
THE EFFECT OF GOVERNMENT SUPPORT
ON E-BUSINESS PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT
WITH INDUSTRY TYPE IN KOREA
Hyun Sook Ahn
1
, Dong Man Lee
2
and Hyun Sun Park
1
1
Graduate School of Business Administration, Kyungpook National University, Korea
2
Department of Business Administration, Kyungpook National University, Korea
Keywords: e-Business, Government support, e-Business industry.
Abstract: This study investigates how government support influences the performance of e-business companies.
Drawing on previous studies, funding support for technology development and marketing support, currently
accounting for the biggest part of the support provided by the Korean government to the e-business sector,
were selected as independent variable. Meanwhile, performance indicators specific to e-business such as
human resources development, competitiveness enhancement, profitability, and growth in technology assets
were chosen as dependent variable. The data was collected through a survey of CEOs and executives of e-
business companies that had received or were receiving government for technology development had a
positive influence on competitiveness enhancement, profitability, and technology assets growth. Marketing
support, while it had a significant influence on competitiveness enhancement and technology assets growth,
proved to have no measurable effect on profitability.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the advent of the information era in the 21th
century, governments around the world are
supporting all the things in competent and highly
profitable field with systematic and overall plans. In
Korea, to assist the industry in gaining technological
independence needed to successfully compete in the
global information race, its government has been
expanding and diversifying its support toward
industry for the development of next-generation
technologies, their commercialization and creation
of new business models based on these technologies.
The goal is to foster new engines for future growth
of the Korean Industry. As is well-known, South
Korea is today among the world’s most advanced
nations in terms of information technology. The
country’s rise as a world IT powerhouse-that
Koreans like to call “IT Korea”-owes much to an
ideal combination of active government support for
technology development with an equally active
investment in technological innovation by its
industry. Up to this time, South Korea has succeeded
in building "IT Korea" in deed as well as in name
due to various complex factors such as supports of
government, constant efforts of enterprise for the
development of new technology and the national
character suitable for IT industry
The number of studies assessing the
achievements of governments of government
support programs in this field is, as a matter of fact,
surprisingly small. Assessments provided by a
handful of existing studies on this topic are hardly
satisfactory, as their focus is too narrow, dealing, for
instance, with a single project carried out by one
particular institution. These studies are at the same
time too general to be informative or useful, as they
measure the effect of a government support program
on the industry as a whole, and not a specific
industry sector. Also, whilst there have been a
sizeable number of studies investigating private-
sector factors influencing the growth of the e-
business industry, very few inquiries have been
made into similar influence factors coming from the
public sector. Most studies on public-sector
influence factors have been broadly concerned with
the industry as a whole, and not with e-business or
any other specific sectors. To address these
shortcomings in the existing literature, a research
model expanding on existing models has been
elaborated, comprising independent variables that
293
Sook Ahn H., Man Lee D. and Sun Park H.
THE EFFECT OF GOVERNMENT SUPPORT ON E-BUSINESS PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT WITH INDUSTRY TYPE IN KOREA.
DOI: 10.5220/0002771202930298
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technology (WEBIST 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-674-025-2
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

are primarily macro-variables and dependent
variables that are primarily micro-constructs. The
independent variables, variables related to
government support in this study, have in their scope
all technology development funding programs and
marketing support programs by government
institutions, while the dependent variables relating to
the effect of government support are exclusively
concerned with e-business; in other words, they only
measure the effect of the support programs on e-
business.
2 THEORETICAL
BACKGROUND
2.1 Government Support Programs
Technology Development funds are programs
through which the government provides funding
toward technology development projects in the form
of interest-free and unsecured loans with no
collateral requirements. The details of support
available under these programs are tax relief,
funding support for technology development, joint
R&D projects, technology business incubation funds
and technical support and training. The Marketing
Support System is the Small and Medium Business
Administration Sponsors exhibition activities by
SMEs and SME associations in an effort to afford
them marketing opportunities and help expand their
sales channels. Funding is provided toward the cost
2.2 Previous Literature
Seoh, S.H.(1998) investigated, in a study in the
context of a research project sponsored by the
institute for industrial policy studies, the evolution
of industrial infrastructure technology and Seoh,
S.H(2000) assessed the effectiveness of the
technology innovation and development program by
the Small and Medium Business Administration,
identifying also key factors influencing the project's
outcome. Kim, H.U.(2004), in his study on the effect
of government funding support on the performance
of SMEs, criticized the existing literature, saying the
most of the previous studies on this subject focused
more on strategies on how to improve funding
programs than measuring the actual effectiveness of
existing programs, and that their evaluations of the
effectiveness of a funding support program based on
more specific evidence, in other words, using
concrete data of individual companies receiving
funding assistance. His analysis, using
Ashenfelter’s(1978) model, found that there was no
real difference in terms of operating profit between
companies that were beneficiaries of government
funding and those that were not, although in some
rare cases, government funding produced adverse
effects on the operating profit of beneficiary firms.
This study also reported that government fund
support proved particularly ineffective, when
provided to recent start-ups and young companies.
Kim, W.G.(2007) estimated the relationship between
labour productivity and R&D intensity, using a fixed
effects model with data results from 18 industrial
and yearly panel data between 1993 and
2005. Song, H.J. et al.(2006) compared SMEs
receiving funding support from government with
compared marketing support programs in place at
that time to determine which of them are most
effective. Marketing support programs by the
government which proved the most effective were
marketing training programs, programs sponsoring
participation in exhibitions, and programs providing
support for designing websites and publishing
catalogues, product certification programs and
overseas market development support
programs. Ashenfelter(1978) investigated the effect
of a job training program by the U.S governments.
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a job
training program conducted by the U.S government,
sometime around 1964 by looking at whether there
was any significant difference in wages between
workers who attended the program and workers who
had not.
3 RESEARCH MODEL AND
HYPOTHESES
3.1 Research Model
Drawing on previous studies, the following research
model was developed to determine how government
support programs for SMEs and venture firms
influence the growth and development of the e-
business industry. For the government support
program, the most dominant technology
development fund support and marketing support
were determined as variables. And for the
development of the e-business industry, its unique
elements vis-à-vis those of other industries-namely,
the fostering of human resources, competitiveness
enhancement, profitability, and increase in
technological – were determined as variables.
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
294
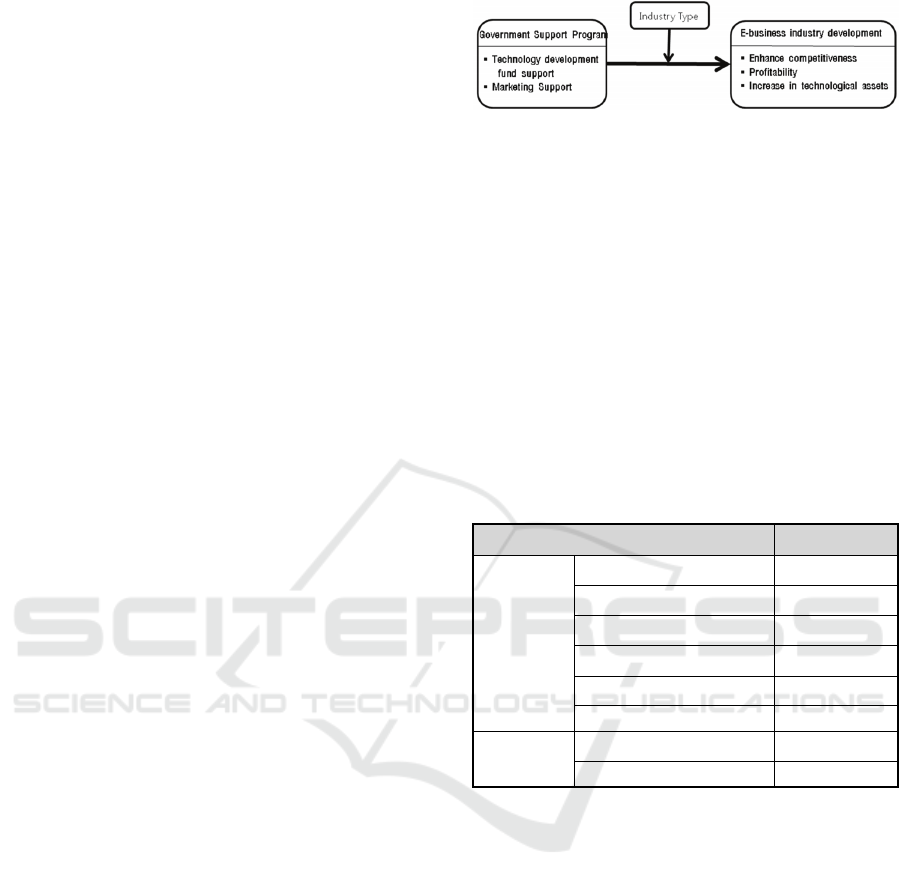
Based on the existing researches examined
above, a research model, as shown in <figure 1>.
All question items were measured on the basis of
a 5-point-Likert scale.
3.2 Research Hypotheses
H1: The government support program will have a
positive (+) impact on enhancing
competitiveness.
H1.1: The technology development fund support
will have a positive (+) impact on enhancing
competitiveness.
H1.2: Marketing support will have a positive (+)
impact on enhancing competitiveness.
H2: The government support program will have a
positive (+) impact on profitability.
H2.1: The technology development fund support
will have a positive (+) impact on profitability
H2.2: Marketing support will have positive (+)
impact on profitability.
H3: The government support program will have a
positive (+) impact on increasing
technological assets
H3.1: The technology development fund support
will have a positive (+) impact on
increasing technological assets.
H3.2: Marketing support will have a positive (+)
impact on increasing technological assets.
H4: The effects of the government's support
program on the development of the e-business
industry will differ according to industry type
H 4.1: The effects of the technology
development fund support on the
development of the e-business industry will
differ according to industry type
H 4.2: The effects of the marketing support on
the development of the e-business industry
will differ according to industry type
4 RESULTS OF EMPIRICAL
ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Characteristic of Research
Sampling
Questionnaires were used when surveying the SMEs
and venture firms which received the governmental
support. Members of KITIA were surveyed online,
while members of the IT SoC Association and of the
Daegu and Gyeongbuk Development Council via e-
mail and clients of various banks were surveyed
Figure 1: Research Model.
offline. 250 answered copies of the questionnaire
were collected from which any copies were removed
from corporations not related to e-business along
with other disqualified copies, leaving a final total of
131 effective copies. Specifically, the CEOs and
other high-ranking officials of corporations were
surveyed who could provide responsible answers
and better know their organizations in an effort to
effectively examine the effects of the government
support program on the development of the e-
business industry. The characteristics of the
respondents and the sampled corporations are
outlined in Table 1, Table 2.
Table 1: Characteristics of the sampled corporations.
Category Count (%)
Industry type
Internet 3(2.3%)
Mobile 9(6.9%)
Structuring Infrastructure 3(2.3%)
IT SoC 27(20.6%)
IT manufacturing 63(48.1%)
Others 26(19.8%)
Location
Seoul metropolitan areas 63(48.1%)
Provincial areas 68(51.9%)
4.2 Analysis of the Reliability and
Validity of the Measurement Tool
The results of the reliability test indicated that the
Cronbach's Alpha value of all the research variables
ranged from 0.6 to above 0.8, showing a good
degree of reliability (Table 3). A factor analysis was
conducted to test the validity of the measurement
tool, the major factor analysis was selected, and for
the factor rotation, the Varimax rotation was
selected from among the orthogonal rotation
methods. Finally factor numbers with an Eigenvalue
over 1 were selected, as shown in Table 4, Table 5.
4.3 Analysis of Correlation between
Variables
The correlation between all variables was found to
be low except in the case of the correlation between
THE EFFECT OF GOVERNMENT SUPPORT ON E-BUSINESS PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT WITH
INDUSTRY TYPE IN KOREA
295
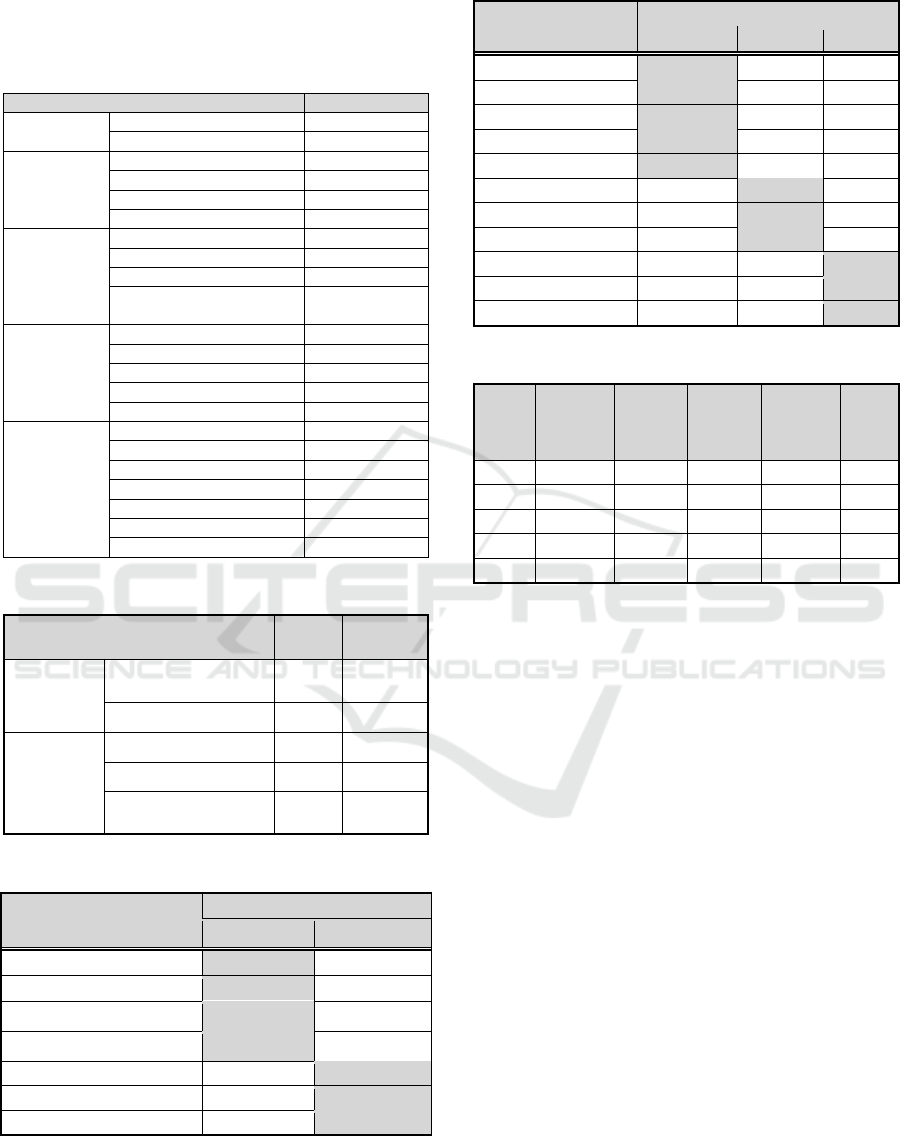
profitability and competitiveness enhancement
which at 0.631 represented a positive correlation, as
in the existing researches Table 6.
Table 2: Characteristics of respondents.
Category Count (%)
Gender Males 124(94.7%)
Females 7(5.3%)
Age <20 years old 2(1.5%)
21-30 years old 34(26%)
31-40 years old 65(49.6%)
>50 years old 30(22.9%)
Education High School or under 2(1.5%)
Junior college(attending) 7(5.3%)
University(attending) 58(44.3%)
Graduate
School(attending)
64(48.9%)
Job R&D 44(33.6%)
Administration 76(58%)
Sales 1(0.8%)
Production 1(0.8%)
Others 9(6.9%)
Position Employees 2(1.8%)
Assistant Managers 12(10.6%)
Managers 11(9.7%)
Deputy General Managers 10(8.8%)
General Managers 9(8%)
Executives 32(28.3%)
CEOs 37(32.7%)
Table 3: Results of the Reliability Test.
Research variables
No. of
items
Alpha’s
coefficient
Government
support
Technology development
fund
4 .608
Marketing support 3 803
e-business
Industrial
development
Enhance competitiveness 5 .627
Profitability 3 .621
Increase technological
assets
3 .624
Table 4: Factor analysis of the independent factors.
Factor
Factor 1 Factor 2
Technology development2
.829
.123
Technology development4
.803
.091
Technology development1
.660
.336
Technology development5
.507
.442
Marketing2 .170
.934
Marketing3 .191
.901
Marketing1 .218
.807
Table 5: Factor analysis of the dependent variables.
Factor
Factor1 Factor2 Factor3
Competitiveness3
.832
.148 .093
Competitiveness2
.811
.168 .117
Competitiveness5
.720
.393 .015
Competitiveness4
.563
.081 .307
Competitiveness1
.517
.414 .137
Profitability4 .170
.854
.115
Profitability1 .259
.812
.149
Profitability3 .292
.761
.091
Technological3 .139 .017
.861
Technological2 .367 .153
.635
Technological1 -.074 .481
.599
Table 6: Correlation between the research variables.
Variable
Technolog
y
Support
(1)
Marketin
g
support(2
)
Competiti
veness(3)
Profitabilit
y(4)
Tech.
assets(5
)
(1) 1
(2) .529
**
1
(3) .461
**
.221
*
1
(4) .277
**
.079 .587
**
1
(5) .303
**
.073 .540
**
.908
**
1
4.4 Verification of the Hypotheses
A multiple regression analysis was conducted to
verify the hypotheses on the relationship between
the government support program and the
development of the e-business industry, the results
of which are shown in Table 8. A moderated
regression analysis was conducted to test the
mediating effects of industry type on the relationship
between the government support program and the
development of the e-business industry. After
industry type was set as a dummy variable(IT
Manufacturing =0, non-IT Manufacturing = 1), it
was established as an interaction term with the
independent variable, i.e. government-supported
industry, and was included in the regression analysis
to test hypothesis 4. As a result, the moderating
effects of industry type were found to be statistically
insignificant at the significance level of 5 of all
interaction terms; therefore, hypothesis 4 was
rejected.
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
296
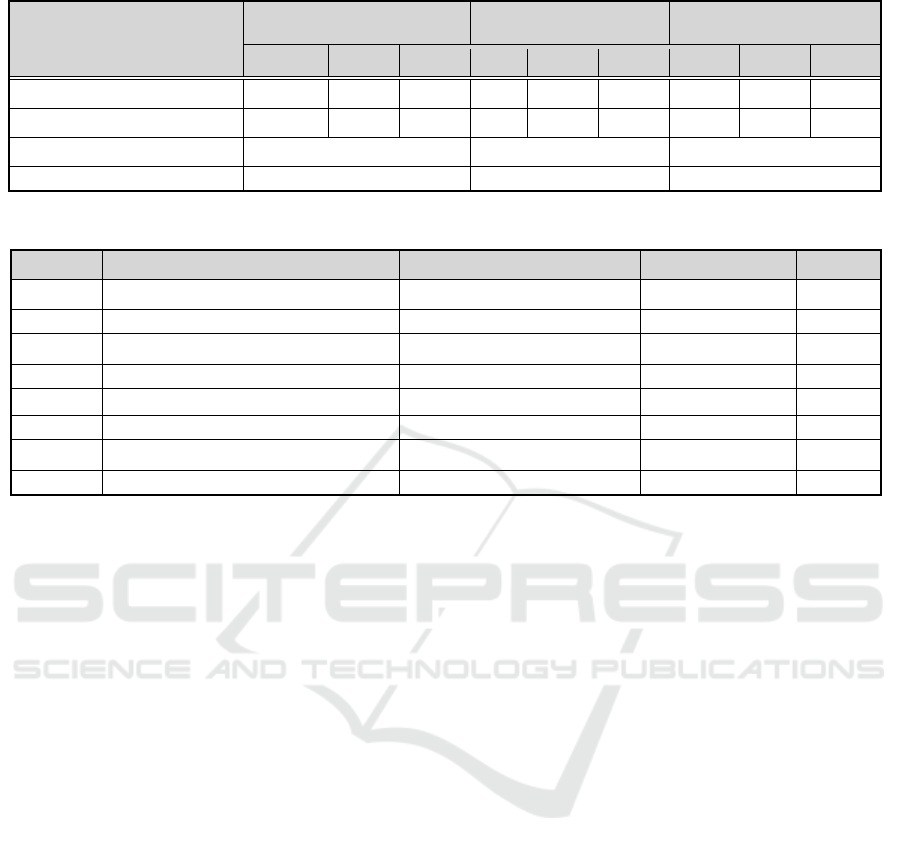
Table 7: Results of the Regression Analysis.
Independent variable
Competitiveness enhancement Profitability
Increase in technological
assets
β t p β t p β t p
Technology Development support .486 5.239 .000
***
.327 3.260 .001
***
.367 3.721 .000
***
Marketing Support .135 2.669 .009
***
-.095 -.944 .347 -.121 -1.226 .222
F value 17.315 5.745 7.305
R
2
.214 .083 .102
Table 8: Results of the Hypotheses.
Hypothesis Independent variables Dependent variables Moderating variables Finding
H1.1 Technology development fund support Competitiveness enhancement Supported
H1.2 Marketing support Competitiveness enhancement Supported
H2.1 Technology development fund support Profitability Supported
H2.2 Marketing support Profitability Rejected
H3.1 Technology development fund support An increase in technological assets Supported
H3.2 Marketing support An increase in technological assets Rejected
H4.1. Technology development fund support e-business industry development Industry type Rejected
H4.2 Marketing support e-business industry development Industry type Rejected
5 CONCLUSIONS
5.1 Summary of the Research
This study, targeting Korea's e-business-related
SMEs and venture firms, examined the effects of the
government support program on the development of
the e-business industry, and verified whether the
effects of the government support program on the
development of the e-business industry differed
according to industry type, i.e., IT manufacturing
and non-IT manufacturing.
The findings of the research indicated the
following: First, as regards the government support
program, the technology development fund support
was found to have significant positive effects on all
areas including the enhancement of corporate
competitiveness, profitability, and increase in
technological assets. The technology development
fund support – whether direct or indirect motivated
corporations to make R&D efforts, thereby
influencing their competitiveness enhancement,
increase in technological assets, and profitability.
Second, as regards the government support program,
market support was found to have significant
positive effects on corporations' competitiveness
enhancement and increase in technological assets,
but not on their profitability. From the short-term
perspective, the marketing support-although small-
scale and indirect-enhance corporations’ marketing
awareness and ability, and thus enhanced their
competitiveness and technological assets, but did not
have any direct effects on their profitability. This can
be interpreted to mean that it may take more time to
improve profitability on the basis of enhanced
competitiveness and an increase in their
technological assets. Lastly, there was no difference
in the relationship between the government support
program and the development of the e-business
industry according to industry type.
5.2 Implications and Limitations of the
Research
This study further developed the existing research
model, and thus re-established independent variables
from holistic and macro perspectives, and dependent
variables from micro perspectives. The study
included all the relevant institutes’ diverse
technology development fund programs and
marketing support programs in the independent
variables, namely the government support program,
and limited the dependent variable to the e-business
industry. In fact, it is the foregoing features which
give this study its particularity.
Also, given the characteristics of the IT industry and
the e-business industry, such as their rapidly
THE EFFECT OF GOVERNMENT SUPPORT ON E-BUSINESS PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT WITH
INDUSTRY TYPE IN KOREA
297

changing speed and their core technologies’
importance, the protection, reliability and
development speed of the technologies of such
industries receive greater emphasis than in other
industries. Thus, these points were conceptualized
into “technological assets”, which was then
established as a dependent variable, giving the study
a profound meaning.
Despite these theoretical and working implications,
the study has several limitations, outlined below,
which it is hoped will be tackled in future research:
First, this study targeted only the beneficiaries of
the government support program, and thus the
possibility that the respondents were led into giving
affirmative answers cannot be excluded. Such, any
future research will be able to produce more accurate
results if it includes non-beneficiaries as well.
Second, apart from questionnaire-based surveys,
if both the government's and the private sector's
databases on the government support program had
been utilized along with their databases on industrial
trends, more objective and precise results may have
been produced.
Third, it would be worthwhile to utilize as a
mediating variable the frontline industries relating to
the e-business industry- such as the IT SoC and IT
industry – in an effort to observe via which paths the
government support program has direct and indirect
effects on the development of the e-business industry.
Lastly, if new variables such as IT support and
education support were added to the independent
variables-technology development fund support and
marketing support of the government support
program and examined, and if dependent variable-
such as technological property- that reflect the major
characteristics of the e-business industry, along with
their measurement items, were developed and
examined.
REFERENCES
Ashenfelter, O.C., 1978, “Estimating the Effect of
Training programs on Earnings”, Review of Economic
and Statistics, 60(1), pp. 47-57.
Kim, Hyeon-uk, 2004, “A Study on the Effects of the
Government Fund support for SMES: A case study on
the government fund for SMEs,” Korea Development
Institute.
Kim, Won-gyu, 2007, “Analysis of the Effects of
Government R&D Support,” e-KIET Industrial
Economic Information, p. 343.
Gwak, Su-geun & Song, Hyeok-jun, 2003, “A study on the
trait factors and Management Performance of SMEs as
Recipients of Government Fund Support: A case Study
on SMEs and Venture Firms,” The KASBS Autumn
2003 Seminar-Decentralized Balanced Development
and Provincial SMEs, 0(0), pp. 31-149.
Jang, Seok-ju, 2006, “A Study on Marketing Support
Measures for Fostering SMEs and Venture Firms: A
case Study on Korean BI firms' Marketing problems,”
Venture Management Research, 9(3), pp. 35-157.
Seo, Sang-Hyeok, 1998, “Analysis of Ten years of
fundamental Industrial Technology Development and
the Establishment of Improvement Measures”, ITEP's
Research Report. Gwacheon.
Seo, Sang-hyeok, 2000, “Analysis of the precision of
SMEs’ Technology Innovation Projects,” SMEA’s
Research Report, Daejeon:SMEA.
Song, Hyeok-jun, Kim I-bae, O Eung-nak & Che Jong-ok,
2006, “A Study on Venture Firms' Taxes”, Venture
Management Research, 9(3), pp. 61-80.
Song, Hyeok-jun, Kim, I-bae, & O, Eung-nak, 2006,
“Effects of the Government Fund Support on SMEs'
Management Performance and Improvement”, SME
Research, 28(4), pp. 65-80 .
STEPI, 2005, “2005 Technology Innovation Activity
Survey Table: Manufacturing
business,” (http://www.stepi.re.kr).
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
298
