
USING A COMPLEX NUMERICAL AND MULTIMEDIA
DATABASE IN INTERNAL MEDICINE
Pre-release Evaluations
Liana Stanescu, Dumitru Burdescu, Cosmin Stoica-Spahiu, Anca Ion
University of Craiova, Faculty of Automation, Computers and Electronics, Romania
Dorin Stanescu
S. C. EDA SOFT, Craiova, Romania
Keywords: Medical application, medical images, color and texture features, content-based image query.
Abstract: The paper presents a software tool implemented using Firebird and Delphi technologies, dedicated for
managing and querying medical multimedia databases. The database contains images related to the internal
medicine area. This on-line application allows creation of complex medical files of patients that can be
viewed and updated both by internist and general practitioner. The main functions of the application are:
managing patients contact information, examinations, imagery and personal folders; simple text based
query; content based query using color characteristic for images provided by medical devices. It can be used
in individual offices, laboratories or in the hospital clinics and departments. The application provides
security and confidentiality for patient’s data.
1 INTRODUCTION
Internal medicine is an important component of the
general medicine that can be regarded as basics for
many specialties: cardiology, pneumology,
gastroenterology, nephrology, haematology,
rheumatology, etc. It needs large amounts of
paraclinical exploration performed by different
devices that generates visual and numerical data
used for diagnosis and for follow-up of treatment or
evolution. Numerical information is given by
functional and biological assays while various
imagistic devices provide image data. In his reports,
the doctor is making qualitative descriptions of
abnormalities he found and elaborates reports that
will be forwarded to the patients or to his colleagues
from other departments. That is why internal
medicine departments usually accumulate huge
quantities of medical data, including thousands of
image files, millions of numerical values and
thousands of written reports.
Because most of the patients in these services are
chronically ill patients, with frequent visits and
frequent use ambulatory services, the rapid access to
an archive containing both numerical and imagistic
data would be an advantage. More than that, because
access to high tech medical services is quite limited
in some countries, many patients are frequently
investigated in geographically dispersed medical
centres. By using a dedicated application, the local
doctor will be able to check simultaneously all the
investigations and to give a diagnosis. Thus, he can
integrate better all diagnostic data, manage the visits
or the therapy taking into account all the
concomitant pathology, or send the patient to
another department for other investigations. As
consequence, other specialists are able to see
information from local or regional database and can
query the archives.
These are some reasons for creating a complex
application for managing and querying a database
containing information and images from medical
domain. Our database is implemented in Firebird
(Interbase) that is a free and modern database
management systems (Interbase, 2006).
The application is implemented using Delphi
programming language that has important facilities
for database management (Kermann, 2001). It can
192
Stanescu L., Burdescu D., Stoica-Spahiu C., Ion A. and Stanescu D. (2008).
USING A COMPLEX NUMERICAL AND MULTIMEDIA DATABASE IN INTERNAL MEDICINE - Pre-release Evaluations.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 192-195
Copyright
c
SciTePress

be used on-line, so the users have access from
distance.
Besides managing patient information, including
their consultations, the application has the possibility
for managing and viewing the images provided by
medical devices.
An element of originality is content-based visual
query using color characteristic. It permits selection
of a query image and finding all similar images from
the database (Del Bimbo, 2001; Smith, 1997). This
option could be very helpful for establishing the
diagnosis.
2 THE DATABASE STRUCTURE
In this section, database structure used by the
application including tables and logical connections
between them is presented in detail. The database
contains a number of tables populated when
installing the application. The tables contain a series
of codes that makes easier the work of updating
patient information and the investigations. These
tables are:
- Medical units with a specific code and name:
the medical units can be an individual office, a
laboratory or hospital clinics and departments.
- Users groups: this table stores information
about user groups, administration rights for
each group (administrators, doctors, nurses
etc.). The table also contains a group identifier
and a group name that can be specified for each
group. Each unit has specific management
rights.
- Users: is a table that contains user
identification, name, password, and
corresponding group.
The data confidentiality is ensured by user name
and password that are provided separately for each
unit. In order to increase the data security, the
password is encrypted. Each doctor has access to
information regarding his own patients, but he can
share some data that can be seen by other specialists.
He can also access both statistical and scientific data
regarding all patients in database but in this case the
identification data about patients is hidden and the
ID number, name and address are blinded. At
information management level, anonimizing all
information concerning clinical data ensures
confidentiality; diagnosis, paraclinical information,
treatments are also blinded and only statistical data
can be viewed. On the other hand, the office
secretary can see personal information about patients
and referring doctors, but no diagnosis and treatment
elements are accessible.
- Diagnosis table is used for storing the diagnosis
code and name.
- Analyses table codifies paraclinical and
biological data. It has the following structure:
code, description, and minimal and maximal
value.
- Clinical examination table includes the
following elements: code, description, and
value.
- Patient groups include code and description.
The patients can be grouped by the category of
disease (digestive, cardiology, renal etc.), by
the medical insurance category or by
participation to different programs (national
health programs or clinical studies).
The following tables are the most important in
the database because they store information about
patients, examinations, investigations and results:
- Patients table is used for storing information
about patient’s visits: personal ID number,
name, doctor, county, city, address, phone/fax
number, email and program – if any.
- A patient might have several examinations, for
each of them storing in the Consulting table,
the diagnosis, date and treatment. Each
examination might contain one or several
clinical examinations (it is stored code,
description, a series of analyses identified by
code and obtained value).
- Images table is storing information about still
or moving images, obtained from a patient
during his whole disease history. These data
are: path and name of the image file, type of
image and color information automatically
extracted for later content-based image query
on color feature.
3 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE
APPLICATIONS
3.1 Set-up
This function permits updating auxiliary tables in
database as for example tables containing diagnosis
codifications, clinical examinations, analyses
codifications, departments, user groups and users.
USING A COMPLEX NUMERICAL AND MULTIMEDIA DATABASE IN INTERNAL MEDICINE - Pre-release
Evaluations
193

3.2 Patients Information Management
This function is one of the main functions in the
application, and the information about patients has
the following organization:
a) Contact information (personal ID number,
name, address, phone, fax, email, category and
National License Number of the examining doctor).
b) Examinations
The management of this information is
implemented in a window that contains several
secondary windows, as seen in figure 1. The first
secondary window contains a record for each patient
examination with the following information:
examination date, diagnosis and results of the visit
(solved/unsolved). This window is associated with
four secondary ones, having the following functions:
1. Collecting data from clinical examination. For
each analyzed system or segment the user can
specify if he found normal or abnormal relations.
A short description of the found abnormalities
can also be added.
2. Collecting numerical data from laboratories
and adding other information about important
data.
3. Storing, as descriptive text, the results of
various investigations: radiological, echography,
endoscopy descriptions.
4. Storing treatment recommendations and
prescriptions resulting from diagnosis.
Data from each secondary window can be easily
updated using coding tables that were created in the
set-up phase. The solution with secondary windows
was chosen because the doctor should have an
instant and easy access to the whole evaluation of
the patient from one examination to another.
c) Imagery
This option gives access to all the functions of
the application referring to the imagistic data
concerning a patient, images provided by different
devices (echograph, endoscope, MRI, CT, etc).
These images can be loaded from saved files or can
be imported directly from medical devices using a
real time acquisition system. The system can be
launched directly from this window. Imported
images will be saved directly in the patient folder. It
is possible to see the images directly, or to select one
as a query image and to execute a content-based
image query for the whole database to search similar
images.
Figure 1: Window for managing patient examination data.
3.3 Database Query
It is one of the most important functions of the
application. There are two types of queries: text-
based query and content-based image query on color
feature.
In the first case there are several search criteria
that might be composed using “and”. These criteria
are: patient name, personal numerical number,
address, clinical exam and analyses. For the first
three criteria it is used the “LIKE pattern’’ operator.
Using this operator the Select command permits
searching a string in all the values existing in
database. For the last criteria, where information is
codified in the database, the user can display a list of
options to select one for search. Some useful queries
that can be used are: list all the patients with a
specified diagnosis, or list of all the patients that
undergone a certain investigation or examination.
Visual data needs more evolved access methods.
Such a method is content-based retrieval, which
takes into consideration attributes or characteristics
extracted from multimedia information. If we take
into consideration the images, the technique is called
content-based visual retrieval (Del Bimbo, 2001;
Smith, 1997). This type of query implies selecting
an image as query image, and finding all the images
in database that are similar with it.
The medical areas where content-based visual
queries methods can bring advantages are well
known (Müller et al, 2004; Lehmann et al, 2004;
Shyu et al, 1999):
• Diagnostic aid
• Medical teaching
• Medical research
• Electronic patient records
HEALTHINF 2008 - International Conference on Health Informatics
194
The reasons presented above generate the need
to implement in the application the content-based
visual query methods using color characteristic.
The color is the visual feature that is immediately
perceived on an image. The color space used for
representing color information in an image has a
great importance in content-based image query, so
this direction of research was intensely studied (Del
Bimbo, 2001).
There is no color system that it is universal used,
because the notion of color can be modelled and
interpreted in different ways (Gevers, 2004).
It was proved that the HSV color system has the
following properties: it is close to the human
perception of colors; it is intuitive; it is invariant to
illumination intensity and camera direction;
The operation of color system quantization is
needed in order to reduce the number of colors used
in content-based visual query: from millions to tens.
The quantization of the HSV color space to 166
colors, solution proposed by J.R. Smith, is the idea
used in this application (Smith, 1997).
The intersection of the histograms is used for
computing the similitude between the query image Q
and the target image T for color feature (Smith,
1997):
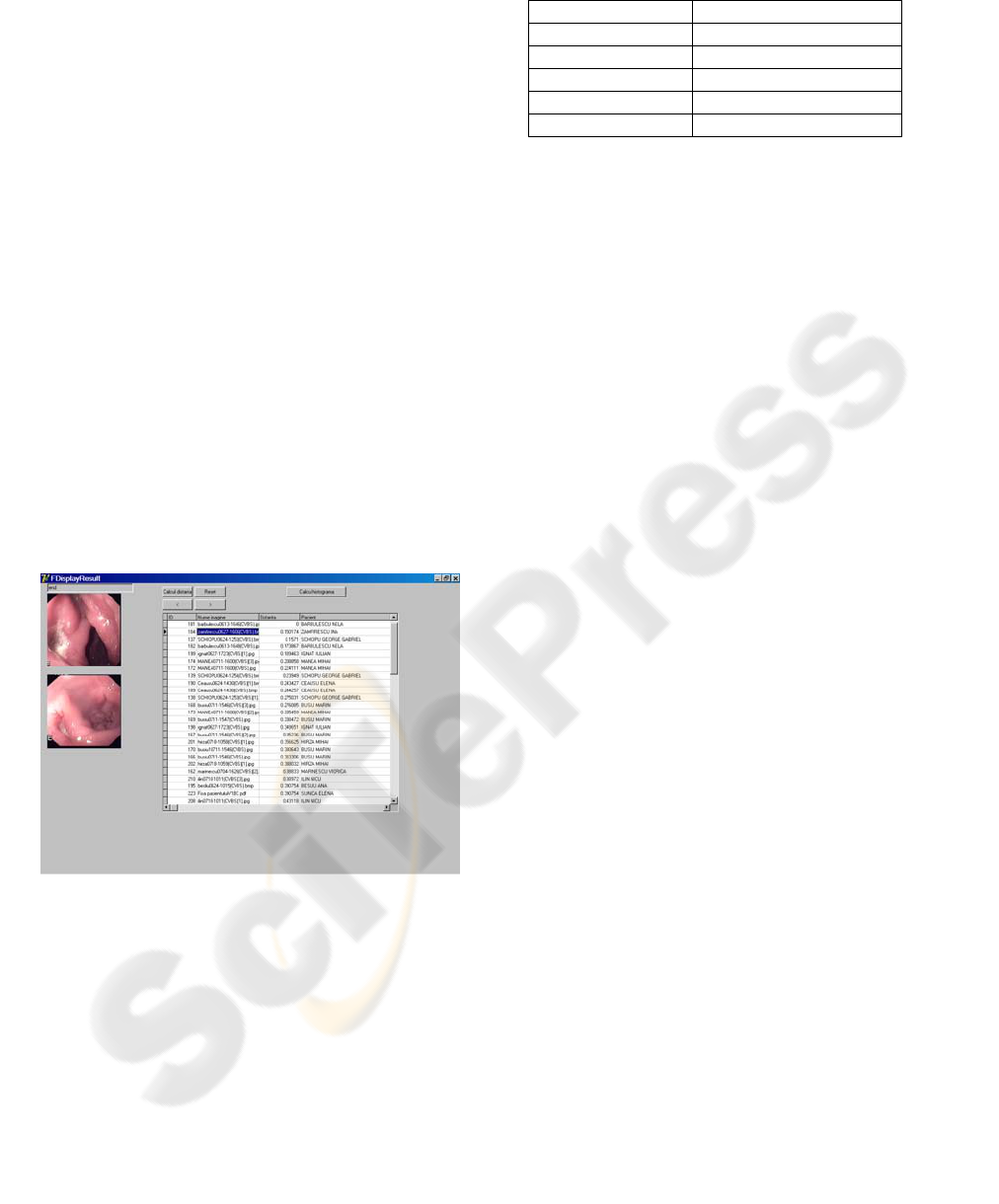
Figure 2: Window for content-based visual query.
The results of the experiments performed on a
database with 960 images from the field of the
digestive area are summarized in table 1.
The values in the table represent the number of
relevant images in the first 5 retrieved images. For
these five types of images (each type representing
one diagnosis) the results are encouraging, but the
experiments must be performed on a larger imagistic
database and taking into account more types of color
images. Only this way the conclusions can be
reliable.
Table 1: Content-based image query experimental results.
Quer
y
N
r. of retrieved ima
g
es
Pol
y
ps 3
Colitis 4
Ulce
r
3
Ulcerous Tumo
r
3
Esophagitis 4
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The paper presents the design of a Firebird database,
containing medical alphanumerical and imagistic
information. The application is implemented in
Delphi and can be accessed on-line. The main
functions of the application are:
- Managing information about patients: contact
information, visits, imagistic recordings,
laboratory results, treatment
- Simple text based query that might combine
several criteria
- Content-based visual query using color
characteristic.
- Generates complete or synthetic reports
REFERENCES
Interbase Documentation,
http://info.borland.com/techpubs/interbase/ , 2006.
Kermann, M., 2001. Programming and Problem Solving
with Delphi, Addison-Wesley.
Del Bimbo, A., 2001. Visual Information Retrieval,
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. San Francisco USA.
Smith, J.R., 1997. Integrated Spatial and Feature Image
Systems: Retrieval, Compression and Analysis, Ph.D.
thesis, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences,
Columbia University.
Müller, H. et al., 2004. A review of content-based image
retrieval systems in medicine-clinical benefits and
future directions. International Journal of Medical
Informatics 73, 1-23.
Lehmann, T.M. et al., 2004. IRMA - Content-based Image
Retrieval in Medical Applications. Proceedings of the
14th World Congress on Medical Informatics, 842-
848.
Shyu, C. et al., 1999. ASSERT, A physician-in-the-loop
content-based image retrieval system for HRCT image
databases. Computer Vision and Image Understanding
75, 111-132.
Gevers, T., 2004. Image Search Engines: An Overview.
Emerging Topics in Computer Vision, Prentice Hall.
USING A COMPLEX NUMERICAL AND MULTIMEDIA DATABASE IN INTERNAL MEDICINE - Pre-release
Evaluations
195
