
ADAPTATION ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
BASED ON FORMAL RULES
Dessislava Vassileva and Boyan Bontchev
Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, Sofia University, 5, J. Baurchier blv., Sofia 1164, Bulgaria
Keywords: AHS, e-Learning, User model adaptation, Formal rules.
Abstract: With last achievements in research and practical development of adaptive hypermedia systems, they start
being more and more promising for e-learning adaptable to personal learner needs, style and performance.
Every year there are constructed new technology enhanced platforms with adaptation engines controlling
content management and delivery. A great problem with adaptation engine designs is that few of them
facilitate a flexible and manageable control over adaptation processes. This paper is focussed exactly on
problems with effective conceptual construction of adaptation engine, by means of formalization of our
adaptation model for hypermedia learning courseware management and delivery. The article describes in
brief a formal definition of both adaptive rules and adaptive process supporting the model. The approach
proposed for adaptive engine’s construction follows a rule-driven approach and is consistent with that
formalization. The implementation of the platform is under development and relies strongly on conceptual
separation of adaptive rules from business logic. This guarantees an ability for editing adaptive rules at run
time and, thus, to manage the adaptation process in a very flexible way.
1 INTRODUCTION
In last decade, many software platforms for
technology-enhanced learning have been developed.
However, only few of them offer adaptation of e-
learning process according needs and expectations
of individual learners. Adaptive platforms such as
adaptive hypermedia system (AHS) are entirely
oriented to individual user’s goals, preferences and
knowledge (Brusilovsky P., 1994). AHS use various
decision mechanisms and methods of assuring
adaptation and of provisioning educational content
in a way most satisfying student needs (Dagger, D.,
Wade, V. & Conlan, O., 2005). Some AHS achieve
it using widespread techniques such as adaptive
navigation, structural adaptation, adaptive
presentation and content selection. These techniques
could be used for implementation of static
adaptation or of dynamic one - driven by an engine
controlling the adaptation. Other of them introduce
additional level of system self adaptability based on
the idea that different forms of learner model can be
used to adapt content and links of hypermedia pages
to given user. All of AHS have built-in engines
controlling adaptation by choosing what adaptive
technique to apply and managing the entire process.
The present paper discusses an approach
construction of adaptive engine by defining and
executing symbolic rules. Symbolic rules tend to be
most suitable for implementing our conceptual
model of an adaptive hypermedia system. Using
symbolic rules for construction of AHS promises to
be very universal thanks to abilities for run time
redefinition and control and, also, possible system
redevelopment for supporting other adaptation
models. After providing a comparison of most
prominent adaptation methods, the paper goes to a
brief description of our triangular conceptual model
of AHS. The functionality of the adaption engine is
formalised and two ways for its construction are
discussed: one by using Drools rule engine (Proctor,
M. et al., 2008) and another one by rule descriptions
in SWRL. Both these ways allow flexible software
construction of the engine allowing easy
expandability and adaptation control at run time.
2 COMPARISON OF
ADAPTATION METHODS
There are various well-established ways for ensuring
adaptation. Following them, the adaptation engine
327
Vassileva D. and Bontchev B. (2009).
ADAPTATION ENGINE CONSTRUCTION BASED ON FORMAL RULES.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 326-331
DOI: 10.5220/0002009203260331
Copyright
c
SciTePress
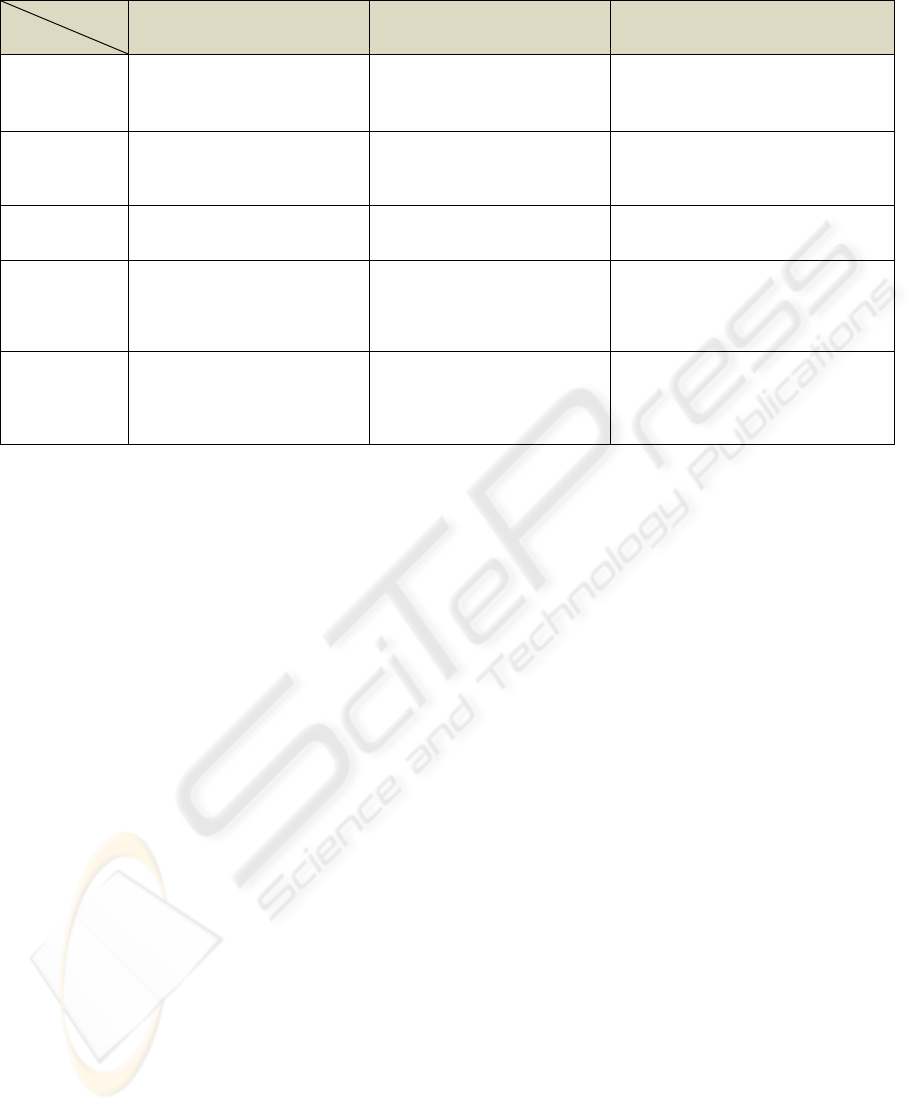
Table 1: Comparison between methods for construction of adaptation engine.
Methods
Criteria
Symbolic rules CBR IMS LD
independence
YES
(adaptation rules are defined
independently)
NO
(it depends on the cases and not only
on adaptation rules)
YES
(by a XML meta-language allowing
scenarios to be separated from learning
materials)
reuse /
repurposing
YES
(adaptation rules are used for each
learning material under certain
conditions)
NO
(a consequence of the independence)
YES
(various pedagogical strategies describing
by XML files can be applying in different
learning materials)
implementation
complexity
NO YES YES
level of adaptation
high
(depending on defined rules, it can
allow possibility for self adaptation)
high
(it allows possibility for self
adaptation)
average
(its adaptation is based on pre-defined
methods, conditions, calculations, etc.)
interoperability
YES
(for rules’ description, there can be
used XML based languages such as
RuleML, SWRL or first-order logic
predicates)
NO
(there is not a standardised way for
CBR description)
YES
(it is a specification and can be used
between systems supporting it)
can be constructed by means of methods as follows:
• symbolic rules – this is one of the most
illustrative methods for presenting
adaptation. The adaptation is described by
setting rules of type <if-then>. The rules set
conditions and actions to be implemented
when these conditions are observed.
• case-based reasoning (CBR) (Zongmin Ma
(Ed), 2006) – an approach that stores a set of
past situations with their solutions and, in
similar or same cases, uses them or a similar
solution. There are four phases of
implementation: retrieve, reuse, revise and
retain. Usually this approach is used to assess
learner knowledge and perform instructional
tasks (Guin-Duclosson, N. et al., 2002).
• IMS Learning Design (IMS LD) (Berlanga, A.
et al., 2006) – this is a meta-language for
learning scenarios description maintained by
IMS Global Learning Consortium.
Adaptation can be provided by defining
conditions for the presentation of learning
content and sequencing of learning activities.
Here we present a comparison between these
three ways for construction of the adaptation engine
as summarised in table 1. The selection criteria are
based on our main requirements to realization of
adaptive engine (namely, it should be flexible and
manageable) and its easy implementation. The goal
of this comparison consists in selection of the most
appropriated method among them. Based on the
results obtained from table 1 and in accordance with
our aims defined in the introduction, we choose to
use symbolic rules for defining of adaptation
mechanism.
3 AHS CONCEPTUAL MODEL
The AHS model described in details in (Vassileva D.
& Bontchev B., 2006) follows a metadata-driven
approach, explicitly separating narrative storyboard
from the content and adaptation engine (AE). Fig. 1
represents the triangular structure of our model
which refines the AHAM reference model (De Bra
P., Houben G.-J. & Wu H., 1999) by dividing in
three each one of the learner’s (or, generally
speaking – user’s), domain, and adaptation models.
At first level, the model is based on a precise
separation between learner, content and adaptation
model, while at second level each of these sub-
model is divided into three others sub-models
(Vassileva D. & Bontchev., B., 2006).
Fig. 1 represents the triangular structure of the
model. Unlike other approaches, in the learner
model we separate goals and preferences from
shown knowledge and performance, as the first sub-
model is static while the second one is rather
dynamic and takes a part in the event-driven
storyboard monitoring. The model of learning style
(learner characters such as activist, pragmatist,
theorist, or reflector) is detached as another learner
sub-model and can be used for choosing contents for
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
328

given learning style. While the learning style can be
determined in the very beginning of the learning
explicitly by the learner or by appropriate pre-tests,
other tests should be exercised during the e-learning
process in order to assess prior or gained knowledge
and performance results of each individual student.
Figure 1: Structure of the triangular conceptual model.
The domain model is composed of content itself
(granulized in learning objects (LOs) according to
the SCORM standard) (López, M. et al., 2006), LO’s
metadata (LOM) and LO’s content assets (images,
text, tables, etc.) forming a logical taxonomy for the
knowledge domain built upon domain ontology
during the course composition process by the course
author. The content LOs are placed by the instructor
on course pages, while pages represent nodes within
course storyboard graph. Content pages delivery is
controlled by the adaptation engine (AE) for
choosing most appropriate content for presenting it
to the user with given learning model. Instead of
choosing dynamically a page (i.e. node of the
storyboard graph) with its content, we propose
choice of best working path within the graph for
specific learner with given learning style on one
hand, and shown prior knowledge and performance
on the other.
The adaptation model (AM) captures the
semantics of the pedagogical strategy employed by a
course and describes the selection logic and delivery
of learning activities/concepts. AM includes a
narrative storyboard sub-model supporting course
story-board graphs, which may differ for different
learning styles. It consists of control points (CP) and
work paths (WP). Moreover, AM should provide a
schema of storyboard rules used for controlling the
e-learning process. Storyboard rules determine
sequencing of the course pages upon inputs from
learner sub-models. The narrative metadata sub-
model sets such rules for passing a CP (e.g., as
threshold level of assessment performance at that
CP) or for returning back to the previous CP.
The core of our model is the adaptation engine
(AE) which is responsible for generating the actual
adaptation outcomes by manipulating link anchors
or fragments of the pages’ content before sending
the adapted pages to a browser. The AE uses an
event-driven mechanism for controlling the
storyboard execution based on the storyboard rules
applied to the inputs from the learner model. AE
selects the best storyboard WP within the graph by
evaluating weight coefficient of the pages within the
WP for the given learner style (Vassileva, D.,
Bontchev, B. & Grigorov, S., 2008).
AE is responsible for performing all necessary
adaptation mechanism for content delivery to a
specific learner. This includes content selection,
content hiding, link annotation, link hiding, etc.
When learner starts a new course, adaptive engine
finds the best path for him/her in the course graph.
The best path is that one with the highest weighed
score. For a particular user, the best path is
calculated by a sum of multiplications between page
parameters values and weights of their
correspondent learner’s characters.
4 FORMAL SPECIFICATION OF
THE CONCEPTUAL MODEL
For description of formal model, there can be used
Object Constraint Language (Richters, M. &
Gogolla, M., 1998) like in the Munich Reference
Model (Koch, N. & Wirsing, M., 2002), descriptive
language for specification like in GAHM (Ohene-
Djan, J. et al., 2003) or predicate logic like in the
Dexter Hypertext Reference Model (Halasz, F. &
Schwartz, M., 1994). In order to assure an easy
construction of adaptation rules, we preferred to use
predicate logic for formal model description.
Predicate logic is extension of propositional logic
with separate symbols for predicates, subjects and
quantifiers. Its formulas contain variables which can
be quantified enabling clearer adaptive process
understanding and more precise adaptive rules
description. By means of predicates, we formalise
the learner model (e.g., by a predicate we show the
level of belonging of a user to given learning style),
the domain model, the adaptation model and, finally,
the adaptation engine. Once we have defined the
predicates describing main functionalities of the
ADAPTATION ENGINE CONSTRUCTION BASED ON FORMAL RULES
329

triangular model we can begin giving adaptive rules.
They can be presented by defining relationships
between the predicates. The adaptive rules can be
divided into three main groups in accordance to their
purpose:
• starting rules - describe learner
knowledge and initial conditions for starting a
new course, for example if the user knows all
learning objects contained in a subject, then
she/he knows that subject:
(1) ∀user
i
∃subject
j
(∀lo
k
lo_4_subject(subject
j
,
lo
k
)∧ user_knows_learning_object(user
i
,
lo
k
)) → user_knows_subject(user
i
, subject
j
)
• pass-through graph rules – consist of
rules for the graph crawling, e.g. if the learner
does not pass the test at a control point, she/he
continues backward:
(2) ∃k(user_performance(user
i
, subject
j
,
control_point
k
, fail)) → next_cp_path(user
i
,
subject
j
, control_point
k-1
)
• rules updating learner model – related to
learner knowledge and performance, such as the
following: if the learner passes all control
point’s tests for particular subject then the
learner knows it:
(3) ∀k(user_performance(user
i
, subject
j
,
control_point
k
, pass)) →
user_knows_subject(user
i
, subject
j
)
5 ADAPTATION ENGINE
In this chapter, there is presented in brief a proposal
for construction of adaptation engine by means of
symbolic rules. For realizing such a goal, the most
suitable means to be used are a rule description
language such as SWRL (Mei, J. & Boley, H., 2006)
and its execution engine, or a rule execution
platform such as Drools (Proctor, M. et al., 2008)
and Jess (Hill, E. J. F., 2006). We have chosen to
present our rules both through Drools and SWRL.
Motives to select exactly them are that on the one
hand, for Drools and SWRL, there are available very
good and convenient graphical editors and tools for
presentation, editing and reviewing rules such as
Protégé for SWRL and RuleFlow for Drools. On the
other hand, SWRL aims to be the standard rule
language of the Semantic Web, which will allow
interoperability between different rule engines. Also,
Drools can reduce complexity of components that
implement the business rules logic in Java
applications, and it is easy to maintain or extend the
business logic by declarative programming.
5.1 Drools Overview
The Drools is an open source rules engine Java
implementation expressing business logic rules in a
declarative way. The Drools architecture is based on
three main components: production memory that
stores the rules, working memory that stores the
facts and the inference engine. The rules can be
writing using a non-XML native language – Drools
Rule Language (DRL), a XML native language as an
alternative of DRL which allows capturing and
managing rules as XML data and in a spreadsheet
format (supported formats are Excel and CSV).
Drools development platform comes in two
flavours: as an Eclipse plug-in Drools IDE and as
Web application Drools BRMS. The Drools IDE
provides developers with an environment to edit and
test rules in various formats, and integrate it deeply
with their applications from within Eclipse. The IDE
has a textual/graphical rule editor, a RuleFlow
graphical editor, a domain specific language editor.
Other advantages of the Drools are:
• it separates your application from conditions
which control the flow:
o rules are stored in separate files
o changing rules does not require to
recompile or redeploy the application
o putting all rules into one place makes it
easier to control the application flow
• problems are not solved using a complicated
algorithm, but via rules, which are easier to
read and understand than code
• Drools is supported by an active community of
Java developers
5.2 Drools Rules
The structure of a Drools’ rule includes one or more
attributes providing a declarative way to influence
the behavior of the rule, one or more conditions (in
when section), and a list of actions (in then section).
For example, the rule (2) given within the previous
chapter can be written as Drools’ rule like this:
rule "Fail the test in control point on level k"
when
UserPerformance(user_i:user_id,
subject_j:subject_id,
control_point_k:control_point_id,
value==”fail”)
then
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
330
eval(NextCpPath(user_i, subject_j,
control_point_k-1));
end;
where in the section when is described the left hand
side of formulas (2) and in the section then is
described right hand side of (2). Thereby, all the
formulas formally defined by predicates should be
converted to DRL rules. The resulted DRL rules are
used by the inference engine together with the facts
(e.g., data about both the learning model and the
adaptation model).
5.3 SWRL Overview
SWRL is intended to be the rule language of the
Semantic Web. SWRL is based on OWL and all
rules are expressed in terms of OWL concepts. A
SWRL file is an OWL ontology, whose axioms are
extended with rule axioms. It thus extends the set of
OWL axioms to include Horn-like rules and enables
Horn-like rules to be combined with an OWL
knowledge base. The SWRL rules can be described
through Abstract Syntax, XML Concrete Syntax and
RDF Concrete Syntax. SWRL allows users to write
Hornlike rules expressed in terms of OWL concepts
to reason about OWL individuals. The rules can be
used to infer new knowledge from existing OWL
knowledge bases.
The SWRL Specification does not impose
restrictions on how reasoning should be performed
with SWRL rules. Thus, investigators are free to use
a variety of rule engines to reason with the SWRL
rules stored in an OWL knowledge base.
5.4 SWRL Rules
In common with many other rule languages, SWRL
rules are written as antecedent-consequent pairs. In
SWRL terminology, the antecedent is referred to as
the rule body (rule_eml:_body tag) and the
consequent is referred to as the head (ruleml:_head
tag). The head and body consist of a conjunction of
one or more atoms. At present, SWRL does not
support more complex logical combinations of
atoms. SWRL also supports literals, built-in
predicates, which greatly expand its expressive
power. For example our rule (3) can be written in
SWRL XML Concrete Syntax like that:
<ruleml:imp>
<ruleml:_body>
<swrlx:individualPropertyAtom
swrlx:property="user_performance">
<ruleml:var type=”xsd:int”>
user_i</ruleml:var>
<ruleml:var type=”xsd:int”>
subject_j</ruleml:var>
<ruleml:var type=”xsd:int”>
control_point_k</ruleml:var>
<ruleml:var type=”xsd:string”>
result</ruleml:var>
<owlx:Individual owlx:name="#pass"/>
</swrlx:individualPropertyAtom>
</ruleml:_body>
<ruleml:_head>
<swrlx:individualPropertyAtom
swrlx:property="user_knows_subject">
<ruleml:var type=”xsd:int”>
user_i</ruleml:var>
<ruleml:var type=”xsd:int”>
subject_j</ruleml:var>
</swrlx:individualPropertyAtom>
</ruleml:_head>
</ruleml:imp>
5.5 Comparison between Drools and
Jess Rule Engines
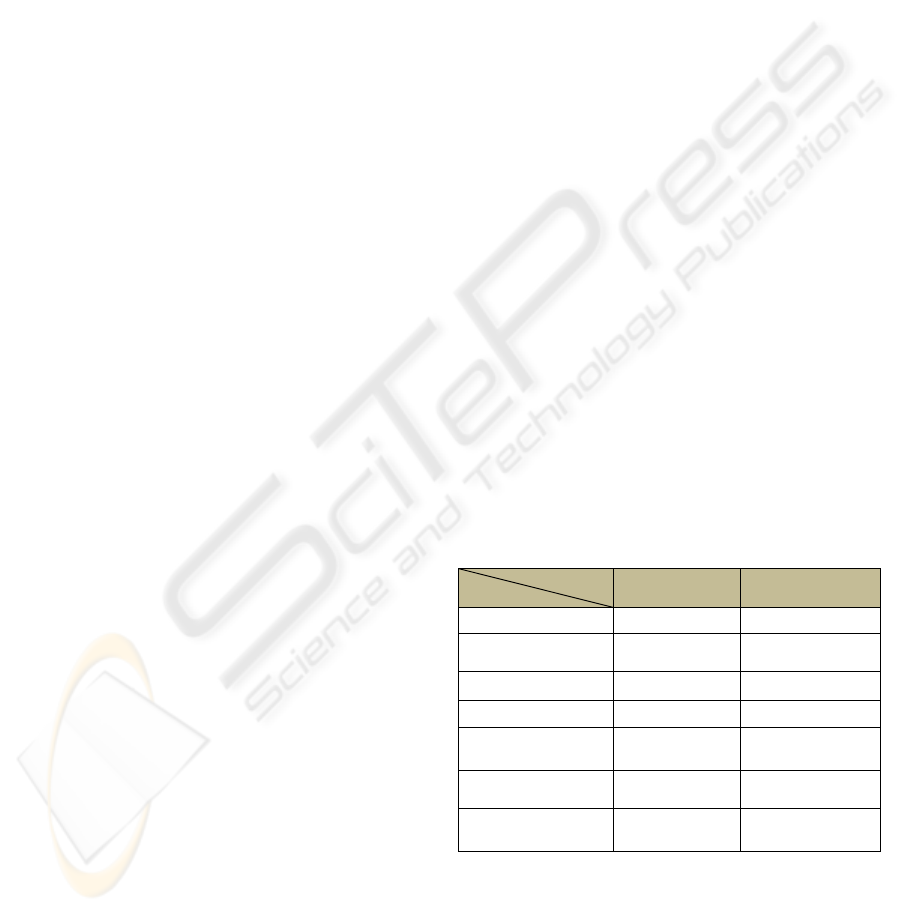
Now, we will do a comparison between the two
rules engines selected above (Drools and Jess) for
construction of our adaptive engine. For the purpose
of comparison we define several criteria (table 2). In
the table, they are described rule engines properties
for each defined criterion. As we see, Drools
outweighs Jess especially because of availability of
very good means for rule creating and editing and of
its maturity and open solution.
Table 2: Comparison between Drools and Jess.
Rule engine
Criteria
Drools Jess
Interoperability
no no
Rules tools
yes (special IDE,
Rule-Flow)
no
JSR94 support
yes yes
Maturity level
++++ ++
Availability
open source
commercial with
academic license
Mode of working
run from JVM
shell or batch,
plugin in Protégé
Classes and
instances
Java objects CLIPS file
6 CONCLUSIONS
Future years will prove the potential and great
promise of adaptive hypermedia proposals being
nowadays under discussion. The present paper
ADAPTATION ENGINE CONSTRUCTION BASED ON FORMAL RULES
331

introduced a new conceptual approach for self
adaptive hypermedia applications using triangular
conceptual model. The proposed model offers many
advantages but the main one consists in assuring
strong independence of any of the building models
and, at the same time, in facilitating a flexible
adaptation of content delivery. The adaptation makes
use of adaptive presentation, navigation support and
content selection; it is not locked to any given
learner model. In order to be able to describe
polymorphic learner profiles, we use concepts of
given domain such as characteristics of the learning
style, psychology characters, etc.
The adaptive process for e-learning content
delivery was formalized through usage of predicates
and relationships between them. On the base of such
predicates, there were built formal rules controlling
the adaptation process and executed by the
adaptation engine. For describing the rules, two
approaches have been considered – Drools Rule
Language and SWRL. Both the approaches are
supported by rule engines which executes rules
described in correspondent language. Thanks to the
fact they both support rules defined by first order
logic predicates, we conclude they are suitable for
constructing an adaptation engine supporting the
conceptual model. Based on this comparison
showing the weaknesses and advantages of the rule
engines, we may choose Drools for the ongoing
implementation of the adaptation engine. The choice
of Drools is strongly influenced by the facts it
provides advanced rule management tools, detailed
documentation, and open source license. The
adaptation engine is going to be integrated and
tested within a adaptive e-learning platform
providing an authoring tool for construction of
learning courseware and an instructor tool
(Vassileva, D., Bontchev, B. & Grigorov, S., 2008)
for structuring the narrative storyboards and
planning the instructional design.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially supported by the SISTER
project funded by the European Commission in FP7-
SP4 Capacities via agreement no.: 205030.
REFERENCES
Berlanga, A. et al. (2006). Authoring Adaptive Learning
Designs Using IMS LD, Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, Volume 4018/2006, ISBN 978-3-540-34696-
8, pp. 31-40.
Brusilovsky P. (1994). Adaptive Hypermedia: An attempt
to analyze and generalize. Proc. of First International
Conf. on Multimedia, Hypermedia and Virtual Reality.
In Brusilovsky P. & Streitz N. (Eds.) LNCS 1077,
Springer Verlag, pp.288-304.
Dagger, D., Wade, V. & Conlan, O.. (2005).
Personalization for All: Making Adaptive Course
Composition Easy. Special issue of the Educational
Technology and Society Journal, IEEE IFETS.
De Bra P., Houben G.-J. & Wu H. (1999). AHAM: A
Dexter-based Reference Model for adaptive
Hypermedia. Proceedings of the ACM Conference on
Hypertext and Hypermedia, 147-156.
Guin-Duclosson, N. et al. (2002). The AMBRE ILE: How
to Use Case-Based Reasoning to Teach Methods,
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, ISBN 978-3-540-
43750-5 , Volume 2363/2002, pp. 782-791.
Halasz, F. & Schwartz, M. (1994). Halasz, F., Schwartz,
M.: The Dexter hypertext reference model.
Communications of the ACM, Vol. 37, Issue 2,
ISSN:0001-0782, pp. 30 - 39.
Hill, E. J. F. (2006). “Jess, the Rule Engine for the Java
Platform”, Sandia, National Laboratories, http://
www.jessrules.com/jess/ docs/70/, October 2007
Koch, N. & Wirsing, M. (2002). The Munich Reference
Model for Adaptive Hypermedia Applications. Proc.
of the Int. Conf. on Adaptive Hypermedia and
Adaptive Web-Based Systems, ISBN: 3-540-43737-1,
pp. 213 – 222.
Mei, J. & Boley, H. (2006). Interpreting SWRL Rules in
RDF Graphs. Electr. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci.
151(2): pp. 53-69.
Ohene-Djan, J. et al. (2003) Understanding Adaptive
Hypermedia: An Architecture for Personalisation and
Adaptivity. In: Workshop on Adaptive Hypermedia
and Adaptive Web-Based Systems AH2003, August
26-30, 2003, Nottingham, UK.
Rey-López, M. et al. (2006). Providing SCORM with
adaptivity. Proceedings of the 15th international
conference on World Wide Web, ISBN:1-59593-323-9,
pp.981-982.
Richters, M. & Gogolla, M. (1998). On Formalizing the
UML Object Constraint Language OCL, LNCS Vol.
1507, ISBN: 3-540-65189-6, pp. 449 - 464.
Vassileva D. & Bontchev B. (2006). Self adaptive
hypermedia navigation based on learner model
characters, Proc. of IADAT-e2006, Barcelona, Spain,
pp.46-52.
Vassileva, D., Bontchev, B. & Grigorov, S. (2008).
Mastering Adaptive Hypermedia Courseware, Proc. of
6th Int. Conf. on Emerging eLearning Technologies
and Applications ICETA2008.
Zongmin Ma (Ed). (2006). Web-Based Intelligent e-
Learning Systems: Technologies and Applications
(ISBN 1-59140-729-3), Chapter IX, pp. 175-193.
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
332
