A NEW SYSTEM DESIGN TO ENHANCE LOCATION-BASED
SERVICES AND POSITIONING ACCURACY
S. Almasri and Z. Hunaiti
Faculty of Science and Technology,Anglia Ruskin University University, Bishop Hall, Chelmsford, United Kingdom
Keywords: Location Based Services (LBS), Global Positioning System (GPS), Geographical information science (GIS),
Signal in Space through the Internet (SISNeT).
Abstract: Location Based Services (LBS) provide resources and information depending on the user’s location. In This
paper three issues related to LBS as a pedestrian navigation system have been identified: the accuracy of
positioning, the volume size of data, and data presentation to the end user. Addressing these issues will
enhance the performance of the system. The proposed system allows the end users to access vital, accurate
and updated information based on their location. Since this location is not fully accurate, particularly in the
urban environments where users are most likely use this system, a new algorithm combines correction data
available from SISNeT can be utilised on the information received from Global Positioning System (GPS)
receiver to enhance the positioning accuracy. Moreover, to overcome the volume of data problem, a new
mechanism can be used to allow the users to load only the data of the town they are travelling to (Zone
based), and not the entire GIS database, depending on their user-profile (e.g. businessman, tourist, etc.). And
to overcome the problem that most of the users are facing (dealing with maps), an alternative technique can
be used which allows providing information in a form of photos, voice and short videos.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last few years, the mobile
communication technology has been developed
rapidly, and the speed of data transferring became
high. This made it possible to work on special
mobile information services such as Location-Based
services (LBS) in which the location of a user plays
a role in the information system (Kubber 2005).
The LBS systems combine the location
information of the user with intelligent application in
order to provide services (Brimicombe and Li,
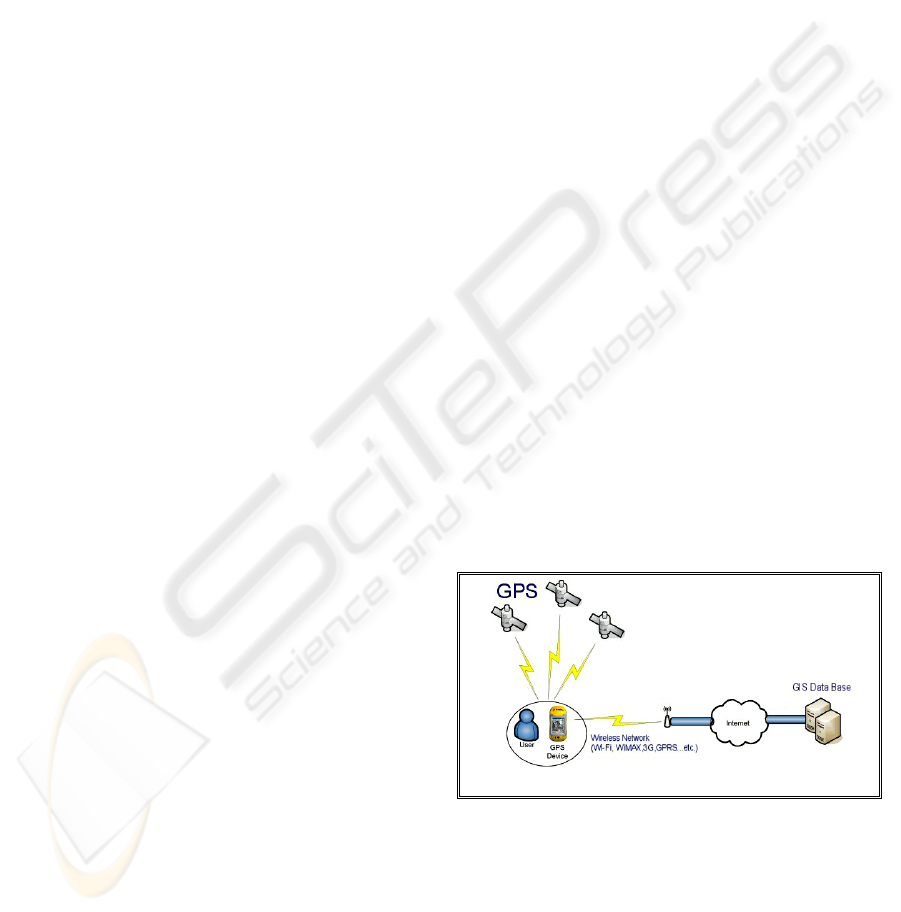
2006). As shown in Figure 1, typical LBS system
consists of Global Positioning System (GPS) and
Geographical Information System (GIS) connected
via wireless connection. The GIS is a computer
system for capturing, managing, integrating,
manipulating, analyzing, and displaying data which
is spatially referenced to Earth (Renault et al. 2005).
LBS systems suffer from several drawbacks,
firstly the obtained position from the GPS system is
not fully accurate particularly or reflection, in urban,
due to the blocking of satellite signals by buildings
(Monteiro et al. 2005). Secondly the size of
information (GIS maps, images, videos, etc.)
integrated in the database is huge comparing to the
users device memory (Brimicombe and Li, 2006).
And thirdly, the way data presented on the map is
not user-friendly, i.e. most of people cannot use it
(Ordnance Survey, 2006).
Figure 1: Location Based Services System.
This paper discusses new mechanisms and
possible solutions to tackle the early mentioned
problems. Also the paper incorporate a proposal for
new LBS system design, which is expected to bring
additive value to LBS application for pedestrians
navigation and mobile information systems.
192
Almasri S. and Hunaiti Z. (2007).
A NEW SYSTEM DESIGN TO ENHANCE LOCATION-BASED SERVICES AND POSITIONING ACCURACY.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on e-Business, pages 192-195
DOI: 10.5220/0002111601920195
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 LOCATION BASED SERVICES
(LBS)
LBS systems provide many services, such as
relevant maps, directions, points of interests (POI)
e.g. filling stations, cash machines, hospitals, shops,
clubs ...etc. The LBS systems are greatly useful in
case of emergency calls for police, fire-fighters or
ambulances (Kubber, 2005).
In order to use the LBS system the end user
needs a smart mobile device such as pocket PC or
Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) connected to the
Internet via wireless connection such as Wireless
Local Area Network (WLAN), or Universal Mobile
Telecommunication System (UMTS), in addition to
the GPS receiver itself which can be embedded with
the mobile device or the PDA. These integrated
systems combine good localization with pocket PC
features such as the wireless connectivity which
made it possible to keep the user of the LBS up to
date with any changes on the maps or the POIs
(Gartner, 2004).
As an overview of some of the most common
location-based services as identified by Urs
Hengartner, 2006:
- Navigation. Users can capture information
regarding their position directly to their POIs
using this service.
- Monitoring. With this service a user can receive
a warning message if a related user entered a
certain boundary. A good example of this would
be parents monitoring children or employers
tracking delivery of their goods or services.
- Nearby information. Includes services such as
places of interest, advertisements, weather and
traffic alerts related to the user’s current location.
- Friends finder. The users could use this service
to find out the current location of their friends.
- Nearby-friends alert. The user receives an alert if
a friend is nearby.
- Locate me. Informs a user of his current location.
This service might be useful for third parties to
know a user’s current location, which can be
beneficial while the user is travelling.
3 ISSUES WITH LBS
3.1 GPS Accuracy
The GPS is well-known to many people especially
the In-Car navigation system users. It uses 24
satellites orbiting the earth (Theiss, David and Yuan,
2005). One of its most common problems is the
inaccuracy within the urban environments (Theiss et
al. 2005). Nowadays, the differential technique
(DGPS) is used to make the positioning process
more accurate. If the essential number of satellites
available is not enough, then another source of
sensing is placed, but this can be applied only up to
100 Kilometres from the station (Monteiro et al.
2005). To overcome such problems, the Wide Area
DGPS was developed, the idea of this method is to
calculate the error from each satellite individually
and then to transmit it to mobile receivers through
geostationary satellites (Chen et al. 2003). A
European project called Signal in Space through the
Internet (SISNET) is utilised to provide access to the
European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service
(EGNOS) messages using the GSM/GPRS or any
other mobile internet connectivity method (Chen et
al. 2003). In the near future a new positioning
system will be lunched in the world called
GALILEO (Hunaiti et al. 2006), this new system
will use 30 satellites instead of 24, and this will
highly improve the positioning accuracy up to
centimetres.
The proposal is to establish a correction
algorithm inside the LBS server, which allows
performing the correction process locally by
comparing the GPS sentence which is received from
the client side with the SISNeT sentence which is
received from the internet (See figure 2), and send
the corrected location to the GIS Database
Management System (DBMS) to perform the user’s
query.
Figure 2: Correction Process.
There are number of advantages for such approach:
- It allows the users to use a nominal standalone
GPS receiver.
A NEW SYSTEM DESIGN TO ENHANCE LOCATION-BASED SERVICES AND POSITIONING ACCURACY
193
- It contributes in saving the power of the mobile
device, i.e. power required to perform the
correction in each device.
- It avoids the impacted delay caused by the
wireless communication link which might result
invalid correction data.
- It is much cheaper to purchase a non
sophisticated mobile device.
3.2 Size of GIS Database
The GIS database contains all the roads, buildings,
images, videos and other points of interest. The user
will be able to navigate, search, view and play so
many services according to his/her position; for
example when the end user pass in front of certain
shop, a popup will appear automatically on his
mobile, showing new prices or telling some news or
it may be a short video clip as advertisement. The
size of this information is so huge, and it needs a
very sophisticated mobile device to deal with. That’s
why the data is divided in a way to load only the
needed information into the user’s mobile system.
In order to overcome the volume size of
information which can be loaded to the user device,
the users are attached to many profiles, for example:
businessman, sports fan, etc (see Figure 3). This
customisation is going to help in loading only the
required information (Images, Videos, etc).
Figure 3: Categorising Data in GIS database.
Those profiles are organized inside the database
and connected with certain services and contents.
For example, the Tourist profile is connected to the
Directions service and to the Hall, Parks and
Stations Contents. This will save the size of memory
and the limitation of power at the client side of the
system.
3.3 Data Presenting
According to the recent surveys conducted by
Ordinance Survey, 66% of people cannot use the
map (Ordnance Survey, 2006). This paper proposes
new way of presenting information to the end user.
This system uses images, voice and short videos in
addition to the digital maps. This is going to help
people to find their way easily, quickly and with less
errors (see figure 4).
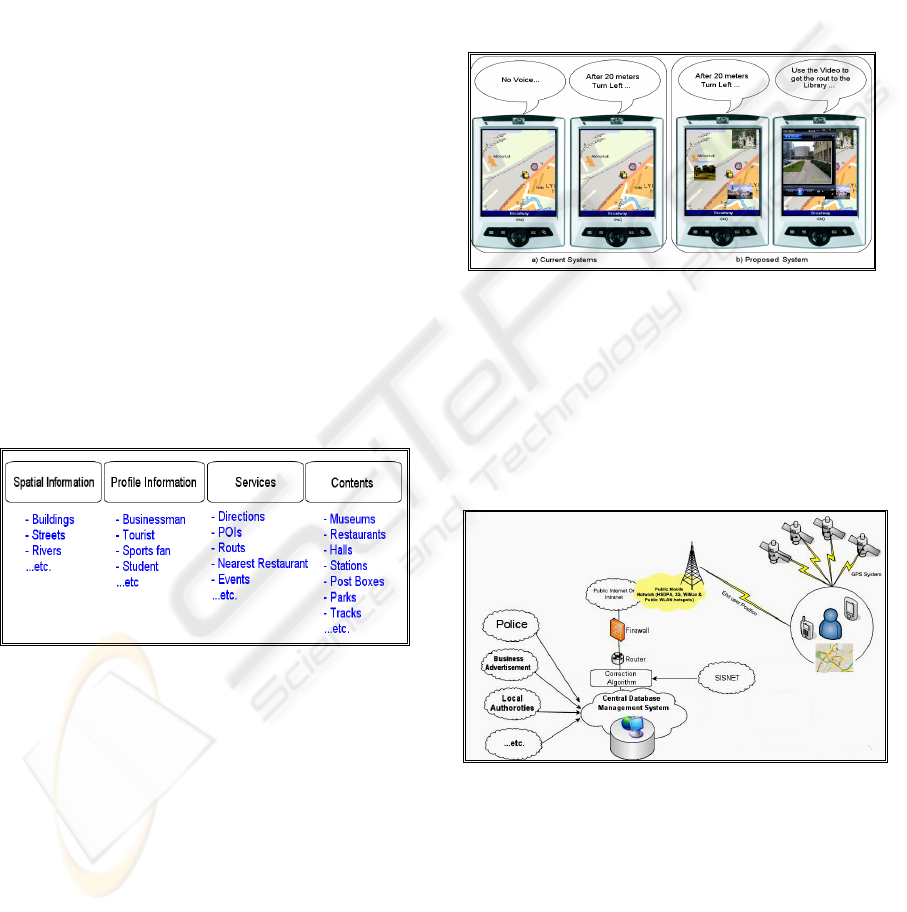
Figure 4-a: shows that the current systems use
only text, maps and voice. But Figure 4-b (Proposed
System) shows how the images and videos are
supporting the map, so the users can see the real
world on their mobile’s display. This information
should be always up-to-date in order not to make
any confusion. That’s why the user should be always
connected remotely to the GIS database.
Figure 4: Current and Proposed User Interface.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system architecture, as it can be
shown in figure 5, is an integration of three main
elements; Satellite navigation (namely GPS), GIS,
and mobile networks.
Figure 5: Proposed System Architecture.
The main functional user equipment is a mobile
device which can be in a form of pocket PC, PDA,
laptop…etc, with built-in GPS receiver and mobile
communication interface (3G, WLAN, …etc.) (Zola
and Barcelo, 2006). At the other side of system is
the Centralised database management system which
is acted as a central hub for all the mobile units
where a comprehensive database is stored. The
centralised server can be also linked with other
ICE-B 2007 - International Conference on e-Business
194

terminals (such as Police, Council …etc) in order to
provide continuous and updated information. In
addition, the centralised server will also perform a
correction process on the received location data, via
applying the correction data provided by other
systems such as SISNeT and OSNet (Chen et al.
2003).
The system is designed to operate as follows.
When the user travels with the mobile unit, the GPS
receiver fixes the position, while the mobile
communication link allows the transmission of the
users location information and the remote access to
the centralize database in the server. Based on the
received location information from the mobile unit,
the centralised server builds and provides the mobile
user with the essential information about that
specific area (Town), in such way, the mobile unit
will store only the information that the user need, for
example if a user is travelling from Colchester to
Chelmsford, at a certain location the system will ask
the user to load only the town of Chelmsford into his
mobile device. That will contribute in reducing the
power consumption of the mobile device by
avoiding loading unnecessary information and
minimizing the processing time required by any
searching query. Also it will contribute in the better
utilization of the mobile device memory and
bandwidth utilization.
Moreover, the proposed system can be integrated
with other systems in order to provide help for
people with disabilities such as the remote guidance
system for visually impaired pedestrians (Hunaiti et
al. 2006).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper focus was on three main issues associated
with LBS system; the GPS inaccuracy, the volume
size of data and the unfriendly data presentation
have been discussed along with possible solutions to
tackle them. Dealing with these issues will enhance
the overall performance of LBS systems, which has
been used as main base on the proposed system
presented in this paper. This system is to design a
pedestrian navigation system to overcome early
mentioned problems. This system uses SISNeT
correction information which is available through
the internet to overcome the first drawback and it
divides the information which is stored inside the
GIS database logically to overcome the second
drawback. And it supports the maps with images and
videos to enhance the way how to present data so as
to overcome the third drawback. In the next phase of
this research, a prototype of the system will be
implemented and evaluation will be carried out to
investigate and validate the new approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research work is supported by Intergraph Ltd,
the world’s pioneers of spatial information
management software, under Registered Research
Laboratory (RRL) program. Maps are supported by
Ordnance Survey. The authors wish to thank Mr
Ralph Diment (Intergraph UK) and Mr Chris Philips
(Ordnance Survey) for their help and support.
REFERENCES
Brimicombe A., Li Y., 2006, Mobile Space-Time
Envelopes for Location-Based Services, Transactions
in GIS, 10 (1), pp. 5-23.
Chen R., Toran-Marti F., Ventura-Traveset J., 2003,
Access to the EGNOS signal in space over mobile-IP,
GPS Solutions, 7 (1), pp. 16-22.
Hengartner U., 2006, Enhancing User Privacy in Location-
Based Services, Centre for Applied Cryptographic
Research (CACR 2006-27) Technical Report available
at URL http://www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/
techreports/2006/cacr2006-27.pdf [accessed on 20
December 2006].
Hunaiti Z., Garaj V, Balachandran W., 2006, A Remote
Vision Guidance System for Visually Impaired
Pedestrians, Journal of Navigation -
journals.cambridge.org, 59 (3).
Hunaiti Z., Rahman A., Denideni M., Balachandran W.,
2006, the Impact of Galileo on Pedestrians Navigation
Systems, Electronics, Communications and
Computers. CONIELECOMP 2006. 16th International
Conference.
Kubber A., 2005, Location Based Services, John Wiley
and Sons, ISBN: 0470092319.
Monteiro L., Moore T., Hill Ch., 2005, what is the
accuracy of DGPS? Journal of Navigation, Cambridge
University, 58, Issue , pp 207-225.
Ordnance Survey, 2006, Research Labs Annual Review
Renault S., Le Meur A., Meizel D., 2005 GPS/GIS
localization for management of vision referenced
navigation in urban environments, Intelligent
Transportation Systems, IEEE, pp. 608-613.
Theiss A., David C., Yuan C., 2005, Global Positioning
Systems: an analysis of applications, current
development and future implementations, Computer
Standards & Interfaces, 27 (2), pp 89-100.
Zola E., Barcelo F., 2006, the location of base stations for
a UMTS system, Journal of communication and
networks (J. commun. netw.) ISSN 1229-2370, 8 (1),
pp. 49-58.
A NEW SYSTEM DESIGN TO ENHANCE LOCATION-BASED SERVICES AND POSITIONING ACCURACY
195
