
LAMARCKIAN EVOLUTION OF NEURAL NETWORKS
APPLIED TO KEYSTROKE DYNAMICS
Paulo Henrique Pisani and Silvio do Lago Pereira
Department of Information Technology of FATEC-SP/CEETEPS, São Paulo, Brazil
Keywords: User profiling, Keystroke dynamics, Evolutionary artificial neural networks, Hybrid training, Lamarckian
evolution.
Abstract: The pace of computing and communications development has contributed to an increased data exposure
and, consequently, to the rise of an issue known as identity theft. By applying user profiling, which analyzes
the user behavior in order to perform a continuous authentication, protection of digital identities can be
enhanced. Among the possible features to be analyzed, this paper focuses on keystroke dynamics,
something that cannot be easily stolen. As keystroke dynamics involves dealing with noisy data, it was
chosen a neural network to perform the pattern recognition task. However, traditional neural network
training algorithms are bound to get trapped in local minimum, reducing the learning ability. This work
draws a comparison between backpropagation and two hybrid approaches based on evolutionary training,
for the task of keystroke dynamics. Differently from most evolutionary algorithms based on Darwinism, this
work also studies Lamarckian evolutionary algorithms that, although not being biologically plausible,
attained promising results in the tests.
1 INTRODUCTION
The evolution of computing systems along with
communication technologies over the past years
brought about the today so-called digital identity
and, as a consequence, more concerns regarding the
exposure of those data (Windley, 2005). The
increasing number of online services, such as e-
commerce and digital communities, worked in favor
of this exposure which contributed for a crime
known as identity theft. Identity theft is commonly
used referring to the crime of a thief that
masquerades as being someone else by illegally
using personal information of the victim (Duserick,
2004).
The process of checking whether an identity
belongs or not to a person is called authentication.
This process can be observed in a variety of
services, for example, user/password verification in
webmail sites. Authentication is performed by the
use of credentials, which may be classified as one or
a combination of the following (Windley, 2005):
What the user knows (e.g. password);
What the user has (e.g. card, token);
What the user is (e.g. biometrics).
The above items are also known as
authentication factors. In general, higher quantity of
factors implies in a higher security level and, as a
result, the authentication process is less likely to fail
(Windley, 2005). However, whatever authentication
factors are applied, usually, after the initial
authentication, an intruder is free to use and access a
system as the legitimate user would do. For
example, even using the most advanced biometric
technology, if someone authenticates to a system
and then go to a meeting leaving the system opened,
without locking it, there is no way to avoid intruder
actions unless the system has other security
mechanisms.
The scenario turns out to be worse when reports
showing that insider attacks (i.e. from employees of
the company itself) pose a threat of growing concern
(Kowalski and Cappelli, 2008). Among the types of
insider attacks, a report from FBI also showed that
the total of unauthorized insider access is about the
total of outsider attacks (Richardson, 2003).
Situations like the one mentioned in the previous
paragraphs can be avoided by the application of
continuous authentication methods, using features
that are harder to be violated. By observing the user
behavior, it is possible to define models that
358
Pisani P. and do Lago Pereira S..
LAMARCKIAN EVOLUTION OF NEURAL NETWORKS APPLIED TO KEYSTROKE DYNAMICS.
DOI: 10.5220/0003084503580364
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Evolutionary Computation (ICEC-2010), pages 358-364
ISBN: 978-989-8425-31-7
Copyright
c
2010 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
represent user's normal behavior. These models will
be called profiles through this paper. The process of
defining these profiles is known as user profiling
(Wang and Geng, 2009). User profiling is one of the
techniques employed by intrusion detection systems
(IDSs) (Di Pietro and Mancini, 2008). An IDS can
recognize an intruder by identifying deviations in the
behavior of a user in a system. Deviations that are
beyond a pre-defined threshold are recognized as an
intrusion. A number of features can be used to
define the profiles (Wang and Geng, 2009), such as
mouse dynamics, keystroke dynamics, e-mail
behavior, system calls, storage activity, just to
mention a few. This paper focuses on keystroke
dynamics for the definition of profiles.
In keystroke dynamics, the rhythm in which a
user types in the keyboard is analyzed. Keystroke
dynamics is classified as a behavioral biometric. In
the context of security, biometrics is the study of
methods to recognize people by physical and
behavioral features (Elftmann, 2006).
The task of pattern recognition in keystroke
dynamics is a complex one as the data collected is
considerably noisy. An artificial neural network
provides a powerful tool to perform this task due to
its intrinsic capacity to process incomplete and noisy
data (Braga et al., 2007). Nevertheless, applying
artificial neural networks involves some issues too.
Researchers showed that local search algorithms
(e.g. backpropagation) are very sensitive to the
initial set of weights (Kolen and Pollack, 1990). In
other words, the same architecture can perform very
differently depending on the initial set of weights
that, commonly, is defined as a set of small random
values (De Castro, 2006).
An attempt to solve this issue is the evolutionary
artificial neural networks (Yao, 1999). Evolutionary
artificial neural networks (EANN) combine two
fundamental forms of adaptation: learning and
evolution. Learning from the neural networks itself
and evolution from evolutionary algorithms. Among
the different levels of evolution in neural networks,
this paper highlights the application of evolutionary
algorithms to define the initial set of weights for
backpropagation (Yao, 1999). More details are
given in the next sections.
This paper aims to propose a method of detecting
intrusions by analyzing keystroke dynamics base
d on
Lamarckian evolutionary neural networks. The next
sections are organized as follows: in Section 2,
keystroke dynamics analysis is briefly described; in
Section 3, concepts of evolutionary neural networks
are outlined and the approach based on Lamarckian
evolution is presented; in Section 4, a methodology
is proposed to employ evolutionary neural networks
on keystroke dynamics; in Section 5, the
experimental results attained by the proposed
methodology are discussed; and, finally, in Section
6, we present our conclusions.
2 KEYSTROKE DYNAMICS
Keystroke dynamics analyzes the way a user types in
the keyboard. As mentioned in the previous section,
the analysis of keystroke dynamics is considered a
behavioral biometric and, as such, its performance is
measured by two fundamental rates (Elftmann,
2006):
False Acceptance Rate (FAR): percentage of
times an intruder is wrongly recognized as being the
legitimate user;
False Rejection Rate (FRR): percentage of times
a legitimate user is wrongly recognized as being an
intruder.
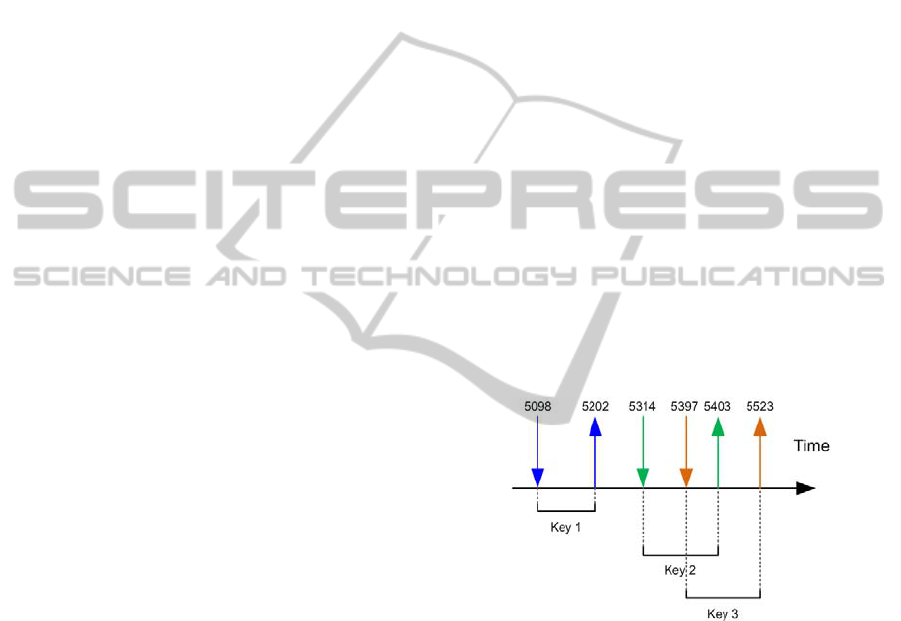
In general, the raw data captured to perform the
task of recognizing a user are a set of times
representing the time of each key down and key up,
as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Hypothetical times for a sequence of 3 keys.
From these raw data, recognition systems can
extract a number of features (Elftmann, 2006), such
as:
Latency: time spent between keys;
Dwell time: time span between a key press and a
key down;
Total typing time: time spent to type the whole
text being analyzed.
2.1 Related Works
The analysis of the way a user type on the keyboard
is far from being new. One of the first experiments
in this field was in 1980 (Gaines et al., 1980). The
LAMARCKIAN EVOLUTION OF NEURAL NETWORKS APPLIED TO KEYSTROKE DYNAMICS
359

first tests involved 7 people and reached a FAR of
0% and a FRR of 4%.
Some years later, profiles were created using a
login composed of username, password, first and last
name. Tests involved 33 people and reached a FAR
of 0.25% and a FRR of 16.67% (Joyce and Gupta,
1990).
Later on, the application of k-means and neural
network MLP were compared. Tests involving 21
users showed that the FRR reached by k-means was
19.5% while the MLP reached 1.0% (Cho et al.,
2000).
In 2004, it was employed support vector
machines (SVM) for the task of pattern recognition
in tests involving 10 people. With a two-class
algorithm it was achieved a FAR of 10% for
alphabetical passwords, while for numerical
passwords it was achieved 20% (a one-class
algorithm was able to reach 2% and 10%,
respectively) (Sang et al., 2004).
More recently, a MLP was again applied to an
experiment involving 22 users with different
computer skills and ages, ranging from 13 to 48
years. The overall performance rates were: FAR of
0.0152% and FRR of 4.82% (Ahmed et al., 2008).
In addition to the ones highlighted in this section,
other tests and methodologies have been applied in
the past years with regard to keystroke dynamics
(Elftmann, 2006). Over this period, huge
performance gaps were observed with FAR ranging
from 0% to 8% and FRR ranging from 0% to 45%
(Elftmann, 2006). Apart from that, almost all of the
tests were performed considering small populations
or a small number of collected samples, fact that
impacted the results of the tests.
3 LAMARCKIAN
EVOLUTIONARY NEURAL
NETWORKS
As it was observed in the previous section, neural
networks have been successfully employed in
several cases, demonstrating that it is a suitable
choice for the pattern recognition task when it comes
to keystroke dynamics. Whilst it is encouraging, it
must also be stated that common MLP training
algorithms, like backpropagation (BP), are sensitive
to initial conditions, such as the initial set of weights
(Kolen and Pollack, 1990).
Evolutionary artificial neural networks are a
special class of artificial neural networks that
combines the existing learning capabilities with
evolution capabilities brought by evolutionary
algorithms. Evolutionary algorithms are search and
optimization tools based on ideas from evolutionary
biology (De Castro, 2006). This approach can be
applied to different levels; however, the most
notable levels are (Yao, 1999): evolution of
connection weights, evolution of architectures and
evolution of learning rules. This work focuses on the
evolution of connection weights as a way to define
the initial set of weights in order to boost the results
reached by backpropagation.
3.1 Hybrid Training
The motivation behind this idea is that
backpropagation is known to get trapped in local
minimum of the error function due to its local search
and, therefore, not finding the best set of weights for
the network. Conversely, evolutionary algorithms
(De Castro, 2006) are known to be able to explore a
wide range of solutions at the same time, by
executing a global search in the solution space.
Nonetheless, evolutionary algorithms are also
known as not being able to reach the best possible
result and, thus, they are not suitable enough for fine
tuning. Considering these statements, evolutionary
algorithms can be used together with
backpropagation as they complement each other
(Yao, 1999).
One of the major questions when considering
this combination is the definition of chromosome
representation. In terms of encoding, there are two
main branches: binary representation and real-
number representation (Yao, 1999).
The former encode weight values as a sequence
of bits. In this form, a trade-off between precision
and length of chromosome must be observed. Few
bits might imply in a lack of learning capacity, while
large number of bits may generate rather long
chromosomes that lead to high use of computer
resources. However, traditional genetic operators
can be employed in this representation without any
change.
In the latter, connections weights are encoded as
a sequence of real-numbered values. In this case,
traditional genetic operators cannot be applied and,
thus, it requires special operators. Despite that, real-
number representation is argued to be a better
choice as it provides greater scalability.
3.2 Lamarckian Evolution
There are some methods of neural network training
that involves the use of learning as a guide to
ICEC 2010 - International Conference on Evolutionary Computation
360

evolution. In this setting, two main approaches are
Baldwinian and Lamarckian evolution. In
Baldwinian evolution (Cortez et al., 2002), at each
iteration of the evolutionary algorithm, a learning
algorithm (e.g., backpropagation) is executed in
order to evaluate the capacity of learning of each
individual. This evaluation is then used to change
the fitness value only. In Lamarckian evolution
(Castillo et al, 2006), the process is the same, but,
differently from the Baldwin approach, the learned
networks are encoded back to the chromosomes,
changing the original ones. Figure 2 shows the basic
flow of Lamarckian evolution applied to neural
networks training.
Figure 2: Lamarck evolution applied to neural network
training.
However, both methods require a high use of
computer resources. This work adopted the Lamarck
approach over the Baldwinian one due to previous
experiments that showed Lamarckian evolution
outperforming Baldwinian evolution (Ku et al.,
2003).
Although the Lamarck theory is not biologically
plausible, it has performed well in a number of tasks
(Castillo et al., 2006), contributing to the concept
that evolution can enhance gradient descent
algorithms. The concept behind the application of
Lamarckian evolution is that the search space is
reduced to minimum values only.
4 APPLICATION
This section presents details of the application
developed to recognize users by their typing rhythm
(Figure 3). The application was designed to protect
sensitive commands, which are the ones that can
either change critical configurations or damage the
operating system. It consists of three main
processes: feature extraction, neural network
training and recognition. The next sections will
further explain these processes.
Figure 3: Application developed for the tests.
4.1 Feature Extraction
After capturing the raw data of a command typed in
by the user, the extraction process takes place to
extract the vector of features that will be used as
input for the neural network. The implementation is
composed of two phases. Firstly, the process
generates a vector considering the time between
keys and dwell times as it is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Feature vector generated in the first phase of
extraction.
Where:
n is the length of characters of the considered
command;
i is the key index;
TA
i
is the dwell time (time spent to press a key)
and is calculated according to (1);
TB
i
is the flight time (time spent between the
instant of a key down and the subsequent key down)
and is calculated according to (2).
In (1) and (2), P
i
and S
i
are the instants of a key
down and a key up, respectively.
(1)
LAMARCKIAN EVOLUTION OF NEURAL NETWORKS APPLIED TO KEYSTROKE DYNAMICS
361
(2)
Secondly, the generated vector is reprocessed to
fit the range [-1;+1], as shown in Figure 5, according
to (3), (4) and (5). As the activation function of the
neurons is the sigmoid, variations in this range imply
in more significant variation of the function output.
Figure 5: Final feature vector.
(3)
(4)
(5)
4.2 Neural Network Training
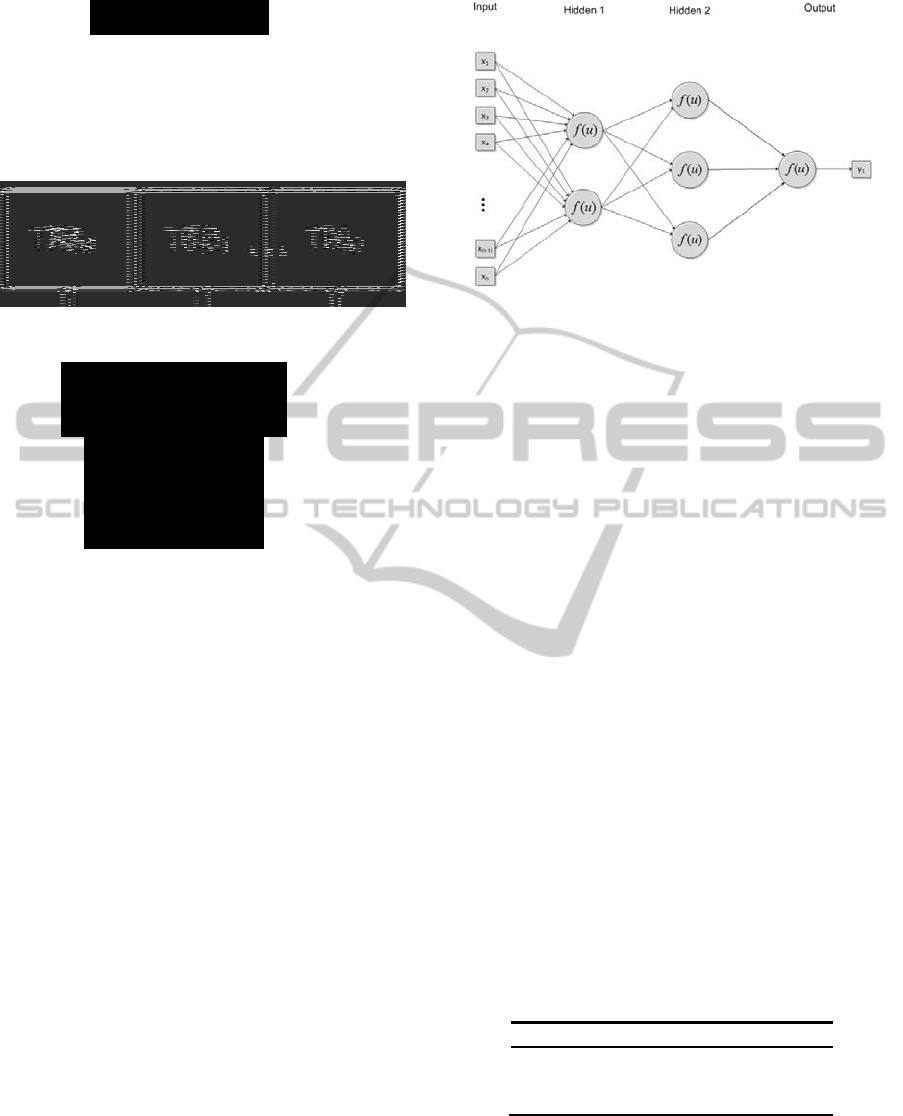
The neural network was defined, in an ad hoc way,
as follows (Figure 6): first hidden layer with 2
neurons, second hidden layer with 3 neurons and
output layer with 1 neuron. The number of input
values is the only aspect of the network that changes
for each command as it depends on its length.
The application supports three training
approaches: single backpropagation, evolutionary
based on Darwinian evolution and evolutionary
based on Lamarckian evolution. These approaches
were implemented in order to make possible the
comparison of their performance for the given task:
verifying users by their typing behavior.
In this application, it is defined a set of weights
for each user and command so that the training set is
composed of samples from the legitimate user and
the possible intruders (that are the captured samples
from other users). Feature vectors from the
legitimate user have output value equals to 1 and all
the others equals to 0. This approach is suitable for
this case as we are considering the fact that a
significant number of attackers are actually insiders
(Kowalski and Cappelli, 2008; Richardson, 2003).
Figure 6: Neural network architecture.
4.3 Recognition
The recognition is simply done by loading the
trained set of weights of a specific command for a
user and then testing the result of a given candidate
feature vector extracted. If the output is higher than
a threshold, the user is recognized as legitimate,
otherwise, it is not.
5 RESULTS
The tests considered three sensitive commands of
the Microsoft Windows operating system (OS):
ipconfig: can change IP configuration;
net stop: can start/stop OS services;
control userpasswords2: allows administration of
OS user accounts.
Each command was typed 10 times by each of
the 10 users that took part in the experiment; all of
them had good computer skills and used it every
day. We used the first 5 samples for training
purposes and the other 5 for the recognition test.
Tables 1, 2 and 3 show values determined for the
parameters of the algorithms under evaluation.
Table 1: Single backpropagation parameters.
Parameter Value
Epochs 1000
Learning rate 0,75
Alfa Momentum 0,15
ICEC 2010 - International Conference on Evolutionary Computation
362

Table 2: Darwinian approach parameters.
Parameter Value
Generations 50
Population 20
Elitism 10%
Chromosome
codification
By value: sequence of weight
values
Fitness function Inverse of the neural network
global error
Epochs 1000
Learning rate 0,75
Alfa Momentum 0,15
Table 3: Lamarckian approach parameters.
Parameter Value
Generations 50
Population 20
Elitism 10%
Chromosome
codification
By value: sequence of weight
values
Fitness function Inverse of the neural network
global error
Epochs 50
Learning rate 0,75
Alfa Momentum 0,15
The parameters shown in the previous tables
were adjusted so as to strike a balance between
neural network precision and processing time. The
second approach differs from the others by the
application of an evolutionary algorithm. In order to
compare the effect of the evolutionary algorithm in
this task, backpropagation parameters were the same
in both cases. Another aspect to be taken into
account is the fact that the second and third
approaches employ evolutionary algorithms. In
order to allow a comparison between these two
approaches, the parameters of the evolutionary
algorithms assumed the same values. Apart from
that, the chromosome encoding method was exactly
the same in the Darwinian and Lamarckian
approaches. In all tests, the definition of the initial
weight values was randomly defined in the range
[0.5;0.5] as recommended in previous researches
(Kollen and Pollack, 1990).
Table 4 shows the results attained by both
training approaches discussed in this paper. We
considered the threshold value as 0.75. As it could
be seen, due to the need to execute a learning
process and encode back the weights to the
chromosome at each iteration of the evolutionary
algorithm, the single backpropagation performed
much better in terms of time.
Table 4: Performance achieved by the algorithms.
Single Backpropagation
Command FAR FRR Training
control
userpasswords2
0,22% 18,00% 3,75s
ipconfig
0,22% 48,00% 2,61s
net stop
0,67% 38,00% 2,70s
Darwinian Approach
Command FAR FRR Training
control
userpasswords2
0,22% 8,00% 5,34s
ipconfig
0,22% 34,00% 3,87s
net stop
0,44% 38,00% 3,97s
Lamarckian Approach
Command FAR FRR Training
control
userpasswords2
0,22% 8,00% 185,61s
ipconfig
0,44% 30,00% 128,11s
net stop
0,44% 32,00% 132,70s
In applications that use dynamic profiles, the
training process would have to be performed several
times to keep the profile updated and, therefore, the
single backpropagation would be recommended.
Conversely, in applications whose profiles are static
or the update rate is reduced, the training time is not
a key concern, hence, the Lamarckian approach fits
better due to its increased performance in terms of
FAR and FRR.
The backpropagation algorithm is known to be
susceptible to initial conditions and, consequently,
may result in decreased performance of the neural
network (Kollen Pollack). An attempt to provide a
more robust training, less susceptible to initial
conditions, is the application of evolutionary
algorithms, which explore various parts of the search
space simultaneously. According to the results
shown in Table 4, both approaches based on
evolutionary algorithms achieved enhanced values
of FAR and FRR. However, the Lamarckian training
accomplished superior values of FAR and FRR,
showing that the concept of searching only on the
minima values of the search space is a suitable
strategy.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The evolution brought about by computing and
communication technologies is notable. However, at
the same time, numerous questions have been raised
with regard to current data exposure, especially in
LAMARCKIAN EVOLUTION OF NEURAL NETWORKS APPLIED TO KEYSTROKE DYNAMICS
363

light of the fact that insider attacks has been
increasing. Consequently, methods of continuous
user authentication became an issue of growing
concern. In general, these methods can recognize an
intruder by identifying deviations in the normal
behavior pattern of a user in a system.
In this paper, by employing the pattern
recognition potential of neural networks, it was
proposed a method for continuous user
authentication based on keystroke dynamics.
Nonetheless, the sensitiveness of traditional training
algorithms to initial conditions is a well-known
problem in neural network applications. In order to
deal with this problem, we tested the application of
evolutionary neural networks based on both
Darwinian and Lamarckian evolution. As it could be
observed, if one considers that training time is not a
limiting factor, since training may be performed
once per user, a Lamarckian evolutionary training
algorithm is an appropriate choice. Nonetheless, the
use of evolutionary algorithms implies the need of
adjusting an increased number of parameters.
In our experiments, biometric rates (FAR and
FRR) were enhanced by the hybrid approaches
(evolutionary training) over a traditional single back
propagation. Besides that, evolutionary artificial
neural networks provide a more reliable training, as
they are less likely to select an inappropriate set of
weights, when compared to a simple set of random
values.
In future works, we intend to extract and analyze
other features from the keystroke dynamics in order
to select a set of features which allows a greater
differentiation between legitimate users and
intruders. Apart from that, additional behavior
features (e.g. mouse dynamics) can be explored to
improve the overall system performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Dr. Luciana Kassab
(FATEC-SP) for her help, and CNPq (grant
304322/2009-1) and FAT for financial support.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, A. A. E., Traore, I., Almulhem, A., 2008. Digital
Fingerprint Based on Keystroke Dynamics. In:
Proceedings of the Second International Symposium
on Human Aspects of Information Security &
Assurance.
Braga, A. P., Carvalho, A. C. P. L. F., Ledermir, T. B.,
2007. Artificial Neural Networks. (in Portuguese)
LTC.
Castillo, P. A., Arenas, M. G., Castellano, J. G., Merelo, J.
J., Prieto, A., Rivas, V., Romero, G., 2006.
Lamarckian Evolution and the Baldwin Effect in
Evolutionary Neural Networks. Computing Research
Repository (CoRR).
Cortez, P., Rocha, M., Neves, J., 2002. A Lamarckian
Approach for Neural Network Training. Neural
Processing Letters, Vol. 15. Springer.
Cho, S., Han, C., Han, D. H., Kim, H., 2000. Web-Based
Keystroke Dynamics Identity Verification Using
Neural Network. In: Journal of Organizational
Computing and Electronic Commerce, Vol. 10. Taylor
& Francis.
De Castro, L. N., 2006. Fundamentals of Natural
Computing. Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Di Pietro, R., Mancini, L. V., 2008. Intrusion Detection
Systems. Series: Advances in Information Security -
Vol. 38. Springer.
Duserick, W., 2004. Whitepaper on Liberty Protocol and
Identity Theft. Liberty Alliance Project.
Elftmann, P., 2006. Secure Alternatives to Password-
based Authentication Mechanisms. Laboratory for
Dependable Distributed Systems. RWTH Aachen
University.
Gaines, R., Lisowski, W., Press, S., Shapiro, N., 1980.
Authentication by keystroke timing: Some preliminary
results. Technical Report Rand report R-256-NSF.
Rand corporation.
Joyce, R., Gupta, G., 1990. Identity Authentication Based
on Keystroke Latencies, Communications of the ACM,
v. 33, p. 168-176.
Kolen, J. F., Pollack, J. B., 1990. Back Propagation is
Sensitive to Initial Conditions. Laboratory for
Artificial Intelligence Research. The Ohio State
University.
Kowalski, E., Cappelli, D., 2008. Insider Threat Study:
Illicit Cyber Activity in the Information Technology
and Telecommunications Sector. Software
Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon.
Ku, K. W. C., Mak, M. W., Siu, W. C, 2003. Approaches
to Combining Local and Evolutionary Search for
Training Neural Networks: A Review and Some New
Results. In A. Ghosh and S. Tsutsui, editors, Advances
in Evolutionary Computation. Springer-Verlag.
Richardson, R., 2003. CSI/FBI Computer Crime and
Security Survey. Computer Security Institute.
Sang, Y., Shen, H., Fan, P., 2004. Novel Impostors
Detection in Keystroke Dynamics by Support Vector
Machine. Parallel and Distributed Computing:
Applications and Technologies, Vol. 3320/2005.
Springer, Heidelberg.
Wang, L., Geng, X., 2009. Behavioral Biometrics for
Human Identification. Medical Information Science
Reference. IGI Global.
Windley
, P. J., 2005. Digital Identity. O'Reilly Media.
Yao, X., 1999. Evolving artificial neural networks. In:
Proceedings of the IEEE, 87(9):1423-1447. IEEE
Press.
ICEC 2010 - International Conference on Evolutionary Computation
364
