
RODIN
A Medium-weight Portal for the Aggregation and Mashing of Heterogeneous
Data Sources
Fabio Ricci and René Schneider
Haute Ecole de Gestion, 7 route de Drize, CH-1227 Carouge, Geneva, Switzerland
Keywords: Personalized web interfaces, Portal strategies, Digital libraries, Ontologies.
Abstract: RODIN (ROue D'INformation) is a project that aims to develop an innovative tool for the bundling and
coupling of user-relevant, heterogeneous information resources. Information specialists and other service
users will be able to gather those information resources which are interesting in relation with their work or
with their personal interests in a dynamic and user-friendly information aggregate. The tool includes a
search engine which allows a simultaneous search in all components of the aggregate and will consist of an
ontology based search refinement algorithm, that links the results with bibliograhpical SKOS data and looks
for broader and narrower results based on the search results. RODIN represents the alternative portal
approach within the context of E-lib.ch-project, the swiss digital library.
1 INTRODUCTION
RODIN is a web-based information management
system that allows the integration, aggregation and
mashing of heterogeneous data sources. The system
also consists of different search functionalities that
store user preferences and are open to semantic web
data formats and corresponding search
functionalities.
In the general use case, the end user himself will
be able to gather and combine creatively the
provided information resources and search
simultaneously within these resources or the
mashing results. Ad-hoc modifications concerning
his actual needs or his current search situation will
be possible at any time. Long term modifications of
the system will be possible through the interaction
between users, key users, information experts and
developers.
The system will be developed for two major
frameworks:
as a personalizable web portal;
as an intranet-like in-house component for
information management.
The latter framework will play a crucial role
within the context of libraries: information
specialists – interacting with publishers and
computer scientists – will be able to create search
environments for their customers and benefit on the
other hand from the end user’s creativity (Hoyer,
2008), but distinct from other previous work (Floyd
2007), the system does not only rely on the fruitful
relationship between the end-user and the
programmer : the system's performance will also
benefit from the role of the information expert that
acts as an intermediate between them.
The paper describes the added values that come
along with this system and gives details concerning
its implementation. The implementation started on
June 2009 with the first prototype being launched
before midst of 2010, involving one web portal and
a scalable number of semantical refinement
interfaces.
2 MOTIVATION
The web portals of libraries usually offer a large
variety of information resources, generally
represented by a list of links leading to the different
interfaces with different search functionalities. As
opposed to that, users only have an interest in a
limited number of these resources that they use in
combination with general search engines or other
sources that are hosted elsewhere.
All these resources (catalogs, digitized books,
journals, photos, movies, and audio-files) are often
available in different media and come along with
147
Ricci F. and Schneider R.
RODIN - A Medium-weight Portal for the Aggregation and Mashing of Heterogeneous Data Sources.
DOI: 10.5220/0002766301470151
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technology (WEBIST 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-674-025-2
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
different kinds of meta data, sometimes sparse,
sometimes rich, but in general different in format.
One possible solution for this problem are
portals that rely on data homogenization as a result
of harvesting repositories. Alternatively, aggregators
allow user-friendly integration of heterogeneous data
sources without any prior harvesting needed.
This alternative approach to heavy-weight
portals is followed in the RODIN project that is part
of the E-lib.ch project (www.e-lib.ch). It focuses on
searchable information resources, makes them
available as widgets and allows simultaneous search.
In addition, search refinement will be enabled
through the integration of semantic web knowledge,
hence the definition of RODIN as a medium-weight
solution that tries to handle with already available
RDF data in a responsible and time effective way.
RODIN will also make strong use of bibliographical
SKOS (Simple Knowledge Organization System)
Data, (Hyvönen 2008) since more and more thesauri
and taxonomies are converted into this format.
3 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
3.1 User Roles
The potential of the system and the functionalities it
covers may be identified through the roles of three
types of actors:
the role of the system provider or developer;
the intermediary role of the information
specialist;
the role of the end-user or consumer.
It should be noted that these roles and the
corresponding activities are connected and
intertwined. The integration of new information
resources and their coupling into new services (see
Table 1) is achieved via a communication process
between end users, information specialists and
system administrators to transform the user needs
into added values for the whole information system.
Table 1: User roles.
EndUser Specialist Developer
Aggregation &
Searching
x
Coupling &
Mashing
(x) x
APIIntegration (x) x
All activities are dedicated to the creation and
use of so called “information universes” that are
populated by widgets. A widget must include a
search functionality to a given information resource.
Gadgets or other widgets that do not include search
functionalities were – for the sake of simplicity -
excluded within this context.
The developer's role is crucial for the
implementation of the system's framework and the
integration of the widget into this framework. This
process starts with the discovery of an information
resource through the specialist, the end-user or the
developer itself. After clearing all questions
concerning licensing, the developer checks all
technical parameters for the integration of the
information resource (also referred here as “data
source”) and the development of the widget.
Therefore, the widget is published for integration,
i.e. users and specialists may integrate them into
their information universes or mash them with other
resources.
The information specialist has an intermediary
role between the end-user and the developer or
maintenance service. His or her role can also be
described as that of a consultant or key-user. After
the widget development, the information specialist
starts integrating several widgets to build an
information universe after the identification of the
customer's needs. He may also mash several data
sources together to create new information services
that can be integrated to the information universe in
the form of widgets again. Thus, the information
specialist may create complete universes for the end-
user, build and promote customized mash ups and
consult or teach the end-user consulting according to
his needs.
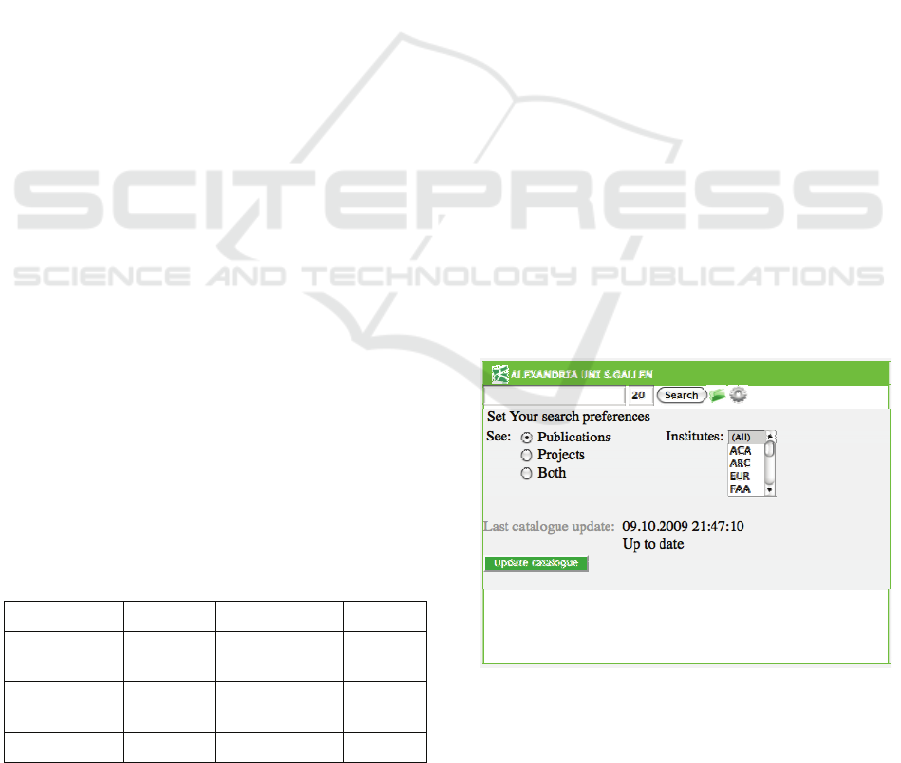
Figure 1: Widget Search Preferences.
The end-user consumes, builds, and re-builds
information universes that consist of an aggregation
of widgets. After searching for widgets in the
system, he will add them to his universe and delete
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
148

them if he is no longer in need of them. This process
includes the creation of different tabs and the
alteration of their position within the tab.
3.2 Use Cases
Due to the context of the E-lib.ch project and the
fact that RODIN will serve as an alternative portal in
the domain of library and information management,
special attention will be given to the search, meta-
search, and mashing functionalities. These search
functionalities build the three general use cases:
Besides the general widget search functionality,
special attention is given to a simultaneous or
federated search that allows the users to search in all
widgets selected. Nevertheless every widget keeps
its own search facility and allows the users to store
search preferences before they start the search
process, a feature that will be very helpful to search
effectively in scientific databases (see Figure 1).
Figure 2: Search Refinement in RODIN.
The search refinement module will make use of
the semantic web technology: whenever the user
chooses a document he is interested in, this
document or entity will be used to narrow the search
and show related data from the aggregated
information universe. In a further, yet not developed
step, it is foreseen that every query will be adapted
to each widget via a formal description of its
semantic properties.
The results of this search will be displayed in a
separate tab in the form of an “information wheel”,
hence the system’s name RODIN (ROue
D’INformation, meaning information wheel in
French) (see Figure 2).
3.3 Implementation
As stated above, within RODIN two different
approaches for the integration and coupling of data
sources will be followed: one generic approach and
another more specific approach that focuses on the
search interfaces developed within the applications
of e-lib.ch.
3.3.1 API Integration
For each application the API is addressed according
to its specific design. Within this context, the
development of a RESTful services (Fielding, 2000)
to simplify and standardize the coupling of APIs
builds an interesting option and any standardization
of APIs will strongly simplify their integration.
Each RODIN widget is implemented inside
portaneo (www.portaneo.net, an open source widget
platform) as a specialization of a finite state machine
with states e.g. for displaying preferences and search
fields, for computing the search, collecting results,
storing them in RODINs database and visualizing
them inside the widget window. The developed
widget framework allows a structured construction
of new widgets and guarantees a uniform look-and-
feel among all RODIN widgets. Data fields coming
from the API are automatically collected from the
data source and added to the user preference panel
for that widget, allowing the adjustment of its result
presentation thus influencing the mashup with
further widgets.
Once a widget is installed inside RODIN, it is
selectable from a widget selection offered by POSH.
We use POSH for its basis feature for portal
personalization through selection/elimination of
widgets.
We describe the response of each widget being
composed of n result documents containing each a
finite number of records.
3.3.2 Searching
Once result documents are collected by each widget,
these are stored record-wise in groups inside the
RODIN database and associated with a unique
search identifier (sid); the latter identifies a complete
search, including the query, the user, the involved
widgets and their data sources and all their results,
thus defining a complete search object – ready to be
(re)used for further economical and efficient
visualizations or refinements.
Despite of the existing numerous different data
source formats, each record is stored in the database
homogeneously substantially as a triple (name, type,
RODIN - A Medium-weight Portal for the Aggregation and Mashing of Heterogeneous Data Sources
149

value), thus supporting the mapping to an RDF
representation layer which will be used as a basis for
the search refinement.
After performing RODIN’s simultaneous search,
each widget shows a collapsed portion of the found
result documents in its own window; the search
refinement is done by selecting a result document or
even a single record of it, thus identifying a refining
word vector to be used as a basis for a further query
inside the other RODIN widgets.
The refining word vector is first cleaned then
semantically enhanced in a specific way for each
involved data source. A new instance of the universe
Tab is then spawned with each widget presenting his
specific response documents to the calculated
refining query. The refining step described here may
be run by the user an arbitrary amount of times, this
being thus a pragmatic alternative to DERI’s
semantic web pipes. (Morbidoni et al. 2007).
3.3.3 Semantic Search Refinement
The use of RESTful services leads to another
enhancement of the system that deals with RDF
data, the latter making content accessible within the
Linked Open Data Project (Shadbolt 2006).
Defining the data structures within the E-lib.ch
context as RDF triples will lead to an optimization
of the search functionalities, be it in the simple
search as described in this chapter, be it in the search
refinement module as described hereafter. This will
also facilitate the integration of semantic web search
technology in RODIN’s search. RODIN will
therefore benefit strongly from the Linked Data
Project. esp. from bibliographical data that is
converted into SKOS, such as the Library of
Congress Subject Headings or the Swiss National
Bibliography
To enable this, RODIN needs a “bridge” to the
data of the semantic web. This bridge might be
enabled through D2R (http://www4.wiwiss.fu-
berlin.de/bizer/d2r-server/), a tool for publishing
relational databases on the Semantic Web, allowing
applications to query the database using the
SPARQL query language.
Beside this “bridge” the semantic search
refinement has to be based on some ontological data
that is close to digital libraries. The basis for this
ontological data might consist of data being
formalized in SKOS (Miles, 2005), e.g. the library
of congress subject headings or the SWD subject
headings of the Swiss National Library.
From the authors’ point of view, the effective
connection of the simple query results with the
ontological data and their mutual transformation will
play a crucial role for the further development of
RODIN.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we described RODIN, an alternative
web portal approach within the domain of libraries
and their digital information services. RODIN will
integrate all information resources of the E-lib.ch
project and allow the building of user-specified
information universes.
Users and information specialists arrange
widgets according to their needs. The system will
integrate semantic web technology with a special
focus on bibliographic meta data by using meta data
described in SKOS as a basis of ontological
reasoning and inference.
RODIN itself will be made usable as an
information resource, through the implementation of
a RESTful service for on line query and result
processing.
REFERENCES
Auer, S., Bizer, C., Kobilarov, G. et al., (Ed.), 2008.
DBpedia: A Nucleus for a Web of Open Data.
Bizer, C., 2003. D2R MAP - A Database to RDF
Mapping. Springer Lecture Notes in Computer
Science. Springer, Berlin.
Proc. WWW2003, The Twelfth International World Wide
Web Conference, Budapest, Hungary.
Fellbaum, C., (Ed.), 1998. WordNet: An Electronic
Lexical Database. MIT Press.
Fielding, R. T., 2000: Architectural styles and the design
of network-based software architectures, University of
California, Irvine, Dissertation.
Floyd, I., Jones, M. Rathi, D., Twidale, M. 2007. Web
Mash-ups and Patchwork Prototyping: User-driven
technological innovation with Web 2.0 and Open
Source Software. Proc IEEE HICSS 2007.
Hoyer, V., Stanoevska-Slabeva, K., Janner, T., Schroth,
C., 2008. Enterprise Mashups: Design Principles
towards the Long Tail of User Needs. IEEE
International Conference on Service Computer
(SCC’08), Volume 2, 601-602.
Hyvönen, E., Viljanen, K., Tuominen, J. Seppälä, K. 2008.
Building a National Semantic Web Ontology and
Ontology Servic Infrastructure – The FinnONTO
Approach. The Semantic Web: Researach and
Applications, Lecture Notes in Computer Sciences,
Springer Berlin.
Miles, A., Brickley, D., Matthews, B., Wilson, M., 2005
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
150

SKOS Core Vocabulary Specification. W3C working
draft, W3C, November 2005.
Morbidoni C., Polleres A.,Tummarello G., Le Phuoc D.,
2007, Semantic Web Pipes, DERI (Digital Enterprise
Research Institue),Technical Report 2007-11-07
Raimond Y., 2007 DBTune – http://dbtune.org/, Centre
for Digital Music, Queen Mary, University of London
Shadbolt, N. Berners-Lee, T., Hall, W., 2006. The
Semantic Web Revisited. IEEE Intelligent Systems,
Volume 21, No. 3, p. 96-101.
RODIN - A Medium-weight Portal for the Aggregation and Mashing of Heterogeneous Data Sources
151
