted average. But this
model did not take into account the factor of time.
Wang Liang et al (Liang and Dan, 2008) (2008)
introduced time attenuation function into their trust
model, and pointed out that the attenuation
coefficient values may be dependent on the user’s
specific strategy. Ma Li et al (Li and Weimin, 2009)
(2009) also pointed out that the trust worthiness is
relevant to time and will decay over time continuity.
They defined this feature of decline property of time.
As a virtual trading method, the auguries of
internet banking look gloomy. The lack of customer
s’ trust on internet banking is one of the most
important reasons of its development restrict
[9,10,11]. Therefore, the issue of customers trust on
internet banking is paid more and more attention at
home and abroad. At present, most scholars consider
internet banking as an information system, they
assumed that trust is one of the factors that affected
customers’ use of internet banking, and through the
use of the technology acceptance model proposed by
Davis (Davis, 1993), they used structural equation
model and empirical methods to test assumptions
reasonable. The results show that: Customers trust
indeed has a positive correlation with their intention
[13,14,15,16,17]. However, whether the customer
choose to use internet banking, it’s closely related to
the trust worthiness, and only it exceeded the
threshold value of the customers, will the customer
use it. But at this stage it is short of research work
specifically on quantitative aspects of customers
trust on internet banking. Therefore, this article tries
to build trust evaluation model about internet
banking customer based on the above-mentioned
research. Through the use of this model, the
managers can detect and manage the customers’ trust
to develop a more reasonable measure to increase the
customers’ trust, so as to promote the healthy
development of internet banking.
This paper is organized as follow: section II
defines the important conceptions used in setting
session; Section III establishes the trust evaluation
model on the stage of before the use of internet
banking and the after phase when the customers have
used; and finally a conclusion should be drawn.
2 DEFINITION
In order to research conveniently, it is needed to
explain several key concepts:
(1) Basic trust
In general, before the customers use internet
banking, it has a trust value, this trust worthiness is
the most primitive trust of the individual on others or
things, known as basic trust.
(2) Recommendation trust
Recommendation Trust is established according
to the recommendation of other entities to a
relationship of trust, but not conducted from the two
entities’ direct deal. And the trust worthiness
between them is based on the results of the
assessment from other entities.
(3) Direct trust
Direct trust is also known as the direct
experience or knowledge-based trust, it generates in
the process of direct contact of a trusted party with
trust party. Trust worthiness will increase along with
their experience and the results would change with
constantly revised.
(4) Trust worthiness
The size of the trust can be quantified, and
usually expressed by trust worthiness. Also it is
known as trust level of or trust value. It can use the
fuzzy variables, such as "trust", "no trust", etc. It can
also use the real numbers or probability in [0,1]. In
this paper it is defined in the interval of [0,1].
3 CUSTOMER TRUST ON
INTERNET BANKING
The formation and evolution of customers trust on
internet banking are dynamic process. With the
increasing of the time of transaction and the level of
transaction satisfaction, their mutual trust worthiness
will be in progressive development of infancy to
maturity (Corritore et al., 2003). This dynamic is
specifically manifested in two aspects: first, the
ICISO 2010 - International Conference on Informatics and Semiotics in Organisations
120
customer trust on internetbanking over changes over
time. At different times, in different scenarios,
customers trust on internet banking will not be on
the same level. For example, the customer trust is
relatively low because of his unfamiliarity with
internet banking when at the first time. But as the
time of transactions and their own experience
increasing continuously, the trust will increase.
Second, factors influencing on trust are at different
stages. In the initial stage of the formation of trust
relationships, customers are unable to conduct and
predict a comprehensive risk assessment because of
unfamiliarity. At this stage, the factors of customer
trust mainly depends on the basic trust and others
recommendation trust. And when the customer
makes trust decisions after using internet banking,
the above two factors will be gradually weakened.
At this moment, the major factor comes from in the
process of the direct interaction and accumulated
experience and knowledge. Customers adjust their
trust based on the experience each time they use
internet banking. If they are able to achieve the
desired effect, then the trust may increase. On the
contrary, the trust will diminish, even disappear (See
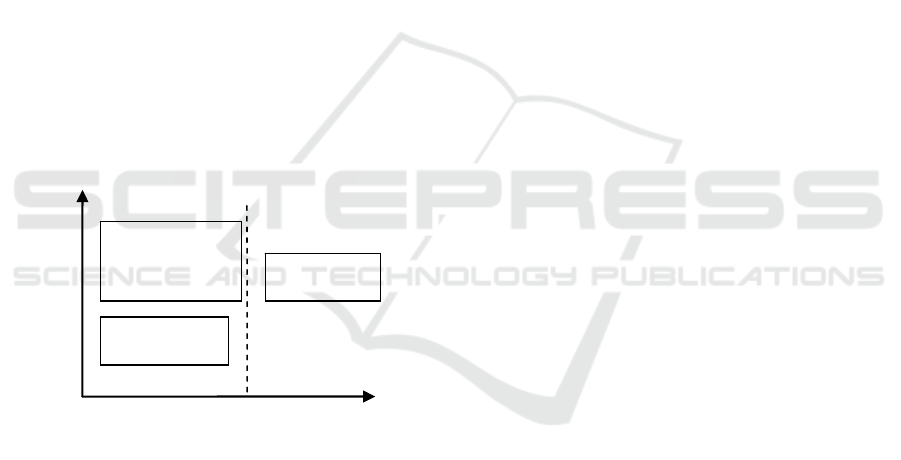
Figure 1).
Trust
source
Time
Pre‐occupancy
Trusteddecision
Afteruse
Recommendation
trust
Directtrust
Basictrust
Figure 1: The Dynamic Process of Customer Trust on
Internet banking.
In general, consumers are called potential
customers before they really use internet banking
transactions. The potential customers will become
real customers once they have used internet banking
transactions. Therefore, then, we establish the
customer trust evaluation model divided into two
kinds of cases: first, trust evaluation model of
potential customers; second, evaluation model of the
reality customers.
3.1 The Evaluation Model of Potential
Customers
3.1.1 Basic Trust
Before customers use the internet banking
transactions, actually they have had an initial trust
already, the trust called initial trust is the basic trust
Marsh has explained, and the basic trust is related to
the tendency of individuals. Trust tendency is
considered general trust and basic position as a
whole of the main body for other persons or things.
In theory, such a general trust can impact on the trust
judge on any specific person or thing. Because they
are all different in their main growth experience and
personality traits, as well as different cultural
backgrounds, so trust will vary accordingly. The
higher the customers trust tendency, the larger the
trust worthiness he has. On the contrary, the initial
trust worthiness is lower. Now, we use a
mathematical model to describe the basic trust of
potential customers.
Suppose that
t
x
TP
is basic trust of customer
x
at the moment
t , basic trust is different for different
customer, therefore:
t
xx
TP
α
=
,
[]
0,1
x
α
∈
(1)
The trust tendency of customer
x
is expressed
by
x
α
. Because each person's trust tendency is
stable, so
x
α
is a fixed constant. If the values of
x
α
is closer to 0, it is indicated that the initial
customer trust is low; if it’s closer to 1, it is
indicated that the initial customer trust is high.
In practical applications, we can use rating scales
to measure customer trust tendency and determine
the value of
x
α
. Rating scale is the most commonly
used psychometric instruments, and the semantic
quantifier is an important part of rating scales
evaluate the amount of psychological applying the
level of natural language. Cicchetti (1985) studies
show that: In the rating scale, the use of seven
quantifiers is the most suitable (Cicchetti and
Showalter, 1985), because if the semantics of
quantifiers rating too few, the sensitivity of scale
will be significantly reduced. On the contrary the
grading will be too much to distinguish the subjects’
areas so that the evaluation results would be affected.
According to the thoughts of Cicchetti et al, we use
seven semantic quantifier to measure the customer's
trust, that is "fully believe," "trust," " a little trust, "
"uncertain," "somewhat do not trust," "do not trust,"
"do not trust at all". The quantitative approach is to
A TRUST EVALUATION MODEL OF INTERNET BANKING CUSTOMERS
121
convert the semantic quantifier to equidistant values,
if "fully trust" means 1, and then "do not trust at all
"means 0.
3.1.2 Recommendation Trust
Trust has transmission characteristics. When the
potential customers are short of understanding of
internet banking or relevant information to judge the
trust, they rely on the recommendation information
of the third parties, such as customer's word of
mouth and the recommendation of some trust
assessment agencies. For example, customer A who
has never used internet banking can consult
customer B who has had such transactions, and
customer B would supply some trust-related
information to customer A, then Customer A will
build his trust on the internet banking through
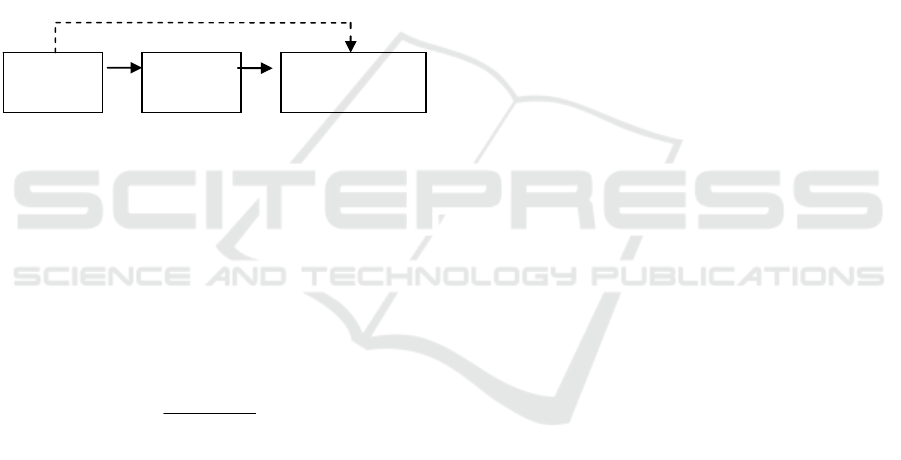
customer B. See figure 2 below:
customer
A
Internet
banking
customer
B
Figure 2: Trust transmission diagram.
Suppose at the moment t , the customer
x
has
received n recommendation trust worthiness from n
recommended persons (or advertising media,
third-party of network trust evaluation certification
agencies),
t
x
TR
is expressed the recommendation
trust worthiness on the internet banking generated by
others’ recommendation. Then,
()
1
1
n
j
j
xx
j
t
x
n
j
x
j
vtr
TR
v
=
=
⋅
=
∑
∑
(2)
[0,1]
j
x
tr ∈
[0,1]
j
x
v ∈
1, 2, 3, ,
j
n= "
.
In the formula above,
j
x
tr expresses the trust
worthiness that person
j
recommends to
customer
x
.
j
x
v represents the customers
x
focus
of the recommended information. If the value of
j
x
v is closer to 1, it is indicated that the
recommendation of the information has great the
impact on customer
x
.On the contrary,
j
x
v is closer
to 0, it indicates the recommendation of the
information has little the impact on customer
x
.
When applied, customers focus can still be
measured by rating scale too. Semantic quantifier
can use the seven levels as" take too much count," "
take much count," " take count," "generally" and
"give a little attention," " give little attention, "" not
give attention at all". If the value of "take too much
count" means 1, "not give attention at all" means 0.
3.1.3 Comprehensive Evaluation of the
Potential Customers Trust
As noted above, the potential customers trust
depends largely on the basic trust and
recommendation trust. Customers will adjust their
own trust based on their basic trust on the internet
banking and the recommendation trust. Suppose that
the basic trust of a potential customer on internet
banking is relatively high, but the recommendation
trust from other people is low, so his trust worthiness
on the internet banking may be reduced. On the other
hand, his basic trust has just started in relatively low
level, but the recommendation trust from other
people get relatively high, his trust will improve.
Therefore, the comprehensive assessment of the trust
should make a synthesis of basic trust and
recommendation trust, and thus get the overall trust
on internet banking. So, how to merge two of them
is the key to the establishment of the model. In order
to study conveniently, we consider the potential
customers as the recommending one by themselves,
so that the basic trust and recommendation trust can
be liable to the same treatment. Hereafter, we use
weighted average method to the synthesis of the
value of potential customers trust on internet
banking.
Suppose that
t
x
Trust
represents the trust of
potential customer
x
at the moment of t ,
t
x
TP
represents the basic trust of customer
x
at the
moment of
t , and
t
x
TR
represents the
recommendation trust of customer
x
. Then,
12
ttt
x
xx
Trust w TP w TR
=
⋅+⋅
(3)
In the above formula,
12
1ww+=,
1
w ,
2
w respectively represents the trust tendency
and the share weight of recommendation trust from
others in the overall trust.
3.2 Trust Evaluation Model of Real
Customers
The real customers have already used internet
banking, so their trust worthiness are associated with
their actual experience. In general, if the customer
has used the internet banking repeatedly, then the
ICISO 2010 - International Conference on Informatics and Semiotics in Organisations
122

customer trust is not only associated with the current
transaction, but also associated with his previous
evaluation. According to their actual experience,
customers will continue to adjust and update their
trust on the internet banking. In normal conditions,
satisfaction with the results of collaboration is basis
of trust relationship, and satisfaction largely
determines the level of trust. So the customers trust
can be measured by their satisfaction with the results
of collaboration. If the customer is satisfied with the
internet banking, his trust on the internet banking
will increase, otherwise that will be reduced. We
describe the different satisfaction by discrete scale
and natural language at the same time, as shown in
Table 3.
The following, we will describe direct trust of
the real customers by mathematical method:
Assume that customer
x
has used internet
banking for
n times, the variable
i
x
dt
indicated
that satisfaction of customer
x
at the
th
i time
transaction,
n
x
D
T represents the direct trust of
customer
x
after the
th
n transaction. Then after
the customer used internet banking for
n times, the
calculation of his direct trust is divided into two
situations:
①when
1n = ,
11
xx
TD td=
(4)
When customer uses internet banking the first
time, his trust is right the first time usage evaluation
because of his short of accumulation about relevant
experience.
②when
1n > ,
1
1
(1 )
1
n
i
ix
nn
i
xx
wtd
TD td
n
αα
−
=
=+−
−
∑
(5)
Among them,
1
1
1
n
i
ix
i
wtd n
−
=
−
∑
indicates average
value of the trust of customer's history, and
i
w (
01
i
w≤≤
) represents the time weighting factor.
α
and
1
α
−
respectively represents the average
value of customer's history and the share of current
trust in the updated trust value. Generally speaking,
if the history of trading is farther away from current,
then the smaller
α
will be, on the other hand, the
greater
α
will be.
The time weighting factors
12 1
,,,
n
ww w
−
"
represent the degree of customer focus at moment.
Scientific determination of weight vectors is the key
to get a reasonable result of evaluation. Time weight
vector can be determined according to different
criteria. Next, we use entropy method to determine
the value of
12 1
,,,
n
ww w
−
" . Entropy is called
average amount of information in information theory,
which is a measure of information. The entropy
value greater, the smaller amount of information
contained.
First, introduce the definition of entropy
I
of
time weighting vector and time-degree
λ
:
1
1
ln
n
kk
k
I
ww
−
=
=−
∑
(6)
1
1
1
2
n
k
k
nk
w
n
λ
−
=
−−
=
−
∑
(7)
The entropy
I
of time weighting vector reflect
different level of information contained included in
the weights.
λ
reflects the degree of emphasis on
the timing (See Table 1). When
λ
is closer to 0, it
is indicated that the more attention paid to the more
recent data by the customer, reflecting the idea of
time decaying.
Secondly, fix
k
w . In the situation of a given
λ
in advance, now we solve the following linear
programming problem:
1
1
1
1
1
1
max ln
1
..
2
1, [0,1]
1, 2, , 1
n
kk
k
k
k
k
n
kk
k
ww
nk
s
tw
n
ww
kn
λ
−
=
−
=
−
=
−
−−
=
−
=∈
=−
∑
∑
∑
"
(8)
Table 1: The Reference Table of Time-degree Scale.
λ
Illustration
0.1 Take highly account of recent data
0.3 Take relatively account of recent data
0.5 Equally in every stage
0.7 Take more account of long-dated data
0.9 Take highly account of long-dated data
0.2 、 0.4 、
0.6、0.8
Corresponds to the middle of the above two
adjacent data to determine
For example, when 0.1
λ
= , 6n = ,
(0.0029,0.0086,0.0255,0.0755, 0.2238,0.6637)w
=
.
A TRUST EVALUATION MODEL OF INTERNET BANKING CUSTOMERS
123

4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper established a two-stage model of
customers trust on internet banking including stage
of Pre-occupancy and after usage. The model has
certain maneuverability so that bank managers can
use it to measure customers trust at different time, so
as to support strong data for bank management
decision-making.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by the National Natural Science
Foundation (70871055); the New Century Talents
plan of Ministry of Education of China
(NCET-08-0615); the Key Programs of Science and
Technology Department of Guangdong Province
(2010); the Key Programs of Science and
Technology of Guangzhou.
REFERENCES
Mayer R C, Davis J H. Schoorman F D. An integrative
model of organizational trust [J].Academy of
Management Review,1995, 20: 709-734.
Marsh. S. Formalizing trust as a Computational Concept
[D]. 1994, University of Stirling: 56-60
T Beth, M. Boreherding, B. Klein: Valuation of trust in
open networks. In Porceedings of The European
Symposium Research in Computer Security [J].
Springe-Verlag, 1994, 3-18.
Abdul-Rahman. Supporting trust in virtual communities
[J]. Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences, 2000.
Tang Wen, Chen Zhong. Research of Subjective Trust
Management Model Based on the Fuzzy Set Theory
[J]. Journal of Software, 2003, 14(8): 1401-1408.
Song S S, Hwang K. Fuzzy trust integration for security
enforcement in grid computer [J]. In.proc.of the Int’l
Symp. on network and Parallel Computer. Berlin:
Springer-Verlag, 2005, 9-21.
Wang Liang, Liu Dan, Trust Modeling and Evaluation in
E-commerce [J]. Journal of Wuhan Bioengineering
Institute, 2008 (6): 77-80.
Ma Li, Zheng Weimin. Synthesize trust degree evaluating
motel for an information grid environment, Journal of
Tsinghua Universty, 2009 (4): 599-603.
Internet banking comes up against crisis of confidence,
financial information technology challedges [EB/0L]
http://industry.ccidnet.com, 2008-5-19.
Customer trust on internet banking declines. [EB/OL].
http://yndt.bank.cnfol.com, 2007-6-25.
“Internet banking” comes up against crisis of confidence
[EB/OL].http://news.2008.sina.com.cn, 2007-4-13.
Davis F D. User acceptance of information technology:
System characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral
impacts [J].Man-Machine Studies, 1993, 38: 475-487.
Marios Koufaris. Applying the technology acceptance
model and flow theory to online consumer behaviour
[J].Information Systems Research, 2002, 13 (2):
205-223.
Gefen David, Karahanna Elena, Straub. Trust and TAM in
online Shopping: An integrated model [J]. MIS
Quarterly, 2003, Vol (27), Issue 1: 51-90.
Yi-Shun Wang, Hsin-Hui Lin, Pin Luarn. Predicting
consumer intention to use mobile service [J].
Information System Jounral, 2006, 16: 157-179.
Jiao Yongbing, Wu Xiaoyun. Influences of Customers’
Trust on the Adoption of Internet Banking [J].Finance
Forum, 2007, 2 (12): 52-59.
Lou Zun. Empirical Research of Early Internet Banking
Adopters and Their behavior characteristics.
[J] .Electronic Payment, 2009 (2): 53-57.
Corritore C L, Kracher B, Thomas C, Wiedenbeck S.
Development and Validation for a Scale for Measuring
Online Trust [A]. Proceedings for Human Computer
Interaction International Conference, Human
Computer Interaction: Theory and Practice (part1) [C].
2003, 716-720.
Chang Junsheng, Wang Huaimin, Yin Gang. DyTrust: A
Time-Frame Based Dynamic Trust Model for P2P
SystemsDytrust [J]. Chinese Journal of Computers.
2006 (8): 1031-6031.
Cicchetti D V, Showalter D. The effect of cumbers of
rating scale category on levels of inter-rater reliability:
a Moute-Carl investigation Aoolied 1'svcholoical
Measuremeut, 1985, Vol (9): 31-36.
Guo Cheng, Li Mingchu, YAO Hongyan, HU
Honggang.Trust Model Based on Recommendation on
P2P Network [J]. Computer Engineeringng, 2008(12):
157-159.
Guo Yajun et al. A Method and Application of Dynamic
Comprehensive Evaluation [J]. Systems Engineering
Theory& Practice, 2007(10): 154-158 (2010).
ICISO 2010 - International Conference on Informatics and Semiotics in Organisations
124
