GENERATING COLLABORATIVE WORK PROCESSES
I. T. Hawryszkiewycz
Department of Information Systems
University of Technology, Sydney
Keywords: Process definition, Collaboration, Workspaces, Software agents.
Abstract: The paper describes ways to support collaboration in business processes. Collaborative processes are
different from predefined processes in the sense that they can change dynamically as the situation emerges.
Such changes can be time consuming as they require users to continually adapt the system to changing
contexts. The solution proposed here to support process evolution is to provide generic work objects and use
software agents to assist users to dynamically change the process by quickly adding or changing work
objects. The paper outlines a way of describing work processes in terms of generic work objects. The
structure of the generic work objects is based on a metamodel, which provides the fundamental concepts to
define generic objects. A prototype implementation is then described.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many business processes now support collaboration
in applications such as distributed project teams,
software development teams (Carmel, 1999), design
teams, planning and evaluation teams, or client
support teams. Because of their distributed nature,
such processes increasingly rely on the InterNet to
support collaboration. However, studies (Cummings,
2002) have found that collaboration on the InterNet
usually does not go beyond simple communicative
acts such as exchange of documents. Often as found
by (Duchenaut and Belotti 2001), users develop their
own personal support systems, usually on their
private systems. Users must then continually
integrate them into collaborative activities as
needed. Such integration can be quite time
consuming to avoid inconsistencies between
individual records on personal systems and the
enterprise context, as well as to transfer user
contributions into the context.
Furthermore collaborative processes tend to
emerge and evolve as they proceed. Such evolution
calls for constant changes to services to be provided
to process participants. This paper suggests a way to
provide customizable work objects that can be easily
configured to different collaborative activities within
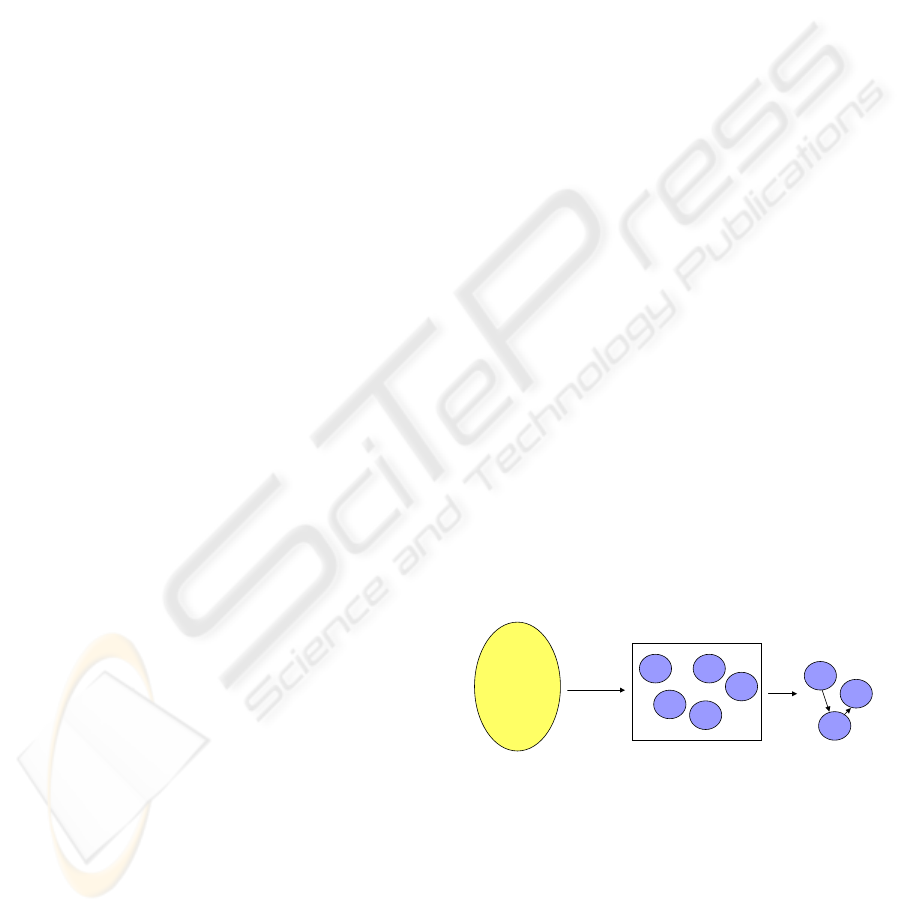
the enterprise context. Figure 1 illustrates the idea.
Here there is a library of work objects. These are
combined into one work process to meet a given
work objective.
To do this the paper proposes a way to define
work objects that are generic in nature and widely
applicable. These objects can be combined to
accomplish an objective within the given context.
The paper provides a metamodel for this purpose.
The metamodel provides the concepts and structure
needed to define the generic work objects. The
metamodel combines both process and social aspects
to represent collaborative activities.
Figure 1: Creating a Process.
The other key requirements are agents to
combine the work objects into work processes. The
process for doing so is shown in Figure 2. It shows
two kinds of agents. The first are agents that assist
users to combine such work objects into a process.
Such agents must support organizational processes
that produce well-defined documents, such as
market reports, which must be developed as part of
WORK
OBJECTIVE
Work
object
Work
object
Work
object
Work
object
Work
object
Select work objects
to meet work
objective
Each work object carries out a specific
set of actions to produce a well defined
output
Construct
and change
process
Work
object
Work
object
Work
object
321
T. Hawryszkiewycz I. (2007).
GENERATING COLLABORATIVE WORK PROCESSES.
In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - ISAS, pages 321-328
DOI: 10.5220/0002347103210328
Copyright
c
SciTePress
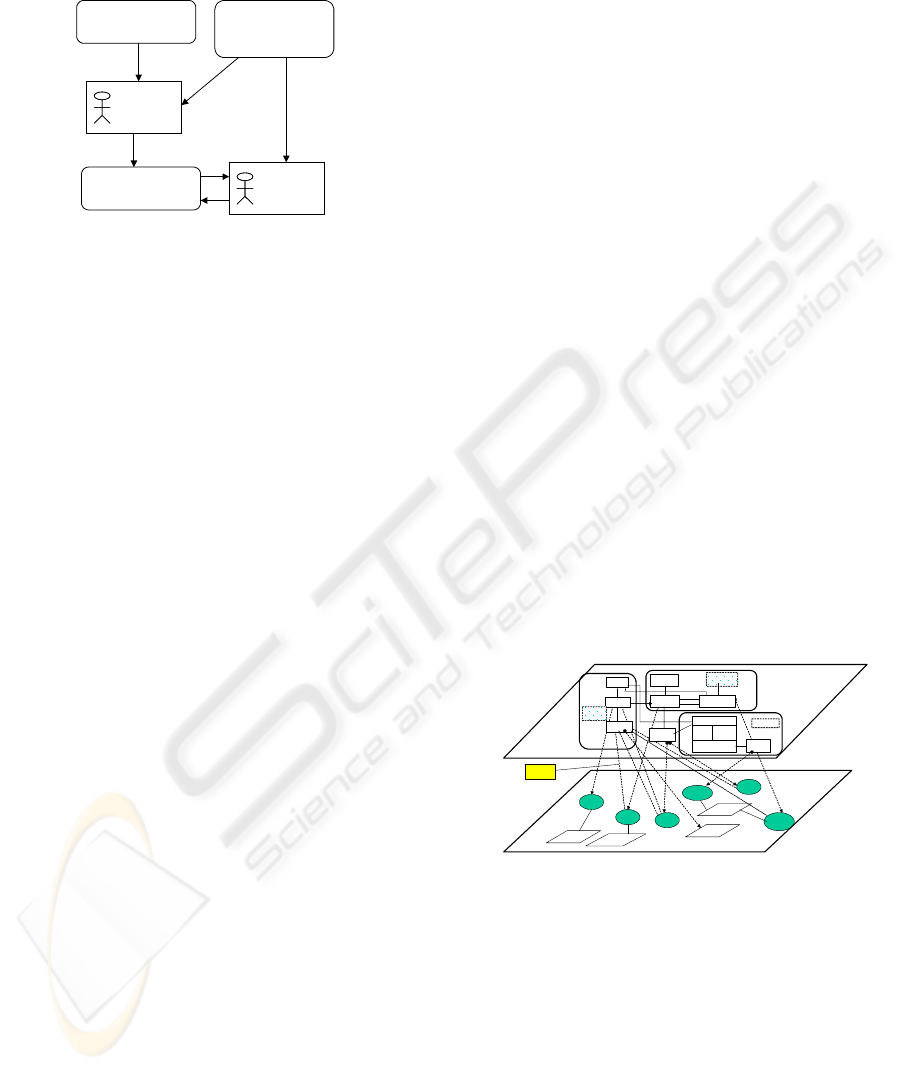
the process. The second are agents that manage and
change the concrete processes.
Figure 2: Generic and concrete units of work.
The goal pof the paper is to describe a way to define
such work units. The paper first defines the
metamodel, which provides the foundation for
defining the work objects in collaborative
environments. The paper then describes some work
objects..
2 SEMANTICS TO DESCRIBE
WORK OBJECTS
The work objects proposed here are generic in the
sense that they can be adapted to many processes.
The metamodel described here combines process
responsibility as well as social networking. It is
shown in Figure 1 and is an extension of a model
described earlier (Hawryszkiewycz, 2005). The
metamodel covers the process parts and has evolved
over a number of years. It builds on concepts from
earlier systems such as Conversation Builder
(Kaplan, 1992) or Oval (Malone, 1992) and has been
verified through a variety of applications that
include business networking (Hawryszkiewycz,
1996), and strategic planning (Hawryszkiewycz,
1997). This paper extends the process model to
incorporate the social awareness network within the
activity structure. The combined model shown in
Figure 1 includes two levels. One is the process
level, which defines the formal roles and activities in
the process. The process structure represents the
arrangements in place for collaboration. It shows the
documents available in the system and their use in
different activities. The second is the social
awareness network, which supports user social
interactions. These in many cases can change as
collaboration evolves.
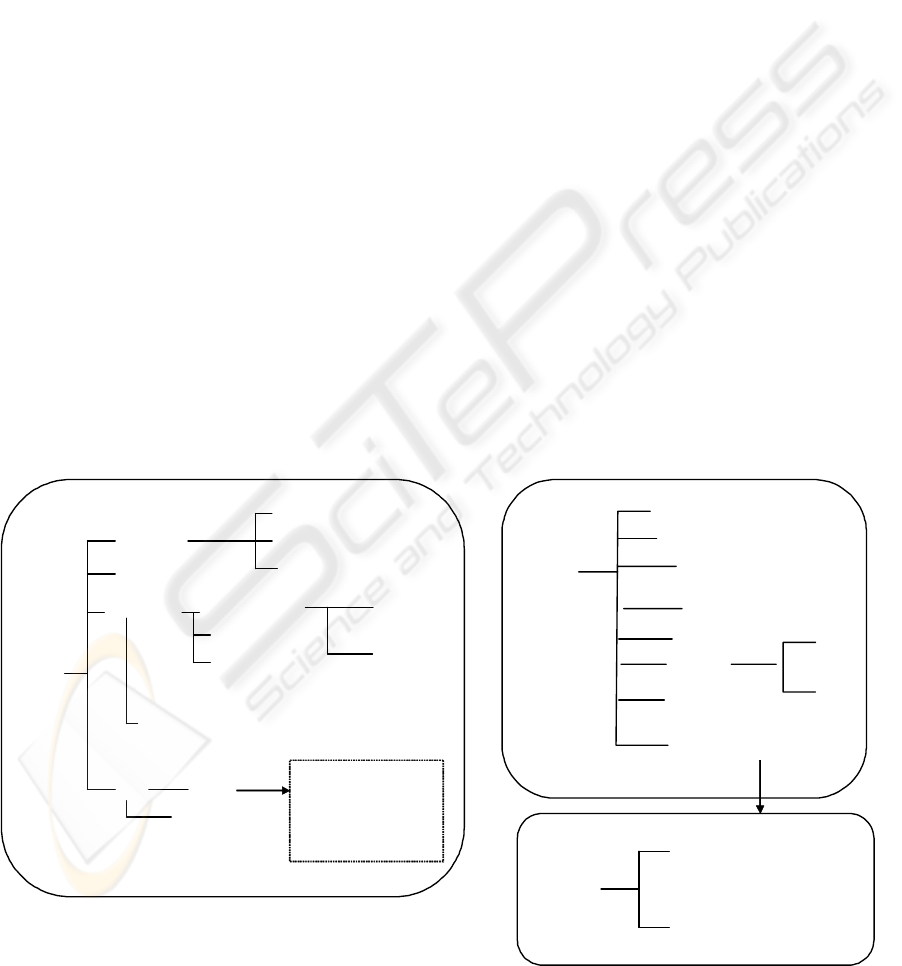
2.1 The Process Level
In the process level, the rectangular boxes represent
concepts whereas lines between the oval shapes are
relationships between the concepts. Figure 3 also
groups the process structure concepts into three
parts, namely:
• The work activities, which are modeled as
activities and actions. These actions usually
refer to or change artifacts. An activity can
include many actions, which in turn can use
many artifacts. Responsibilities for such actions
are assigned to designed roles.
• The people and how they are organized into
groups. .Any person or participant can be part
of a number of groups, and each group can
have any number of participants. Groups can
include groupings into departments or other
units. The groups can then assume roles with
defined responsibilities in organizational
activities. This part of the metamodel provides
ways to combine work-actions into activities
with members of groups assigned
responsibilities through roles for those work-
items
• Workflows, which are supported by
associating events with roles. People associated
with these roles can initiate completion events,
which in turn trigger initiation events that
notify roles to carry out their tasks.
Figure 3: A Metamodel for Defining Process
Communication Patterns.
These three kinds of concepts are essential for
modeling business applications. Most business
processes follow a workflow, they involve
organizational activities and they require social
interactions to share knowledge.
2.2 The Social Level
This paper examines ways to extend the process
network to include social aspects. It places a social
Repository
of generic
work objects
Work unit
metadata
Unit of
work
Customizing
agent
Customizing
agent
Managing
agent
Managing
agent
Action
reports
Activity
comments
Social awareness network
Group
issues
Project
issues
Artifact
comments
Workfl ow
planning
Activities
Events
Workflow steps
Completion
events
Initiation
events
Workflow
Workflows
Rol es
Groups
Participants
*
*
1
People
structure
*
*
Artifacts
Vie ws
Work-actions
Work
activities
own
Process network
Part icipa tion
conditions
Issues
Progra m
board
Comments
and changes
Calendar
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
322
awareness network in parallel with structured formal
activities. The social network is composed of
discourses that emerge as collaboration evolves.
These are represented by oval shapes. Each
discourse is an oval shaped box. In addition there is
a collaborative database where such interactions are
recorded. Usually each such database is created by
one component of the process structure. This can
include issues boards, discussions, or various
comments on progress. Eventually the kind of
discourse would be supported by the most
appropriate technology (Barton, 2005). A typical
definition of a discourse is:
Discourse (<discourse-type>, <initiated by>,
<associated collaborative database>, {participants,
rules})
Participation in discourses is defined by rules
with rules chosen to ensure a desired level of
collaboration. As an example we could have:
<group-membership-issues> (issues and comments,
’project team-1’, ‘participation rules’, all
members of team)
This defines discussions about adding members to
project team-1. It defines that all existing members
of the team can participate and issues and comments
raised are kept in a database called ‘participation
rules’.
2.3 Level Integration
The relationship between the process and social
levels is defined by the dotted lines in Figure 3. The
dotted line that starts with the circle shows the
concept that initiates a discourse. Other dotted lines
show the participants and groups that participate in
the discourse.
2.4 Structure of Work Objects
The semantic model provides the guidelines for
specifying work objects. Figure 4 is a structure of a
work object, which is composed of elements that
correspond to the process level concepts in the
metamodel shown in Figure 3.
The work objective here is to collect
requirements in a software development project. The
plan follows the normal process of collecting
information, resolving any conflicts by negotiation
and then developing a specification. Only one work
object is shown – collecting information. The
collecting information work object, which is chosen,
will depend on the social context.
The work instance includes a plan to choose
work objects depending on the social context and as
specified by the selection rules. Thus it is possible to
choose an object that supports interviews, or an
ethnographic approach.
Figure 4: Work descriptions.
JOB TYPE
Work objective
Keyword type (Req. Eng.
Specs..)
Work
characteristics
WORK OBJECTS
OBJECT RULES defining input
situation
EXCEPTIONS
PLAN
Work process
objective
Work
outcome
OBJECTIVE
CONTEXT (social
context , process type)
Rules
Develop specification
requires agreed upon
requirements, following
negotiation, following
analysis, following
elicitation.
Work object
selection rules
OBJECTIVES
Work objective
Structure part
Work object
Work description (eg. Interviews,
ethnography)
Structure (roles, tasks,
content: artifacts)
Output
Social links (Planning, issues)
Conditions
Tool support (editors,
conversation tools)
Start condition
Context subset
Social part
Social work
object
Collaborative
database
Interaction
support
GENERATING COLLABORATIVE WORK PROCESSES
323

Each work object can have any number of links
to social objects as often occurs in collaborative
activities. These can be discussions, blogs or wikis
depending on the type of relationships to be
maintained (Barton, 2005).
3 WORK OBJECTS FOR
COLLABORATION
The work objects commonly found in collaborative
work include:
e-portfolio – Supports working on an artefact by a
number of people. It supports a collection of
artefacts developed by a number of people.
Different responsibilities are assigned in the e-
portfolio. Examples include – education with
teacher and student responsibilities. Strategic
documents with planning and expert
responsibilities or paper preparation with author
and reviewer responsibilities. The parameters of
this e-portfolio will be document names, roles
and role responsibilities for each document.
The e-portfolio can also be defined grammatically as
follows:
e-Portfolio: portfolio-name;
Work-goal: (Text with keywords);
Work-roles:+{<role-
name>,+{<responsibilities>}};
Content:
work-content: +{<artifact-name>};
services: + {<service-name>};
+actions: {{artifact:+{artifact-name}},
{services: +{<service-name>}},
+{action:{+{<role-
name>},services:+{service-name},
information:+{artifact-name} };
There are also constraints and permissions, as for
example, role permissions to access information, and
what kind of access is permitted. The kinds of
semantics include:
Create-e-portfolio,
Invite people to take up a role,
Add artefacts to the e-portfolio,
Alert people of actions taken by others in the e-
portfolio,
Setup services to support actions in the e-
portfolio.
The e-portfolio in this case can be seen as
collaboration in the small being carried out within a
larger framework. The issues then are how to
subdivide a process into e-portfolios while
maintaining links to the entire context.
Workflow instance – To arrange work actions
associated with an activity. Here a workflow is
defined in terms of events, which are assigned to
roles. A completion event initiated by one role
can result in an initiation event for some other
role. The process can change dynamically by
adding new events dynamically.
Group management – managing a group of people,
which may be an organizational unit or people
with common interests. Usually requires support
for sharing information, managing group
changes and maintaining group memory in
general.
Team formation – requires support for keeping
track of activities and responsibilities of
individual team members. Important aspects are
new members joining teams, resolution of issues
and distributing work between team members,
including negotiation for assigning and carrying
out tasks..
Program and issues boards – There are a number
of advantages of using such higher level
concepts in collaborative systems. One is to
provide a social construct that can be easily
understood. Another is that interactions as
particularly suitable as a way of integrating
processes. It provides such a basis ranging from
predefined processes to emerging processes that
include supporting mobility in the workforce. It
can be used as the basis for supporting
communication beyond the simple exchange of
messages to supporting more goal oriented
communication that integrates a number of
messages into the one interaction. It however
sees that support must be provided to manage
such interactions and suggests agents as suitable
for this purpose. Conceptually it can be viewed
as a composite object [5] that can be represented
in terms of modeling concepts such as entities or
relationships.
Low collaboration levels usually require e-
portfolios and perhaps group management.
Higher levels of collaboration will require
engagements such as team formation or
workflow instance.
An example of a process defined in terms of generic
objects is shown in Figure 5. It starts with
developing an e-portfolio on requirements identified
though interviews and other conversations. It then
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
324
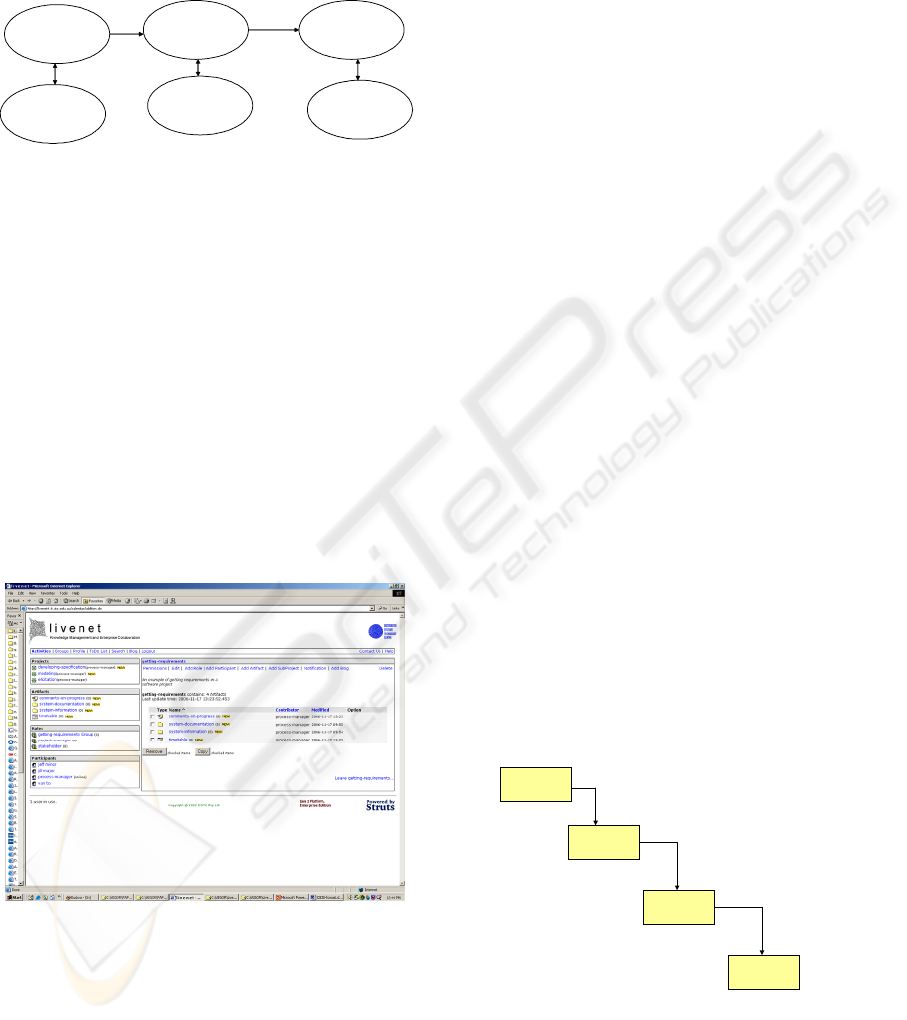
continues with a negotiation to set priorities. The last
step is an e-portfolio that results in a specification.
Part of the specification is an e-portfolio of system
models.
Figure 5: A Work Instance.
4 AN IMPLEMENTATION
We are developing prototype generic agents for our
workspace system, LiveNet. Figure 6 illustrates a
typical workspace that supports the capturing user
requirements. This is the top level workspace that
describes the work process.
It lists the three work-activities in the selected plan,
namely, elicitation, modeling and specification
development. It also shows the work context
including the system description and other
organizational information.
Figure 6: A workspace for determining user requirements.
4.1 Creating Work Activities
Figure 7 illustrates one of the work objects that
make up requirements elicitation. It now shows the
participants in the process and their roles – user,
analyst and manager. It also shows a social object,
namely a blog space, which is used to clarify various
issues identified during interviews. Each analyst in
this workspace has a view that contains a collection
of interview reports. These can be accessed by other
analysts in the team for comment. Furthermore each
analyst can construct a blog to collect comments on
their activities and outputs.
The participants of the workspaces must now carry
out the actions defined for the activity.
5 AGENTS FOR CUSTOMIZING
WORKSPACES
Our goal as shown in Figure 2 is to develop agents
to construct workspaces to support collaborative
processes.
Figure 8 shows the principal activities of the
customizing agents.
Customizing agents predominantly match open
parameters to user preferences.
Subgoal:setup Custom-UOW
If work-metadata(work-description) matches
UOW(work-description) then create custom-UOL
from UOL; add UOW(work-content) to Custom-
UOW(work-content); if UOW(work-output)
matches work-output (work-output-description) then
add work-metadata(work-output(name): to
UOW(work-output);
Subgoal: setup custom-work-plan
If sum of work-plan(activity-objectives) includes
all keywords in Custom-UOL(work-description)
and
work-plan (plan-type) matches Custom-
UOL(unit-plan-options) then create custom-work
plan from work plan.
Level 1
Creates UOW from
work metadata
Level 2
Select work plan
OUW is used by
agent to select plan
Level 3
Select work
activities
Work plan steps
used to by agent to
select activities
Level 4
Select work
services
Activities used by
agent to select
services
Plan steps specified
as objectives
The agents build up the
workspace progressively
Figure 8: Constructing units of work.
E-portfolio
(Collect requirements)
Negotiation
(Identify issues)
E-portfolio
(Create specification)
Conversation to
collect information
Issue resolution
(Set priorities)
E-portfolio
(system models)
GENERATING COLLABORATIVE WORK PROCESSES
325
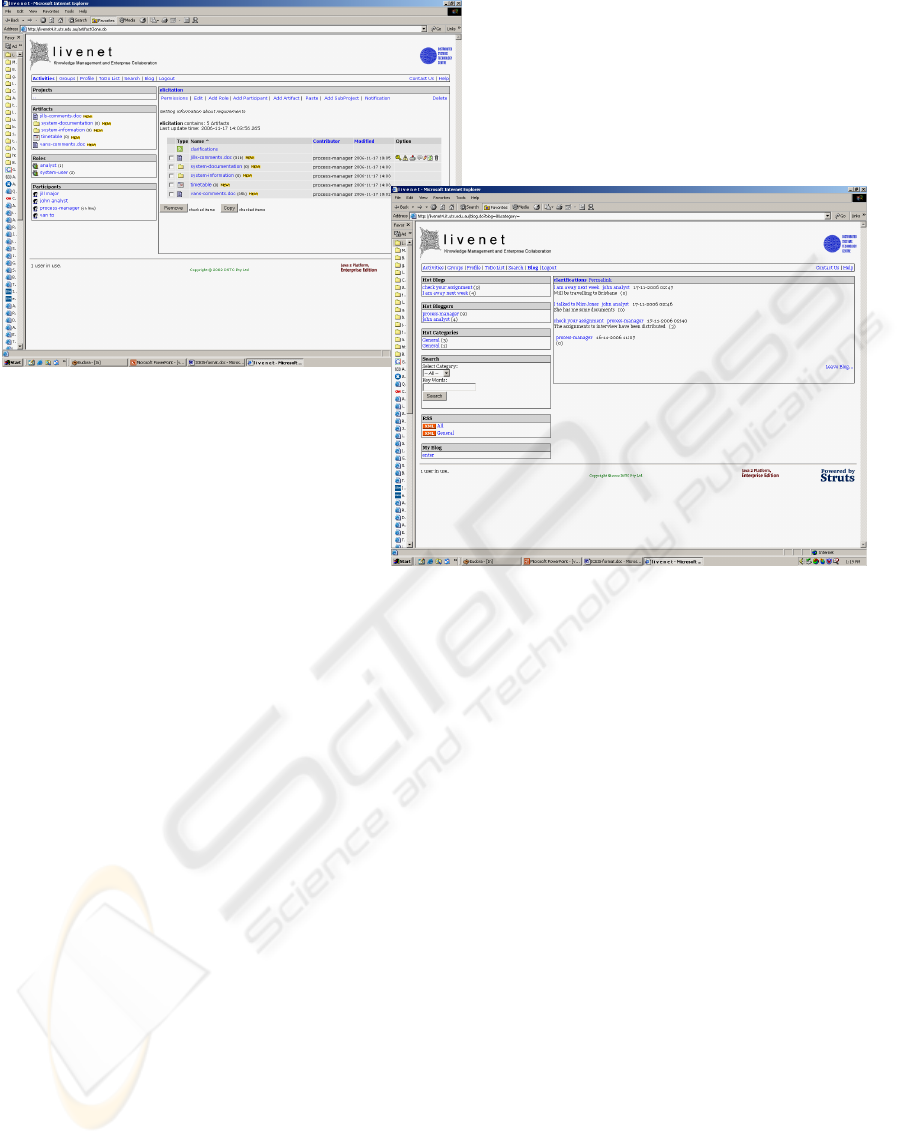
Figure 7: Work object for eliciting requirements.
5.1 Managing Agents
The general rules here are that each work object has
an associated agent. The type of agent corresponds
to the kind work object. Our earlier work
(Hawryszkiewycz, Lin, 2003) defined a set of
generic agents for managing collaborative processes.
These were based on a metamodel of collaboration
and included:
5.2 Defining the Agents
At a more detailed level, we use the usual reasoning
model of agents shown in Figure 6 and implement it
using the three layer architecture (Müller, 1996)
chosen from a number of alternative architectures
(Woodridge, 1999). Agents are used to achieve goals
using plans defined by agent users. A plan is
composed of event-condition-action rules, each of
which specifies the actions to be executed when
condition is true.
An example is support for personalized learning
(Pan, Hawryszkiewycz, 2006) for creating
workspace created for learning.
An example is shown in Figure 9. It shows a
sequence of workspaces generated by agents to
support a learning work process. It first identifies a
learner goal and then suggests a plan to be followed
to satisfy the learning goal. It then displays the
selected plan. Once accepted the agents will
generate workspaces to support the learning
activities of the plan.
6 SUMMARY
This paper described the development of specifying
collaborative processes that are supported by
software agents. It described a generic set of
software agents. The paper then describes a way of
customizing generic work-units into work processes.
It then proposed a set of customizing agents to
construct concrete processes and managing agents to
support these processes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work described here was supported by an ARC
Discovery grant. The contribution of Aizhong Lin in
defining the agent architecture is also acknowledged
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
326
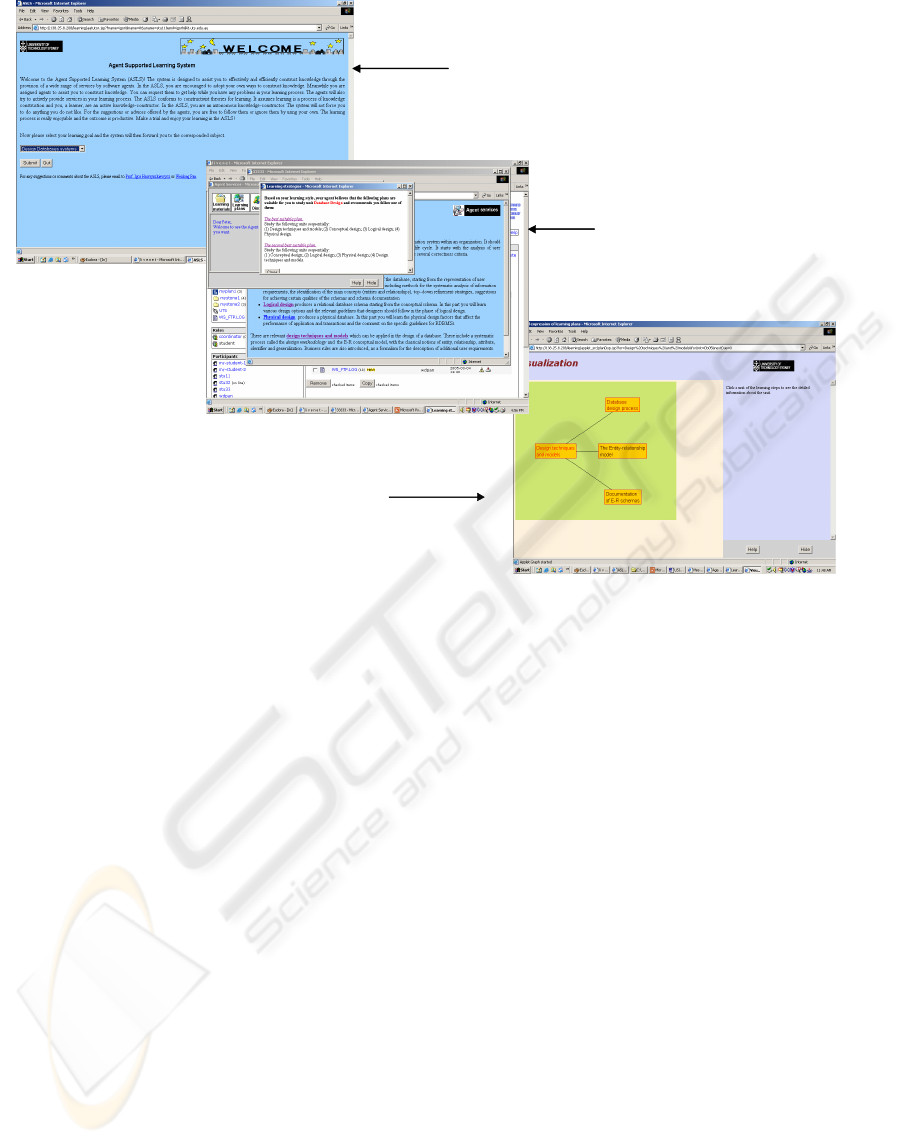
1. Identifying the learner goal
2. System suggests
alternate plans
ranking them based
on the learner
profile
3. System displays
selected plan
Figure 9: Evolving workspaces for learning.
REFERENCES
Barton, M.D. (2005): “The future of rational-critical
debate in online public spheres” Computers and
Composition 22, pp. 177-190, Elsevier Press.
Belanger, F. (1999): “Communication Patterns in
Distributed Work Groups: A network Analysis” IEEE
Transactions on Professional Communication, Vol. 42,
No. 2, December 1999, pp261-275.Carmel, E. (1999):
“Global Software Teams” Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle
River.
Carmel, E. (1999): “Global Software Teams” Prentice-
Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Cummings, J.N., Butler, B. and Kraut, R. (2002): “The
Quality of OnLine Social Relationships”
Communications of the ACM, Vol. 45, No. 1, July,
2002, pp. 103-111.
Ducheneaut, N. and Bellotti, V. (2001): “E-mail as
Habitat’ Interactions, September-October, 2001, pp.
30-38
Hansen, M.T., Nohria, N. and Tierney, T. (1999): “Whats
your Strategy for Managing Knowledge” Harvard
Business Review, March-April, 1999, pp. 106-116.
Hattori, F., Ohguro, T., Yokoo, M., Matsubara, S. and
Yoshida, S. (1999): “Socialware: Multiagent Systems
for Supporting Network Communities”,
Communications of the ACM, March, 1999, pp. 55-
59.
Hawryszkiewycz, I.T (2005): “A Metamodel for Modeling
Collaborative Systems” Journal of Computer
Information Systems, Vol. XLV, Number 3, Spring
2005, pp. 63-72.
Hawryszkiewycz, I.T. (June, 1996):” Providing Computer
Services For Business Networks” Proceedings of the
Ninth International Conference on EDI-IOS, ISBN-
961-232-000-4, Bled, June, 1996, pp. 398-411.
Hawryszkiewycz, I.T., Steele, R. (2005): “A Framework
for Integrating Mobility into Collaborative Business
Processes” Proceeding of the Conference on Mobile
Business, Sydney, July, 2005, pp. 89-93.
Hawryszkiewycz, I.T. and Lin, A.(2003): “Process
Knowledge Support for Emergent Processes”
Proceedings of the Second IASTED International
Conference on Information and Knowledge
Management, Scottsdale, Arizona, November, 2003,
pp. 83-87.
Kaplan, S.M. , Tolone, W.J., Bogia, D.P. and Bignoli, C.
(1992): “Flexible, Active Support for Collaborative
Work with ConversationBuilder” Proceedings of the
CSCW’92 Conference, November 1992, Toronto, pp.
378-385.
LiveNet: http://livenet4.it.uts.edu.au
Malone, T.W. and Fry, C. (1992): “Experiments with
Oval: A radically Tailroable Tool for Collaborative
GENERATING COLLABORATIVE WORK PROCESSES
327

Work” Proceedings of the CSCW’92 Conference,
November 1992, Toronto, pp. 289-297.
LiveNet, http://livenet4.it.uts.edu.au
Müller J. P. (1996). The design of Intelligent Agents.
Springer Verlag. 1996. Pp. 7-44
Pan, W., Hawryszkiewycz, I.T. (2006): “Assisting
Learners to Dynamically Adjust Learning Processes
through Software Agents” International Journal of
Intelligent Information Technologies, Vol. 2, No. 2
April-June, 2006, pp. 1-15.
Wooldridge, M. (1999): “Intelligent Agents” in Chapter 1
"Computational Organization Theory" by KM Carley
& L Gasser in "Multiagent Systems" Gerhard Weiss
(Ed) MIT Press – 1999
ICEIS 2007 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
328
