
FACTORS INFLUENCING CUSTOMER RETENTION AND
SWITCHING IN THE KOREA BROADBAND
INTERNET SERVICE MARKET
MoonKoo Kim, JongHyun Park
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, Gajeongno 138 Yuseong-gu, DaeJeon, Korea
JongHyun Paik
Telecommunications Technology Association, 267-2,Seohyeon-dong, Bundang-gu, Seongnam, Korea
Keywords: Switching Incentives, Customer Behaviour, Switching Barriers.
Abstract: Korea’s high-speed Internet markets have all these characteristics, which is why the providers are doing
their utmost to retain their current subscribers and attract other companies’ subscribers. Therefore, the
starting point of a basic customer strategy involves 1) the identification of the characteristics of those
subscribers who maintain their membership or who have switched to another provider in Korea’s high-
speed Internet market, where switching between providers is becoming increasingly frequent among
subscribers, and 2) analysis of the factors affecting their behavior. One of the common findings of most
telecommunication service sectors including Korea’s high-speed Internet market is that customer
satisfaction does not always match customer behavior. In general, customers maintain their subscription to a
specific provider when they are satisfied, and drop their subscription otherwise. However, even satisfied
subscribers often switch to another provider and vice versa. This happens when factors other than customer
satisfaction affect customer behavior. In this regard, we examine the factors which affect customer behavior
in Korea’s high-speed Internet market in terms of service differentiation, facilitating conditions, the cost of
switching, and the attractiveness of the alternatives.
1 INTRODUCTION
There is a main characteristic in Korea’s high-speed
Internet market, which exhibits the features of the
typical maturity stage, where the saturation point has
been reached or even surpassed, with 90% of the
entire population enrolled. As new additional
services emerge - such as the Internet phone and
IPTV - the providers find themselves in the strategic
situation of having to market new services for the
existing subscribers. As the market is entering the
maturity stage, it is getting harder to attract new
customers, and as the market is making the transition
to a new service, Korea’s high-speed Internet
providers are engaged in relentless competition to
keep their customers and attract each other’s
subscribers. Therefore, the starting point of customer
strategy consists 1) in identifying the characteristics
of the subscribers who are maintaining their
membership or who have switched to another
provider in Korea’s high-speed Internet market and
2) in analyzing the factors which affect their
behaviour (Kim et al., 2004; Ahn et al., 2002).
When we put together the previous studies of the
factors affecting customer behaviour, we can see
that customer satisfaction is the primary reason why
the subscribers stay (Rust et al., 1993): thus, while
the satisfied customers stay, those who are
dissatisfied seek another service provider. In some
situations, however, customer satisfaction does not
explain everything. Even customers who are not
satisfied with the service they get sometimes stay
enrolled, and vice versa. The switching barrier
theory, which was introduced to explain this
phenomenon, argues that dissatisfied customers stay
enrolled due to what is referred to as the switching
barrier (Kim et al., 2004). However, only a few
analyses of the reasons why satisfied customers
move to another provider appear to have been
294
Kim M., Park J. and Paik J. (2009).
FACTORS INFLUENCING CUSTOMER RETENTION AND SWITCHING IN THE KOREA BROADBAND INTERNET SERVICE MARKET.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 294-297
DOI: 10.5220/0002228302940297
Copyright
c
SciTePress
conducted so far. In this study, an attempt is made to
systematically identify the factors which affect the
customer’s continuance/switch of subscription in
Korea’s high-speed Internet market, and on this
basis, we will state some of the implications for
Internet providers.
2 SUMMARY OF MARKET
SURVEY
We conducted a market survey of members of the
public across the country. The target sample
consisted of 800 people aged between 15 and 49
living in Seoul, the capital region, and six
metropolitan cities. The survey was conducted in the
form of one-on-one interviews, which some leading
research institutes were commissioned to carry out.
The variables of this survey are composed of
maintain or switching, satisfaction or dissatisfaction,
service differentiation, facilitating conditions,
switching cost and unattractiveness of alternatives.
3 ANALYSIS OF THE FACTORS
AFFECTING CONTINUED
SUBSCRIPTION AND
SWITCHING AMONG
HIGH-SPEED INTERNET
USERS
3.1 Factors Affecting continued
Subscription to High-Speed
Internet
We studied the influence of the cost of switching
and the attractiveness of the alternatives in order to
identify the factors which affect the users’ continued
subscription to the high-speed Internet as shown in
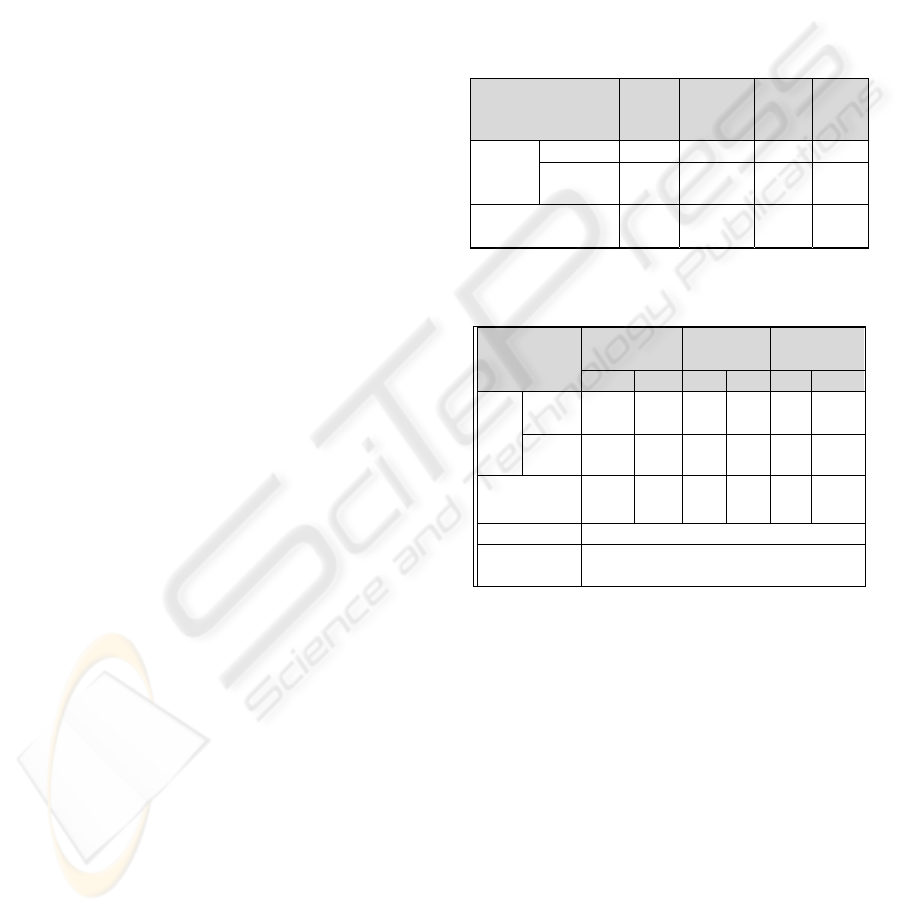
Table 1. Among the group of satisfied continuing
subscribers and the group of dissatisfied continuing
subscribers, the cost of the switching procedure and
the unattractiveness of the alternatives were both
found to have an influence. That is, even dissatisfied
subscribers tend to remain enrolled if the early
termination process is burdensome or if the other
providers are not attractive. Accordingly, the cost of
switching and the unattractiveness of the alternatives
can be said to be factors which incline dissatisfied
subscribers to remain with their service provider.
We conducted a multiple logit analysis of Group
2 with the others, the results of which are shown in
Table 6 below. Group 1 was found to be affected by
the switching cost and the unattractiveness of the
other service providers; Group 3 was affected by the
switching cost; and group 2 by the switching cost
and the unattractiveness of the other service
providers. In short, the cost of switching and the
unattractiveness of the other service providers were
found to influence dissatisfied subscribers into
remaining with their service in general.
Table 1: The factors affecting continued subscription.
Factors Satisfied Dissatisfied F Value
Signific
ance
level
Cost of
switchin
g
Penalty 0.08 0.11 0.875 0.350
Termination
procedure
0.07 0.40 44.284 0.000
Unattractiveness of the
alternatives
0.11 0.45 41.167 0.000
Table 2: Factors which influence customers to remain with
their provider.
Factors
Group1/
Group 2
Group 3/
Group 2
Group4/
Group 2
B S.E B S.E B S.E
Cost
of
switc
hing
Penalty -0.260 0.679
-
0.187
0.540
0.39
9
0.618
Switchin
g
3.075
0.603
*
**
0.952
0.577
*
1.88
3
0.616
***
Unattractiveness
of the alternatives
2.907
0.506
*
**
0.516 0.469
1.19
9
0.529
**
-2log likelihood 86.603
Chisquare/degree
s of freedom
118.568
***
/ 9
*: <0.1, **<0.05, ***:<0.01
3.2 Factors Affecting Subscribers’
Decision to Switch Providers of the
High-Speed Internet
We examined the influence of service differentiation
and the facilitating conditions to identify the factors
which affect the decision to switch providers of the
high-speed Internet, as shown in Table 3. Among the
group of dissatisfied people who switched and the
group of satisfied people who switched, facilitating
conditions such as service upgrade, additional
discounts, and free gifts were found to have an
influence on their decision. That is, even satisfied
subscribers are likely to switch due to such
facilitating conditions. This shows that service
FACTORS INFLUENCING CUSTOMER RETENTION AND SWITCHING IN THE KOREA BROADBAND
INTERNET SERVICE MARKET
295
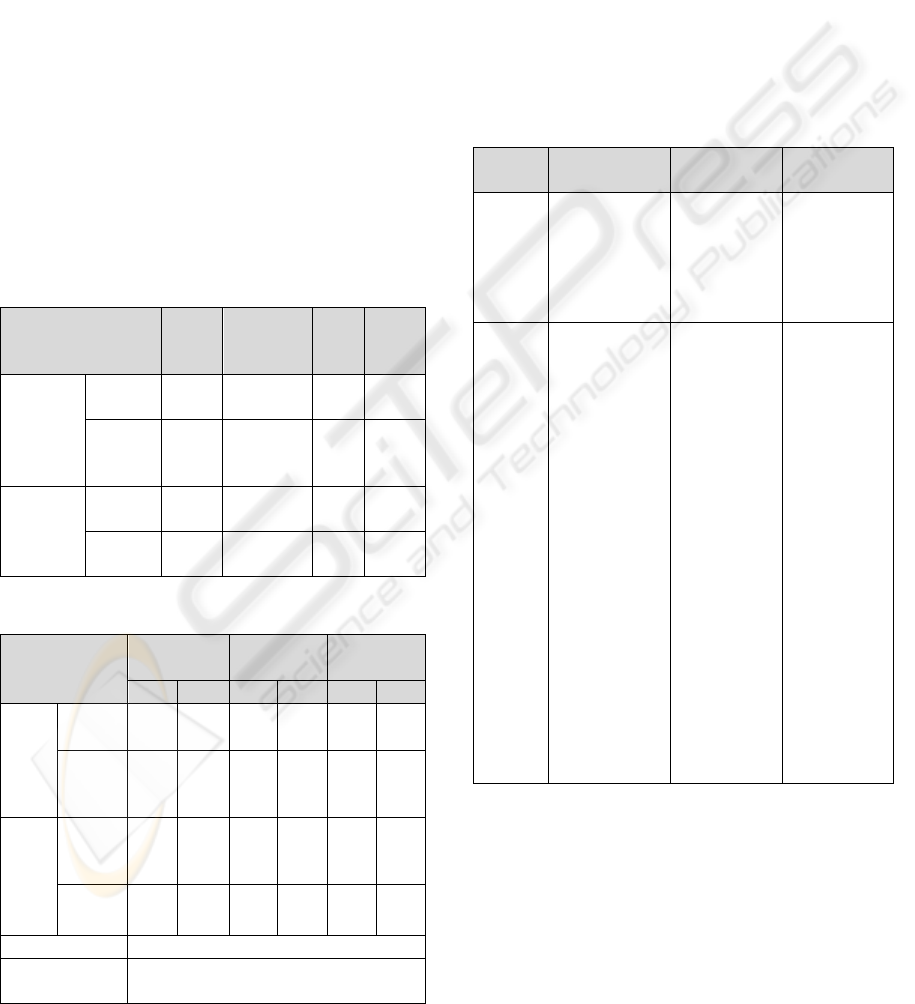
differentiation and the facilitating conditions can
persuade satisfied subscribers to switch.
We further divided the subscribers who switched
into 4 groups in order to study more deeply the
factors which affect the decision to switch providers
of the high-speed Internet. Group 4 (26) was
composed of those who were dissatisfied with both
the quality and the charges; Group 3 (59) of those
who were satisfied with both the quality and the
charges; Group 1 (69) of those only dissatisfied with
the quality; and Group 2 (45) of who were only
dissatisfied with the charges. We conducted a
multiple logit analysis of group 4 with the others, the
results of which are shown in Table 4. Compared to
Group 4, Group 3 was affected by the additional
discounts and free gifts, while Group 1, like Group
2, was not affected by service differentiation and
facilitating conditions. In summary, the factors
affecting switching differed between those who were
dissatisfied overall and those who were only
partially dissatisfied.
Table 3: Factors affecting switching.
Factors
S
atisfie
d
Dissatisfied
F
Value
Signific
ance
level
Service
differentia-
tion
Service
upgrade
0.20 0.08
4.09
4
0.044
Contents
improveme
nt
0.07 0.11
0.96
3
0.328
Facilitating
conditions
Additionas
l discount
0.25 0.15
2.77
5
0.097
Free gifts 0.22 0.07
7.05
7
0.009
Table 4: Factors affecting switching.
Factors
Group3/
Group 4
Group 1/
Group 4
Group2/
Group 4
B S.E B S.E B S.E
Servic
e
diffe-
rentia-
tion
Service
upgrade
0.755 0.723 0.330 0.700 0.355 0.746
Contents
improve-
ment
1.144 0.853
-
0.641
0.950 0.298 0.915
Facilita
-ting
condi-
tions
Additio-
nasl
discount
1.083
0.625
*
*
-
0.502
0.676 0.819 0.638
Free gifts 1.513
0.689
*
*
-
0.319
0.752
-
0.010
0.783
-2log likelihood -99.404
Chisquare/degrees
of freedom
35.424
***
/ 12
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this context, we studied the characteristics of
continuing and switched subscribers analyzed the
factors which affect their behavior, and tried to give
the implications in order to provide useful
information for high-speed Internet providers’
customer strategy. We recommend that the providers
adopt the following customer strategy shown in
Table 5. Thus, the appropriate customer strategy is
summarized as one of retaining their own customers,
attracting other companies’ customers, and
strengthening their services.
Table 5: Customer strategy for Korea’s high-speed
Internet providers.
Strategy
Retain existing
customers
Attract
customers
Strengthen
services
Direction
Raise
customer
satisfaction
Raise cost of
switching
Strengthen
brand
Differentia
te
Strength
facilitating
conditions
Strengthen
service
values
Extend
service
lines
Details
Enhance
quality
continually
Offer
continued
discounts by
economy of
scale and
scope
Continue the
development
of payment
plans suitable
for a
segmented
market
Raise cost of
switching
such as long
subscriber
discount
Strengthen
brand relative
to the
competitors
Performance
differentiati
on of
service
Differentiate
service itself
Differentiate
company
image
Develop
differentiate
d payment
plans
Differentiate
facilitating
conditions
Strengthen
service
values by
IPTV and
Internet
phone (TPS
or QPS)
Develop
bundle
packages of
high-speed
Internet and
WiBro
Adopt up-
selling
strategy
The customer retention strategy can be divided
into: enhancing customer satisfaction, raising the
cost of switching, and strengthening the brand, as
follows.
Customer satisfaction is the primary factor in
persuading subscribers to remain with the provider.
Therefore, in order to enhance customer satisfaction,
the providers should continue to enhance their
service quality, reduce costs through economy of
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
296

scale and scope, and create a mechanism whereby
charges decrease incrementally. As shown in the
aforementioned analysis, they need to segment the
market to reflect the demographic statistics and the
usage characteristics of the IT services and high-
speed Internet as much as possible, and continue to
develop the payment plans appropriate for the
characteristics of the segmented market. Especially
as the charges of telecommunication services are
becoming ever more burdensome as a proportion of
household expenditure, the development of various
payment plans will be significant. Another key to
ensuring customer satisfaction is that of
strengthening customer services continually in
addition to enhancing quality and lowering the
charges. The strategy of systematically
strengthening the mileage service, customer
response service, and after service, for example,
would be desirable.
Attention should also be paid to the fact that
what is commonly observed with most
telecommunication services - including Korea’s
high-speed Internet, is that customer satisfaction
does not always match their behaviour. Satisfied
customers generally remain with the service and get
out when they are dissatisfied; however, even
satisfied customers might switch, and the opposite
case may also happen. That is why the strategy of
raising the cost of switching is essential for retaining
the existing customers, which was analyzed in depth
above. The cost of switching refers to the
psychological, economic, and non-economic costs
that have to be paid when an existing subscriber
switches to another provider. Employing the
switching cost properly is therefore useful for
retaining one’s customers. A long-term contract
offers a good example in this respect. Although an
early termination penalty is effective, too, such a
strategy needs to bed modified because it is likely to
arouse customer complaints in the long term.
Strengthening the brand over those of the
competitors is also a good strategy for retaining the
existing customers, because the overall reliability of
the brand reinforces the customers’ loyalty to the
provider. Put another way, strengthening the brand
means strengthening the attractiveness of the current
provider over the competitors, for which strategic
means of strengthening the brand image, brand
association, and brand preference are required.
The strategy of attracting the competitors’
subscribers broadly divides into differentiation and
strengthening the facilitating conditions.
Differentiation in turn divides into the differentiation
of the product, service, and image. The
differentiation of service performance is the most
important factor for the high-speed Internet, as
providers especially need to provide services that are
at least equal to or better than their competitors
through continued investment in speed and
performance. It would also be desirable to achieve
differentiation in all aspects of the service by
differentiating the service itself. Effective
advertising and promotion is also recommended to
strengthen the company’s image. Furthermore, not
only absolute differentiation but also relative
differentiation is important: that is, differentiation
relative to the competitor is more efficient in terms
of cost and effectiveness. The strategic approach is
also effective in leading the customers to perceive
that the service is giving more benefits at a lower
price by continuing the differentiation of pricing.
Differentiation of the facilitating conditions is
also a good strategy for attracting the competitors’
customers. Attracting the competitors’ customers
should be done carefully because it might backfire.
Lavishing free gifts or discounts extravagantly, for
example, is likely to obtain no results because it
might harm profits and accelerate overheated
competition. Additional discounts might also bring
about losses rather than gains for the same reason.
Therefore differentiation should be based on gaining
slight advantages over the competitor or on other
means. A system which combines an additional
discount, long contract, and point system is one
example of this.
The strategies of strengthening the service value
and extending the service line exemplify the strategy
of extending the uses of a service. To that end, such
TPS or QPS strategies as strengthening the service
value through the IPTV and Internet phone,
extending the service line with bundle packages with
other telecommunication or mobile services such as
HSDPA, and adopting the up-selling strategy are
required. Because IPTV and the Internet phone, the
core elements of the Triple (Quattro) Play service,
are additional services that can be provided through
high-speed Internet networks with high
marketability, Korea’s high-speed Internet providers
should secure subscribers to those services in the
initial stages and thereby link it to the existing
customer strategies. Since it is hard to attract new
subscribers, and up-selling by the existing customers
are the key to creating profits, the providers need to
concentrate their resources and capabilities on them.
A bundle strategy of linkage with WiBro or HSDPA
is also required. For this, the customer strategy of
extending the high-speed Internet to wireless would
be desirable.
FACTORS INFLUENCING CUSTOMER RETENTION AND SWITCHING IN THE KOREA BROADBAND
INTERNET SERVICE MARKET
297

REFERENCES
Ahn, K.H. D.H. Kim and Y.C. Kim(2002), Marketing
Strategy, HakHyunSa.
Kim, M.K. M.C. Park, and D.H. Jeong(2004), “The effects
of customer satisfaction and switching barrier on
customer loyalty in the Korean mobile
telecommunication services,” Telecommunications
Policy, 28(2), 145-159.
Rust, R.T. and A.J. Zahorik(1993), “Customer
satisfaction, customer retention, and market share,”
Journal of Retailing, 69, 193-215.
Http://www.mic.go.kr
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
298
