
AN ANALYSIS PATTERN FOR MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION SYSTEMS TOWARD
MUNICIPAL URBAN ADMINISTRATION
Bruno Rabello Monteiro, Jugurta Lisboa Filho, José Luís Braga and Waister Silva Martins
Departamento de Informática, Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV), Viçosa – MG, Brazil
Keywords: Analysis Pattern, Mobile Geographic Information Systems, Urban Administration.
Abstract: This paper introduces an analysis pattern for Mobile Geographic Information Systems (Mobile GIS) focused
on urban administration applications. This pattern provides a class and associations diagram and can be used
in the development of an urban Mobile GIS application. The paper also describes a process that guided us in
obtaining this analysis pattern, presenting an example of its use in the conceptual modeling of an actual
application.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Brazil, many municipal public administrations
have been using Geographic Information Systems
(GIS) technologies both as supporting tools for
decision-making and for operational activities.
With the recent rise of mobile computation, a
new type of GIS has appeared, enabling the access
to spatial data from any place and at any time: the
Mobile Geographic Information Systems, or simply
Mobile GIS. The Mobile GIS applications allow
broad use and sharing GIS technologies with the
public (Xiaoqing & Qingquan, 2005).
According to (Tsou, 2004), Mobile GIS is an
integrated hardware-software framework to access
services and geo-spatial data using mobile devices
via cable or wireless networks. In addition, a Mobile
GIS application is not equivalent to a conventional
GIS application modified to operate in a smaller
device: they are systems based on a new paradigm
(Maguire, 2001). This new paradigm implies, among
other things, considering non-functional
requirements like the limited bandwidth of the
wireless communication network, the low
processing and storage power of the mobile devices
when compared to the usual desktop computers and
the differences in the screen size and properties to
display maps and results.
However, as it also happens in developing GIS
applications, the success of Mobile GIS applications
depends heavily on the extraction, analysis and
representation of requirements from the domain.
Lisboa Filho et al. (2002) pointed out that the
disciplines to be followed in requirement analysis
and database conceptual design are complex
activities that demand long working hours.
Patterns in general are one way of avoiding effort
repetition, and database conceptual design can be
greatly favored by using analysis patterns.
Analysis patterns are used to describe solutions
adopted during the steps of requirement analysis and
data conceptual modeling. Fowler (1997) argued that
an analysis pattern is an idea that has been proven
useful in a practical context and it will probably be
useful in other similar situations. In addition,
(Lisboa Filho et al., 2002) pointed out that
in the urban administration domain the basic
environment that makes up the digital cartographic
basis (e.g.: streets, blocks, plots and districts) can be
reused by several different applications.
This paper proposes an analysis pattern to be
applied in the analysis and conceptual modeling
steps of geographic database construction for Mobile
GIS applications for the urban administration
domain. Section 2 describes the UML-GeoFrame
approach used in the conceptual modeling of Mobile
GIS applications and in the presentation of the
proposed solution for the proposed pattern. Section 3
presents the step-by-step modeling of a Mobile GIS
application for the urban administration domain.
Section 4 describes the analysis patterns we propose
for these applications. Section 5 presents the use of
311
Rabello Monteiro B., Lisboa Filho J., Luís Braga J. and Silva Martins W. (2008).
AN ANALYSIS PATTERN FOR MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS TOWARD MUNICIPAL URBAN ADMINISTRATION.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 311-318
DOI: 10.5220/0001703803110318
Copyright
c
SciTePress
the proposed analysis pattern. Finally, Section 6
presents the final conclusions and prospects of future
developments.
2 THE UML-GEOFRAME
MODELING METHOD
GeoFrame is a specified conceptual framework
based on the class model of the Unified Modeling
Language (UML), which serves as a guide for
modeling GIS applications. GeoFrame provides a
basic class diagram to assist the designer in the
initial steps of the database conceptual modeling of a
new GIS application. It also provides a stereotype
set (Figure 1) that allows obtaining data schemes
easily understandable by users (Lisboa Filho &
Iochpe, 2008).
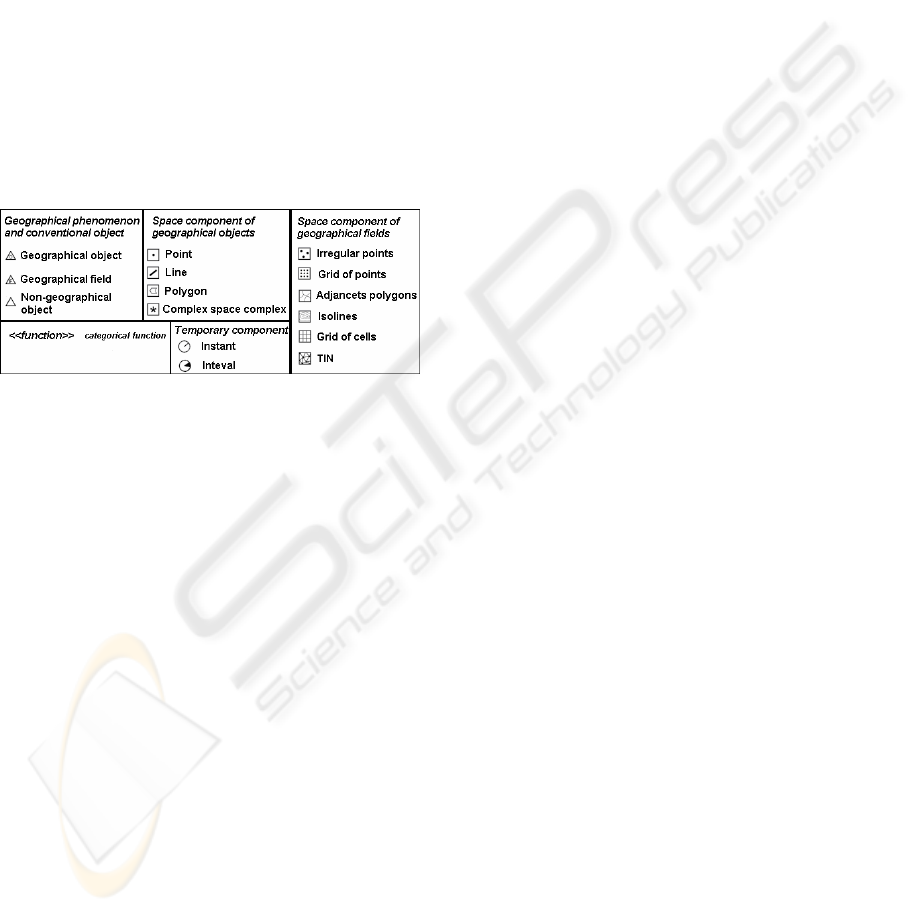
Figure 1: Stereotypes for the UML-GeoFrame model.
In Figure 1, the first three stereotypes to the left,
are used to differentiate the main types of objects
belonging to database of geographic applications:
geographic object []; geographic field [∵] and
non-geographic object [].
The two other stereotype sets are used for
modeling of spatial components of geographic
phenomena. The set located at the center represents
the spatial component of geographic phenomena,
according to the object view, and the set more to the
right represents the geographic phenomena
according to the field view. It is also possible to
generate several representations by combining
stereotypes. The stereotype <<function>>
characterizes a special type of association that
occurs in a categorical function modeling, whereas
the stereotypes Instant [] and Interval [] are used
for temporal aspects modeling.
The UML-GeoFrame method consists of the
following 5 steps. More details on each step can be
found in (Lisboa Filho & Iochpe, 2008).
• Step 1: identify themes and sub-themes for each
application target region;
• Step 2: draw the class diagram for each
identified theme;
• Step 3: model the spatial characteristics of each
geographic phenomenon;
• Step 4: specify the integrity constraints for the
spatial relationships;
• Step 5: model the temporal aspects.
(Lisboa Filho & Iochpe, 2008) also emphasized
that these five steps need not necessarily be followed
in this order, some steps can be carried out
simultaneously, depending on the designer’s
experience. In the next section, we show a modeling
example using the UML-GeoFrame method.
3 DATABASE MODELING FOR
URBAN MOBILE GIS
APPLICATIONS
Aiming at determining which geospatial basic
dataset is necessary for developing Mobile GIS
applications focusing on a specific urban area, the
following applications were modeled:
• School cataloguing system;
• School location system;
• Hospital and health center cadastre system;
• Medical emergency system;
• Traffic sign cadastre system;
• Meter reading system.
The applications were modeled using the UML-
GeoFrame method, with the ArgoCASEGEO
support tool (Lisboa Filho et. al, 2004), an open
source CASE tool built upon ArgoUML (ArgoUML,
2007) that supports modeling geographic application
databases based on the UML-GeoFrame model.
In section 3.1 we introduce a step-by-step
modeling of a Mobile GIS application for Traffic
Accident Reports as an example of the use of the
UML-GeoFrame method. We omitted the other
conceptual modeling steps because of space
constraints, they can be seen in (Monteiro, 2007).
3.1 Mobile GIS Application for Traffic
Accident Reports
This type of application seeks to assist the user in
the recording of data on traffic accidents occurred in
a town. The functionalities that this application
should include are: road network viewing and road
circulation traffic network; recording of the accident
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
312
location in the map; recording of other data related
to the accident; searching accident records per street,
vehicles, and drivers, among others.
The steps of UML-GeoFrame method are as
follows.
Step 1 - Identify the themes and sub-themes for
each geographic area.
The referred geographic area is the municipality
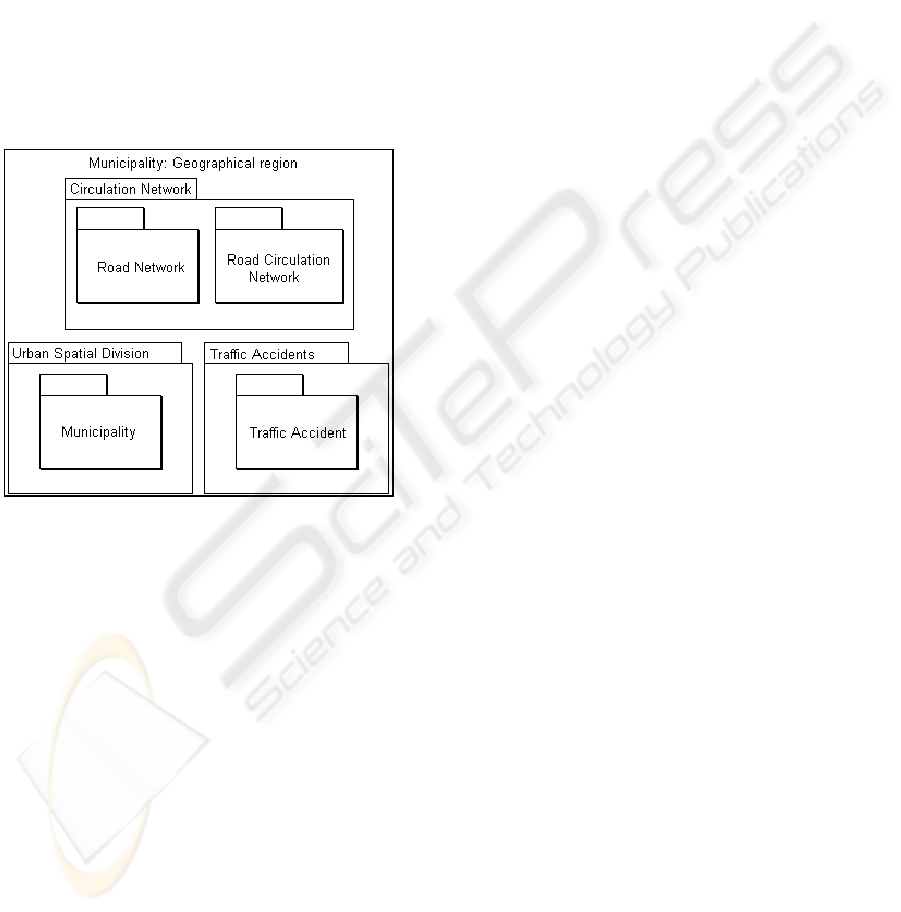
itself. Figure 2 shows the themes and sub-themes of
the application, which include: Circulation Network,
with the sub-themes Road Network and Road
Circulation Network; Urban Spatial Division,
including the theme Municipality; and Traffic
Accidents, with the sub-theme Traffic Accident.
Figure 2: Step 1 - Themes of the application.
Step 2 - Draw the class diagram for each
identified theme and sub-theme and Step 3 - Model
the spatial characteristics of each geographic
phenomenon.
Figure 3 shows the result of steps 2 and 3,
containing the class diagram of the modeled
geographic phenomena. The spatial characteristics
were also modeled according to the stereotypes
present in the UML-GeoFrame approach.
Data on traffic accident, required for the
application, were defined based upon the instruction
manual "Basic Instruction of Traffic Statistics"
(FGV, 2001), together with the document “Basic
Concepts and Definitions”, from the “Detran Traffic
Accident Information System” (DETRAN/DF,
1989). The modeling of the Road Circulation
Network was carried out based on an analysis
pattern described by (Lisboa Filho et al., 2002).
Following, we present a description of each class
of the diagram showed in Figure 3.
The Municipality class has spatial representation
in the form of a polygon [] and is composed by
one or more Administrative Departments.
The Administrative Departments class is
specialized in the classes Districts and
Neighborhoods that have spatial representation in
the form of polygons [].
A thoroughfare is considered a non-geographic
object []. It is composed by several thoroughfare
segments modeled as geographic objects of the type
line [].
The classes Thoroughfare, Thoroughfare
Segment and Intersection represent the road network
of the city.
Road Circulation Network is composed by the
road network and the classes Traffic Flow Section
[] and Conversion Point [].
The Accident class was modeled as a geographic
object of the type point [], allowing a spatial
representation of the accident location. An accident
can take place in both a Thoroughfare Segment and
an Intersection []; this condition is indicated in the
scheme through the restriction XOR (Dietrich &
Urban, 2005).
The scheme also indicates that an accident can
involve several vehicles, and each vehicle is
associated with one single driver. The classes
Vehicle and Driver are modeled as non-geographic
objects [].
The Victim class [] is specialized in six other
subclasses (Driver, Passenger, Pedestrian, Cyclist,
Motorcyclist and Others).
Step 4 - Specify the integrity constraints for the
spatial relationships and Step 5 - model the
temporal aspects.
Only the semantic relationships were modeled,
the spatial relationships (Step 4), that is, the spatial
integrity constraints, are not shown in the diagram.
Regarding the temporal aspects (Step 5), only the
Accident class has temporal characteristics,
indicated by the stereotype Instant [].
AN ANALYSIS PATTERN FOR MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS TOWARD MUNICIPAL
URBAN ADMINISTRATION
313
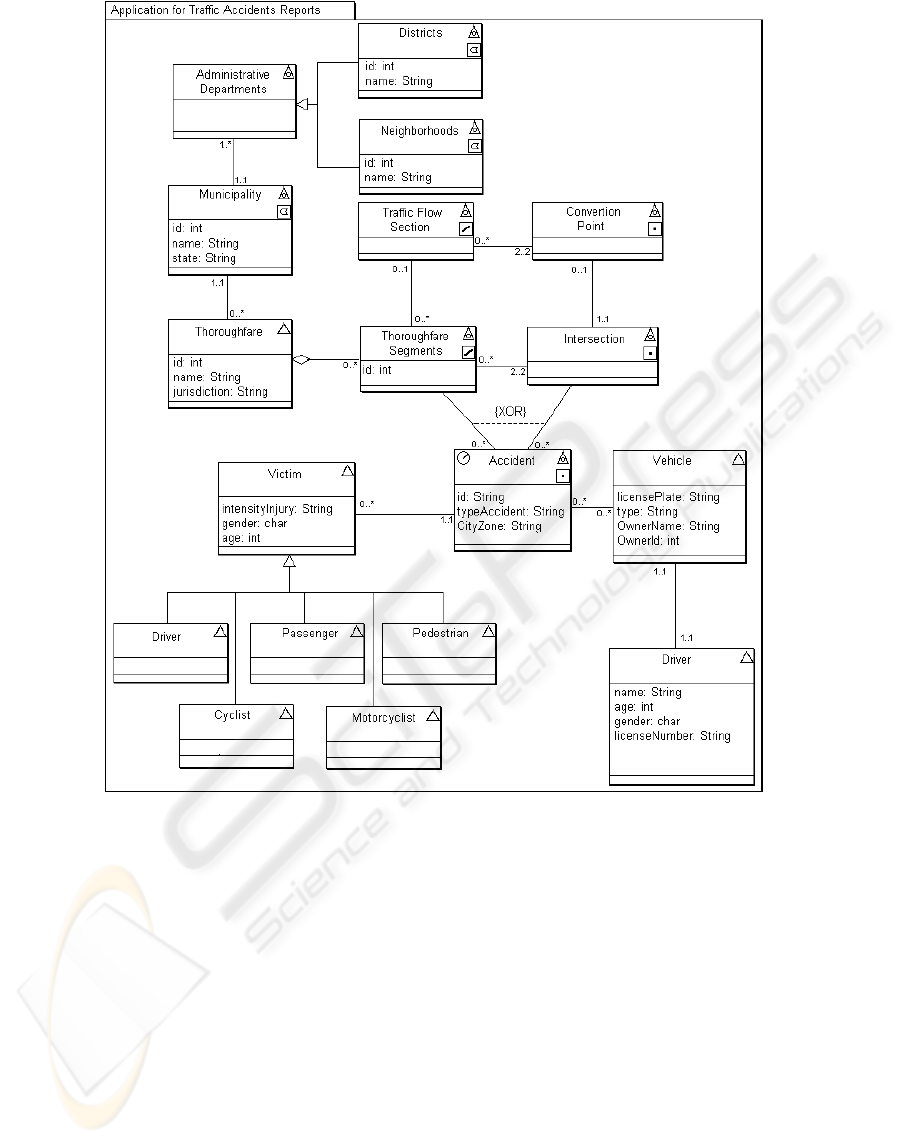
Figure 3: UML-GeoFrame Class Diagram for the Traffic Accidents Report Application.
4 THE URBAN MOBILE GIS
BASIS ANALYSIS PATTERN
The analysis of the conceptual diagrams of the
Mobile GIS application for Traffic Accidents
Report, as well as of the others mentioned in the
previous section, have shown classes of common
objects. By analyzing these classes, relationships
were extracted based on the conceptual schema of
each application, and then these elements were
organized in the form of an analysis pattern.
Next we introduce the analysis pattern named
“Urban Mobile GIS Basis” to be reused in the
development of Mobile GIS applications in the
domain of urban areas. The structure used for the
presentation of the analysis pattern is the one
defined by (Meszaros & Doble, 1998), in which the
pattern specification should contain, at least, the
following items: Problem-Context-Forces-
Participants-Solution.
Pattern Name: Urban Mobile GIS Basis.
Problem
What are the data for developing Mobile GIS
Applications and how they should be structured?
Context
The development of Mobile GIS applications for
urban administration begins with the creation of a
minimum cartographic base regarding the structure
of the municipality in question. This minimum base
can be used by several applications for the most
varied areas of a municipal public administration,
such as: Education, Health, Public Safety,
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
314
Transportation, etc. The necessary basic information
to those applications is the plan of districts, blocks
and plots and the road network of the municipality.
Forces
- The level of granularity of the proposed
analysis pattern depends on the existence of spatial
data for the municipality being modeled. In this
pattern, the highest granularity level is the plot, but it
could be a building in the plot, for example.
- The most common types of administrative
municipal divisions are neighborhoods and districts.
Other subdivisions can be easily included if
necessary.
- The concept of neighborhood can vary quite a
lot among municipalities. Thus, it is possible that a
same block belongs to more than one neighborhood
and that the boundary of a neighborhood can even
cross a plot.
- The set of administrative divisions, blocks and
plots comprise the division of the urban space of a
municipality.
- A thoroughfare segment corresponds to the
street segment comprised between two intersections.
Several segments correspond to a thoroughfare.
- The set formed by the intersections, or terminal
points and thoroughfare segments constitute the
urban road network.
- The packages Road Network and the Urban
Space Division comprise the analysis pattern Urban
Mobile GIS Base.
Solution
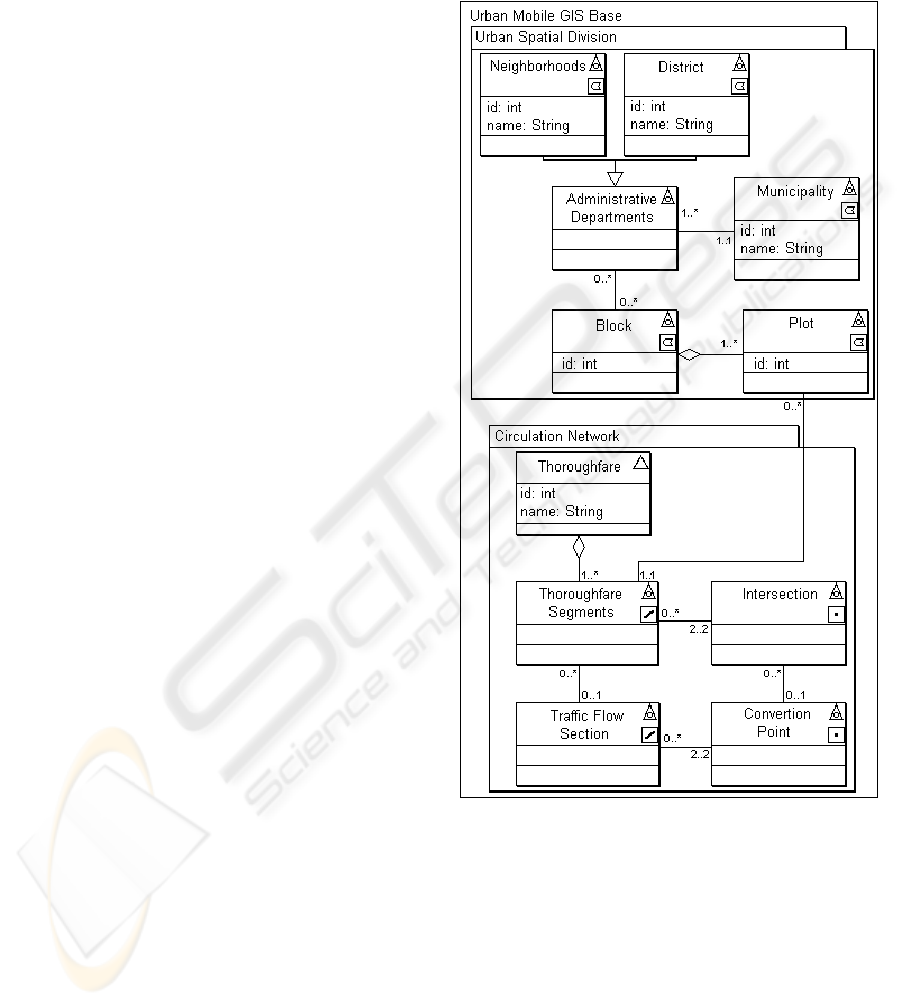
Figure 4 shows the diagram of classes belonging
to the Urban Mobile GIS Base pattern.
Participants
The Municipality class is associated with the
Administrative Division class through a "one-to-
many" multiplicity. In this solution, the
Administrative Division class is specialized in the
classes Neighborhood and District, but in some
cases, it can be specialized in other municipal
subdivisions such as: census sectors, police
surveillance zones, etc.
The Administrative Division class relates with
the Blocks class through a many-to-many
cardinality. In this way, it is supposed that a
neighborhood boundary (or any other administrative
division) may cross a block. In municipalities where
this does not happen, the cardinality can be changed
to one-to-many.
The Plot class is associated with the classes
Block and Thoroughfare segment. A group of plots
make up only one block, whereas a plot has its front
access to only one thoroughfare segment.
Several thoroughfare segments are part of a same
thoroughfare, here represented by a non-geographic
phenomenon. Besides, several thoroughfare
segments can be connected by intersections that
represent the knots forming the road network.
Figure 4: Class diagram of the analysis pattern Urban
Mobile GIS Base.
5 USING THE PROPOSED
ANALYSIS PATTERN
In this section we present the use of the Urban
Mobile GIS Base Analysis Pattern in the conceptual
modeling of the Pocket-GIS’s database, which is a
Mobile GIS application for recording Property
Cadastre Bulletins – PCB (Martins et al., 2007).
AN ANALYSIS PATTERN FOR MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS TOWARD MUNICIPAL
URBAN ADMINISTRATION
315
Pocket-GIS was developed by Computer Science
Department of Federal University of Viçosa.
The Pocket-GIS system assists users in the data
collection for the Property Cadastre Bulletin, using
spatial data to improve the identification and
location of properties and the urban allotment within
the system.
Pocket-GIS’s development was done in two
steps. In the first, requirements and use-case
identifications was accomplished. In the second step,
the Pocket-GIS was codified.
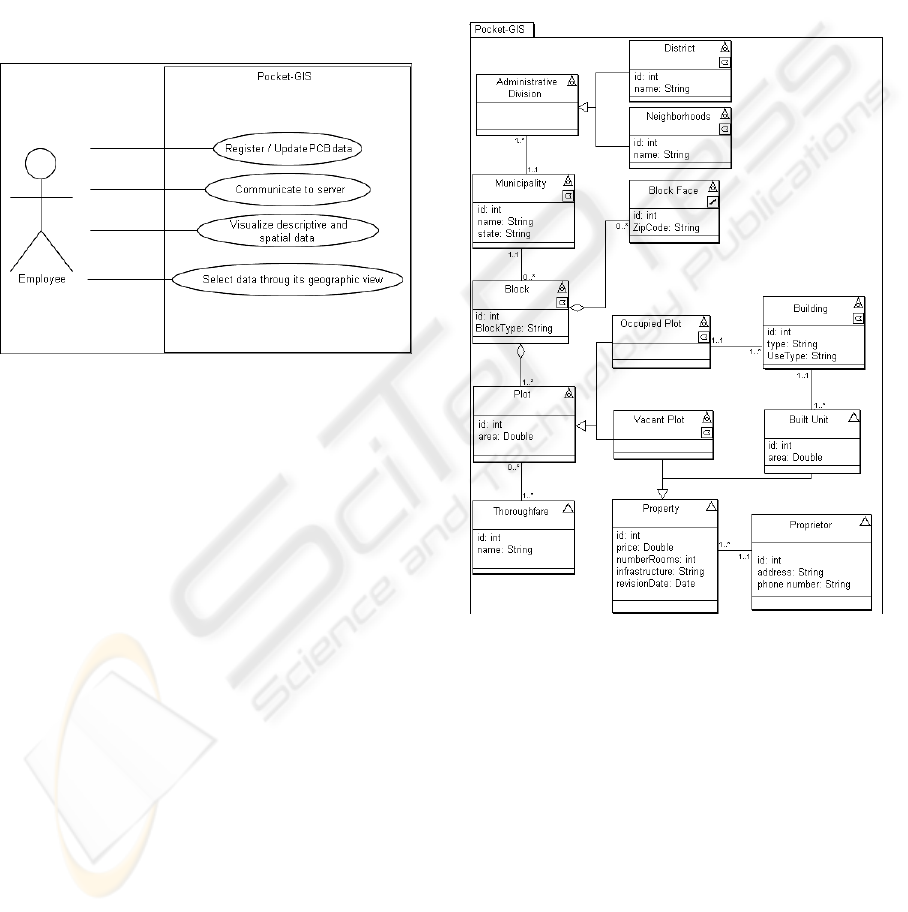
Figure 5 shows the UML use case diagram.
Figure 5: Pocket-GIS Use cases.
The systems’ actor is an employee responsible
for obtaining the PCB’s data in field. The use cases
identified were:
• Register / Update PCB data
• Communicate to server
• Visualize descriptive and spatial data
• Select data through its geographic view
The “Register / Update PCB data” use case allows
user to accomplish inclusions and updates to the
PCB data onsite. The data are temporarily stored on
a PDA (Digital Personal Assistant) for later server
update.
Server communication allows actor to download
data to the client PDA, and it allows uploading data
to the server. While downloading data to the PDA,
the user can select which data he wishes, in other
words, he can select which spatial data themes and
descriptive data he wants.
The “Visualize descriptive and spatial data” use
case allows user to visualize geo-spatial data (Rio
Branco-AC City maps) and non-geographic data.
The descriptive data visualization was made from an
interaction with other system, called Cupuaçu.
Cupuaçu is the first system made through a
partnership between the Computer Science
department of Federal University of Viçosa and City
Hall of Rio Branco-AC. This system aims to help
the collection of the PCB descriptive data process
using mobile devices as PDAs.
This use case is closely related to “Select data
through its geographic view” use case, which allows
selecting objects through its spatial representation.
The data conceptual modeling was done by
reusing the proposed analysis pattern. Figure 6
illustrates the resulting data conceptual schema.
Next, each class is briefly described.
Figure 6: Conceptual scheme of Pocket-GIS.
- The Municipality class has spatial
representation in the form of a polygon and consists
of one or more Administrative Divisions, which are
specialized in Neighborhood and District classes,
both represented in the form of polygons.
- Each Administrative Division is related with
the several Blocks, as well as a same Block can be
related with several Administrative Divisions.
- Each Block is formed by several Block Faces.
These block faces are the lines that form the
polygon.
- One or more Plots form a Block.
- Thoroughfare is modeled as a non-geographic
object, since only the thoroughfare name is
important for the application.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
316
- Each Plot, in its turn, is specialized in Occupied
Plot or Vacant Plot.
- An Occupied Plot can have one or more
Buildings, which are represented by polygons. A
Building, in its turn, is in a single Occupied Plot.
- A Building has a one-to-many relationship with
the class Built Unit, which has no spatial
representation.
- The classes Built Unit and Vacant Plot are
generalized for the class Property, which represents
the entity without geographic representation that will
store the data related to PCB.
- Last of all, a Proprietor (owner) who does not
have geographic representation may have one or
several Properties.
The spatial relationships corresponding to Step-
Four of the UML-GeoFrame method were not
modeled. Only the semantic relationships were
considered for modeling this system. As for
temporality (step 5), Pocket-GIS has no temporal
characteristic.
Pocket-GIS was developed to operate in PDAs
that run the Microsoft Windows CE 4.x operational
system or above. The mobile device used was a
PDA, Jornada HP 220 Pocket PC, 64 MB memory,
400 MHz processor.
The system was developed in C# language. The
library used for spatial data visualization was the
Map Suite Pocket PC® (Evaluation Edition). The
database used in the server was the SQL Server
2000, with SQL Server CE in the client side. All the
communication between the client and the server
was carried out via Web Services.
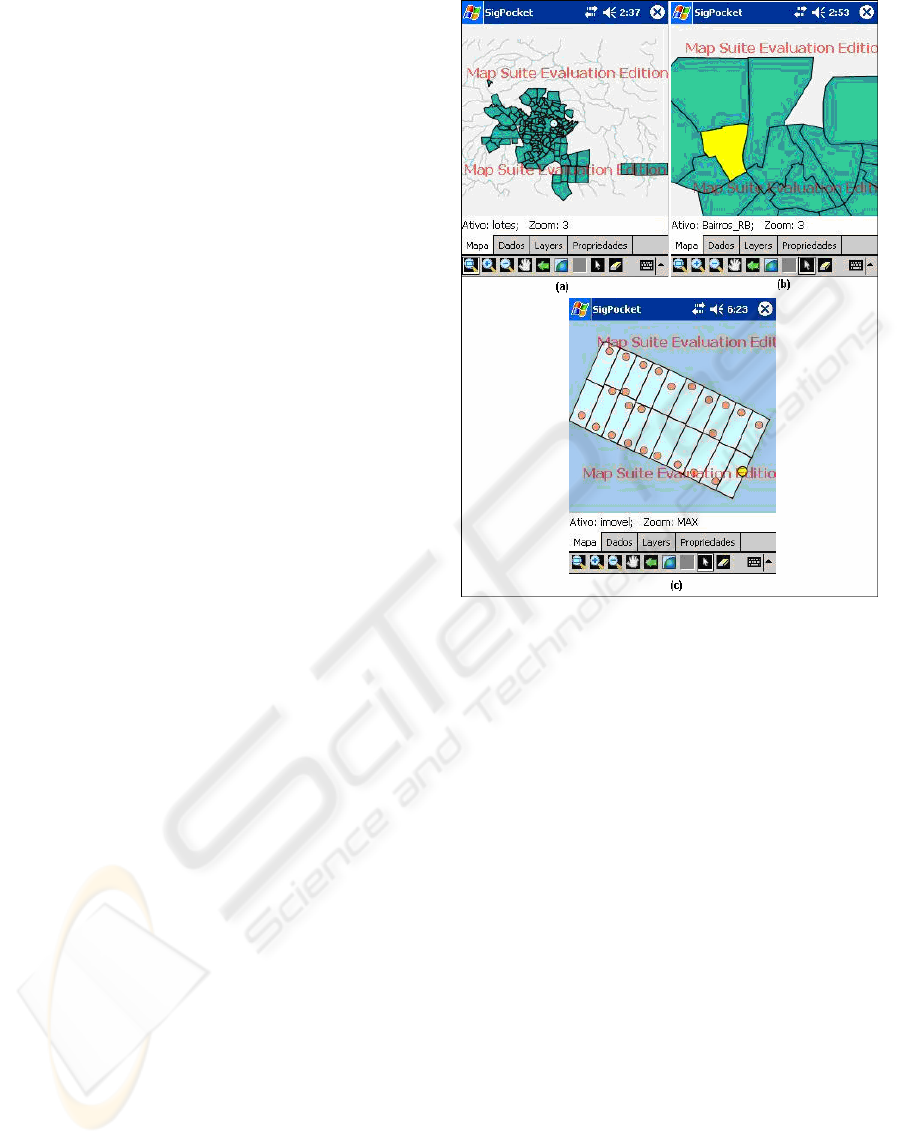
Figure 7 shows (a) the main system interface, (b)
the feature selection screen and (c) the Property
layer.
The interface screen basically contains: a map
display area; tabbed browsing, which allows the
visualization of some properties and functionalities
of the system; and a toolbar for handling maps.
The Pocket-GIS main functions are:
- Map display in the shapefile format;
- Map browsing: to zoom in and out of the map,
move the map and view browsing history;
- Choice of zoom level, allowing more zoom in
and out of the map, for greater or less map
detailing;
- Management of active layers;
- Display of descriptive data associated with the
shapefile.
Figure 7: (a) Pocket-GIS Main Interface, (b) Process of
neighborhood selection (c) Properties layer.
Finally, some of these functionalities were
implemented to attempt to minimize the limitations
existing in mobile devices. The possibility of
managing layers that will be viewed avoids the
unnecessary computation in the layer drawing
process in the PDA screen. The zoom level choice
provides fast viewing of searched information to the
user.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Mobile GIS applications focused on urban
administration have a great potential for reusing
solutions. The proposed analysis pattern can be used
in assisting in the development of many applications
for the most varied areas that form a municipal
public administration.
The development of the Pocket-GIS system
made it possible to test the use of the analysis
pattern, partly or fully. The use of the analysis
pattern reduces the time for the data conceptual
modeling, assisting designers by indicating a
AN ANALYSIS PATTERN FOR MOBILE GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS TOWARD MUNICIPAL
URBAN ADMINISTRATION
317

possible solution in the identification of the kinds of
data necessary to the application.
Other applications using the pattern should be
developed to allow pattern refinement and
enhancement, thus making it possible to test its
usefulness in actual applications.
The definition of an analysis pattern for non-
urban areas of a municipality is also suggested for
further research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project was partially supported by the Minas
Gerais State Foundation for Research Support
(FAPEMIG), the National Council for Scientific and
Technological Development (CNPq) and the
Coordination for Improvement of Personnel of
Superior Level (CAPES).
REFERENCES
ARGOUML – Disponível em <http://argouml.tigris.org/>.
Acesso em: dezembro, 2007.
DETRAN/DF – Conceitos e Definições Básicas. 1989.
Disponível em <http://www.detran.df.gov.br/sites/
200/240/00000020.pdf> Acesso em: agosto, 2007. (in
Portuguese)
Dietrich, S. W.; Urban, S. D. An Advanced Course in
Database Systems: Beyond Relational Databases.
Arizona: Prentice Hall, 2005.
FGV. Instrução Básica de Estatística de Trânsito. 2001.
Disponível em: <http://www.denatran.gov.br/
publicacoes/show_public.asp?cod=9> Acesso em:
agosto, 2007. (in Portuguese).
Fowler, M. Analysis Patterns: Reusable Object Models.
Menlo Park, CA: Addison Wesley Longman, 1997.
Lisboa Filho, J.; Iochpe, C.; Borges, K. A. Analysis
patterns for GIS data schema reuse on urban
management applications. CLEI Electronic Journal,
v.5, n.2, p.1-15, 2002.
Lisboa Filho, J., Sodré, V.F., Daltio, J., Rodrigues, M.F.,
Vilela, V. (2004) A CASE tool for geographic
database design supporting analysis patterns. Proc.
Conceptual Modelling for GIS, ER2004. LNCS 3289.
Lisboa Filho, J.; Iochpe, C. Modeling with a UML profile.
In: Shashi Shekhar and Hui Xiong. Encyclopaedia of
GIS. Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2008.
Maguire, D. Mobile geographic services come of age:
ESRI Drives into Wireless Markets. Geoinformatics,
n.4, 2001.
Martins, W. S.; Monteiro, B. R.; Lisboa Filho, J.;
ROCHA, M. N. Um SIG Móvel para Aplicações de
Gestão Urbana. REIC - Revista Eletrônica de Iniciação
Científica, 2007. (in Portuguese)
Meszaros, G. Doble, J. A pattern language for pattern
writing. Disponível em: < http://www.hillside.net/
patterns/writing/patternwritingpaper.htm> Acesso em:
outubro de 2007.
Monteiro, B. R. Aplicações de Sistemas de Informações
Geográficas Móveis: um estudo voltado para
iniciativas de governo eletrônico na administração
pública municipal. 2007. 106f. Dissertação (Mestrado
em Ciência da Computação) – Universidade Federal
de Viçosa, Viçosa, MG, 2007. (in Portuguese)
Tsou, M. Integrated Mobile GIS and Wireless Internet
Map Servers for Environmental Monitoring and
Management. Cartography and Geography
Information Science, v. 31, n. 3, p. 153-165, 2004.
Xiaoqing, Z.; Qingquan, L. The Deliver and Visualization
of Geospatial Information in Mobile GIS. In:
WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, NETORKING
AND MOBILE COMPUTING CONFERENCE, 1st,
2005, Wuhan, China. Proceedings…Wuhan: IEEE,
2005, v. 2, p. 1348-1351.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
318
