
AN ACCURATE ALGORITHM FOR AUTOMATIC STITCHING
IN ONE DIMENSION
Hitesh Ganjoo, Venkateswarlu Karnati, Pramod Kumar and Raju Gupta
Newgen Software Technologies Limited, A-6, Satsang Vihar Marg
Qutab Institutional Area, New Delhi – 110067, India
Keywords: SIFT, RANSAC, Blending, ANMS, GLOH, Probability Density Function and Image Registration.
Abstract: The paper addresses the issues in accuracy of various image-stitching algorithms used in the industry today
on different types of real-time images. Our paper proposes a stitching algorithm for stitching images in one
dimension. The most robust image stitching algorithms make use of feature descriptors to achieve
invariance to image zoom, rotation and exposure change. The use of invariant feature descriptors in image
matching and alignment makes them more accurate and reliable for a variety of images under different real-
time conditions. We assess the accuracy of one such industrial tool, [AUTOSTICH], for our dataset and its
underlying Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) descriptors. The tool’s performance is low in certain
scenarios. Our proposed automatic stitching process can be broadly divided into 3 stages: Feature Point
Extraction, Points Refinement, and Image Transformation & Blending. Our approach builds on the
underlying way a casual end-user captures images through cameras for panoramic image stitching. We have
tested the proposed approach on a variety of images and the results show that the algorithm performs well in
all scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
Algorithms for image stitching usually fall under
two categories – one that requires manual
intervention (semi-automatic) and second, fully
automated stitching. Whereas the former provides
high accuracy in all types of scenarios, the accuracy
of the latter heavily depends upon the ability to
match corresponding points between images. Image-
matching methods are broadly classified in two
categories: Direct and Feature-based. Feature-based
methods are invariant to image scale and rotation,
and are shown to provide robust matching across a
substantial range of affine distortion. The first work
in this area was by (Schmid and Mohr, 1997). Lowe
extended the approach to incorporate scale
invariance (Lowe, 2004). In comparative research
presented by (Mikolajczk and Schmid, 2003), the
SIFT method has shown superiority over classical
methods for interest point detection and matching. In
most of the tests, Gradient Location Orientation
Histogram (GLOH) obtained the best results, closely
followed by SIFT.
In our approach we iteratively used K-d trees
(Friedman et al., 1977) matching algorithm to
choose the best matches in the image pair. We then
used a match refinement approach, which uses the
slopes of the imaginary lines formed by joining the
corresponding feature points, if the two images are
stacked horizontally. Further, RANSAC (Fischler
and Bolles, 1981) was used to reject many false
matching points. The Probabilistic model (Matthew
Alun Brown, 2000; Lowe, 2004) is used for image-
match verification to distinguish correct image
match and incorrect image match based on the set of
inliers/outliers generated by RANSAC. The
sufficient and well-distributed matching points
selected through adaptive non-maximal suppression
(ANMS) are used for image transformation.
Projective transformation is suitable for our cases,
and gives better image-aligning results compared to
other transformation methods for chosen matching
points.
416
Ganjoo H., Karnati V., Kumar P. and Gupta R. (2007).
AN ACCURATE ALGORITHM FOR AUTOMATIC STITCHING IN ONE DIMENSION.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications - IFP/IA, pages 416-419
Copyright
c
SciTePress
2 PROBLEMS DURING IMAGE
STITCHING
We found the occurrence of many false matching
pairs in image matching. When used for image
registration, this produced undesirable results.
Further duplicate matches in one image result in
wrong transformation for the image .We tried
stitching our dataset images, shot under a variety of
conditions, using the demo version of AutoStitch.
AutoStitch failed to stitch images in some cases.
Information loss, such as number plate of the vehicle
happens during stitching. Such information might be
needed further. Alignment in a few results is
incorrect even in the presence of perfectly matching
points found through SIFT features.
3 OUR 3-STAGE APPROACH
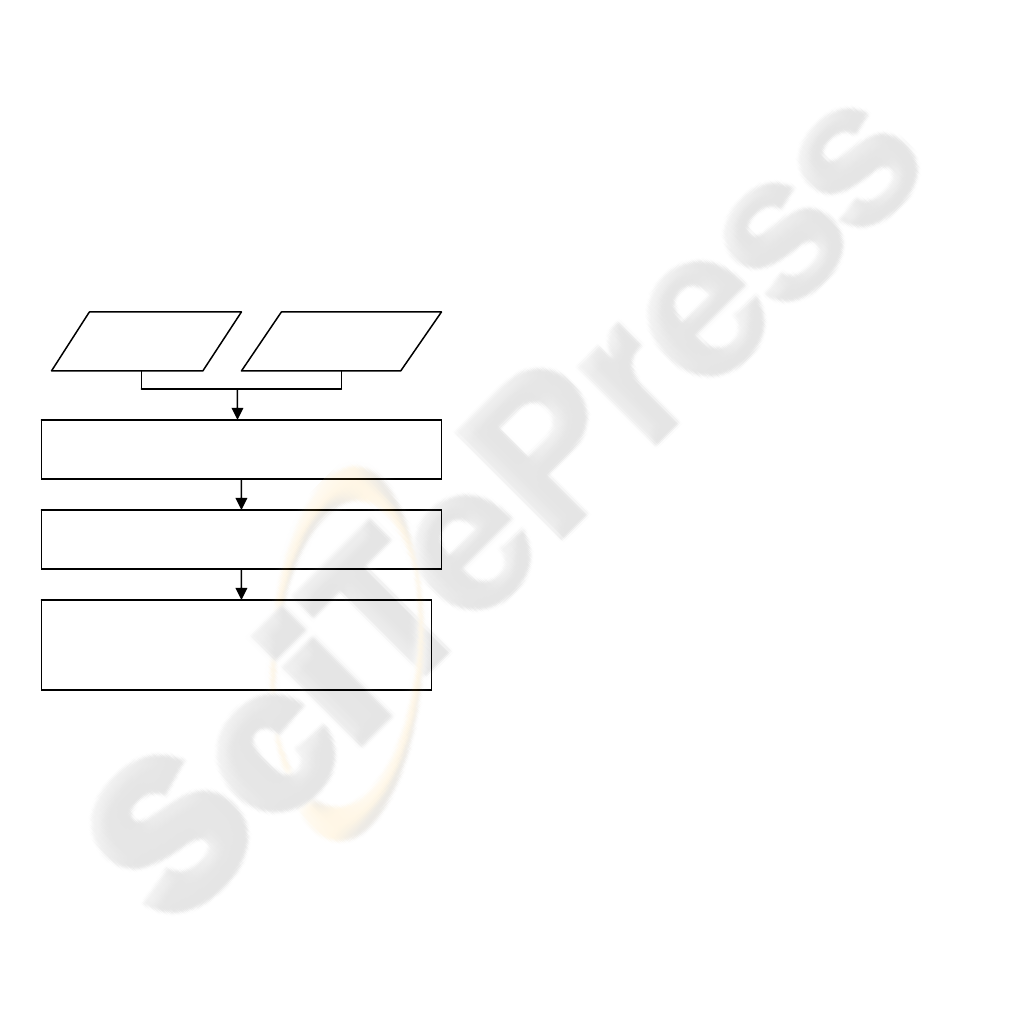
The following flowchart shows the overview of our
proposed approach.
Figure 1: Flow Chart of Our proposed three-stage
Automatic Stitching Process.
3.1 SIFT Features Matching
We extract the SIFT features from all the images and
use them for image matching and alignment (Lowe,
2004). In order to choose strong keypoints, we
consider the extrema in the local neighbourhood by
a threshold, which is determined as follows:
Threshold = 0.04 / S
(1)
where S is the number of scales in each octave of
the Difference of Gaussian Scale Space. We
iteratively change this value and obtain a sufficient
number of matching key points.
3.2 Refinement of Match-Points Using
Slope Orientation
The basis of this step lies in the way people shoot
panoramic images. It is rare for people to twist the
camera relative to the horizon. We analysed the
dataset extensively and found a high degree of
consistency regarding the shooting patterns. The
matches we arrived at after the feature-points-
matching stage still had false and/or duplicate
matches. We chose to refine these matches in order
to reject the false matches by exploiting the above-
mentioned heuristic.
The refinement approach was used to find the
primary match that would always be a correct match
of points between two images, and to find all other
matches, which agree with the primary match.
After we get 20 strongest matches from the
previous step, we plot these points on the two
images stacked horizontally, and draw imaginary
lines connecting the corresponding points.
For each match – Xmi corresponds to Xnj, where
ith feature in Xm image matches with jth feature in
Xn image, we calculated the slope of the imaginary
line formed by connecting the corresponding points.
Using all these slopes, we found the slope, M, such
that the sum of deviation of all the slopes from M is
minimum. Through extensive analysis on our
dataset, we found that this slope M always
corresponds to the correct matching points between
the images. We identified all other matching points
whose slopes were within a threshold of the slope
M. RANSAC has been added to filter false matching
points based on geometric property using the
RANSAC algorithm (Fischler and Bolles, 1981) It
has the advantage of being largely insensitive to
outliers, but fails if the outliers are more than 70-
75%.
3.3 Image Transformation
3.3.1 Adaptive Non-Maximal Suppression
(ANMS)
After getting correct matching points, the required
number of matching points for image transformation
is to be selected. Because for image-stitching
applications the area of overlap between a pair of
images is small (about 20% to 30%), the selected
matching points for image transformation should be
spatially well distributed over the image. This can be
Input
Ima
g
e 1
Input
Ima
g
e 2
SIFT feature extraction and feature matching using
Kd trees
Filtering of match points using Slope Refinement
a
pp
roach followed b
y
RANSAC for Inliers re
j
ection
ANMS for points to be used in Projective
transformation followed by Gradient Blending to get
the Stitched Image
AN ACCURATE ALGORITHM FOR AUTOMATIC IMAGE STITCHING IN ONE DIMENSION
417

done using ANMS to select a fixed number of
interest points from each image (Carneiro and
Jepson, 2003). Based on a maximum in the
neighbourhood of the radius r, desired number of
pixels are retained. Conceptually, we initialise the
radius to zero and then increase it gradually till the
desired number of interest points is obtained. These
points are obtained by taking one matching point
and suppressing other matching points within the
updated radius.
3.3.2 Projective Transformation
Affine transformation maps any coordinate system
in a plane to another coordinate system that can be
found from above projection. Under affine
transformation, parallel lines remain parallel and
straight lines remain straight. When we look at an
object at a finite distance in a plane from an arbitrary
direction, we get an additional "keystone" distortion
in the image. This is a projective transform, which
keeps straight lines straight but does not preserve the
angle between lines. This warping cannot be
described by a linear affine transformation.
Therefore, we have used projective transformation
for image aligning.
3.3.3 Gradient Blending Method
In the overlapped area, the image-blending
algorithm calculates the contribution of the new
image and the composite image at every pixel. A
look-up table is created for each new image. This
table contains the size and shape of the overlapped
area. This look-up table is normalized to define what
proportion of intensities of two overlapped regions is
used for generating the new composite image. One
value of the normalized look-up table can be
perceived as a weighing factor (α) at every pixel,
which is calculated as the distance from the image
edge as shown in the equation (2).
N(x, y) = α * I(x, y) + (1- α) * C(x, y) (2)
where C(x, y) is the composite image pixel
(before placing the new image), I(x, y) is the new
image pixel, and N(x, y) is the new composite image
pixel (with new image added).
4 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
Figure 2: (a) Left Image. Figure 2: (b) Right Image.
Figure 2: (c) Our Method Matching Points.
Figure 2: (d) Selected Matching through ANMS for image
transformation.
Figure 2: (e) Stitching Result by our method.
VISAPP 2007 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
418

Figure 2: (f) AutoStitch Result.
Figure 2 (f) shows the result of stitching of input
images, which are shown in figures 2 (a) & 2(b),
using AutoStitch. It shows the misalignment of the
input images at overlapping car portions of the
stitched image, which is shown in the figure 2 (f).
The result of our method is shown in the figure 2 (e),
which is perfectly aligned. We also observed that
there is a loss of information in another set of image
during image stitching for vehicle number plate. Our
results are robust for these types of losses due to
perfect alignment using good refinement methods to
select correct matching points for the image
transformation. We can also observe misalignment
in AutoStitch image-stitching results. This
misalignment is addressed properly in our approach
results.
Figure 3: Comparison of our approach versus Autostich.
5 CONCLUSION & FUTURE
SCOPE
We could stitch the images perfectly where
AutoStitch gives incorrect results such as wrong
alignment of images or loss of information during
image stitching. Also we could stitch images had a
small difference in the Depth Of Field view and
which could not be stitched by AutoStitch We
restricted ourselves to 1-D panoramic stitching
problem, though our approach can be extended to 2-
D stitching as future work.
REFERENCES
Brown and Lowe, D.G., 2002. Invariant features from
interest point groups. In Proceedings of the 13th
British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC02), pages
253–262.
Brown, M., and Lowe, D.G., 2003. Recognising
Panoramas. Proceedings of the 9th International
Conference on Computer Vision (IC0.CV), Vol. 2, pp.
1218-1225.
Carneiro, G., and Jepson, A., 2003. Multi-scale local
phase-based features. In Proceedings of the
International Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition (CVPR03), Vol. 99, pp.736–743.
Fischler, M. A., and Bolles, R. C. 1981. Random sample
consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with
applications to image analysis and automated
cartography. Communications of the ACM, Vol.24,
No.6, pp. 381–395.
Friedman, J.H., Bentley, J.L. and Finkel, R.A., 1977. An
algorithm for finding best matches in logarithmic
expected time. ACM Transactions on Mathematical
Software, Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 209-226.
Lowe, G., 2004. Distinctive image features from scale-
invariant keypoints. International Journal of
Computer Vision, Vol.60, No. 2, pp. 91–110.
Matthew Alun Brown, 2000. Multi-image Matching using
Invariant Features, Phd Thesis, The University Of
British Columbia, Canada.
Mikolajczk, K., and Schmid, C., 2003 A performance
evaluation of local descriptors. Proceedings of IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR), Vol. 2, pp. 257-264.
Schmid, C., and Mohr, R., 1997. Local gray value
invariants for image retrieval. IEEE Transactions on
Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 19,
No. 5, pp. 530-535.
Properly
stitched
Improper
stitching
Not s titched
at all
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
Comparison with AutoStitch
AutoStitch
Our Approach
Number Of Images
AN ACCURATE ALGORITHM FOR AUTOMATIC IMAGE STITCHING IN ONE DIMENSION
419
