
INTEROPERABILITY IN PERVASIVE ENTERPRISE
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
A Double-Faced Coin between Security and Accessability
Dana Al Kukhun and Florence Sèdes
IRIT, Paul Sabatier University
Keywords: Pervasive Information Systems, Enterprise Information Systems, interoperability, accessibility, security.
Abstract: As transparency becomes a key requirement for assuring service quality and user satisfaction, Enterprise
Information Systems are seeking to become pervasive in order to deal with the heterogeneity problem of
their sub components. In this position paper, we expose the challenges that face Enterprise Information
Systems in achieving better data integration, representation and management, while ensuring homogeneous
interaction between different software sub components, improving the interaction between different
customers and business partners and providing services on different terminals with dynamic connectivity
constraints. Finally, we highlight the importance of applying adaptive, proactive and interoperable access
control policies that would differentiate between providing local system users with full data accessibility
and providing external users with multi-levelled security controls.
1 INTRODUCTION
The growing need of transparency in digital services
has promoted the notion of Pervasive Computing.
Pervasive or Ubiquitous Computing was first
introduced by Weiser as his vision for the computing
future in the 21st century, where computing
elements will disappear from user’s consciousness
while functioning homogeneously with his
environment (Weiser, 1999). In pervasive
computing, users can communicate and compute
with each others whenever, wherever and however
(Park et al., 2004).
Pervasive computing allows the coupling of the
physical world to the information world, and
provides a wealth of ubiquitous services and
applications that allow users, machines, data,
applications and physical spaces to interact
seamlessly with one another (Ranganathan et al.,
2005).
While analyzing pervasive computing and
studying it’s progression, it was found that for
hardware and computing elements to disappear,
software needs to disappear and the spatial temporal
relationships between people and objects has to be
well defined in the early design phase within
dynamic ubiquitous computing environments (Want,
2002).
In this section, we have presented a brief
introduction about pervasive computing. In the next
section, we’ll introduce our vision for Enterprise
Information Systems EIS as Pervasive Enterprise
Information Systems PEIS. In section 3, we present
the sub components of the proposed systems. Then,
in section 4, we will explore some important
requirements for PEISs. Finally, we present some
software technologies that help in implementing
interoperable PEISs and that would balance between
accessibility and security.
2 PERVASIVE ENTERPRISE
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Due to the revolution of Information Technology, a
new computing era is taking place. Many challenges
need to be met, especially in a mobile and dynamic
environment where users are interacting with
different devices and constructing ad hoc networks,
while systems are supposed to provide them with
proactive and value-added services.
As new technologies prove to be more
productive and efficient, public and private sectors
tend to employ online services in order to
accomplish different missions.
237
Al Kukhun D. and Sèdes F. (2007).
INTEROPERABILITY IN PERVASIVE ENTERPRISE INFORMATION SYSTEMS - A Double-Faced Coin between Security and Accessability.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 237-242
DOI: 10.5220/0002396502370242
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Technological progression is following an
exponential curve and is including different axes
such as: data, software, hardware and connectivity
(Al Kukhun et al., 2006). In current EISs, data
content and structure are highly dynamic and
heterogeneous. Thus, data integration is becoming a
challenging mission.
Hardware is advancing exponentially in storage
capacities, shrinking size and weight but these
advancements are affecting negatively the usability
and the Human Computer Interaction.
With ad hoc networking, connectivity has
become an easy mission but at the other side, it has
become a risky, dangerous and unreliable channel.
Finally, software has evolved and will always
continue to evolve in order to improve the
adaptability and proactivity of system functionalities
and thus ensure user satisfaction.
While studying pervasive systems, we found that
these systems are interactive systems that facilitate
the interaction of users with unfamiliar systems so
facilitating this interaction is highly recommended.
Pervasive environments should adapt with the
dynamic, changing and distributed computing
systems that extend the boundaries of physical
spaces, the building infrastructures and even the
devices contained within these environments.
Pervasive environments should be aware of the
context (Zimmermann et al., 2005) and should be
able to capture situational information in order to
integrate them with users and devices. The
interaction between these components should be as
transparent as possible and this transparency can be
applied using quality metrics along with run-time,
automatic adaptation for both content and context
starting from the early stage of design till late testing
and execution of the system.
3 THE COMPONENTS OF
PERVASIVE ENTERPRISE
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
In this section, we’ll analyse the different actors of
an EISs and expose the challenges that stand in the
face of a homogeneous interaction between the
different components and the user especially in a
real time processing environment.
3.1 Users
Users of an EIS might have different levels of
familiarity with the system (novice or professional
clients, novice professional users). In a pervasive
environment, users are not interacting to one
machine anymore; they are interacting with multiple
technologies, moving around non familiar,
untrustworthy environments. Users try to stay
focused while manipulating and relocating data
across devices while their access rights might be
changing over time (Duan et al., 2004).
A pervasive computing environment should be as
mobile as its users and should be able to adapt
according to the availability of its resources.
With the growing complication of technology
and multimodality, novice experts are facing
difficulties in using systems. Mean while, even
professionals are facing problems in their interaction
with pervasive systems and are demanding for more
adaptive and powerful interaction that would
increase the reliability of the system and would
enable them to work efficiently.
Multimodal interaction aims to break the barriers
between users and technology and to enable smooth,
spontaneous adaptive interaction so that users would
forget the fact that they are using computers.
We find that users are a changing and dynamic
element that has multidimensional evolutionary
needs but still limited capabilities, so our mission is
to gain user satisfaction that is highly demanded in
pervasive applications by taking in mind some
quality metrics such as usability, security and
adaptability in order to optimize user interaction in
pervasive environments.
3.2 Data
Data in pervasive environments come in different
forms and formats. In the age of multimedia it can
be a text, an image, a video stream, etc. So data is
heterogeneous in kind and also in source where it
could be located in different locations within
decentralized systems or coming from different
sources. That’s why we think that the most
important aspect in pervasive environments is the
accessibility, integrity and disposal of redundant and
useless data in order to assure the system’s
efficiency and transparency.
Easier access to relevant and valuable data
(information) is the final objective of using these
pervasive computing environments. In pervasive
environments, data is often generated dynamically,
in different formats, is streaming at high rates over
heterogeneous networks or devices and is dealt in
real time. As multimedia and multimodal interaction
is advancing, data is becoming of central
importance.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
238
Aiming achieve a PEIS, we need to unify,
integrate and structure different sourced data content
that comes from various data formats in order to
handle information in an easier way and to cope with
the heterogeneity.
3.3 Hardware
Hardware devices are the physical components of
pervasive environments and they are often different
COTS “Commercial of The Shelf” products that
have advanced networking capabilities such as
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Invisible embedded devices
and sensors are turning physical spaces into active,
smart surroundings making the space interactive and
adaptable (Munoz et al., 2005), (Campel, 2002).
Nowadays, a huge evolution in the computing
machinery performance has been achieved; this
progression affected positively ubiquitous
computing and has realized successful resource
usage and sharing between multiple users.
Many improvements took place and helped to
adapt with the mobility and dynamicity of pervasive
environments, specially the shrinking size and
weight of hardware devices; where users are moving
freely while handling their small, light devices that
are provided with high connectivity and wireless
networking capabilities (Campel, 2002).
Processing capabilities are increasing over time to
offer higher efficiency levels especially with the
development of storage capacities and the quality of
displays that help the user in forgetting the barriers
and allow him to acquire the underlying information
unconsciously without effort.
Hardware devices have entered a huge development
lifecycle but still have many limiting factors such as
the growing interaction complexity caused by the
machine size shrinkage and the increasing cognitive
overload due to the inadaptable interface design,
especially that a user could be a novice user who
needs a user-friendly environment or a professional
who needs a highly developed environment.
Pervasive EISs require devices that can be used
and integrated easily while balancing between
providing users with high security levels, total
privacy protection and high interoperability.
3.4 Software
Software is the logical component in pervasive
environments and it’s of central importance; it
enables the connection of users with different
heterogeneous devices by performing suitable
mappings between each task and the desired services
that users require (Chen et al., 2004).
To deal with dynamic devices, situations, users
and environments, the software should be highly
adaptable and flexible. The software of a pervasive
system integrates many devices and external
software systems in order to provide services that
meet user needs and assure the homogeneity and
collaboration between its components.
The use of XML was proposed to enhance the
flexibility, interoperability and integrity of systems
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
Internal data
Internal data
Interoperable
Interoperable
Access to data
Access to data
Full data accessibility
Full data accessibility
Secure data access
Secure data access
* Internal Enterprise structure : Homogeneous Components (data, software, hardware)
*** External Resources : Heterogeneous & dynamic components (data, software, hardware)
A
B
C
D
*
***
***
***
***
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
CAO
CAO
CAO
CAO
PDM
PDM
Internal data
Internal data
Interoperable
Interoperable
Access to data
Access to data
Full data accessibility
Full data accessibility
Secure data access
Secure data access
* Internal Enterprise structure : Homogeneous Components (data, software, hardware)
*** External Resources : Heterogeneous & dynamic components (data, software, hardware)
A
B
C
D
*
***
***
***
***
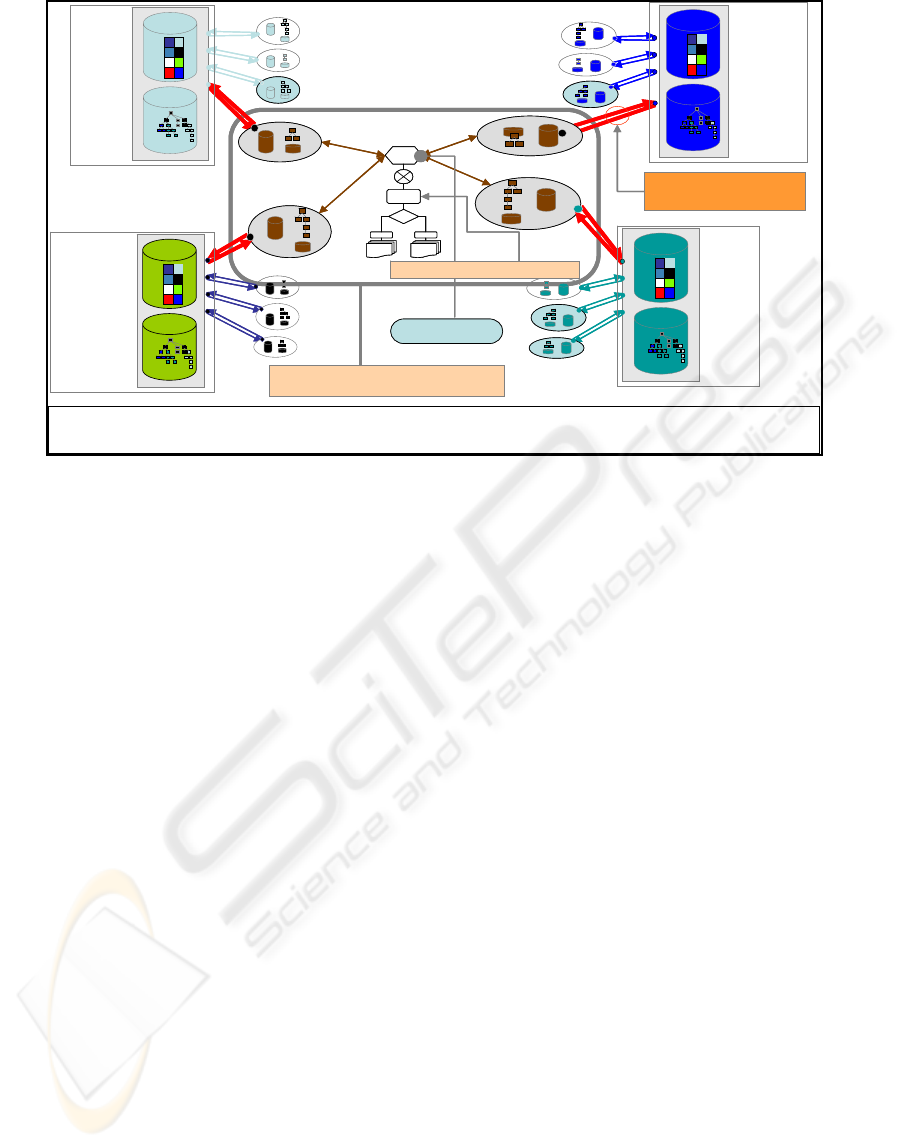
Figure 1: How to ensure interoperability in Pervasive Enterprise Information Systems.
INTEROPERABILITY IN PERVASIVE ENTERPRISE INFORMATION SYSTEMS - A Double-Faced Coin Between
Security And Accessability
239

by enabling adaptable mappings between a task and
it’s provided services (Chen et al., 2004).
Aiming for better specification and
implementation of productive pervasive systems
with no complexity, a domain specific language
Perv-ML Pervasive Modeling Language was
proposed in (Graham, 1999) along with the
combination of two software engineering trends;
software factories and MDA model-driven
architecture. MDA deals with the low abstraction
level that is caused by the heterogeneity of used
technologies. Software factories were used to
enhance the programmability and reduce the amount
of programming code.
Being in a real time streaming environment, a
system requires multi channel streaming over
heterogeneous networks and devices and must
support multi channel protocols to ensure system
interoperability (Park et al., 2004).
The demanding need for security, privacy,
authentication and access control in order to prevent
unauthorized access attempts within open dynamic
pervasive environments has motivated the
emergence of a new standard XACML eXtensible
Access Control Markup Language that helps to
automate several managerial tasks and ensures
secure and interoperable interactions between
several applications(Almenárez et al., 2004).
XACML standard represents a policy language
and an access control decision request/response
language. Being an XML based standard language
has enabled XACML to interoperate easily with
other applications.
XACML is a generic language that can be
embedded and used in any environment. Its policies
can be distributed in arbitrary locations. It’s
considered as a highly powerful language because of
its ability to support a wide variety of data types,
functions and rules that enables combining the
results of different policies (OASIS, 2003).
In order to increase the productivity, quality and
interoperability, the implementation of a pervasive
computing environment can follow one of two
different programming models as follows:
1) Context Driven Model where several contexts
can be defined in advance using description logic.
On runtime, the system will explicitly know the
behaviour that it should follow according to its
current state; this model assures the interoperability,
extensibility and scalability of the system. It’s ideal
for discovering contradictory system behaviours,
conflicts and adapt with multimodal environments.
2) Service Oriented Model which is considered
as a more expressive, proactive and procedural
model that allows higher programming control
levels and concentrates on the services that should
be provided using several decision making
techniques that memorize past actions along with the
environment’s history during a service lifecycle
(Yang et al., 2006).
For business applications, a Universal Business
Language UBL was introduced by OASIS (OASIS,
2004) as a way to unify the different heterogeneous
formats that aim to accomplish similar business
missions. UBL proposes to solve heterogeneity by
defining a generic XML interchange format for
business documents that can be extended to meet the
requirements of particular industries.
UBL provides a domain specific library of XML
schemas for reusable data components, a set of XML
schemas for common business documents that are
constructed from the UBL library components and
can be used in a generic context. Finally, UBL can
be customized to adapt to trading relationships. UBL
introduces a standard for XML business schemas
which is highly advantageous in assuring lower
integration costs, among and within enterprises,
through the reuse of common data structures. As an
XML based standard, UBL provides easily
programmable with low cost commercial software.
UBL has an easier learning curve, lower cost of
entry and therefore quicker adoption by small and
medium-size enterprises (SMEs). UBL enables
standardized training, easier system integration and
standardized, inexpensive data input and output
tools. Finally, the use of UBL would enhance the
system interoperability and integrity.
4 INTEROPERABILITY:
BETWEEN SECURITY AND
ACCESSIBILITY
As we show in fig. 1, EISs need to ensure
homogeneous interaction between their different
heterogeneous sub components that have
dynamically changing configurations over time.
As service-based systems, PEISs should provide
their employees with maximum accessibility to data
sources in order to enable them to accomplish their
missions easily. At the same time, employees should
be granted different accessibility levels according to
their roles (Role Based Access Control). Using
RBAC policies will enable the system to adapt to the
user according to his role, where each role has
security policies that describe his access rights.
While EISs should provide their employees with
high accessibility, they should provide highly
secured access procedures for external users or
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
240

intruders. Security is highly demanded in pervasive
information systems because the user might access
the system using an unreliable ad hoc connection or
could be displaying confidential data in public.
PEISs should balance between the accessibility
needs of internal users and external users’ security
constraints to ensure system interoperability.
We highlight the importance of employing XML
based standards that will ensure easier integrity and
data representation. Applying XACML will confirm
secured accessibility to heterogeneous and dynamic
data sources and employing UBL will ensure lower
integration coasts and high interoperability.
Finally, the interoperability is demanded not only
to assure data integration and representation but
should also be used to ensure homogeneous software
integrity and proactive interaction that would allow
users to access the system using different devices
and ad hoc networks and would provide users with
applications that adapt automatically to his situation
by following a service oriented architecture.
5 INTEROPERABLE SOFTWARE
TECHNOLOGIES
Pervasive information systems enable users to
employ different hardware devices and networking
technologies to access a particular dynamically
changing application online. Providing a system that
enables a homogeneous communication between
different applications with dynamic connectivity
constraints can be a cumbersome task.
5.1 Software Components
Software engineers have exploited the fact that
pervasive systems could be distributed in different
physical locations and thus introduced the usage of
software components. A component is an
independently deployable piece of software that
resides on a hardware element and provides a
service. Web services are components that reside on
the server side, pervasive systems aims to apply the
concept of components in a peer-to-peer design
architecture using a well defined protocol
(Gschwind et al., 2002).
In order to go beyond the limits and turn
computing applications into pervasive ones, the
adaptation process should be performed
automatically at run-time and should meet the
application and context needs just as the user needs.
Automatic adaptation can be done by employing
TBA Type-Based Adaptation which solves the
incompatibility problem between the different
interfaces by selecting a previously written adapter
from an adapter repository and automatically
determine the adapter to be combined in order to
translate between the different components.
The advantage of using software components is
that the application architecture is taken in mind in
the process of service composition (Davis et al.,
2005) and that components matching and the
adaptation process can be applied automatically.
5.2 Middleware
The adaptation process in pervasive systems has to
deal with the context volatility and unpredictability
so the adapter repository might be maintained at the
communication end parties. Adapting and matching
different software components is only efficient if
these components have similar architectures and if
the adaptation functions are available at the server or
the end parties. Therefore, software engineers
thought about constructing middle ware technologies
as a solution.
Pervasive computing connects many applications
together and as matching a lot of software
components is not a practical solution, the use of a
powerful and generic middleware would transform
these components and facilitate the integration of
this collection of components, their composition and
finally would ensure homogeneous communication.
A uniform and adaptive middleware technology
is not available yet, but if provided will assure the
interoperability between different services within ad
hoc networks.
Although standards, reference architectures and
generic software technologies provide the basis for
future ubiquitous software development, new micro
architectures, development methods and software
technologies are needed (Niemela et al., 2004).
5.3 Design Patterns
In order to facilitate the design, implementation and
development of pervasive systems, standard
solutions to common problems in software design
were generated and gathered. Design patterns take a
systematic approach that focuses on the patterns of
interaction instead of focusing on how individual
components work. Design patterns describe abstract
systems of interaction between classes, objects, and
communication flow (Chung et al., 2004).
Design patterns communicate insights into
design problems, capturing the essence of recurring
problems and their solutions in a compact form.
INTEROPERABILITY IN PERVASIVE ENTERPRISE INFORMATION SYSTEMS - A Double-Faced Coin Between
Security And Accessability
241

Patterns capture design knowledge, such as
guidelines and heuristics, in three ways.
First, patterns offer low-level solutions to
specific problems rather than providing high-level
and abstract suggestions. Second, patterns are
generative, helping designers create new solutions
by showing many examples of actual designs. Third,
patterns are linked to one another hierarchically
(structured), helping designers address high-level
problems as well as low-level ones. Patterns are
intended to complement guidelines and heuristics.
Patterns are simply another tool for helping
designers create high-quality solutions.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this article, we define clear boundaries for PEISs
and we highlight the importance of ensuring
accessibility, security and interoperability by
applying an adaptive service oriented security policy
such as: RBAC. We show the challenges that face
the integration of different system sub components
and we stress on the importance of providing a
system that satisfies the user needs, simplifies his
interaction with highly advanced devices in highly
dynamic environments.
REFERENCES
Al Kukhun, D. and Sedes, F., 2006. “Towards a pervasive
computing benchmark”. In MAPS 06, Multimodal and
Pervasive Services Workshop, ICPS406, IEEE
Conference on Pervasive Services, IEEE, pp. 29-34.
Almenárez, F., Marín, A., Campo, C. and García, C.,
2005. “TrustAC: Trust-Based Access Control for
Pervasive Devices”. In The 2nd International
Conference on Security in Pervasive Computing,
Boppard, Germany, pp 225-238.
Campbel, R., Al-Muhtadi, J., Naldurg, P., Sampemane, G.
and Mickunas, M. D. 2002. “Towards Security and
Privacy for Pervasive Computing”. In Proceedings of
International Symposium on Software Security, pp. 1-
15.
Chen, E., Zhang, D., Shi, Y. and Xu G., 2004. “Seamless
Mobile Service for Pervasive Multimedia”. In
PCM’05, 5th Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia,
IEEE, pp.194-198.
Chung, E. S., Hong, J. I., Lin, J., Prabaker, M. K., Landay,
J. A. and Liu, A. L., 2004. “Development and
evaluation of emerging design patterns for ubiquitous
computing”. In 2004 conference on Designing
interactive systems: processes, practices, methods,
and techniques, Cambridge, MA, USA, pp. 233 - 242.
Davis, J., Tierney, A., Chang, E., 2005. “A User-
Adaptable User Interface Model to Support
Ubiquitous User Access to EIS Style Applications”. In
COMPSAC’05, The 29th Annual International
Computer Software and Applications Conference,
IEEE, pp. 351 – 358.
Duan, Y. and Canny, J., 2004. “Protecting User Data in
Ubiquitous Computing: Towards trustworthy
environments”. In PET’04, Privacy Enhancing
Technologies, Springer, pp. 167-185.
Graham, L., 1999. The principles of Interactive design. In
Delmar Publishing.
Gschwind, T., Jazayeri, M. and Oberleitner, J., 2002.
“Pervasive Challenges for Software Components”. In
RISSE’02, 9th International Workshop on Radical
Innovations of Software and Systems Engineering in
the Future, Springer, pp. 152-166.
Munoz, J. and Pelechano V., 2005. “Building a Software
Factory for Pervasive Systems Development”. In
Advanced Information Systems Engineering, Springer
Berlin / Heidelberg, pp. pp 342-356.
Niemela, E., Latvakoski, J., 2004. “Survey of
Requirements and Solutions for Ubiquitous Software”.
In The 3
rd
International Conference on Mobile and
Ubiquitous Multimedia, College Park, Maryland, pp
71 – 78.
OASIS, 2003. “A brief Introduction to XACML”. In
http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/download.php
/2713/Brief_Introduction_to_XACML.html , consulted
on april 2007.
OASIS, 2004. “Universal Business Language 1.0”. In
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ubl/cd-UBL-1.0 , consulted
on april 2007.
Park, I., Kim, W. and Park, Y., 2004. “A Ubiquitous
Streaming Framework for Multimedia Broadcasting
Service with QoS based mobility Support”. In
Information Networking, LNCS 3090 in Springer-
Verlag (SCI-E), pp.65-74.
Ranganathan, A., Al-Muhtadi, J., Biehl, J., Ziebart, B.
Campbell, R.H. and Bailey, B., 2005. “Towards a
pervasive computing benchmark”. In PerCom 2005,
Third IEEE International Conference on Pervasive
Computing and Communications, IEEE, pp.194-198.
Want, R., Pering, T., Borriello, G. and Farkas, K. 2002
“Disappearing hardware”. In Pervasive Computing,
IEEE, Vol 1, Issue 1, pp. 36 – 47.
Weiser, M., 1999. “The computer for the 21st century”, In
ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and
Communications Review, vol 3, ACM, pp. 3 - 11.
Yang, H., Jansen, E. and Helal, S., 2006. “A Comparison
of Two Programming Models for Pervasive
Computing”. In SAINT Workshops 2006, International
Symposium on Applications and the Internet, IEEE,
pp134 – 137.
Zimmermann, A., Lorenz, A. and Specht, M., 2005.
“Applications of a Context-Management System”, In
Modeling and Using Context, Springer Berlin/
Heidelberg, pp 556-569.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
242
