TOWARDS E-LEARNING QUALITY
A Proposal of e-Learning Quality Model
Rosa Cabedo Gallén
Dpto. de Lingüística Aplicada a la Ciencia y Tecnología. E.T.S.I. Montes, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
Ciudad Universitaria s/n, Madrid, Spain
Keywords: Quality e-Learning, Quality, e-Learning, Quality of Service.
Abstract: The final purpose of this paper is to present the project of my Doctoral Thesis, the development of a quality
model for Spanish e-Learning teaching that provides an evaluation tool at service of managers and
professionals in charge of training actions. This educational innovation research performs on quality
environment, but from a didactic perspective. Computer science, quality, pedagogy, linguistics, psychology
and sociology environments converge at this research. The study of models, best practices and quality
guidelines, contributions of e-Learning training and the characteristics of Spanish teaching build up the
project. An online survey and interviews are taken into account too. The goal of this Thesis project is
covering the absence of a specific quality model for e-Learning environment that meets the specific needs of
e-Learning organizations and deals with the services management.
1 INTRODUCTION
The adaptation of the society to a new way of
information and knowledge access goes through
formation. In particular, e-Learning is associated
with a new educational concept that integrates the
use of technology and new pedagogical guidelines,
which promotes the use of Information &
Communication Technologies (ICT) and prepares
users in their insertion in the knowledge society.
The study of several international initiatives
(COM, 2002; COM, 2003) and European
Commission projects have been focused on
education and e-Learning. Deepening on quality and
e-Learning issues has revealed the need of a quality
e-Learning (Dondi, 2006; Ehlers, 2007a; Ehlers,
2007b) that should enable a better management of e-
Learning services.
Many organizations have their main topic on
aspects such as quality of services and adopt a
customer-oriented approach. This innovative
research involves the commitment to work towards a
continuous improvement culture in customers’
satisfaction, which culminates in the implantation
into the organizations of this culture in the quality of
services.
Systems Quality Assurance (SQA) represent a
set of heterogeneous and very varied alternatives
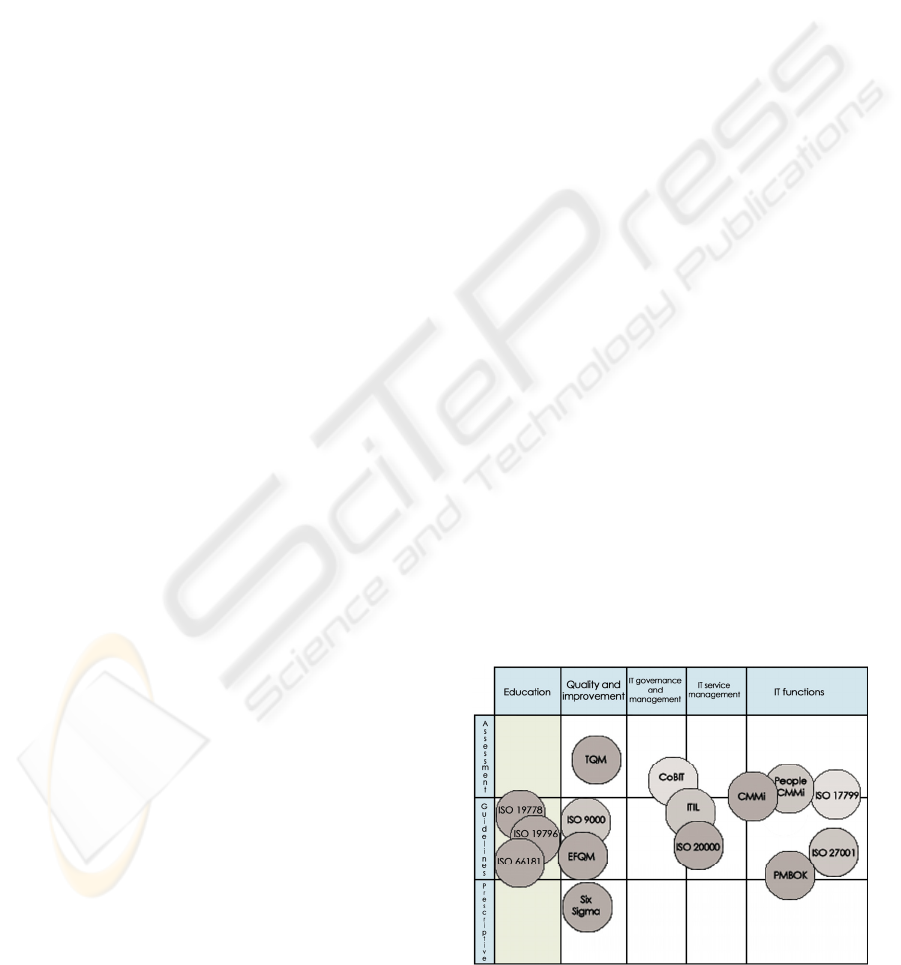
that need to be investigated more thoroughly. Figure
1 aims to clarify the scope in which each of the
models, best practices and quality guides are suited,
especially for the IT services management-oriented
ones.
Several alternatives with a clear orientation
towards TI services management, such as ITIL
framework and standard ISO 20000, are shown in
Figure 1. ITIL provides a framework, which the
standard ISO 20000 is based on, the first certifiable
international standard for TI services management-
oriented.
Figure 1: Topology of IT-related standards (adapted from
ISACA).
455
Cabedo R. (2010).
TOWARDS E-LEARNING QUALITY - A Proposal of e-Learning Quality Model.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 455-460
DOI: 10.5220/0002876704550460
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The quality management of virtual training is
supported by its first standard publication, the
standard UNE-EN-ISO 66181:2008 (AENOR,
2008), and it has the intention of serving as a guide
both for customers and for providers to proceed
certifying virtual environments quality.
It is important to note that the new quality e-
Learning model will not be the result of comparing
the alternatives stated on Figure 1, but the best ideas
are the core of the future quality model.
The framework selected for this research is the e-
Learning framework of Badrul Khan, guidance for
the design, development, implementation and
evaluation of flexible, open and distance learning
environments. Khan recommends eight dimensions
(Khan, 2005, p. 14) with a set of factors to take into
consideration in each one (sub-dimensions) (Figure
2). This framework is the reference guide and with
the help of its dimensions, training actions will be
analyzed in detail.
Figure 2: E-Learning framework of Khan (Khan, 2001).
The ICT applied to Spanish learning has been the
selected research field, which is going to be made
the development of the project. Spanish, regardless
of personal and professional interests, is regarded as
an economic asset that gives rise to a growing
interest in academic, cultural and business areas.
However, while Spanish is emerging as one of the
languages with most future projection of the 21st
century, there is a long way to cover in the ICT
application to Spanish learning, as stated in the I
Acta Internacional de la Lengua Española, that took
place in 2006 in San Millán de la Cogolla.
In view of the need of a e-Learning quality,
joined the importance of TI administration and the
impetus on Spanish teaching, comes the need to
develop a new specific quality model for e-Learning
services management that covers the particular
needs of languages e-Learning teaching, specifically
Spanish.
The Figure 3 shows the theoretical model, which
represents the main elements of the framework
proposal, including the end-user.
This framework is made up on the one hand of
processes that will support specific formation
services (examples of those services are
administration, tutoring or assessment services) and
on the other hand of other services that give support
to those processes, such as services that manage any
incidents, including help-desk.
The framework covers the whole e-Learning
organization, which forces to consider those
processes that are used in the own courses
development, such as content creation processes.
However, the framework scope goes beyond e-
Learning organization borders (customers and
providers of the organization).
Pedagogy has an important role on this proposed
framework, although its relationship with the quality
area is indirect (see Figure 3). Khan’s framework
will be in charge of building the bridge between
them. Activities such as instructional design, the
pedagogical model adopted, the content selection,
etc are examples of this situation.
Finally, the focus moves on IT Governance
processes, which have to be aligned with e-Learning
organizations strategies.
This project aims to turn into a quality model for
Spanish teaching in the e-Learning environment that
provide policy-makers and managers with a tool that
helps them in the e-Learning products and services
evaluation.
Figure 3: Cabedo’s Framework proposal (2009).
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
456

2 METHODS AND MATERIALS
This innovation project has a clear technological
approach. For this reason it is important the
information obtained through digital resources.
There are four clearly delimitated stages in this
project that have been carefully planned.
2.1 Initial Stage: Research
Formation, languages and quality are being studied
in depth on this first stage.
A study of several training actions is going to
help to delimit the scope of the project with
reference to formation area. The result of this study
is the e-Learning definition adjusted to research
context, that is to say, aligned with framework
proposal philosophy. Other decisions of pedagogical
and technological nature are taken all along this
stage. Going into details, the study on e-Learning
characteristics, advantages and disadvantages result
to a group of success and failure e-Learning factors.
These factors, which belong to this formative
modality, will be directly incorporated into the third
stage project.
These factors will be converted to a subset of
indicators of e-Learning quality and their impact will
have to be periodically measured, according to the
philosophy of continuous improvement.
Teaching languages, in particular Spanish, have
several peculiarities for deepening at this stage. The
pattern of education followed is the Common
European Framework of Reference for Languages
(Instituto Cervantes, 2002). This document fixes the
guidelines for the development of languages
programmes.
Technology is the tool that allows a greater
expansion of training actions in Spanish eLearning
teaching. It allows the access to learners who can’t
or don’t want to assist to a face-to-face instruction.
Spanish e-Learning formation pursues that learners
obtain a list of competences, which are going to feed
the framework that will manage the e-Learning
quality model.
The adoption of a customer satisfaction-oriented
approach by the organizations forces to understand,
evaluate, define and manage their expectatives, so
that their requirements are met. Customers’ demands
with reference to a product and/or service change
constantly and have an evolution along the time.
Hence it is necessary a procedure that allows the
organizations anticipate customers’ wishes and
expectations. Among all the existing tools, I quote
two examples as Kano Model of Customer
(Consumer) Satisfaction and the satisfaction cycle of
the customer’s needs and expectatives of virtual
formation (AENOR, 2008, p. 7).
The quality is becoming a strategic tool for many
organizations that provide services. That fact forces
them to make an effective management of services.
The introduction and evolution of different models
of SQA is one of the axes of this project. A
comprehensive analysis of these models, especially
those TI services management oriented, has as result
a first approach to the best-known alternatives in
quality market.
EFQM Excellence model, maturity model
CMMI, or ITIL as framework for TI service
management are some of the more representative
alternatives. ISO/IEC 20000 is the first specific
standard for TI service management, although I note
the appearance of the standard UNE-EN-ISO
66181:2008, the first standard on virtual formation.
The components of the project scope will be
periodically revised for updating based on advances
in study areas (formation, languages, quality) from
the Thesis project or customers’ specific needs.
This first stage is the result of the study of
multiple reports from public and private agencies,
analysis of cases and experiences. Special mention
has the documentation concerning on European
Union, projects and policies, which subject is e-
Learning.
2.2 Intermediate Stage: Measurement
The starting point of this stage is the reception of the
information of the project scope. This information is
the result of formation, languages and quality
environments study. The product Spanish e-
Learning course can be defined as the union of
content and services associated to the training
action. This course is identified as a unique and
unrepeatable training action, a learning experience
for each learner.
Khan’s e-Learning framework becomes the
thread of the project. Khan’s eight dimensions will
form the components body, both the content and the
e-Learning services. Each dimension of this e-
Learning framework is discussed in detail along this
stage. This way, Khan’s dimensions are present in
all processes of training action, because they flow
transversally through content and services. The list
of Khan’s framework dimensions is the following
(Khan, 2001):
• Pedagogical: teaching and learning needs for e-
Learning.
TOWARDS E-LEARNING QUALITY - A Proposal of e-Learning Quality Model
457

• Technological: technology infrastructure,
hardware, and software.
• Interface Design: overall look and feel of e-
learning programs.
• Evaluation: assessment of learners, instruction
and programs.
• Management: maintenance of learning
environment, distribution of information.
• Resource Support: online and technical support.
• Ethical: such as social and cultural diversity,
copyright and so on.
• Institutional: administrative matters of education.
The result of this stage is a set of indicators of e-
Learning quality. Identifying indicators is the most
important step toward improving the e-Learning
quality model and predicting the consequences of e-
Learning environment changes.
Planning project implies to arrange interviews
with different professionals linked to virtual
formation and quality, among other areas such as
psychology, pedagogy, computer science engineers,
etc.
A survey online is needed for covering aspects of
e-Learning and e-Learning quality in different
organizations. This survey is going to reduce the
impact of the quality subjectivity and feed the e-
Learning quality model with data of special
relevance.
Working papers, attending conferences and
papers whose content are related with any field
closed to the project, as for example the present
document, are going to provide updated information
to the project.
2.3 Final Stage: Operation and
Monitoring
E-Learning quality indicators are the result of a
detailed analysis of the content and services,
together with the indicators derived from the success
and failure e-Learning factors. These factors will
feed the e-Learning quality model directly from the
first stage. The study and optimization of all these
indicators will allow working with Data Warehouse
and/or Data Mining tools.
The stage of feeding the data model consists of
inputs of e-Learning quality indicators, as well as the
results of the different interviews, surveys and
feedback received from various contacts, actions
carried out all of them along the intermediate stage.
2.4 Cross Stage: Continuous
Improvement
The PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) cycle, also called
Cycle of Deming, is a quality tool that helps
organizations to implement a continuous
improvement oriented approach of their processes.
Organizations pursue designing a product or service
that meets the customers’ needs. This product or
service also has to be made without defects, in the
shortest possible time and with a minimal use of
resources.
The scope project feeds the intermediate stage
and generates as result a set of indicators that will be
continuously reviewed and will evolve together with
the assessment of several training actions.
The project scope will also receive the indicators
feedback, as second alternative of continuous
improvement cycle.
The indicators of e-Learning quality will allow
knowing the starting point of a training action and its
evolution over time. These will be optimized by the
development of successive training actions and by
the inclusion of the information derived from the
interviews and the survey online.
A continuous active participation in professional
discussion forums, specialized magazines and
journals, and so no is needed for getting updated
information for feeding the innovative model.
3 RESULTS
Organizations want to achieve their objectives with
the delivery of successful e-Learning projects. I
hope that the e-Learning quality model meets the
current needs of the organizations that make use of
the virtual training and becomes a useful tool for the
evaluation of their training actions.
The general scheme presented in Figure 4 shows
the steps needed for achieving the set of e-Learning
quality indicators. Their measurement and operation
are the following actions. At this point, note the
importance of the continuous improvement
philosophy and its application on training actions.
As shown in the Figure 4, the specific quality
model for the e-Learning environment is expected to
cover lacks concerning the e-Learning quality and
suppose a starting point for the development of new
quality models, whose scopes could be more
ambitious than this one.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
458
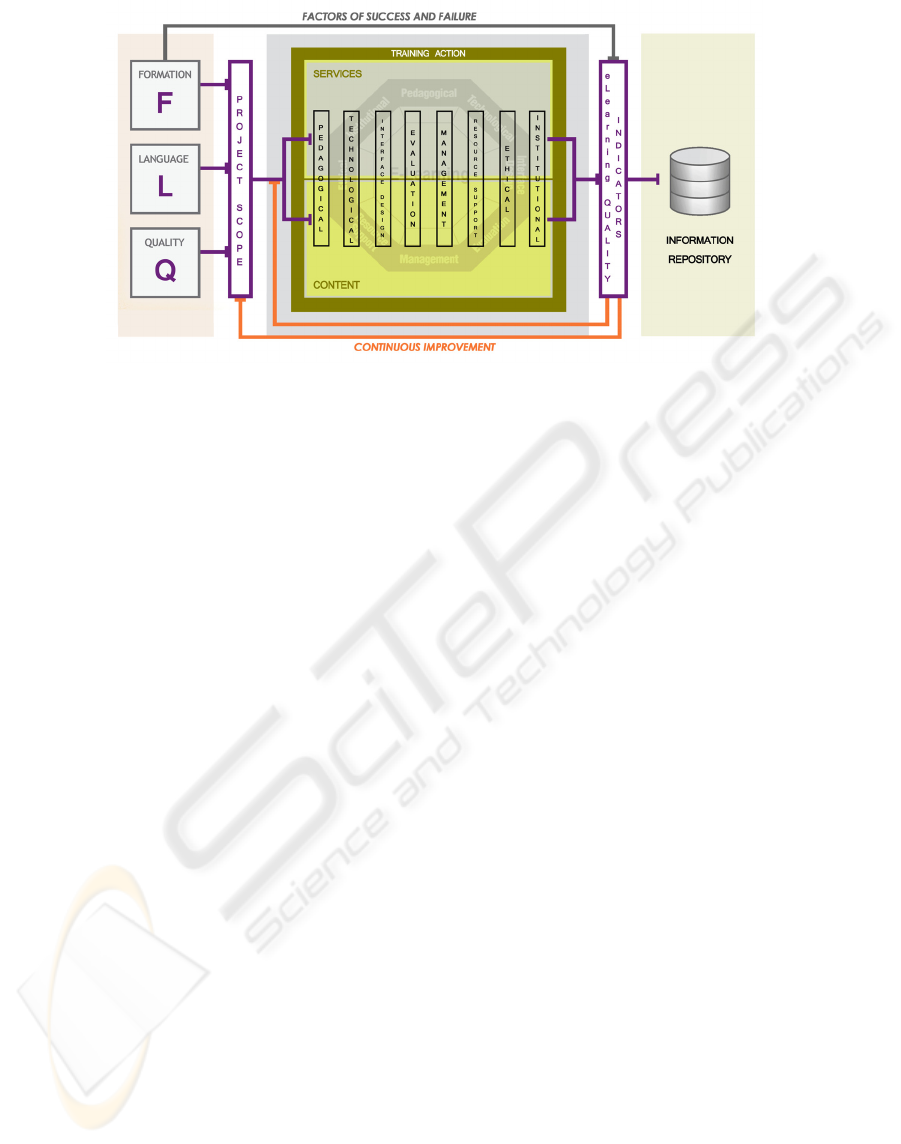
Figure 4: General schema of project stages.
4 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
At present I am researching with partial conclusions
of the three study areas. The scope of the project is
justified on the establishment of effective
relationship between formation, languages and
quality. Of course, these conclusions are going to
evolve, since the first stage of the project is not yet
complete.
Studying in depth different training methods I
consider that e-Learning has its origin in the
Distance Education (DE). The emergence of the
Internet and its adaptation to the change of paradigm
that has been the emergence of ICT have helped
towards what I consider it is a new training model
with significance, the e-Learning.
There are a lot definitions for quality provided by
multiple authors. I initially understand it as the
satisfaction of customer’s needs and expectations,
and all from a services perspective. The
minimisation of quality subjectivity is a critical
issue. Thus, tools that reduce the impact of
subjectivity levels that could be present in obtaining
and evaluating indicators are needed.
Measurement of processes is not a simple task,
and more if it is done on services. Often customers’
needs and expectations are really different, so their
perception of the quality is not the same and is
expressed in subjective terms. Indicators are not
easy to identify, there is an additional difficulty of
moving the customers’ subjective feelings to
quantifiable indicators. It is necessary to obtain
those quantifiable indicators for taking the
appropriate measures.
The work done in the first stage of the project on
different models, best practices and guidelines,
primarily on those marked by its TI orientation,
flows into a set of important points in the TI service
management that can be part of the project scope
and feed the formative action frame.
The proposed framework implies an innovation
process that born of the need of introducing a new
model of e-Learning quality for Spanish teaching
that responds to the e-Learning organizations needs
and deals with the management of their services.
The distribution of the actions along these three
stages is based on this framework.
This project of Doctoral Thesis aims to become a
quality model for the Spanish teaching in the e-
Learning environment that will provide managers of
training actions of a tool that helps them in the e-
Learning products and services evaluation.
This model of e-Learning quality should include
some benefits as:
• Improving the teaching and learning
environments that ensure the acquisition of the
competences and skills offered at the beginning
of the training action.
• Providing the structured content with an effective
and efficient use of the e-Learning standards and
technology.
• Tracking of the services management focused on
student learning.
• Presence of a continuous improvement cycle that
covers the training processes. This cycle acts as a
quality tool at the service of the e-Learning
quality model.
TOWARDS E-LEARNING QUALITY - A Proposal of e-Learning Quality Model
459

As Doctoral student, this project that is my Doctoral
Thesis is my first research challenge. Within this
paper I am trying to explain the importance of
getting a new quality e-Learning model. I am
working with great motivation for getting the goals
and I hope they could be of interest for learning
innovation community.
REFERENCES
AENOR, 2008. Norma UNE-EN-ISO 66181:2008.
Gestión de la calidad. Calidad de la Formación
Virtual. Madrid. URL: <http://www.aenor.es>
COM (2002). SEC (2001) 236. E-Learning: Concebir La
Educación Del Futuro. URL:
<http://ec.europa.eu/education/programmes/elearning/
sec_2002_236_es.pdf>
COM (2003). SEC (2003) 905. E-Learning: Designing
Tomorrow’s Education. A Mid-Term Report. URL:
<http://ec.europa.eu/education/programmes/elearning/
doc/mid_term_report_en.pdf>
Dondi, Claudio, 2006. La calidad del e-Learning. I
Jornadas andaluzas sobre calidad del e-Learning.
QUALITAS. Observatorio para la Calidad de e-
Learning en Andalucía. Sevilla.
<http://prometeo.us.es/qualitas/jornadas/claudio_dondi
.pdf>
Ehlers, Ulf D., 2007a. Towards greater quality literacy in
a e-Learning Europe. eLearning Papers. Nº 2. Enero
2007. URL:
<http://www.elearningeuropa.info/files/media/media1
1559.pdf>
Ehlers, Ulf D., 2007b. The “e“ – Empowering Learners:
Myths and Realities in Learner-Orientated e-Learning
Quality. eLearning Papers. Nº 2. Enero 2007. URL:
<http://www.elearningeuropa.info/files/media/media1
1560.pdf>
itSMF International, 2005. Fundamentos de Gestión de
Servicios TI basado en ITIL. Van Haren Publishing.
itSMF España, 2006. UNE-ISO/IEC 20000-1. Tecnologías
de la Información – Gestión del servicio – Parte 1:
Especificación.
itSMF España, 2006. UNE-ISO/IEC 20000-2. Tecnologías
de la Información – Gestión del servicio – Parte 2:
Código de prácticas.
Juran, J.M., 1995. A History of Managing for Quality. The
Evolution, Trends, and Future Directions of Managing
for Quality. ASQC Quality Press. Milwaukee
(Wisconsin).
Khan, B.H. (Ed.), 2001. Web-based instruction.
Educational Technology Publications. URL: <
http://bookstoread.com/bestseller/khan/tocwbt.htm >
Khan, Badrul. 2001. A Framework for E-learning,
Learning and Training Innovations. URL:
<http://www.elearningmag.com/ltimagazine/article/art
icleDetail.jsp?id=5163>.
Khan, B.H., 2005. Managing e-Learning Strategies:
Design, Delivery, Implementation and Evaluation.
Information Science Publishing.
Instituto Cervantes (2002). Marco Común Europeo de
Referencia para las lenguas: Aprendizaje, Enseñanza,
Evaluación. URL:
<http://www.cvc.cervantes.es/obref/marco/cvc_mer.pd
f>
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
460
