
OSS FACTORY: DEVELOPMENT MODEL BASED AT OSS
PRACTICES
Ana Isabella Muniz and José Augusto de O. Neto
Universidade Federal de Campina Grande (UFCG)
Av. Aprigio Veloso, 882- Cx Postal: 10.106, Paraíba, Brazil
Keywords: Open Source, Architecture Pattern, Student, business model.
Abstract: In this paper we present OSS Factory (Open Source Software Factory), an ecosystem aligning software
demands, undergraduation Computing students qualification and Open Software practices in a collaborating
relation, dedicated to produce open software applications to cope with market demands, using students
codification potential. A contest among students attending software engineering courses (or volunteers),
guided by professors and coordinated by a central entity is the force to move OSS Factory. To validate the
elements and interaction proposed, experiments applying the structure described in the paper have been
performed, and positive results were achieved.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since its first moves, Open Software (OS)
phenomena has gained credibility as a concrete
alternative to response world wide TI demands, no
mater if in simple home based activities or, mainly,
corporations´ needs. It’s hard to point a TI
department which does not use or has considered
adopting an OS based technology.
In the other hand, the volume of demand for
OS software’s, or improvements on those largely
used, has grown fast in last years. A research
recently developed in Brazil among small
municipalities, with no more than one hundred
thousand inhabitants, has pointed OSS software as a
promising alternative to their need of business
processes automation. In the scenario researched,
technological limitations to develop applications
using internal staff and budget shortage were main
factors to suggest OS software as an alternative. In
addition, software houses have not showed interest
in exploiting this small municipalities market.
A third issue concerning OS software its how
the popularity it has reached did not push any
expressive transformation into academy bounds.
There is no remarkable reordering in Software
Engineering curriculum, towards accommodates OS
community practices, or any orchestrated movement
to drive students closer to OS world.
The objective of this paper is to present OSS
Factory (figure 1), which is an iteration model
conceived from practical experiments, where the
three factors mentioned before were integrated to
overcome their difficulties.
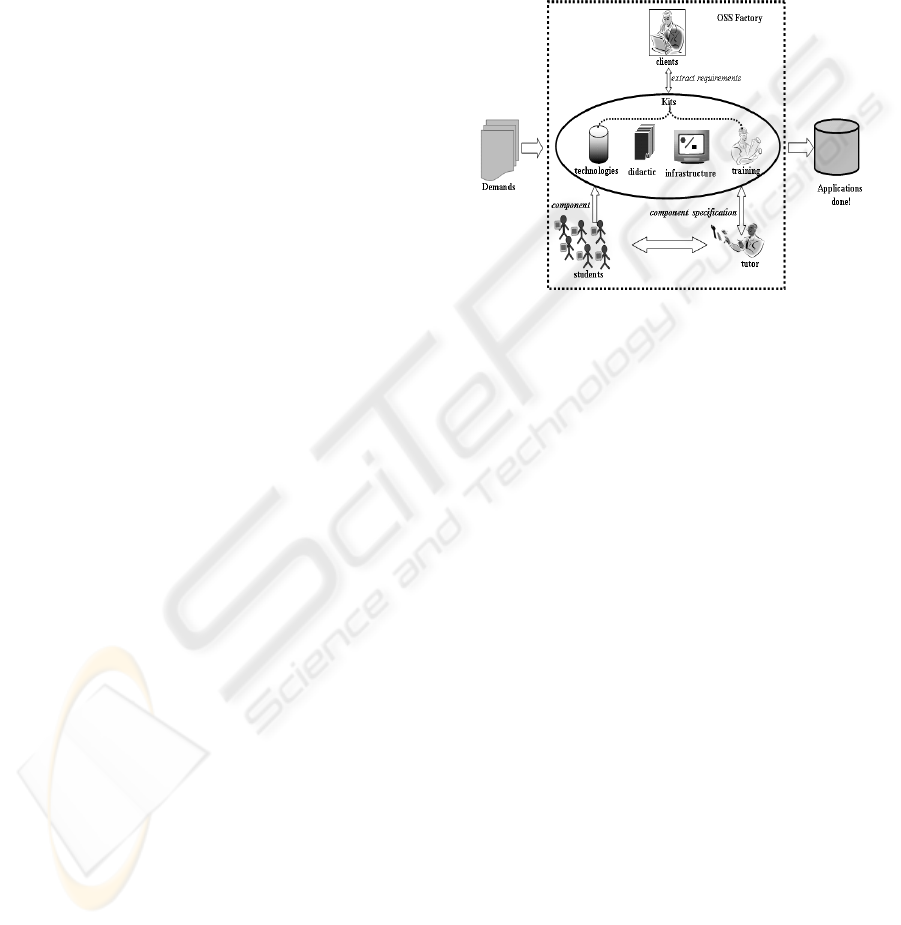
Figure 1: OSS Factory architecture.
OSS Factory engine, detailed in section 2, will
integrate the three vertices of figure 1, associating
ones needs to others abilities, in continuous
interactions that will bring positive outcomes to all
involved.
Open Software world can expand its limits of
influence and actuation, so far mostly restricted to
technologies directed to support back office
services, such operating systems, and web, e-mail
and application servers. In this new scenario, OS can
Software
Demand
SE Teachin
g
OS Practices
OSS
Factory
616
Isabella Muniz A. and Augusto de O. Neto J. (2007).
OSS FACTORY: DEVELOPMENT MODEL BASED AT OSS PRACTICES.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 616-623
DOI: 10.5220/0002395806160623
Copyright
c
SciTePress
expand today communities to include less
specialized personnel, different from high or
medium expertise profile typically found in present
communities (Lima, 2005). In present days, taking
part as an affective member, with frequent
contributions accepted, of an OSS community is a
privilege of high level programmers, because the
complexity of low level software they hostage.
Observing OS Software popularization, we can
notice that main steps in their success walk were
moved by their militant’s enthusiasm, as a
spontaneous process, lacking of any systematic
coordination capable of, for instance, to make OS
culture natural part of TI professional qualification.
Today, OS software reach academy simply through
communities and the products they offer freely to
students access (MySQL, 2006) (Hibernate,
2006)(Eclipse, 2006). Except by few and eventual
conferences, commonly dedicate to a restrict public,
with no high scale publicity, the very first contact
between students and OS world comes from student
individual attitude, downloading and installing the
most popular OS tools.
Fallowing a predefined flow of activities,
combined to OS practices of software engineering,
students attending undergraduation Computing
courses are able to establish a contact with Free
Software culture under a new and different
perspective. Instead of mere OS technologies users,
under-qualification professional take part of OS
world as member of a development community,
contributing with applications engineering. In this
process students are lead by Software Engineering
best practices, in a way that they can improve their
analysis, design and coding, and extend those
abilities with OS related aspects, giving them a more
extensive and distinct qualification.
Software manufactured by OSS Factory will be
able to support deficient areas, with low/none
technological capacities do develop their own
solution or with funding impossibilities to purchase
available property software. In the experiments we
relate further in this paper, software applications
were dedicate to automate Brazilian small
municipalities business process. However, as
described in section 2, OSS Factory can easily
reconfigured do address other business process
demands.
The rest of paper is organized according to the
following structure: section 2 presents OSS
overview, along with detailed description of each of
its elements. Section 3 related contest dynamic.
Section 4 shows a real experiment applying OSS
Factory production dynamics, followed by outcomes
obtained from the experiment Section 5 points some
related work. Final concerns are related on section 6,
titled Conclusions, bring final impressions and
overall results obtained from OSS Factory
experiments.
2 OSS FACTORY OVERVIEW
Figure 2: OSS Factory overview.
2.1 Demands
Demands are the source of OSS Factory motivation.
As already menssioned, the tipical demands filled
out by OSS Factory operation come from segments
with TI needs and no technological capacity to
produce, or fund capacity to acquire them.
In study case presented in Section 4, small
municipalities in Brazil are responsible for OSS
Factory demands. According to diagnosis resulted
from SOFTEX researches (Softex, 2004), 96% of
these municipalities are habited in maximum by 100
thousand people (IBGE, 2001). They are similar in
administrative structure, as well, they have few or
none capacity to make IT infra-structure
investments. From these two characteristics (low
budget and similar business process), comes the
insight that OS applications, modelled and built
according to one of these municipalities business
processes, could be applied to the most part or all of
them, because of their process compatibility and no
costs of license, natural for OSS.
In the experiments where OSS Factory was put
in operation, demands were presented by direct
contact with small municipalities. One of their main
demands comes from business process hardly tied to
legal constraints, which the administrator is
obligated to be compliant with. Frequent changes in
legislation result in considerable efforts to keep
OSS FACTORY - DEVELOPMENT MODEL BASED AT OSS PRACTICES
617

compliance. Other common class of demands come
from social programs, supported by Federal
Government. These programs impose some pattern
procedures to the municipalities, impacting directly
in their business process and, in most cases,
requiring a minimum level of automation. In both
case, each demand of automation or support
originate in municipalities fulfils Demands box, to
be dealt by OSS Factory movements.
2.2 Contest (Competition)
Once demands are identified, a contest involving
professors and undergraduation Computing courses
students are is carried out. Contest is managed by an
entity that will be mainly responsible supervision,
with predefined activities towards software
application development that will fill out demands
found in first phase of OSS Factory. From now on,
that entity will be referred as Coordinator Entity
(CE). One single contest can address either one
demand or a group of them, depending on
professors/CE convenience and applications
complexity.
In each edition, application functional
requirements elicited from demands are divided
through contest time window. How long is this
period also must be set up among professors and
CE? Following an iterative process, students submit
the code they produce for evaluation, made by
professors and CE consultants. Grades are assigned
to the code, ranking participants in a partial result
for that phase. After that, a new phase is started,
considering requirements not addressed yet. When
all phases are accomplished, partial results are
joined and those students who have summed higher
score are the concert winners.
2.3 Tutor
Typical undergraduation Computing curriculum
include courses dedicated to Software Engineering
practices. In this context, practices mean laboratory
activities, going beyond theorical teaching and
demanding from students analysis, design,
codification, test and deployment activities. The
whole cycle is supported by classical processes and
oriented by professor in charge of the course.
Every semester, professors are obligated to
repeat efforts to find adequate applications to be
delivery as practical project to his courses. Adequate
means in a complexity and time consumption
compliant to students background and scope bounds
of his course. After not much long, this procedure
extinguishes professor possibilities and the same
applications are repeated time after time, or
professor is forced to specify application associated
to no imaginary projects, with now real clients and
requirements.
When inserted in the contest, professor will be
provided periodically with projects specifications,
arisen from real demands identified from real
clients, ready to assign among students during his
course.
2.4 Students
Students that participate to the contest can improve
their Software Engineering abilities, going beyond
traditional courses, mainly for the following reasons:
Motivation: they will work on real requirements,
elucidated from clients that will truly adopt the
application they will build, instead of usual mock
applications assigned by professors every year;
Besides, according to their performance, they may
be monetarily rewarded by his efforts, gain good
exposition to software houses market, personal
satisfaction and pride
Good practices: having contact with tutorials, being
pressured to obey recommended design,
architecture, documentation and interface patterns
delivered by CE, because they are considered in
evaluations, students will leave the process with
Software Engineering best practices naturally
incorporated.
Focussing the big picture, in the former scenario
we can find productive capacity of hundred or
thousand students being allocated in to-be-never-
used applications. Signing this great amount of
students contests, CE will have a small software
development army, obtaining the same benefits that
Open Software communities currently get from great
numbers law (Moura et. all, 2006). In addiction,
client demands are solved with no cost in software
production phase.
2.5 “done” Applications
Every time OSS Factory repeats the production
process (a contest edition) the set of application
ready to use is increased, offered with no licensing
restriction, except those typical for OS software
(keeping it OS, making modifications always public,
etc.). The mechanism used to deploy applications is
a collaborative web portal (Flo-pref Library, 2006),
where the community composed by CE, Software
Engineering professors, students signed in OSS
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
618

Factory development activities and clients who have
applications installed (or interested in adopting any
of them) may freely interact, evolving the software
already built, in the same dynamics found in OS
software communities.
Clients can access applications through different
manners. The most simple of them is just
downloading directly from web portal. Depending
on complexity, application deployment may require
support for installation, personnel training and
preliminary data insertion before being ready to use.
These activities may be accomplished by specialized
small companies, inserted in a regional economic
development context (Moura et. all, 2006).
There are few details hid in OSS Factory
structure described above. Those details must be
addressed end actually resolved to allow smooth
interaction among factory’s parts. When the whole
structure runs into operation, there are a number of
convention that must be previously defined, in order
do permit that each of participants may play his role,
offering the services expected from him and, at the
same time, receiving all the benefits from others
players.
We mention now some of details and convention
that need to be set before OSS Factory operation:
1) How to present demands in a clear
language, enough to guarantee that the
application will correctly address demands
requirements?
2) How professor will hear about the contest?
What support material will he count with to
deal with his students, besides demands
description?
3) Which criteria will be used to classify and
rank contest participants? Different
paradigms and technologies can be
evaluated under horizontal, no-distinction
criteria?
4) Who coordinates the contest? How
coordination is carried out?
5) How communication process, assumed to
be fluent among participants, will happen
in OSS Factory domains?
Next section describes details of OSS Factory
components, capable to answer questions above,
providing a more realistic understanding of factory’s
operation.
2.6 Technology kits
An Architectural model, followed by technological
patterns, was proposed to be adopted by all
participants of OSS Factory. This model helps to
maintain compatibility among applications
conceived during students contest. For instance, a
specific application selected to a contest edition may
be just a fraction of client demands, which has been
divided to be accommodated in time window
available to that edition. In the next edition,
remaining demands will be implemented and it is
desirable that they can easily extend the first part,
without any compatibility drawbacks. The
architectural model defined aims to mould
applications to become easy to maintain, to evolve
and to be integrated each other.
Along with compatibility issues, architecture is
expected to be easy do learn and work with.
Students with basic development abilities must be
able to adopt it. In the other hand, the same
architecture must be well designed, up to current
development patterns, otherwise will face resistance
from more advanced developers. As a final
requirement, the architecture must allow students to
produce plain application (1-tier, browser-servlet,
for example) or more scalable designs (2, 3, n-tiers),
that will contribute to their development capacities.
2.7 Training Kit
Technological Patterns established to OSS Factory’s
applications intend to contribute to students software
engineering qualification. Students can access
information kits, built based on software
engineering best practices, a technologies adequate
to market current expectations.
The training process is coordinated through
pedagogical support items, available on contest web
portal, freely accessed by all participants, students
and professors as well. Training kit is composed by
the following items:
a) Architectural mode description.
This document presents the architecture
overview. Each of its elements identified and
briefly described, based on the role played in
the structure. The document is detailed enough
to be comprehensive and followed by
beginners, who had never built applications
under that type of architecture;
b) Tutorials comprehending each of technologies
defined as OSS Factory pattern.
Considering architecture definitions include a
series of technologies constraints, it is
fundamental to provide OSS Factory’s players
with pedagogical support to domain those
technologies. The tutorials go through
technologies details, and can be compacted by
OSS FACTORY - DEVELOPMENT MODEL BASED AT OSS PRACTICES
619
professors, according to students profile and
needs, to accelerate students learning;
c) Complete applications example to download.
Small applications, fully implemented, where
all technological patterns defined in OSS
Factory’s architecture can be found and
analyzed, with entire source code and full
documentation. This material obeys a practice
typically adopted by software developers, when
trying to learn new technologies solving
problems never faced before. In these situations,
developers use to search source code of already
done (and working well) applications, compare
with the code they are writing, trying to map
similarities and differences between them, in a
way to understand new technology or a
puzzling problem.
2.8 Didactic Kit
This kit is mostly dedicated to professors. Before
starting a new course, is part of professor’s work to
plain carefully the activities to be developed. Define
book and reference material to be followed, to
prepare didactic material, presentation slides,
exercises, to prepare web page to interact with
students during the course, to define examinations
and to schedule topics through course period, are
example of such activities.
These preparative activities are determinant to
the quality of course and can, therefore, interfere in
student learning.
Didactic kit provide by OSS Factory hold, in
resume, the items listed bellow:
a) A web page template;
b) Class scheduling, proposing a division of
discipline content along course period;
c) Class content, offered in presentation
slides;
d) Exercise lists;
e) Examination proposal, per chapter;
f) Spreadsheet models to grades registration;
g) Bibliography recommended;
h) Free e-books.
The kit motivates professors to join OSS
Factory, gaining qualification to him and his
students. Besides, taking part of the process,
professors will propagate OS practices in under
graduate students, as a real alternative for software
development.
Qualification offered by Didactic Kit is based on
well succeeded experiences and classical authors;
2.9 Infrastructure Kit
OSS Factory is supported by a web portal used to
give publicity to activities and, mainly, to provide
and coordinate communication flow among
participants. Among most important features,
students, volunteers and professors subscriptions,
Kit’s hostage and distribution, information
concerning appraisals, schedules and description of
contest dynamics.
This web portal is also OSS application
repository, where students will upload source code
and documentation they produce in every phase of
contest.
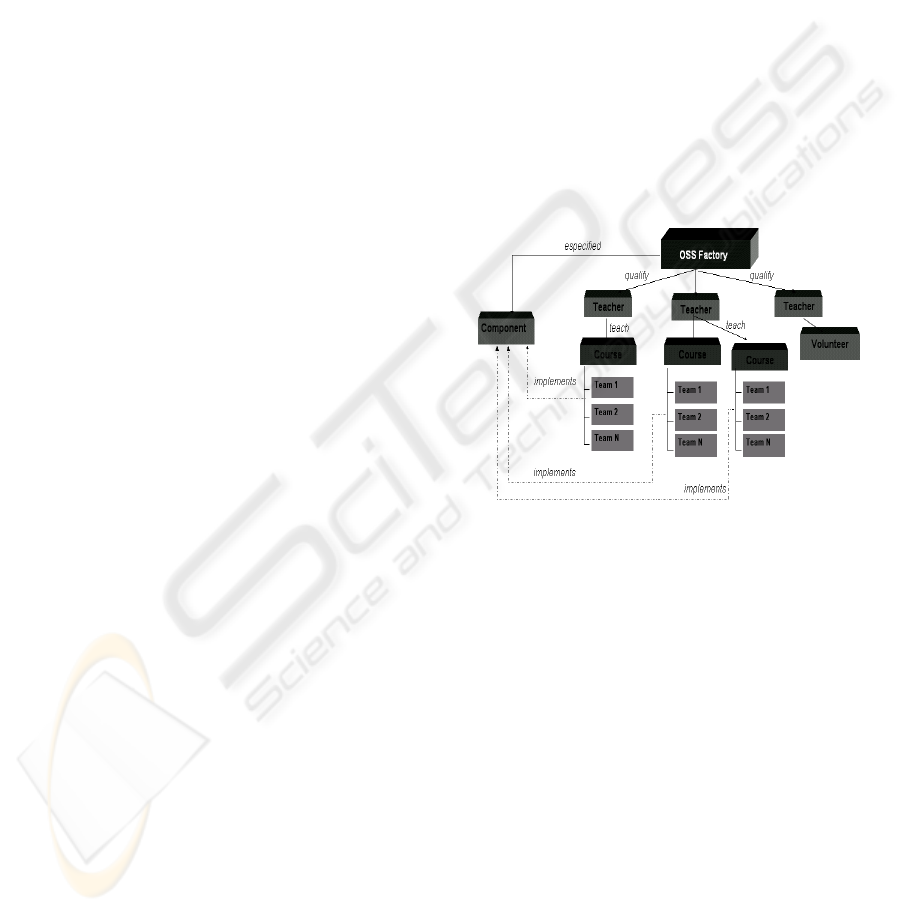
3 A MODEL OF FREE
SOFTWARE CONTEST
Figure 3: OSS Contest model.
The contest was managed by Entity Coordinator
(CE), represented by the nucleus of Via Digital (Via
Digital, 2006) project, located at the Federal
University of Campina Grande (UFCG -
www.dsc.ufcg.edu.br), whose role can be
undertaken by an institution or an involved OS
community. This entity has as fundamental
attributions:
a) Select and authorize professors to perform
during the contest.
b) Define the standard architecture of the
applications.
c) Define the software requirements.
d) Construct and maintain the contest portal.
e) Awards.
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
620
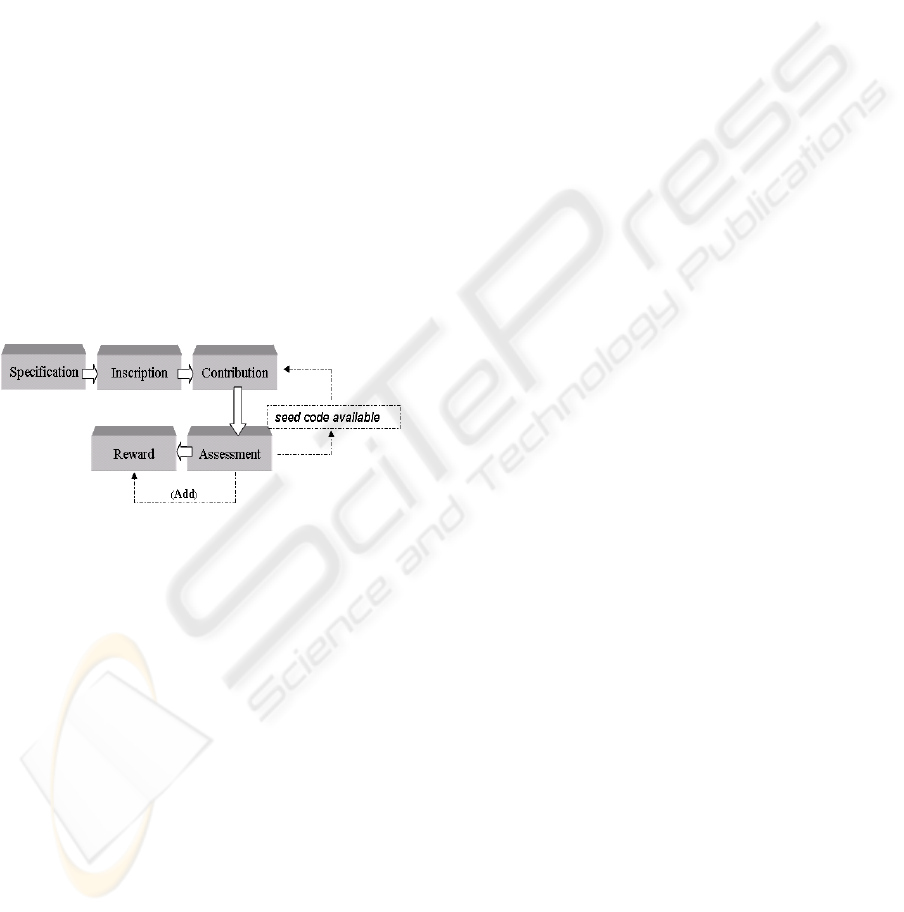
3.1 Contest Dynamics
The coordinating entity
The contest begins when publishes on web portal the
list (or single) applications to be CE portal
availability of the components to be developed.
After this event, comes enrolment of the
competing teams and volunteers. The difference
between the two types of participants is that first
ones are taking a course from a professor with
credentials by CE, while the others have personal
interest in the contest and seek insertion in the
competition by the professor. It is up to the
professor with credentials, according to his/her
possibilities and management, to limit the number of
volunteers enrolled under his/her responsibility – the
professor with credentials himself/herself does this.
After enrolment, the period of contributions by
the enrolled groups and volunteers begins.
Depending on the modality of contest, the
contributions can be offered or not. Figure 4 shows
the dynamics of the contest. Notice that the traced
elements report the activities concerning only to
interactive modality.
Figure 4: Contest dynamics.
In the first modality, the phase after the
specification and enrolment is along period of
implementation, which will end with the submission
of contributions completely constructed by the
students. CE will define which applications each
credentialed professor will evaluate and these
evaluations will compose the ranking of the ones
who will be awarded prizes. In none of the
modalities a professor will be allowed to evaluate
participants under his/her own guidance.
In the interactive modality, the implementation
will happen in cycles, fulfilling a sequence
requirement in which the CE will fraction the initial
specification of the applications. At the end of the
deadline for implementing a requirement, the
submitted contributions will be judged by the
credentialed professors. After the contributions are
evaluated, a ranking iteration will be formed for
each application and a score will be attributed
according to the position of the participant (group or
volunteer) in the ranking.
At the end of the last iteration, the score obtained
by the groups in each stage will be computed,
defining the winner of the contest.
4 A CASE STUDY
In the section, a real case will be presented, where
the proposal described in item 2 goes through some
practical experiences
.
Conception
With the beginning of the school year at the Federal
University of Campina Grande (UFCG) and the
Integrated College of Patos (FIP), the deficiency for
new software projects with real applications in the
market is great. After the creation of the business
model [6] to be implemented by Via Digital (Via
Digital, 2006), we found the opportunity to create an
inter-city contest among students of these two
universities.
Construction
The first contest was implemented in UFCG’s
Software Engineering Laboratory (SEL) discipline
of the Computer Science course. In this class, there
were 12 students enrolled, thus forming six groups
of two students each. The professor of this discipline
exerted the role of tutor of all the groups, lecturing
about the process, as well as about the technologies
that were used during all of the life cycle of the
software. In this case the development process YP
(easYProcess, 2006) was adopted.
The groups received professor’s tutorship on
their questions, and were evaluated by a committee
formed by three chairs. These were responsible for
choosing the application which would be the target
of the contest. For this choice a list of demands was
surveyed, involving six city halls in Brazil during an
event of Free Software (SOLISC, 2005). This
assessed priorities from 1 (low) to 5 (high). The
demand reaching the highest priority would be
chosen for the contest. At the time, the chosen
component was the Pharmacy and Medicine Control
(ViaCOM). The CE met all the desired requisites at
the city hall (specifically the Health Department).
After that, a chronogram with all the activities and
deliverables was elaborated to be given to each
group.
OSS FACTORY - DEVELOPMENT MODEL BASED AT OSS PRACTICES
621
Evaluation
In a previous phase of interaction with city halls,
two other teams of discipline of SEL developed two
applications, as project of disciplines, established in
the demands of these city halls. That experimental
phase tried to create an architectural standard that
could allow interoperability among applications
(done and to be done). Besides, the experiments
were base to documentation standards (code, user
guide and configuration and installation manuals)
aiming to optimise communication and
understanding of application. In addition, interface
design standard was established, in order to allow
easy recognition and use of application. This has
revealed important to accelerate users learning
curve. The evaluation of these results can be
observed in (Moura et. all, 2006).
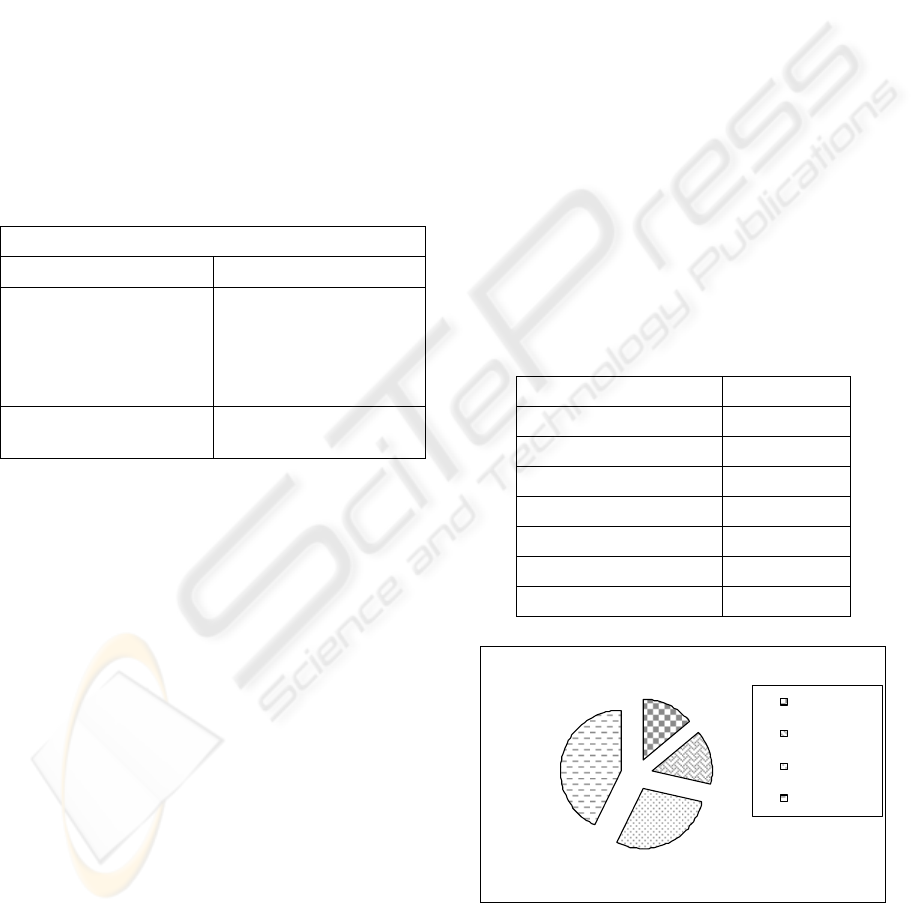
Table 1: Evaluation criteria.
Criteria
Eliminatory Classificatory
Conforming to the
architectural structure
• Code parameters
9 Tests
9 Project patterns
9 Cohesion e coupling
Functionalities
(specific/delivered)
• Conformity with
documentation pattern
These standards had collaborated in the
definition of kits that have been described in section
2. CE forwards these kits to professors, who
divulged specifications to the groups. All of these
initial artefacts were displayed on a web page, used
to follow-up of the groups. On this page, each group
could obtain information about the deliverables
dates, case studies, patterns (architectural,
documentation, and interface), observations about
each group, as well as evaluation criteria adopted by
the CE, as describe at table 1 following.
Evaluation was made in of ten days intervals,
due to the chronogram of the disciplines. All the
groups used CVS (CVS, 2006) to manage system
changes and versions. The CE, in turn, downloaded
the projects and evaluated them according to the
criteria described above. After each deliverable, a
winning group was chosen, and the other groups
began using that group’s code, not necessarily
having to erase the previous project, but taking
advantage of the best part of each one and thus
creating an even better project.
Experience of code exchanging among groups
have been not positive and found strong resistance
from students, because of considerable overhead
demanded to continue other group’s source code.
Based on these results current evaluation
methodology does not recommend any exchange of
source code among participants.
At FIP, the Information Systems course, not
having the same reality in the formation of students,
the professor of the Information Systems Laboratory
discipline divided the class into 5 groups, and
contrary to UFCG, opted not to follow the patterns
conceived by the CE. Instead, he used all this
material (Didactic, Technology and Training Kits)
and performed training with the students so that they
could create a application with quality, even without
following any patterns. At every iteration (fifteen
days), the professor performed an evaluation of the
groups. The one that obtained the best grades was
evaluated by the CE examining the UFCG groups.
At the end of all the stages of the process, the
group with the best performance had its system
(code and documentation) awarded.
To the end of the contest some data had been
raised referring the production of the implemented
applications, as it shows the table 2:
Table 2: Pós-Contest results.
Indicators: Numbers:
Tutors 2
Students 30
Applications 7
Use Cases 300
Documentation (JavaDoc) 10.504 (lines)
Unit/Accept Testes 140/350
City halls (Clients) 5
14%
14%
29%
43%
conception
construction
implantation
production
Figure 5: Distribution map of applications.
From table 2 the great contribution can be
observed to be given by the academy in the
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
622

production of information systems with real
applications. In an only period of learning stage (4
months) 30 students of software engineering had
obtained to produce 7 software applications. In
figure 5, is shown the distribution of applications in
phases, has that 43% of these systems are in full use
in city halls and 29% already are being implanted.
Also it can be observed, the strong concern in the
good attendance to the customer, therefore the
necessity to carry through tests, to register and
possess a friendly interface.
5 FUTURE WORKS
A next stage of experiments involving all the aspects
of the OSS Factory is in an elaboration phase. In this
round, the same elements will be working, only the
community of students and professors included will
be increased.
The purpose of the experiment is to evaluate the
complexity of managing a larger quantity of people
involved, geographically spread out, with more
heterogeneous institutions, students and professors
than in the first edition of the contest.
With the results to the second experiment, it is
intended to launch a more ambitious edition of the
contest in 2007, with national extension, and
probably involving the construction of more than
one application in the competition, where the
aspects conceived in the first phase and improved in
the second phase will escalate to quantities of
participants near the communities of the most
popular OSS.
At present, we have only a sentiment of
compatibility with the model proposed with the
modus operandi of the OSS community. With a
greater popularization of OSS, this contact could be
extended. We intend to more precisely detect the
community’s acceptability of the model OSS
Factory, with the development induced by requisites
and awards, consequently less free than dynamics of
classic communities.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The proposal of the OSS Factory is to have
coordination among its three vertexes, so as to
extract potentialities from each one of them,
attending to the demands of the others.
Each element and relative activities within OSS
Factory context was conceived and defined in an
incremental set of experiments, under Via Digital
project.
Recent experiments performed show that its
dynamics contributes on teaching of practical
software engineering courses, with real and
motivating activities using specialized didactic
material, which makes possible improvements in
students qualification process. These results have
been obtained in real cases of OSS Factory
operation. At the same time, the performance of
OSS Factory showed to be capable of responding to
demands and solving real problems at small city
halls, through typical practices of OSS
communities.
With new experiments, scalability of the model
will be assessed, as well as its performance in
producing applications that will produce the
automatization to other business processes.
REFERENCES
Lima, C. A. Práticas para Gerência e Desenvolvimento de
Projetos de Software Livre. Federal University de
Campina Grande, 2005.
MySQL – Available at: http://www.mysql.org – Last
access: December 11/2006.
Hibernate - Available at: http://www.hibrenate.org – Last
access: December 11/2006.
Eclipse - Available at: http://www.eclipse.org – Last
access: December 11/2006.
SOFTEX, Report - Projeto Aplicação de Software Livre
em Prefeituras. SOFTEX Association, 2004.
IBGE, Censo 2001, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e
Estatística (IBGE - The Brazilian Institute of
Geography and Statistics). Available at
www.ibge.gov.br , 2001.
Moura, A. et. All. Open Source Software in Small City
Governments and the Promotion of Regional
Entrepreneurship. eChallenges Proceedings 2006.
Barcelona, october 2006.
FLOApp - Available at:
http://flopref.paqtc.org.br:8080/flop/ – Last access:
December 11/2006.
Via Digital – O caminho inteligente para a informatização
pública.Available at: http://www.viadigital.ufsc.br –
Last access: December 11/2006.
easYProcess Development Process. Available at:
http://www.dsc.ufcg.edu.br/~yp – Last access:
December 11/2006.
SOLISC - Available at: http://www.solisc.org.br – Last
access: December 11/2006.
CVS - Available at: http://www.cvshome.org – Last
access: December 11/2006.
OSS FACTORY - DEVELOPMENT MODEL BASED AT OSS PRACTICES
623
