
A MDA-BASED TESTING
A Comparative Study
Arturo H. Torres, María J. Escalona, Manuel Mejías and Javier J. Gutiérrez
Department of Computer Languages and Systems, University of Seville, Avd. Reina Mercedes sn. 41040, Seville, Spain
Keywords: MDA, MDWE, Model-Based Testing, Web Testing.
Abstract: Software testing is any activity aimed at evaluating an attribute or capability of a program or system and de-
termining that it meets its required results. Moreover, it is a critical element in order to ensure the system
quality. However, researchers and practitioners are still trying to find effective ways to test Web applica-
tions. One way is related with the MDA (Model-Driven Architecture) paradigm. This paper presents a com-
parative study of existing proposals for this paradigm. The aim of this study is to find research opportunities
to take the challenge of automating the tests in the context of meta-models MDWE (Model-Driven Web
Engineering).
1 INTRODUCTION
Software testing is a fairly broad term which covers
a wide range of various activities; from the tests con-
ducted by the developer, a small piece of code (unit
tests) to the client validation of a large information
system (acceptance tests).
At all phases, the test cases can be designed with
very different objectives, such as validate if there are
deviations in the user requirements, assess the com-
pliance of a standard specification, to evaluate the
robustness of the loading conditions, or measure the
performance or usability, etc.
In addition, the activity of the tests could be per-
formed by various formal procedures, such as plan-
ning and thorough documentation, or as informal
and ad hoc (exploratory tests). As a result of this va-
riety of objectives and scopes, there are a multi-
plicity of terms for software testing, which has ge-
nerated confusion and many problems in research on
software testing.
To clarify and organize these terms and in order
to show them in a unified view, Bertolino (Bertoli-
no, 2007) presents a classification of the common
problems and the several meanings of software
testing. Bertolino proposed that the common deno-
minator may be a very abstract view. That is, given a
piece of software, irrespective of their typology, size
and scope, tests are always observed in a sample of
the test executable, and give a verdict on them. From
this definition, is suggested a roadmap, which is a
plan that provides directions to research works in
software testing. This roadmap is divided into three
parts: the latest achievements in software testing, the
destination desired, which is represented in the form
of dreams and the challenges and future research
that are aimed at fulfilling the dreams.
In this paper, we address three challenges for-
mulate by Bertolino. The challenges addressed are
the obtaining efficient oracles tests, achieve 100%
automatic testing and model-based testing. And
specifically within the models-based tests, we tried
modeling the test with the MDA paradigm, because
the MDA levels abstraction can also be applied to
the testing modeling (Gross, 2003).
Moreover, because our interests are the Web a-
pplications, these challenges will be oriented to-
wards this type of software. That is, take the cha-
llenge to get 100% automated testing, with appro-
priate test oracles in a context MDWE.
The structure of this paper continues with Sec-
tion 2, which presents a theoretical background spe-
lling out the concepts needed to present the related
works in Section 3. Then, in Section 4 provides a
comparative analysis of the existing proposals in or-
der to identify research opportunities of software
testing for Web applications. Finally, the section 5
presents conclusions and future works.
269
H. Torres A., J. Escalona M., Mejías M. and J. Gutiérrez J. (2009).
A MDA-BASED TESTING - A Comparative Study.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 269-274
DOI: 10.5220/0002281902690274
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 BACKGROUND
The UML (Unified Modeling Language) is a visual
language that supports the design and development
of complex object-oriented systems. With the in-
creasing complexity of systems, solid tests are
needed. But UML itself, even with the new version
2.2 (UML, 2009) does not provide the means for
describing test models. Thus, it has defined the
profile of UML for the tests, called UML 2.0 Testing
Profile (U2TP) (UML Testing Profile, 2009) and has
become the official OMG standard since March
2004.
U2TP fills the gap between designers and testers
by providing the means to use UML in system mo-
deling and tests specification. This allows for reuse
of UML design documents for the tests and allows
the development of tests at an early stage of system
development.
In addition, TTCN-3 is a specification and im-
plementation language for defining black box test
procedures for distributed systems. Testing and Test
Control Notation version 3 (TTCN-3, 2009) has
been developed by the ETSI (European Teleco-
mmunications Standards Institute) and also has been
standardized in the International Telecommunica-
tion Union (ITU-T). One of the main goals is to inte-
grate TTCN-3 tools into the processes and infra-
structure based on MDA.
According to the philosophy of MDA, the same
mechanism for modeling can be reused for multiple
purposes (Siegel, 2001). The philosophy of MDA
can be applied both to the system modeling as the
test modeling. As shown in Figure 1, the system
design model in a platform independent o PIM
(Platform Independent Model) can be transformed
into models of system design in a platform specific o
PSM (Platform Specific Model). In another step of
transformation, the system code can be derived from
the PSM. Indeed, the completeness of the code
depends on the completeness of the design model of
the system.
Researchers have made transformations between
different abstraction levels of the system or the
different levels of abstraction of the tests (vertical
arrows in Figure 1) (Bézivin, 2001) (Born and
Schieferdecker and Gross and Santos, 2004). But
only a few researchers have made the transformation
between model system and model tests (horizontal
arrows in Figure 1).
Furthermore, the test design models can be
processed directly from the system design models.
Figure 1: System design models vs. Test Design Models
(Dai, Z.R., 2004).
This allows an early integration of test deve-
lopment within the global development process.
Once defined the model of system design at the PIM
level, we can derive the test design model in a
platform independent o PIT (Platform Independent
Test). This model can be transformed directly into
code or to test design model for a specific platform
(PST) (Schieferdecker and Din, 2005). The same
transformation technology can be used to derive the
PSTs from PSM. After each processing step, the test
design model can be refined and enriched with the
specific properties of the test. Although the test
design model can be transformed and contain static
and dynamic aspects, the behaviour must be com-
pleted to cover all the expected behaviour of the sys-
tem. Moreover, issues such as testing, control testing
and deployment information, must be added ma-
nually to the model of test design. Finally, the test
design model can eventually be transformed into
executable code for testing, both from PST and PIT.
The next section presents the related works that
use this approach based on transformations with the
MDA paradigm for the development of software
testing.
3 RELATED WORKS
This section presents related works with the models
of software testing that use the MDA pa-radigm.
Among the proposals of test presented by the
enterprise based on models, only a few have a MDA
approach. These proposals are listed in Table 1 and
are marked in the last column of the table:
Objecteering Software (Objecteering Software,
2009), Tau Generation 2 (Telelogic Tau, 2009) and
Test Designer (Test Designer™ v3.3, 2009).
Objecteering Software combines UML mode-
ling, code production, testing and debugging of Java
applications in a simple environment. It is a models-
ICSOFT 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
270
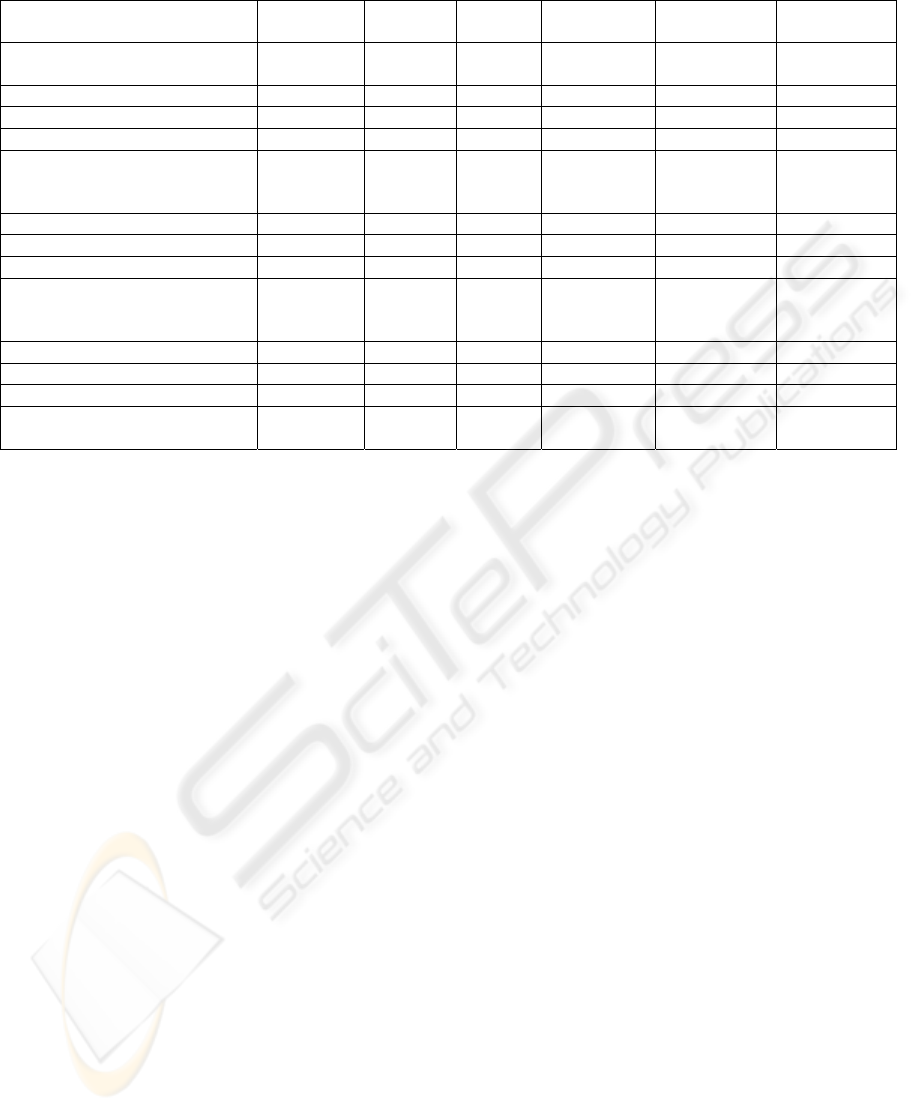
Table 1: Comparison of models-driven tools.
Tool Validation Metrics
Anti-
Pattern
Navigation
Visualizatio
n
Tests - MDA
All Fusion Component
Modeler (AllFusion, 2009)
√ × × × × ×
ArcStyler (ArcStyler, 2009) √ × × × × ×
iUML (iUML, 2009) √ × × × √ ×
NetBeans (NetBeans, 2009) N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A ×
Objecteering
Software (Objecteering
Software, 2009)
√ √ × × × √
Poseidon (Poseidon, 2009) √ × × √ √ ×
Rhapsody (Rhapsody, 2009) √ × × √ × ×
SD Metrics (SD Metrics, 2009) √ √ ×
Tau
Generation 2 (Telelogic Tau,
2009)
√ × × √ √ √
Together (Together, 2009) √ √ √ √ × ×
WayPointer (WayPointer, 2009) √ × × N/A N/A N/A
XDE (Rational XDE, 2009) √ × × × × ×
Test Designer (Test Designer™
v3.3, 2009)
√ × × × × √
oriented tool, supporting the MDA technology. Test
Designer v3.3 tool automates the design of tests,
including various phases. Test Designer generates all
the test cases from the specification of a functional
model, e.g. UML.
Tool Test Designer v3.3 implements the concept
of Smart Testing. Smart Testing are tests that, based
on theory or experience, have a high probability of
detecting errors. In addition, Test Designer v3.3
supports models-based testing.
Finally, Telelogic TAU Generation2 represents
the advanced generation of development and testing
tools, wich supports industry standards for visual
systems and software development (U2TP) and
integration testing (TTCN-3).
The Telelogic team provides a method that
automates testing activities covering the specifi-
cation, development and implementation of tests.
U2TP is selected as a modeling language for the
specification of test cases. The models are then
transformed into the language TTCN-3, which is
used to describe the executables use cases.
On the other hand, we have academic proposals
related to model-based testing in an MDA context.
There are several proposals, such (Busch and Chapa-
radza and Dai and Hoffmann and Lacmene and
Ngwangwen and Ndem and Ogawa and Serbanescu
and Schieferdecker and Zander-Nowicka, 2006)
(Dai and Deussen and Lacmene and Busch and
Ngwangwen and Herrmann and Schmidt and Grid,
2005) (Pietsch and Stanca-Kaposta, 2008), using this
approach. However, for the purposes of this section,
we chose three proposals that identify common
concepts.
The proposals have a common denominator in
the development of their proposals. They use the
concepts presented in the previous section, the ob-
taining of testing models through of transformations,
U2TP and TTCN-3.
Dai (Dai, 2005) introduces a methodology on
how to use the profile U2TP to transform a model of
UML system design in models tests. To formalize
the methodology, the transformation rules Query /
View / Transformation (QVT) defined CBOP / IBM
/ DSTC (QVT, 2009) are considered.
Zander et al. (Zander and Dai and Schieferdecker
and Din, 2005) presents a method to automatically
derive executable tests from UML diagrams using
the U2TP profile.
They present a transformation between the UML
2.0 specifications and U2TP used to represent PITS
and TTCN-3.
Transformations can be specified as transforma-
tion rules between U2TP and TTCN-3 meta-model.
Subsequently, the output generated is completed and
compiled into executable test code in Java (Testing
Technologies, 2009). The U2TP meta-models and
TTCN-3 models are defined by Meta Object Facility
(MOF, 2009).
The transformation rules define relationships bet-
ween source and target meta-classes of these meta-
models. Meanwhile the transformations are imple-
mented in the model level (instance), i.e., leading
parts of TTCN-3 modules of parts specifications
U2TP.
A MDA-BASED TESTING - A Comparative Study
271

Pérez et al. (Pérez and Reales and García and
Polo, 2008) presents a proposal for testing in the
context of Model Driven Engineering. From the sys-
tem design models in UML, it is proposed to make
transformations to test models based on UML testing
profile.
For the automatic generation of test defines an
extension to the UML meta-model, so that they can
record the sequence diagrams with information that
then can be used to generate the test oracle. This
information is recorded in OCL as pre and post-
conditions in the diagram.
Moreover, is presented a proposal for the au-
tomatic generation of test cases in the context of
MDA, based on the meta-model of UML 2 and the
U2TP, making the transformation from UML mo-
dels to the test model, using a model as description
of behavior of the UML sequence diagram. Within
the proposal, it addresses the automatic generation
of test oracles as these are dependent on the domain
of application.
4 A COMPARATIVE STUDY
In this section, the objective is to identify re-search
opportunities from work related. This iden-tification
is done by taking the advantages and disadvantages
of each proposal.
First, Dai’s proposal introduces a methodology
about using the profile U2TP to transform a model
of UML system design in models tests. Also, it pre-
sents the definition of transformation rules, but the
downside is not yet fully completed. Therefore, it is
an open front for future work.
Also due to lack of tool support for UML 2.0 and
U2TP, they are unable to test the transformation
rules. Dai explains that in future work, they will
investigate tools that support the concepts U2TP and
the automatic derivation of testing design models
from of system design models. Therefore, it is not
considered the development of a process automation
tool.
Moreover, Zander et al. presents a method to
automatically derive executable tests from UML
diagrams using the UML 2.0 Testing Profile profile.
The proposal presents a transformation between the
UML 2.0 specifications U2TP used to represent
PITS and TTCN-3. The main advantage of this
proposal is that it provides the rules transformation
between the meta-model U2TP and the meta-model
TTCN-3.
Another advantage of this method is that it pre-
sents an automatic execution environment; Eclipse
was used to demonstrate the feasibility of this work
together with the plug-in UML 2.0 (Eclipse UML2,
2009) and developed to support U2TP. They also
use a plug-in to support TTCN-3.
The models with the concepts U2TP are inte-
grated with Eclipse platform, in the same way that
the team Objecteering. The team also develops the
transformation of models from U2TP to TTCN-3 as
provided by Telelogic, but this paper defines the
rules on the level of meta-model using the methods
available for implementation in Eclipse.
Finally, the proposal of Perez et al. presents a
proposal for testing in the context of Model Driven
Engineering. From the system design models in
UML, it is proposed to make transformations to test
models based on UML testing profile.
This proposal has as main advantage the
treatment of test oracles, which may result in test
data automatically. Therefore, they have defined an
extension of the UML meta-model which expresses
the pre and post-conditions for each sequence
diagram using the OCL language. This proposal
does not have an automation tool to help validate the
proposal.
Next, in Table 2 presents the proposed studies,
both the business proposals, as well as academic
proposals. The table shows the characteristics nece-
ssary to cover the three challenges of software test-
ing.
• Challenge 1: To achieve this objective,
requires obtaining a method that provides
the expected outputs for each test case
given, i.e. an efficient test oracle.
• Challenge 2: To get the challenge of 100%
automated testing, requires that the testing
processes are automated.
• Challenge 3: To get to the challenge of
test-ing based on models requires that the
proposed process should have the following
characteristics: an MDA or MDWE a-
pproach, provide the necessary transfor-
mation rules, and in the case of Web
applications, based on navigational models.
The ψ symbol indicates that although the proposal
satisfies the property, is not covered completely; i.e.
it is incomplete. The δ symbol indicates that
automation is semi-automatic. Finally, the θ symbol
indicates that although the feature is a-ddressed, the
details are unknown, covering the property. In this
way, with the help of this comparative table identify
research opportunities, and from these, in the next
section we will carry out our proposal. The first
opportunity is for the treatment of test oracles as
ICSOFT 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
272
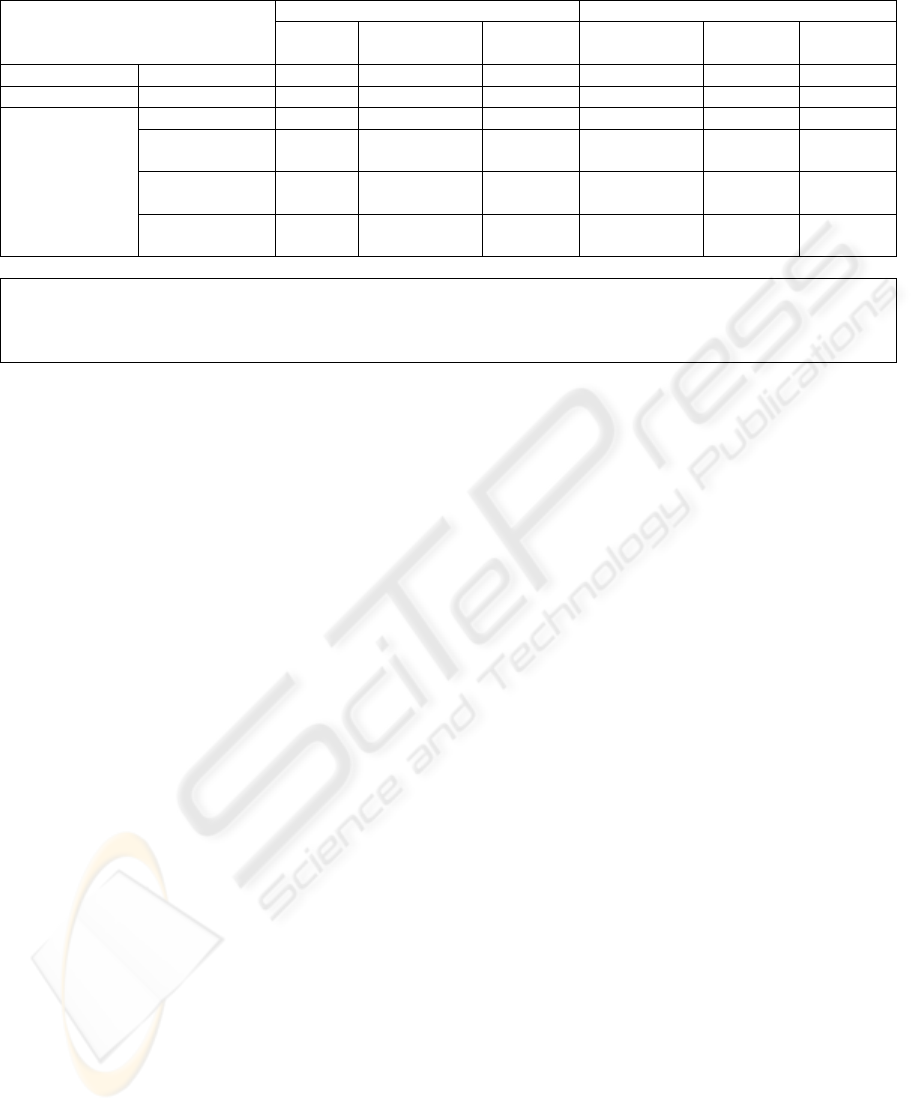
Table 2: Table of opportunities.
Academic proposals Business proposals
Dai
Z.R.
Zander et al.
Pérez et
al.
Objecteering
Software
Test
Designer
Telelogic
TAU
Challenge 1
Test oracles × × √ × × ×
Challenge 2
Automation × √ × √
δ
√
δ
√
δ
Challenge 3
MDA paradigm √ √ √ √ √ √
Transformation
rules
√
ψ
√
ψ
× √
θ
√
θ
√
θ
MDWE
paradigm
× × × × × ×
Based on
Navigation
× × × × × ×
Legend:
ψ
Incomplete
δ
Semi-automatic
θ
Unknown
Bertolino, this is the main obstacle to achieving
automation 100 % of the testing process. The tests
oracles in a MDA context are addressed only by
Perez et al., but only with the artifacts of sequence
diagrams.
Therefore a major challenge is to achieve effi-
cient mechanisms to obtain a robust test oracle, since
it still lacks methods that we provide. The table also
shows that all the above proposals are based on the
MDA approach, but not all provide the trans-
formation rules for this approach.
While the business proposals cover this feature,
they do not recognize details and nature of them.
There are some proposals that have academic
transformation rules, but they are incomplete.
The last and most important opportunity for our
research is that the proposals, whether academic or
corporate, are not geared to the development of Web
applications. Therefore, they do not use the MDWE
approach and are not based on navigational models.
The next section presents the conclusions and
future works, based on the opportunities raised,
taking the strengths of related works to fill the me-
thodological gaps.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work has highlighted a number of important
aspects related to Web applications. Web Enginee-
ring has assessed that the need to study in a concrete
way to navigation, which is a feature of the software,
which in recent years, is defined as critical in the
development process (Cachero and Koch, 2002).
Also, one of the important aspects are related to
the current challenges in software testing, and from
these, we identified opportunities for research rela-
ted to development of the testing process in a con-
text of transformation models.
Based on all the above is possible exploiting the
opportunities identified in the analysis of this re-
search, aims to meet the great challenges of testing
software for achieving a safe and efficient appli-
cations Web.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported by the project
QSimTest (TIN2007-67843-C06 03) and by the
RePRIS project of the Ministerio de Educación y
Ciencia (TIN2007-30391-E), Spain.
REFERENCES
AllFusion, 2009. http://www.astrom.se/allfusion
ArcStyler, 2009. http://www.arcstyler.com
Bertolino, A., 2007. Software testing research:
Achievements, challenges, dreams. In FOSE ’07: 2007
Future of Software Engineering, pp 85–-103. IEEE
Computer Society, Washington.
Bézivin, J., 2001. From object composition to model
transformation with the MDA. In TOOLS ’01:
Proceedings of the 39th International Conference and
Exhibition on Technology of Object-Oriented
Languages and Systems (TOOLS39), pp. 350. IEEE
Computer Society, Washington.
Born, M., Schieferdecker, I., Gross H., Santos, P., 2004.
Model-driven development and testing - a case study.
Technical report, Fraunhofer Publica, Alemania.
Busch, M., Chaparadza, R., Dai, Z., Hoffmann, A.,
Lacmene, L, Ngwangwen, T., Ndem, G., Ogawa, H.,
A MDA-BASED TESTING - A Comparative Study
273

Serbanescu, D., Schieferdecker, I., Zander-Nowicka,
J., 2006. Model transformers for test generation from
system models. Technical report, Fraunhofer FOKUS,
Germany and Hitachi Central Research Laboratory
Ltd., Japan.
Cachero, C., Koch, N., 2002. Conceptual navigation
analysis: a device and platform independent navigation
specification. In: 2nd International Workshop on Web-
oriented Software Technology (IWWOST’02), Málaga.
Dai, Z.R., Deussen, P.H., Lacmene, L.P., Busch, M.,
Ngwangwen, T., Herrmann, J., Schmidt, M: Grid.,
2005. Automatic test data generation for TTCN-3
using CTE. In: 18th International Conference
Software & Systems Engineering and their
Applications, Paris.
Dai, Z.R., 2004. Model-driven testing with UML 2.0. In:
Proceedings of the Second European Workshop on
Model Driven Architecture, pp. 179--187. University
of Kent, UK.
Eclipse UML2, 2009. http://www.eclipse.org/uml2
Gross, H., 2003. Testing and the UML a perfect fit.
Technical report, Fraunhofer IESE Report 110.03E,
Alemania.
iUML, 2009. http://www.kc.com/products/iuml.php
MOF, http://www.omg.org/technology/documents/formal/
mof.htm
NetBeans, 2009. http://www.netbeans.org
Objecteering Software, 2009. http://www.object-
eering.com
Pérez, B., Reales, P., García, I., Polo, M., 2008. Propuesta
para pruebas dirigidas por modelos usando el perfil de
pruebas de UML 2.0. In: Actas de los Talleres de las
Jornadas de Ingeniería del Software y Bases de Datos,
Gijón.
Pietsch, S., Stanca-Kaposta, B., 2008. Model-based testing
with UTP and TTCN-3 and its application to HL7.
Technical report, Conquest Potsdam, Germany.
Poseidon, 2009. http://www.gentleware.com
QVT, 2009. http://tefkat.sourceforge.net/publications/ad-
04-01-06.pdf
Rational XDE, 2009. http://www.ibm.com/
developerworks/rational/products/xde
Rhapsody, 2009. http://www.telelogic.com/products/
rhapsody/index.cfm
Schieferdecker, I., Din, G., 2005. A meta-model for
TTCN-3. In: Applying Formal Methods: Testing,
Performance, and M/E-Commerce. LNCS, vol. 4, pp.
226-245. Springer.
SD Metrics, 2009. http://www.sdmetrics.com
Siegel, J., 2001. Developing in OMG's model-driven
architecture. OMG white paper.
Telelogic Tau, 2009. http://www.telelogic.com/products/
tau/index.cfm
Test Designer™ v3.3, 2009. http://www.smartesting.com/
cms/en/explore/products
Testing Technologies, 2009. http://www.testingtech.de
Together, 2009. http://www.borland.com/us/products/
together/index.html
TTCN-3, 2009. http://www.ttcn-3.org
UML Testing Profile, 2009. http://utp.omg.org
UML, 2009. http://www.uml.org
WayPointer, 2009. http://www.jaczone.com/product/
overview
Zander, J., Dai, Z.R., Schieferdecker, I., Din, G., 2005.
From U2TP models to executable tests with TTCN-3 -
an approach to model driven testing. In: Testing of
Communicating Systems. LNCS, vol. 3502/2005,pp.
289-303. Springer, Berlin.
ICSOFT 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
274
