STUDY ON IP TRACEBACK SYSTEM FOR DDOS
Cheol-Joo Chae
1
, Bong-Han Kim
2
and Jae-Kwang Lee
1
1
Dept. of Computer Engineering, Hannam University, Korea
2
Dept. of Computer & Information Engineering, Chongju University, Korea
Keywords: IP traceback, DDoS, security system, iTrace.
Abstract: The rapid growth in technology has caused misuse of the Internet like cyber Crime. There are several
vulnerabilities in current firewall and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) of the Network Computing
resources. Automatic real time station chase techniques can track the internet invader and reduce the
probability of hacking Due to the recent trends the station chase technique has become inevitable. In this
paper, we design and implement IP traceback system. In this design no need to modify the router structure
and we can deploy this technique in larger network. Our Implementation shows that IP traceback system is
safe to deploy and protect data in Internet from hackers and others.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to rapidly developed IT technology, internet
based technologies are increasing these days. On the
other hand, the side effects such as hacking, virus,
and message fake also have been increased too. In
order to respond these side effects, security systems
such as firewall and IDS (intrusion detection system)
have been developed and utilized. Nevertheless,
these systems can not protect enough from the
internet attacks since to the systems are passive, and
hacking accidents are continuously increasing.
Therefore, it is necessary to study for reducing
hacking accidents by applying the automatic real
time chasing which can trace the intentional internet
invaders. To solve the problem, the active security
system utilizing IP traceback technology is proposed
in this paper.
To trace and isolate the network invader based
on the active security system, the security
mechanism was established by implementing ICMP
(internet control message protocol) type traceback
message for IP traceback, and designing the agent
put in local area network and the server framework
put in management network were implemented.
In this paper, we design and implement IP
traceback system using iTrace message for response
attacker. Section 2 give proposed IP traceback
system architecture. Section 3 give implement of IP
traceback system using iTrace message. The paper
concludes with section 4.
2 PROPOSED IP TRACEBACK
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
2.1 IP Traceback System
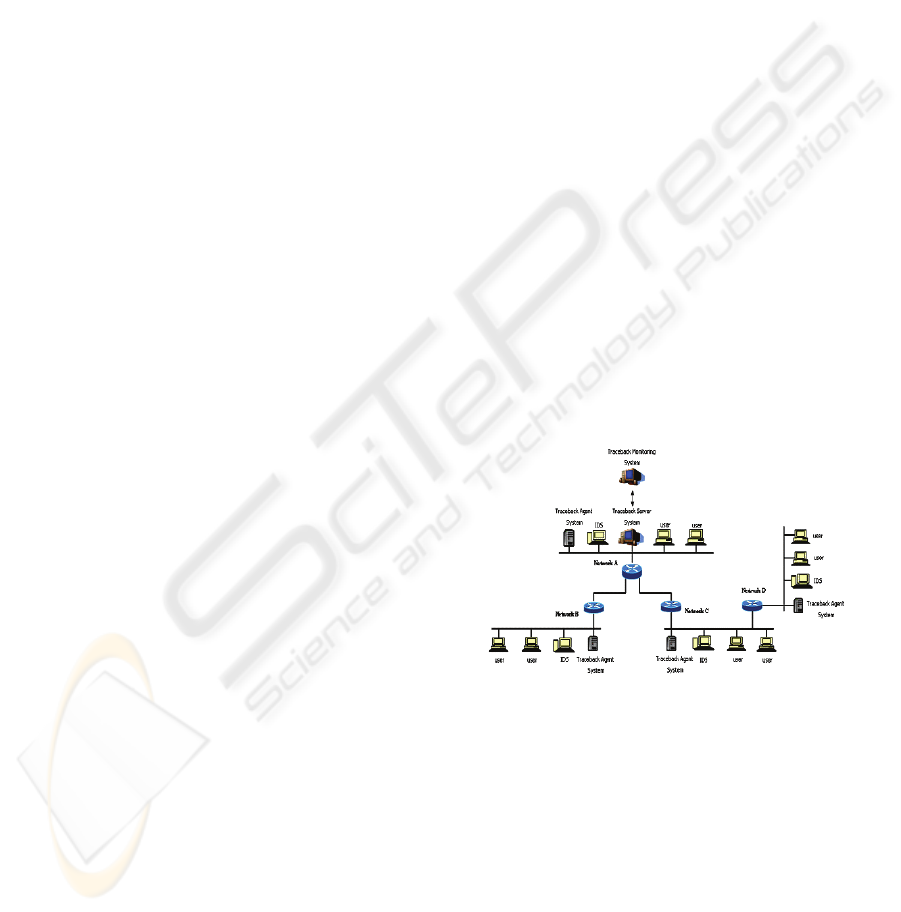
Figure 1: Proposed IP Traceback System Architecture.
Proposed IP Traceback system creates iTrace
message and send it to the destination system.
Destination system analyzes the iTrace message for
an attack. If attack is detected, Destination system
collects relevant information. Then, the destination
system can traceback attacker using collected
relevant information. I-Trace System contains agent
system and sever system. Agent system creates
iTrace Message and sends to server system. Also,
agent system report if abnormal traffic phenomenon
happens, it watches relevant IP, and detects system
problem, in case of problem occurrence the
279
Chae C., Kim B. and Lee J. (2008).
STUDY ON IP TRACEBACK SYSTEM FOR DDoS.
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 279-282
DOI: 10.5220/0001702102790282
Copyright
c
SciTePress
information of relevant system and its Source IP is
provided to the server system.
2.2 Proposed Agent System
Figure 2 shows proposed Agent system. Agent
systems are installed in router. Router develops
authentication host DB at local domain. Router also
creates decision router packet using authentication
hosts DB. On the other hand, non-authentication
hosts are stored in non-authentication hosts DB if
hosts source address is not valid or if it causes a
quick surge in traffic. This non-authentication host is
candidate attacker and cannot forward route packet
anymore. If authentication host sends packet, iTrace
message is generated with a low probability of about
1/20000.
Figure 2: Proposed Agent System.
Agent and Server system share secret key(k) for
the Attacker’s iTrace Message. Server system create
secret Key(k) and send to Agent system. Then Agent
system send iTrce Message and hash-value using
secret key(k) to Server system. Server system check
the iTrace Message and hash-value using secret
key(k). Figure 3 shows iTrace Message create
module.
Figure 3: iTrace Message create Module.
2.3 Proposed Server System
Server system monitors entire network by installing
many Agent system. Server system monitors entire
networks status in real time. If Server system reports
attack from IDS, then traceback commences using
iTrace message. Figure 4 shows proposed Server
System.
Figure 4: Proposed Server System.
If receive intrusion information in Intrusion
Detection System(IDS), server system relevant
packet discard and send a iTrace Message creation
direction. Server system’s authentication verifies
iTrace Message
Figure 5: Validate iTrace Message using secrete key.
First, create secret key K
n
to share with each
Agents in secret key creation module of Server.
Server stores secret key K
n
that create to secret key
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
280
DB and is shared with each Agents. After intrusion
occurrence, iTrace Message's validation test that
receive from agent uses secret key K
n
that before
exchange. Figure 5 shows when attacker transmits
fake iTrace Message to server through Agent 2. But,
server is discard fake iTrace Message that attacker
sends creating hash value using secret key K
2
that
exchange with Agent 2.
3 PROPOSED IP TRACEBACK
SYSTEM
System is developed to be accommodated in any
current network configuration. Agent system creates
iTrace message and then send it to Server system.
As, It is very difficult to load the programming
module into router, we use Agent system to analyze
incoming/outgoing packet in router. Agent system is
developed by using RedHat 9, kernel version
2.6.12.5. And we use C language, gcc egcs-2.91.66
as complier. Although we use Linux system, it can
also be module by embedded program. And this
module is then included into router.
Agent system linked to each router analyzes the
packet coming from Server system for a predefined
attack type. Packets that agree with relevant attack
type are termed as attack packet. Traceback
information stored in DB sorts and identifies victim
IP and make a traceback within group by using time
stamp.
3.1 Agent System
Packet collection that is being followed in network
has critical value that administrator establishes in
agent system, and transmit packet header
information in iTrace message creation module.
Figure 6 shows image that establish critical value in
agent system.
Figure 6: Implement of Agent System.
3.2 Server System
As following figure 7, Server System control entire
network and local network traffic. And if received
intrusion information from Intrusion Detection
System(IDS), Server system validate iTrace
Message using secrete key.
Figure 7: Implement of Server System.
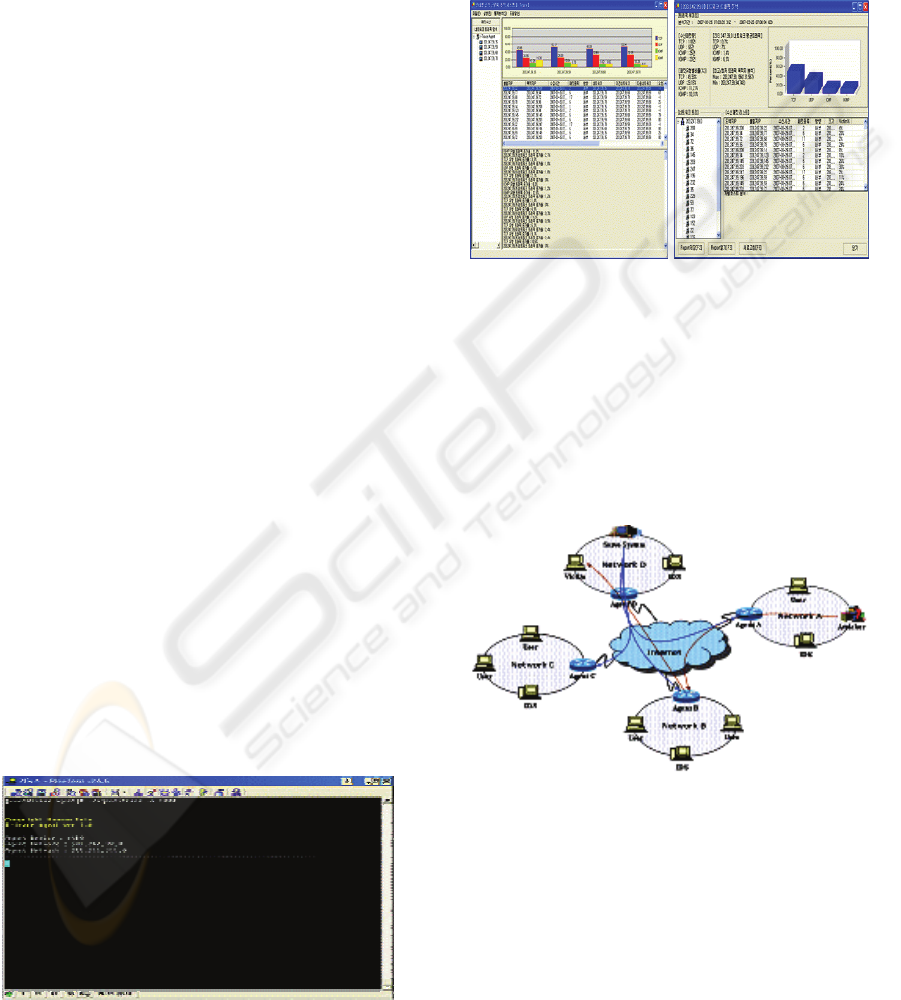
3.3 Attack Path Reconfiguration
Then, continuously keep track of router(Agent)
address, traceback node through which packet flow
within each group. This process in each network
repeatedly reconfigures attack path. Figure 8 shows
the attack path and way of traceback.
Figure 8: Implement of Server System.
Step 1. Attacker who belong to Network A
attempts to attack the victim system belong to
Network D.
Step 2. Intrusion Detection System present in
Agent detects attack and report it to Server
system.
Step 3. Server system identifies and notifies the
attack on I-Trace Agent system linked to each
router.
STUDY ON IP TRACEBACK SYSTEM FOR DDoS
281

Step 4. Server system denies the flow of packets
that are forwarded to victim system.
Step 5. Server System analyzes traceback packet
included in iTrace message that are received
from Agent system and begin traceback. First,
Server system check validate of iTrace Message
using secrete key(k
n
)
Step 6. Server system chose iTrace that have
maximum Timestamp. And Server system store
RouterID, Backward Link, Forward Link.
Step 7. Find iTrace Message that have Forward
connect to Forward Link and establish traceback
path.
Step 8. Repeate step 6, step 7 until do not
connect to iTrace Message.
Step 9. Server System make complete traceback
path. Traceback attack source.
Figure 9 shows result of IP traceback. In figure
10, we sure do not cause much traffic than PPM
packet of basis by way that transmit creating iTrace
Message about something wrong packet, and also do
not create traffic that iTrace Message can bear to
whole network.
[ 공격 근원지 탐색정보]
Source1 IP : 203.247.47.65
Source2 IP : 203.247.47.66
Source3 IP : 203.247.47.67
Source4 IP : 203.247.47.68
Source5 IP : 203.247.47.69
Network : 203.247.47.0
Attack Type1 : TCP SYN flood
Attack Type2 : TCP SYN flood
Attack Type3 : TCP SYN flood
Total Attack Traffic : 356,446/s
[ 공격 근원지 탐색정보]
Source1 IP : 203.247.47.65
Source2 IP : 203.247.47.66
Source3 IP : 203.247.47.67
Source4 IP : 203.247.47.68
Source5 IP : 203.247.47.69
Network : 203.247.47.0
Attack Type1 : TCP SYN flood
Attack Type2 : TCP SYN flood
Attack Type3 : TCP SYN flood
Total Attack Traffic : 356,446/s
[ 공격 피해 시스템 정보]
Victim IP : 211.101.95.59
Attack Type : TCP SYN f lood
Network : 211.101.95.0
Attack Time(term) : 01:00.18
Total Attack Traffic : 356,446/s
[ 공격 피해 시스템 정보]
Victim IP : 211.101.95.59
Attack Type : TCP SYN f lood
Network : 211.101.95.0
Attack Time(term) : 01:00.18
Total Attack Traffic : 356,446/s
Figure 9: IP Traceback analyzes Attacker and Victim.
Figure 10: Analysis packet traffic.
4 CONCLUSIONS
IP Traceback is an important technique to traceback
attack source address. Many techniques have been
proposed but all these techniques have a problem
when applied in internet environment. As, it is not
easy to load programming module into router, we
use linux system as the administrator can access
linux router. We design and implement IP Traceback
system that uses iTrace message, which can be
applied in internet environment. We use
authentication/non-authentication host DB for
protecting network hosts from attacker and also due
fall in traffic rate. We use iTrace message (draft-ietf-
itrace-04) that is undergoing advancement due to
iTrace message’s standardization. Future work is to
concentrate on how to implement IP Traceback
system in ubiquitous environment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the MKE(Ministry
of Knowledge Economy), Korea, under the ITRC
(Information Technology Research Center) support
program supervised by the IITA(Institute of
Information Technology Assessment) (IITA-2008-
C1090-0801-0027)".
REFERENCES
Chun He, Formal Specifications of Traceback Marking
Protocols, June 14, 2002.
Steve Bellovin et al, ICMP Traceback messages, IETF
Internet Draft draft-ietf-itrace-04.txt, Feb 2003.
D. X. Song, A. Perrig, Advanced and Authenticated
Marking Scheme for IP Traceback, Proc. Infocom
Vol2, pp 878-886, 2001.
S. Savage, D. Wetherall, A. karlin, and T. Anderson,
Network Support for IPTraceback, IEEE/ACM
transactions on networking, vol. 9, No. 3, June 2001.
K. Park and H. Lee, On the effectiveness of probabilistic
packet marking for IP traceback under denial of
service attack, Proc. IEEE INFOCOM 01 pp 338-347,
2001.
Stefan Savage et al, Practical network support for IP
traceback, ACM SIGCOMM 2000.
A.C Snoeren, C. Partride, L.A. Sanchez, W.T. Strayer.
C.E. Jones. F. Tchakountio, and S.T. Kent, Hash-
Based IP Traceback, BBN Technical Memorandum
No.1284, February 7, 2001.
Tatsuya Baba, Shigeyuki Matsuda, Tracing Network
Attacks to Their Sources, IEEE Internet Computing,
pp. 20-26, March, 2002.
ICEIS 2008 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
282
