
BALANCING MODULARITY AND KNOWLEDGE IN DESIGNING
AGILE ORGANIZATIONS
The Case of Outsourcing
Kris Ven, Benazeer Shahzada and Jan Verelst
Department of Management Information Systems, University of Antwerp
Prinsstraat 13, B-2000 Antwerp, Belgium
Keywords:
Modularity, Knowledge, Absorptive capacity, Outsourcing, Agility.
Abstract:
The ability to innovate is of increasing importance for organizations to increase their competitiveness. Since
organizations are becoming increasingly dependent on information technology (IT) to support their operations,
IT nowadays plays a crucial role in stimulating innovation in organizations. It has also been shown that
IT offers opportunities to organizations to increase their agility. In this paper, we argue that in order for
organizations to innovate with IT, design parameters are needed which can be governed by organizations. Our
focus in this paper is on how modularity and knowledge can be used as design parameters. Although the
importance of knowledge has been widely acknowledged in literature, organizational modularity has received
far less attention. We will demonstrate that attention to both design parameters is essential to innovate with
IT. We focus hereby on an application within the context of IT outsourcing. We provide a framework that
has a strong theoretical foundation which illustrates how the concepts of modularity, knowledge, outsourcing,
agility, and innovation are related to each other.
1 INTRODUCTION
The ability to innovate is of increasing importance for
organizations to increase their competitiveness. Sev-
eral authors have indeed argued that the ability to in-
novate successfully will to a large degree determine
the competitiveness of organizations (Hamel, 1998).
In today’s increasingly volatile environments, organi-
zations must be able to respond quickly to their en-
vironment in order to innovate successfully (Teece
et al., 1997; Eisenhardt and Martin, 2000). By being
able to detect changes in its environment and to re-
spond to these changes in an effective and swift man-
ner, an organization can become more agile. Agility
can be considered a measure of an organization’s abil-
ity to change and adapt to its new environment (Neu-
mann and Fink, 2007).
Organizations are becoming increasingly depen-
dent on information technology (IT) to support their
operations. As a result, IT nowadays plays a crucial
role in stimulating innovation in organizations (Bryn-
jolfsson and Saunders, 2010). It has indeed been
shown that IT offers opportunities to organizations
to increase their agility and flexibility (Neumann and
Fink, 2007; Sambamurthy et al., 2003).
Lately, it has been argued that organizations
should be designed. An organization designed using
design rules can be more agile and is therefore bet-
ter able to react to changes in the environment. This
issue is explored in the Enterprise Architecture (EA)
domain. Unfortunately, current EA models and arti-
facts have a descriptive, rather than prescriptive na-
ture. In addition, it is not fully clear yet which design
rules exist. We therefore argue that a strong theoreti-
cal basis is required to identify design parameters that
can be governed by organizations. In this paper, we
discuss how modularity and knowledge can be used
as design parameters. Both knowledge and modular-
ity represent hands-on design parameters that can be
governed by organizations. We illustrate this within
the context of IT outsourcing. IT outsourcing is an
interesting topic, since it offers many opportunities,
but at the same time it may also pose some threats to
organizations. We will demonstrate that attention to
both design parameters is essential to innovate with
IT. In addition, it will be shown that both modular-
ity and knowledge are strongly interrelated and that
organizations need to find a balance between both de-
sign parameters. To this end, we provide a frame-
work that has a strong theoretical foundation which il-
189
Ven K., Shahzada B. and Verelst J. (2010).
BALANCING MODULARITY AND KNOWLEDGE IN DESIGNING AGILE ORGANIZATIONS - The Case of Outsourcing.
In Proceedings of the Multi-Conference on Innovative Developments in ICT, pages 189-194
DOI: 10.5220/0002967101890194
Copyright
c
SciTePress
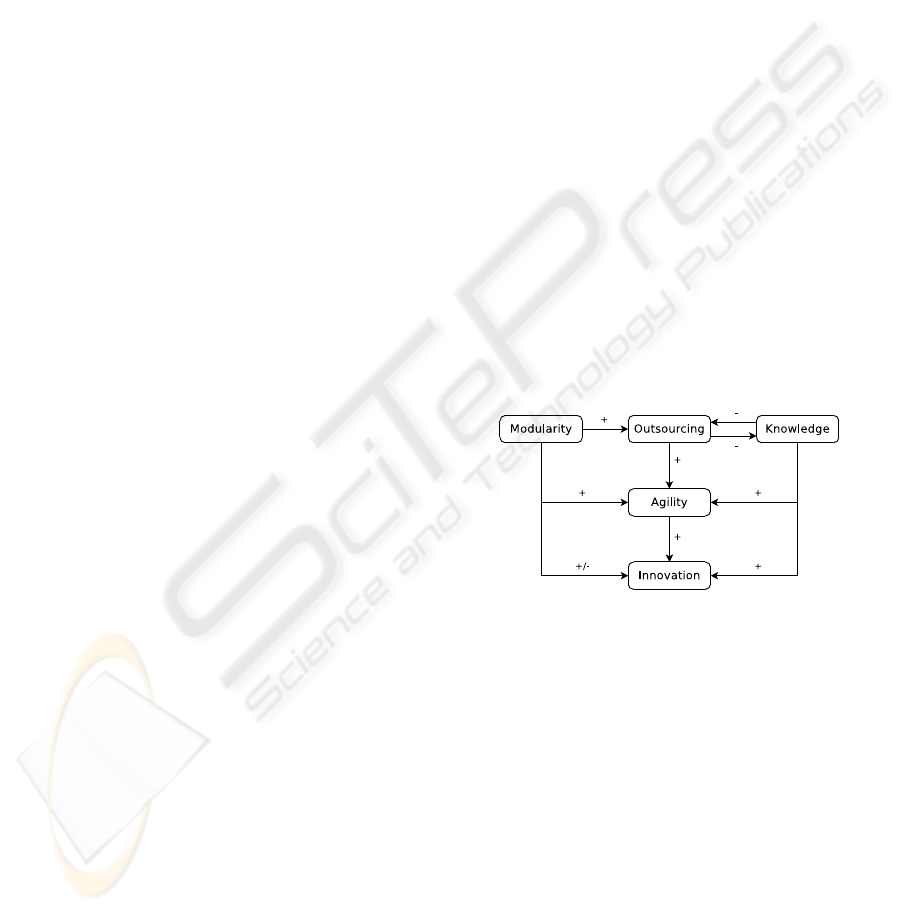
lustrates how the concepts of modularity, knowledge,
outsourcing, agility, and innovationare related to each
other.
2 BACKGROUND
In this section, we briefly introduce the concepts of
modularity and knowledge.
2.1 Modularity
Modularity is a concept from systems theory that has
been used in several domains. A common theme un-
derlying the concept of modularity in each of these
domains is agility and flexibility (Sanchez and Ma-
honey, 1996; Baldwin and Clark, 2000). The idea be-
hind modularity is that a system should be composed
in such a manner that all components are loosely cou-
pled. To this end, system elements that must in-
tensively interact with each other should be isolated
in a separate module to ensure that changes to this
module do not have an influence on the rest of the
system. Communication between modules is man-
aged by well-defined interfaces (Baldwin and Clark,
2000). The concept of modularity has, amongst oth-
ers, been used in software engineering and product
design. More recently, modularity has also been used
with respect to the design of organizations (Tiwana,
2008; Campagnolo and Camuffo, 2010; Sanchez and
Mahoney, 1996; te Winkel et al., 2008). This re-
search area investigates how organizations can be
constructed using loosely coupled autonomous orga-
nizational units that allow organizationsto adapt more
quickly to changing environments (Sanchez and Ma-
honey, 1996; te Winkel et al., 2008).
2.2 Knowledge
The importance of organizationalknowledgehas been
acknowledged in several fields, including manage-
ment and information systems (Teece et al., 1997;
Eisenhardt and Martin, 2000; Kogut and Zander,
1992; Attewell, 1992). It has been noted that activities
such as skill acquisition, the management of knowl-
edge, and know-how and learning are key strategic
issues (Teece et al., 1997). Knowledge is also con-
sidered a particularly important dynamic capability
that allows organizations to compete in volatile mar-
kets (Eisenhardt and Martin, 2000; Kogut and Zan-
der, 1992; Grant, 1996). Some scholars even con-
sider knowledge to be the most important resource
of an organization (Grant, 1996). Hence, it is im-
portant that organizations invest in further expand-
ing their knowledge base. This is emphasized by the
absorptive capacity theory which starts from the as-
sumption that external sources of knowledge are crit-
ical to guide the innovation process within organiza-
tions. Organizations will differ in their ability to ex-
ploit this external knowledge and will therefore ex-
hibit different patterns of innovation. The higher the
organization’s absorptive capacity, the greater the or-
ganization’s ability to create new knowledge (Cohen
and Levinthal, 1990). Exposure to outside sources of
knowledge is crucial to the innovation process within
organizations, since the organization can then com-
bine this external knowledge with the internally avail-
able knowledge and put it to new use (Cohen and
Levinthal, 1990). This requires that some knowledge
transfer takes place from the environment to the orga-
nization (Cohen and Levinthal, 1990; Kogut and Zan-
der, 1992).
3 OUTSOURCING
In this section, we will show how organizational mod-
ularity and knowledge can be used as design parame-
ters and how they can impact an organization’s agility
and ability to innovate. We illustrate this within the
context of IT outsourcing decisions.
Figure 1: Theoretical framework.
The theoretical framework developed in this study
is shown in Figure 1. This framework can be used
to balance the modularity and knowledge design pa-
rameters with respect to the outsourcing decision. In
this framework, it can be seen that there is a positive
link between the use of outsourcing and the agility of
the organization. Previous studies have indeed sug-
gested that the use of outsourcing can increase the
agility of organizations (White et al., 2005; Mason
et al., 2002). Through the use of outsourcing, organi-
zations can become more flexible since they can gain
access to specific knowledge possessed by the service
provider, without having to invest in a learning pro-
cess. Conversely, when specific expertise is no longer
needed by the organization, outsourcing contracts can
be relatively easily terminated without having an im-
pact on the internal human resources. By being more
INNOV 2010 - International Multi-Conference on Innovative Developments in ICT
190

agile, organizations increase their ability to innovate,
as it allows them to react more quickly to changes in
the environment (Sambamurthy et al., 2003; Eisen-
hardt and Martin, 2000). We will now discuss how
modularity and knowledge influence the outsourcing
configuration and innovation.
3.1 Modularity and Outsourcing
Previous literature on product modularity indicates
that there is a positive link between modularity and
the use of outsourcing (Frigant and Talbot, 2005;
Sako, 2003; Campagnolo and Camuffo, 2010). In or-
der to be able to outsource certain tasks to external
organizations, some degree of modularity is required
(Campagnolo and Camuffo, 2010; Sako, 2003). This
ensures the definition of clear interfaces that allow ef-
ficient communication between the customer and ser-
vice provider which form a basis for the outsourcing
contract (Baldwin and Clark, 2000). Relatively few
studies have investigated this link with respect to or-
ganizational modularity. The few studies so far sug-
gest that modularity also has a positive effect on the
use of outsourcing in such contexts (Tiwana, 2008;
Campagnolo and Camuffo, 2009). This can be ex-
plained by the fact that some level of organizational
modularity is required to be able to outsource cer-
tain tasks to a service provider. Moreover, the more
loosely coupled the organizational structure, the eas-
ier it is to outsource certain components. Neverthe-
less, additional research on this topic is required.
3.2 Modularity and Innovation
Several studies have explored the impact of modu-
larity on innovation. However, the exact nature of
the relationship is not very clear. Some studies have
suggested that modularity has a positive impact on
innovation. Those studies have argued that modu-
lar product architectures provides increased flexibil-
ity, thereby allowing organizations to innovate with
respect to product features that are important to cus-
tomers such as speed, convenience, and customiza-
tion (Baldwin and Clark, 2000). In addition, mod-
ular structures are preferred over integrated struc-
tures when flexibility and rapid innovation are impor-
tant (Baldwin and Clark, 2000). Other authors have
warned that modularity can also have a negative im-
pact on innovation. It has been noted that increased
modularity generally reduces the need for knowl-
edge sharing between customer and service provider,
given the increased codification of knowledge and the
specification of standard interfaces (Tiwana, 2008).
This reduction in the degree of knowledge sharing
may become an obstacle to innovation, since the cus-
tomer may have insufficient knowledge of—and con-
trol over—the activities of the service provider. Fi-
nally, although higher modularity may facilitate the
identification of emerging technologies, organizations
may lack the absorptive capacity to assimilate it and
to innovate(Cohen and Levinthal, 1990). The link be-
tween organizational modularity and innovation has
received very little attention in literature. One of the
very few studies on this topic suggests the presence of
a positive link (te Winkel et al., 2008). It has also been
noted that modular organizational forms are more
likely in industries with a higher number of product,
process and organizational innovations (Campagnolo
and Camuffo, 2009). Hence, the exact relationship
between modularity and innovation is not fully clear.
3.3 Knowledge and Innovation
Literature provides strong evidence for the positive
influence of knowledge on innovation (Cohen and
Levinthal, 1990; Wheeler, 2002; Fabrizio, 2009;
Kogut and Zander, 1992). The importance of inter-
nal knowledge, and the need for organizations to ex-
pand their knowledge base forms the basis of the ab-
sorptivecapacity theory (Cohen and Levinthal, 1990).
Organizations with a higher absorptive capacity will
be able to recognize the potential of emerging tech-
nologies more quickly, and adopt them before their
competitors to innovate (Cohen and Levinthal, 1990;
Wheeler, 2002). Having a broad knowledge base also
facilitates the identification of new opportunities by
making connections between different pieces of in-
formation that have not been made before. The ab-
sorptive capacity theory therefore considers external
sources of knowledge to be critical in guiding the in-
novation process within organizations. Although ex-
ternal knowledge can be obtained through outsourc-
ing, the organization still requires a minimum level
of internal knowledge to recognize opportunities for
the organization to innovate (Cohen and Levinthal,
1990). Otherwise, it is fully dependent on external
parties to support its innovation process. In today’s
information economy the production of information
goods becomes increasingly important (Brynjolfsson
and Saunders, 2010). Since the production of infor-
mation goods relies on IT, innovation becomes in-
creasingly a knowledge-intensive activity.
3.4 Knowledge and Outsourcing
Knowledge and outsourcing can influence each other
in two ways. First, the availability of internal knowl-
edge can have an effect on the outsourcing configu-
BALANCING MODULARITY AND KNOWLEDGE IN DESIGNING AGILE ORGANIZATIONS - The Case of
Outsourcing
191

ration. If sufficient internal knowledge is available,
the need for outsourcing may be small. Conversely,
if specific knowledge that is required by the organi-
zation is not available internally, this knowledge can
be obtained from service providers (Tiwana, 2008).
Second, the outsourcing configuration can also have
an effect on the knowledge base of the organization.
If the organization decides to outsource certain ac-
tivities that were previously performed in-house, the
organization risks loosing the knowledge related to
those activities (Earl, 1996). Conversely, if the orga-
nization decides to cancel an outsourcing contract and
to perform these activities in-house, the organization
will have to (re)acquire the necessary knowledge to
perform these activities. Some scholars have indeed
warned about the potential negative impact of out-
sourcing on organizational learning, the competence
of the internal IT staff and the loss of innovative ca-
pability (Earl, 1996). Outsourcing a set of activities
may reduce the organization’s ability to bring those
activities back in-house at a later time. If the organi-
zation decides to reverse its decision to outsource a set
of activities, this means that the organizationwill have
to invest in a process of organizational learning since
the knowledge required to perform these activities has
to be reacquired. The ease with which this process of
organizational learning can take place depends on the
absorptive capacity of the organization (Cohen and
Levinthal, 1990). Once an organization ceases to in-
vest in absorptive capacity, it will become difficult to
acquire external knowledge in the future, even if this
knowledge was once present in the organization (Earl,
1996). In the extreme case, this may even create a sit-
uation in which the organizationis locked out from fu-
ture opportunities (Cohen and Levinthal, 1990). The
longer it takes the organization to complete this learn-
ing process, the lower the ability of the organization
to react to changes in its environment. As a result, the
agility of the organization decreases and so does the
ability of the organization to innovate.
4 DISCUSSION
In this paper, we developed a comprehensive frame-
work that integrates the results from previous stud-
ies and that provides a better understanding of the
various relationships between modularity, outsourc-
ing, knowledge, agility and innovation (see Figure 1).
This framework provides one possible explanation for
the conflicting evidence with respect to the impact of
modularity on innovation. Although a positive rela-
tionship exists between modularity and outsourcing,
the use of outsourcing may have a negative effect on
the knowledge base of the organization. This will
have a negative impact on the agility of the organi-
zation and its ability to innovate. Whether this neg-
ative impact on innovation will take place, depends
on how both modularity and knowledge simultane-
ously impact innovation. Hence, organizationsshould
consider both effects when making outsourcing deci-
sions.
Both modularity and knowledge are therefore im-
portant design parameters. Organizations can make
strategic decisions to make changes with respect to
both parameters in order to increase their agility and
ability to innovate. Evidently, some trade-off will
have to be made with respect to both parameters. We
have provided an example of how such evaluation
can take place within the context of outsourcing. It
is important to note that our framework does not in-
tend to assign a priority to modularity and knowledge,
or even agility and innovation. Rather, organizations
should decide on the importance of these parameters
within the organization-specific context and depend-
ing on their strategy. Based on the goals of the organi-
zation, they should find a balance between the design
parameters of modularity and knowledge.
Outsourcing is an important topic to study in
this regard. In the past, outsourcing has primar-
ily been used to externalize non-core and non-
knowledge-intensive activities (e.g., programming).
Currently, outsourcing is increasingly used for highly
knowledge-intensive activities that affect the core of
the organization. For example, service providers are
gaining knowledgeabout the business processes of or-
ganizations. The outsourcing of business processes
requires highly modular structures, but this may im-
ply that little knowledge transfer takes place between
customer and service provider, and as a result valu-
able knowledge leaves the organization (Earl, 1996;
Tiwana, 2008). In discussions with informants in Bel-
gian organizations, we have noted that several orga-
nizations are loosing valuable knowledge about their
IT infrastructure and their business processes. This is
an issue that has been understudied in literature with
respect to innovation, and current management tools
and frameworks pay too little attention to this issue.
Our findings have important practical implica-
tions. It is commonly known that European orga-
nizations are—on average—smaller than US organi-
zations. Eurostat statistics show that 98.7% of Eu-
ropean organizations have less than 50 employees.
Even when omitting so-called micro-organizations
with less than 10 employees, organizations between
10 and 49 employees still represent 84.2% of the Eu-
ropean organizations with 10 or more employees (Eu-
rostat, 2010). We have learned from meetings with
INNOV 2010 - International Multi-Conference on Innovative Developments in ICT
192

informants in Belgian organizations that in many of
these organizations, no internal technical IT staff is
present, with the exception of one person who is re-
sponsible for making decisions with respect to IT.
Frequently, this person also has other responsibili-
ties. This especially applies to organizations that do
not make intensive use of IT. As a result, all activ-
ities related to IT are outsourced to a local service
provider. Given the lack of internal resources, this ser-
vice provider will provide the organization with an IT
infrastructure and will continue to maintain it, while
no knowledge is being transferred between both or-
ganizations. Hence, the organization does not learn
about the opportunities IT could offer to the organiza-
tion, and its ability to innovate with IT remains lim-
ited. Traditionally, literature has suggested a positive
link between organization size and innovation, due to
the fact that large organizations have more resources
that can be used to innovate(Rogers, 2003). However,
it has recently been argued that smaller organizations
may be more agile and better able to react to changes
in the environment (te Winkel et al., 2008). When
organizations grow, they may adopt a bureaucratic or-
ganizational structure. This structure may slow down
their ability to change, or even kill innovative ideas
that arise within the organization and that are not in
line with the strategy of the organization. We there-
fore argue that many small organizations in Europe
have much unrealized potential to innovate with IT
by not having sufficient internal knowledge.
In large organizations, there is an increasing trend
towards the outsourcing of IT. Various—legitimate—
reasons exist for this: increasingly modular structures
that facilitate outsourcing, the lower cost of offshore
developers,and a lack of skilled domestic labor. How-
ever, if all IT-related activities are outsourced, this
also means that valuable knowledge leaves the orga-
nization, and the absorptive capacity of the organiza-
tion decreases. We are aware of large organizations in
Belgium in which only a few (1–3) persons are still
knowledgeable about the IT infrastructure. Evidently,
this seriously restricts the ability of the organization
to innovate with IT, and poses a considerable risk if
that person leaves the organization.
Both scenarios imply that organizations develop
little IT knowledge, or even loose their existing IT
knowledge. As previously noted, IT is becoming in-
creasingly important to support the innovation pro-
cess in organizations (Brynjolfsson and Saunders,
2010). This implies that organizations should try to
adopt new IT that may offer opportunities to the orga-
nization to innovate. However, it has been shown that
the adoption of IT is frequently knowledge-intensive
(Attewell, 1992). It is reasonable to expect that this
will certainly apply to IT that allows organizations to
truly innovate. In order to adopt knowledge-intensive
IT, organizations must engage in a process of orga-
nizational learning (Attewell, 1992). Organizations
with a higher absorptive capacity will be able to move
more quickly through the learning process, and will
therefore be able to react more quickly to the envi-
ronment by innovating with IT. However, both sce-
narios described above imply that organizations have
a low absorptive capacity. This considerably limits
their ability to identify, assimilate and exploit emerg-
ing technology that becomes available on the market
(Wheeler, 2002; Cohen and Levinthal, 1990). Hence,
organizations with little internal IT knowledge are
in this respect rather limited in their ability to inno-
vate. As a result, they tend to take a more reactive
stance with respect to new technology by relying on
the judgment of service providers, rather than proac-
tively exploring the opportunities of new technology.
This suggests that—rather than begin provided
with black-box IT solutions—organizations should
seek to learn form their service provider. Such al-
ternative outsourcing models include co-sourcing al-
liances and transaction exchanges. Research has
shown that although the success rate for both are
higher than for traditional outsourcing arrangements,
the organization must exhibit a higher maturity in
terms of its modular enterprise architecture (Ross and
Beath, 2006). This further illustrates that the design
parameters of modularity and knowledge should be
considered simultaneously.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have argued that in order for orga-
nizations to innovate with IT, design parameters are
needed which can be governed by organizations. We
have focused on the role of knowledge and modular-
ity as hands-on parameters that have a strong theoret-
ical foundation and that can be controlled by organi-
zations. Our results imply that managers should find
a balance between both design parameters to assess
their impact on the agility of the organization and its
ability to innovate with IT.
This study has two important contributions. First,
we have developed a comprehensive framework that
integrates literature on modularity, knowledge, and
innovation within the context of outsourcing. Sec-
ond, we have shown that both modularity and knowl-
edge are essential design parameters for construct-
ing organizations. We have further shown that both
knowledge and modularity are strongly intercon-
nected within the context of outsourcing and how they
BALANCING MODULARITY AND KNOWLEDGE IN DESIGNING AGILE ORGANIZATIONS - The Case of
Outsourcing
193

both simultaneously influence innovation.
Our study providesseveralopportunitiesfor future
research. The framework developed in this paper can
provide a basis for future empirical studies to study
how organizations consider the influence of modular-
ity and knowledgein their strategy for innovatingwith
IT. In future research, we also intend to further vali-
date this framework to investigate how managers take
into account knowledge and modularity in making de-
cisions on IT outsourcing.
REFERENCES
Attewell, P. (1992). Technology diffusion and organiza-
tional learning: The case of business computing. Or-
ganization Science, 3(1):1–19.
Baldwin, C. Y. and Clark, K. B. (2000). Design Rules: Vol.
1: The Power of Modularity. MIT Press, Cambridge,
MA.
Brynjolfsson, E. and Saunders, A. (2010). Wired for Inno-
vation: How Information Technology is Reshaping the
Economy. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Campagnolo, D. and Camuffo, A. (2009). What really
drives the adoption of modular organizational forms?
an institutional perspective from italian industry-level
data. Industry & Innovation, 16(3):291–314.
Campagnolo, D. and Camuffo, A. (2010). The concept of
modularity in management studies: A literature re-
view. International Journal of Management Reviews.
Early view.
Cohen, W. M. and Levinthal, D. A. (1990). Absorptive ca-
pacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation.
Administrative Science Quarterly, 35(1):128–152.
Earl, M. J. (1996). The risks of outsourcing IT. Sloan Man-
agement Review, 37(3):26–32.
Eisenhardt, K. M. and Martin, J. A. (2000). Dynamic capa-
bilities: What are they? Strategic Management Jour-
nal, 21(10/11):1105–1121.
Eurostat (2010). Summary indicators: Employment
size classes for EU27 (all nace activities). Statis-
tics retrieved from http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu on
February 8, 2010.
Fabrizio, K. R. (2009). Absorptive capacity and the search
for innovation. Research Policy, 38(2):255–267.
Frigant, V. and Talbot, D. (2005). Technological determin-
ism and modularity: lessons from a comparison be-
tween aircraft and auto industries in Europe. Industry
and Innovation, 12(3):337–355.
Grant, R. M. (1996). Prospering in dynamically-
competitive environments: Organizational capabil-
ity as knowledge integration. Organization Science,
7(4):375–387.
Hamel, G. (1998). The challenge today: Changing the rules
of the game. Business Strategy Review, 9(2):19–26.
Kogut, B. and Zander, U. (1992). Knowledge of the firm,
combinative capabilities, and the replication of tech-
nology. Organization Science, 3(3):383–397.
Mason, S. J., Cole, M. H., Ulrey, B. T., and Yan, L.
(2002). Improving electronics manufacturing supply
chain agility through outsourcing. International Jour-
nal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management,
32(7):610–620.
Neumann, S. and Fink, L. (2007). Gaining agility through
IT personnel capabilities: The mediating role of IT
infrastructure capabilities. Journal of the Association
for Information Systems, 8(8):440–462.
Rogers, E. M. (2003). Diffusion of Innovations. The Free
Press, New York, NY, 5th edition.
Ross, J. W. and Beath, C. M. (2006). Sustainable IT out-
sourcing success: Let enterprise architecture be your
guide. MIS Quarterly Executive, 5(4):181–192.
Sako, M. (2003). Modularity and outsourcing. In Prencipe,
A., Davies, A., and Hobday, M., editors, The Business
of Systems Integration, pages 229–253. Oxford Uni-
versity Press, Oxford.
Sambamurthy, V., Bharadwaj, A., and Grover, V. (2003).
Shaping agility through digital options: Reconceptu-
alizing the role of information technology in contem-
porary firms. MIS Quarterly, 27(2):237–263.
Sanchez, R. and Mahoney, J. T. (1996). Modularity, flex-
ibility, and knowledge management in product and
organization design. Strategic Management Journal,
17:63–76.
te Winkel, J. W., Moody, D. L., and Amrit, C. (2008).
Desperately avoiding bureaucracy: Modularity as a
strategy for organisational innovation. In Golden,
W., Acton, T., Conboy, K., van der Heijden, H.,
and Tuunainen, V., editors, Proceedings of the 16th
European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS
2008), pages 2330–2341.
Teece, D. J., Pisano, G., and Shuen, A. (1997). Dynamic
capabilities and strategic management. Strategic Man-
agement Journal, 18(7):509–533.
Tiwana, A. (2008). Does interfirm modularity complement
ignorance? a field study of software outsourcing al-
liances. Strategic Management Journal, 29(11):1241–
1252.
Wheeler, B. C. (2002). NEBIC: a dynamic capabilities the-
ory for assessing net-enablement. Information Sys-
tems Research, 13(2):125–146.
White, A., Daniel, E., and Mohdzain, M. (2005). The role
of emergent information technologies and systems in
enabling supply chain agility. International Journal of
Information Management, 25(5):396–410.
INNOV 2010 - International Multi-Conference on Innovative Developments in ICT
194
