
WEB KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR SMALL AND
MEDIUM-SIZE ENTERPRISES
WebTour: A Case Study From the Tourism Sector
María M. Abad-Grau
ViveGranada S.L.L. and department of Software Engineering, University of Granada, Granada, Spain
Francisco Araque
Department of Software Engineering, University of Jaén, Jaén, Spain
Rosana Montes, M. Visitación Hurtado, Miguel J. Hornos
Department of Software Engineering, University of Granada, Granada, Spain
Keywords: Value-Added Services, Web-Based Services, Web Knowledge Management, Decision Support System,
Data Warehousing, On-Line Analysis Processing.
Abstract: The current enterprise world has become global and complex. Knowledge management is a key to have a
competitive advantage as it allows detecting in advance customer trends and market evolution. While
knowledge management systems are usually unaffordable for small or even medium-size enterprises, a tool
to be shared between them is a more realistic solution. The system, based on client/server architecture with a
web interface, is able to provide top Information Technology (IT) solutions for a low cost so that small and
medium business can also use these systems to acquire competitive advantage. We have developed a
solution for a IT enterprise providing an on-line reservation system for small tourist lodgings and travel
agencies. It consists of a Data Warehouse (DW) and a Decision Support System (DSS) which is currently
being offered as a value-added service for providers and customers. The DSS is also used by the Acquisition
Component of a Knowledge Management System (KMS).
1 INTRODUCTION
Most of the Small and Medium-size Enterprises
(SMEs) cannot afford sophisticated information
systems for strategic decision making process. Even
the data cannot be organised in order to easily
accomplish queries from the point of view of
business executives. Therefore, DW, DSS and KBS
are not yet common systems in many SMEs. The
lack of strategic resources is currently one of the
main causes for these companies to loose
competitive advantage. Even worse, for very
dynamic business, large enterprises can take over
SMEs just because of the difference in the
development of software tools for strategical
purpose.
To face this problem, SMEs have basically two
solutions: (1) to create strategic alliances so that
costs for these systems to be developed can be
shared and (2) to choose a provider able to offer
knowledge management as a value-added service.
Both solutions are now more than never before
technically feasible. By using a web-enabling
implementation, they are also more affordable, and
easy to use.
In this work we introduce a practical solution for
small or medium-size business to share knowledge
management software, so that they can compete with
larger enterprises. These systems, which have been
called Web Knowledge Based System (KBS) or
Web KMS (Bartenstein et al., 2003), are based on a
DW and they are able to provide knowledge
management by using DSS and/or data mining tools
239
M. Abad-Grau M., Araque F., Montes R., Visitación Hurtado M. and J. Hornos M. (2006).
WEB KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZE ENTERPRISES - WebTour: A Case Study From the Tourism Sector.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - DISI, pages 239-244
DOI: 10.5220/0002487402390244
Copyright
c
SciTePress

through a client/server architecture with a web
interface. Opposite to just data warehousing, which
reduces the creation of massive data, a new step in
these systems includes development of tools for
these data to be interpreted and the opportunity for
the companies to create value from their intangible
assets. Information from several sources, such as
data bases, IT web pages, e-business, e-commerce,
on-line transactions, etc. is transformed into
knowledge to take full advantage of the current huge
amounts of data.
The solution that we present has already been
implemented and it is actually being offered to more
than 400 tourist SMEs, as a value-added service
provided by ViveGranada S.L.L., an on-line
reservation center for small tourist lodgings in
Spain. Other enterprises belonging to completely
different business sectors can make use of these
systems, either for IT enterprises to provide as a
value-added service to their customer SME or for
any SME to adopt as a solution to be shared among
other enterprises in the same branch. The global
connectivity provided by a web-based system allows
SMEs to establish strategic alliances with similar
enterprises that can reside in different countries and
have different markets, so that they are not
competitors. As an example belonging to the tourism
sector, SMEs providing lodging, as vacation rentals,
rural houses or small hotels can share costs if they
share not only an on-line reservation system but a
web KMS. If they provide lodgings from different
geographical points, they are not competitors but
strategic partners.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
contains an introduction to web KMSs. In Section 3
we describe in detail WebTour, the web KMS that
we have proposed to ViveGranada and that we have
already implemented, as a case study of how these
systems can be used for SMEs to achieve
competitive advantage. Moreover, a description of
the main subsystems to be used by SMEs, the
reservation Data Mart (DM) and the DSS, is
provided. Finally, the conclusions and future work
are given in Section 4.
2 WEB KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT
A Web Knowledge Management System refers to
the Knowledge Management that is accomplished by
using a client/server architecture and a web
interface, so that access from every Internet-access
point, no matter the operative system or the web
browser, is possible without software installation.
2.1 Knowledge Management
Knowledge management has different meanings
depending on the field. From an IT point of view,
the one in this paper, it refers to more advanced
systems than standard information systems able to
assist the enterprises to acquire knowledge from
information. In contrast, from the point of view of
the social and financial sciences, knowledge
management refers primarily to assessing, changing
and improving human individual skills and/or
behaviour (Sveiby, 2001).
Although knowledge management is a very wide
concept, all KMSs and the more specific Expert
Systems (Castillo et. al, 1997) have in common to be
made up of at least three components: the
Knowledge Base, in which data and rules are stored,
an Inference Mechanism, in order for the system to
produce new knowledge and an Acquisition
Component, to feed up the Knowledge Base.
In order to build reusable information systems,
able to share data and components, they can be
related in a layer architecture, in which a KMS will
be in the external layer while a Data Base
Management System (DBMS) will be in the core.
On top of the DBMS, in the second layer, a DW
models the data to corporate standard and fulfils the
reporting requirements or demands of decision
makers, ensuring that data to be used are clean and
consistent. The capabilities of DW to provide a large
amount of relevant and pre-calculated information,
together with the fact that Internet has grown to
become a major media for information diffusion in
any organization can have positive impacts on
decision performance. In the third layer we can have
models and analytical tools specifically designed in
order to assist in decision making, so that we will
have a DSS. A DSS is a computer program
application that analyses business data and presents
it so that users can make business decisions by using
knowledge automatically generated from it. Typical
information that a decision support application
might gather and present would be comparative sales
figures between one week and the next, projected
revenue figures based on new product sales
assumptions and the consequences of different
decision alternatives, given past experience in a
context that is described. A DSS may present
information graphically.
In the fourth layer there will be a Knowledge
Base, an Acquisition Component, used to add
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
240
knowledge to a Knowledge Base from the DSS and
an Inference Mechanism used in order to obtain new
knowledge upon the Knowledge Base, all of them
making up the KMS. The Acquisition Component
must be able to incorporate information to the
Knowledge Base each time an executive makes use
of the stored information for decision making.
2.2 Web Enabling Application
These applications are based on a client/server
architecture that describes two processes. The first is
the proactive client that sends requests to the server.
The server process is the reactive portion of the
system that does nothing but processes requests from
client. As we want a web-enabled KMS, we would
still have a client/server application. The Internet is
just a specific type of client/server implementation.
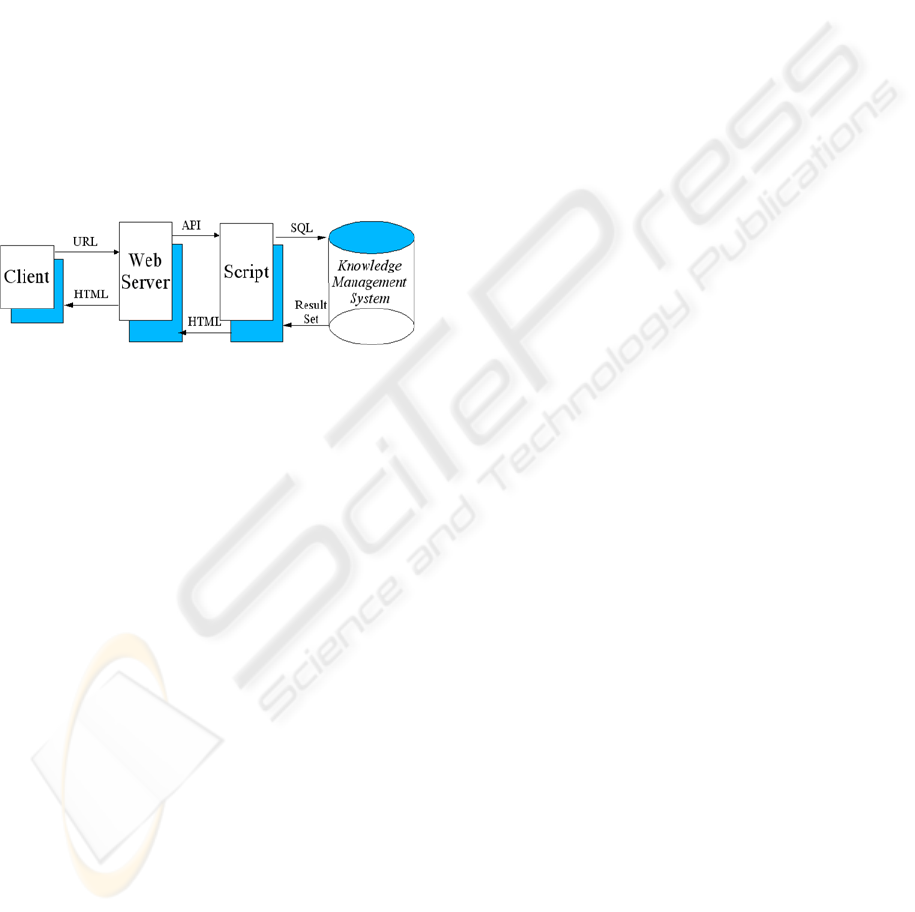
Figure 1: Web interface for a KMS.
Figure 1 shows the web interface for a KMS. The
browser is the presentation layer of the application.
Through it the user communicates with the Web
server. Since the Web server directly communicates
with the browser, the client system is invisible to the
application. Any client capable of supporting a
browser can access any Web-enabled client. The
strategist would click on the report icon that causes
the browser to send a URL (Uniform Resource
Locator) to the DW's Web server. The URL contains
the reference to a Common Gateway Interface (CGI)
to a script or computer program able to access the
data. Upon receiving the result, the web server
converts the report into HTML, which is passed to
the browser on the client.
By web-enabling the KBS we shift the
processing from the client to the server. The client
simply runs the browser. The processing of the data
is done back on the server. Also, the client's actual
hardware and software are invisible to the
application scripts.
Shifting the processing from the client to the
server has other important benefits. Most of them
translate into cost reduction, as a reduced
administration and maintenance or an easy
distribution of data. Others regard with the
willingness of a user to use specific software, as the
intuitive Graphical User Interface (GUI) that has the
web.
3 WEBTOUR: A WEB KMS FOR
TOURISM ENTERPRISES
We provide a case study of an IT company focused
on the tourist sector. Some specific solutions for this
sector have been proposed in order to integrate
different information systems (Kirkgöze & Tjoa,
1998) or to use a DW to help in the decision making
process (Haller et al., 2000). However, integral
solutions for this sector seem to be less frequent.
The enterprise, ViveGranada S.L.L., has developed
an on-line availability and reservation system of
lodgings owned by SMEs. Their providers, about
200 SMEs, benefit of an e-commerce system for a
low cost that can be used by travel agencies all over
the world or by end users. They provide also,
through an extranet, other e-business services,
including account and invoice management,
electronic fund transfer and a query system to obtain
information about reservations and payments.
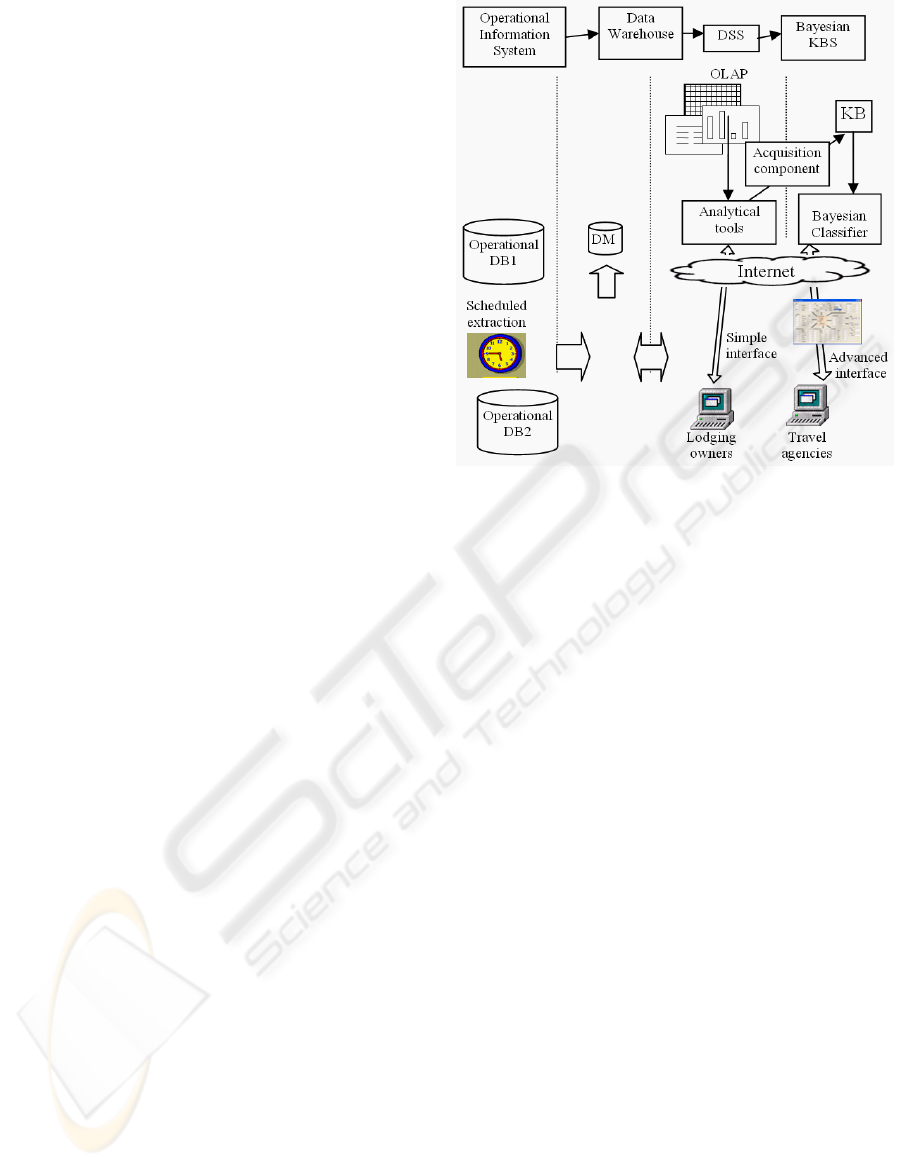
WebTour is a web KMS made up of several
subsystems interconnected as it is shown in Figure 2
and described in this section. ViveGranada offers to
their providers, the owners of tourist lodgings,
access to one of the DMs already implemented, a
DM focused on the reservation systems and to the
DSS. This is offered as a value-added service. Other
DMs, as human resources, suppliers and Customer
Relationship Management (CRM) are planned to be
developed in the next phase.
3.1 The DW
The advantages of using DW are a better knowledge
of the business, the possibility of improving the
service to customers, a better awareness of the
business risks, and an improvement of the business
processes, being able to make more tailor-made
products and services.
Inmon (2002) defined a DW as “a subject-
oriented, integrated, time-variant, non-volatile
collection of data in support of management’s
decision-making process.” A DW is a database that
stores a copy of operational data whose structure is
optimized for query and analysis. By definition, the
scope of a DW is the entire enterprise. Related to a
more reduced scope, a DM has to be used, which is a
highly focused DW and its scope is a single
WEB KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZE ENTERPRISES - WebTour: A Case Study
From the Tourism Sector
241
department or subject area. The DW and DMs are
usually implemented using relational databases
(Hammer et al., 1995), (Harinarayan et al., 1996)
defining multidimensional structures.
In a generic architecture of a DW (Chaudhuri &
Dayal, 1997), data sources include existing
operational databases and flat files (i.e., spreadsheets
or text files) in combination with external databases.
The data are extracted from the sources and then
loaded into the DW using various data loaders and
ETL (Extract, Transform and Load) tools (Araque &
Samos, 2003). The DW is then used to populate the
various subject (or process) oriented DMs and On-
Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) servers. DMs
are subsets of a DW categorized according to
functional areas depending on the domain (problem
area being addressed) and OLAP servers are
software tools that help a user to prepare data for
analysis, query processing, reporting and data
mining. The entire DW then forms an integrated
system that can support various reporting and
analysis requirements of the decision-making
function.
There are two approaches to build a DW. In the
first approach, stand-alone DMs assigned to
individual business units or processes are developed
and later integrated into an enterprise-wide DW. In
the second approach, a complete DW made up of
distributed DMs is built. These DMs are populated
with data either at the time of initial development or
at different stages depending on the availability of
time and resources (Inmon, 2002), (Kimball & Ross,
2002). The first approach is adopted by WebTour as
it fits with the scope of this research. However, in
the first phase of WebTour, already concluded, the
reservation DM has been the only one that was
developed.
The DW is built in MySQL, a relational database
with a web-based interface. The database, different
from the operational databases of ViveGranada, is
composed of 25 tables.
The DW extracts information on a daily basis
from two operational databases of ViveGranada, one
implemented with MySQL and the other being
implemented by a proprietary system. Extraction is
automatically done.
The main functionality of a Web-enabled DW
allows specialists to access specific data as a report
after querying the DW. Following the star schema of
the reservation DM, there are two types of tables in a
DM: the fact table and a set of dimension tables.
Figure 2: Architecture of WebTour.
The DM design essentially consists of three steps
as follows (Kimball & Ross, 2002):
1. Identifying facts and dimensions. Facts represent
quantitative (or factual) data about a business
entity, while dimensions contain descriptive data
that reflect the dimensions of that entity.
2. Designing fact and dimension tables. The
dimension tables are connected with the fact
table by foreign keys. As a result, a fact table
contains facts and foreign keys to the dimension
tables.
3. Designing DM schemas. The schema is a
database design containing the logic and showing
relationships between the data organized in
different tables (or relations). A DM is composed
of a central fact table and a set of surrounding
dimension tables.
The fact table is the reservation table, so that
each fact in this DM corresponds to a lodging
reservation. The application web interface includes
the possibility to query directly these tables to see
their contents. Also we can create and destroy
grouping conditions that define new entries.
Grouping conditions are stored in a GP-table (there
is one for each dimension table) which plays an
important role in the final report. The user must
specify a field of that table, a condition to be
imposed on the field and the name of the grouping.
As an example, the form to create a group can be
filled in order to create a group for those lodgings
that have swimming pool. The name of the new
group could be WithSwimmingPool and the group
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
242

condition is imposed on the Boolean field
Swimming Pool of dimension table Lodging.
The OLAP server is accessed by using scripts. In
a report only dimension tables and its associated GP-
tables can be used. Using a form, the user decides
which of them to choose. With a PHP script, the
HTML page will show a field list for the previous
tables so that the user can select the fields to include
in the report as well as the grouping condition.
3.2 The DSS and KMS
The use of new technology, such as Data
Warehousing, Decision Support Systems, Data
Mining, data integration, etc., has been proposed
previously in many fields, not only in tourism. Thus,
some applications of these technologies are, for
example: the use of DWs and Data Mining as a basis
for strategic decision in tourism (Kirkgöze & Tjoa,
1998); the integration of heterogeneous tourist
information data sources using a three-tier
architecture, consisting of a Data Source Adapter
Layer, a Mediation Layer and a Client Layer (Haller
et al., 2000); and the application of DW and
Decision Support System in Soaring site
recommendation (Araque et al., 2006).
The purpose of the DSS is to enable analysts to
easily extract information. The system has to
provide a way to analyse data depending on the user
profile. For experienced users with a clear idea of
the contents of the DM, the system allows them to
develop ‘ad hoc’ parametric queries. In contrast, for
novel users, the system provides a set of high-
interest predefined queries. There are also other
criteria affecting the type of queries that the system
allows. One of them regard with costs and it
includes mainly computational time — the allowable
time to run a query — and space — the total number
of information that can be returned from a query —
(Chau et al., 2002).
These two criteria have been taken into account
by the DSS of WebTour. While no restriction is
imposed to Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and
Chief Information Officer (CIO) of ViveGranada,
for all other staff and the providers only predefined
queries to the DSS with a limited quantity of time
and information to be displayed are allowed.
Figure 3 shows the DSS form to develop
parametric queries. A graphical report given by the
WebTour DSS is shown in Figure 4. It corresponds
to a query about the average number of individual
per reservation, considering the origin country of the
travel agency that made the reservation and the
location (province) of the tourist lodging.
In addition, the user interface for the DSS of
WebTour has been designed to provide end users
with a comfortable and easy to use environment
.
One of the most important attractions of this
interface is its ability to make dynamically queries,
to aggregate and analyse data, and to present and
visualise results.
Once a DSS returns a report to a query, the
Acquisition Component of the KMS receives also
the information and the executive must select the
output variable representing the decision making
process s/he is working on. The KBS is a
probabilistic one (Castillo et. al, 1997) as it uses a
Bayesian network instead of rules in the Knowledge
Base. For each type of decision, i.e. for each class or
output variable, a new Bayesian classifier will be
created. The Inference Mechanism will allow the
user to decide if a feature selection mechanism is
required and to choose among different architectures
for Bayesian classifiers. Accuracy in knowledge
acquisition has been probed for different Bayesian
classifiers in order to decide relationships between
Operation Strategy and Flexibility in engineering
consulting firms (Abad-Grau & Arias-Aranda,
2006).
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
We have proposed the use of shared web KMS as an
affordable way to provide knowledge management
for SMEs, by means of strategic alliances or as a
value-added service provided by IT providers.
As future work, we plan to use other data mining
engines in order for the Acquisition Component to
directly obtain information from the DW. In
addition, we plan to investigate methods to
incorporate more sources of information into a DW
as XML or other semi-structured sources. While it is
getting more common to find web sites which output
information from their databases in XML code for
consumption by a variety of agents or applications,
to read XML documents and to integrate that
information into databases is not a trivial task.
WEB KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZE ENTERPRISES - WebTour: A Case Study
From the Tourism Sector
243
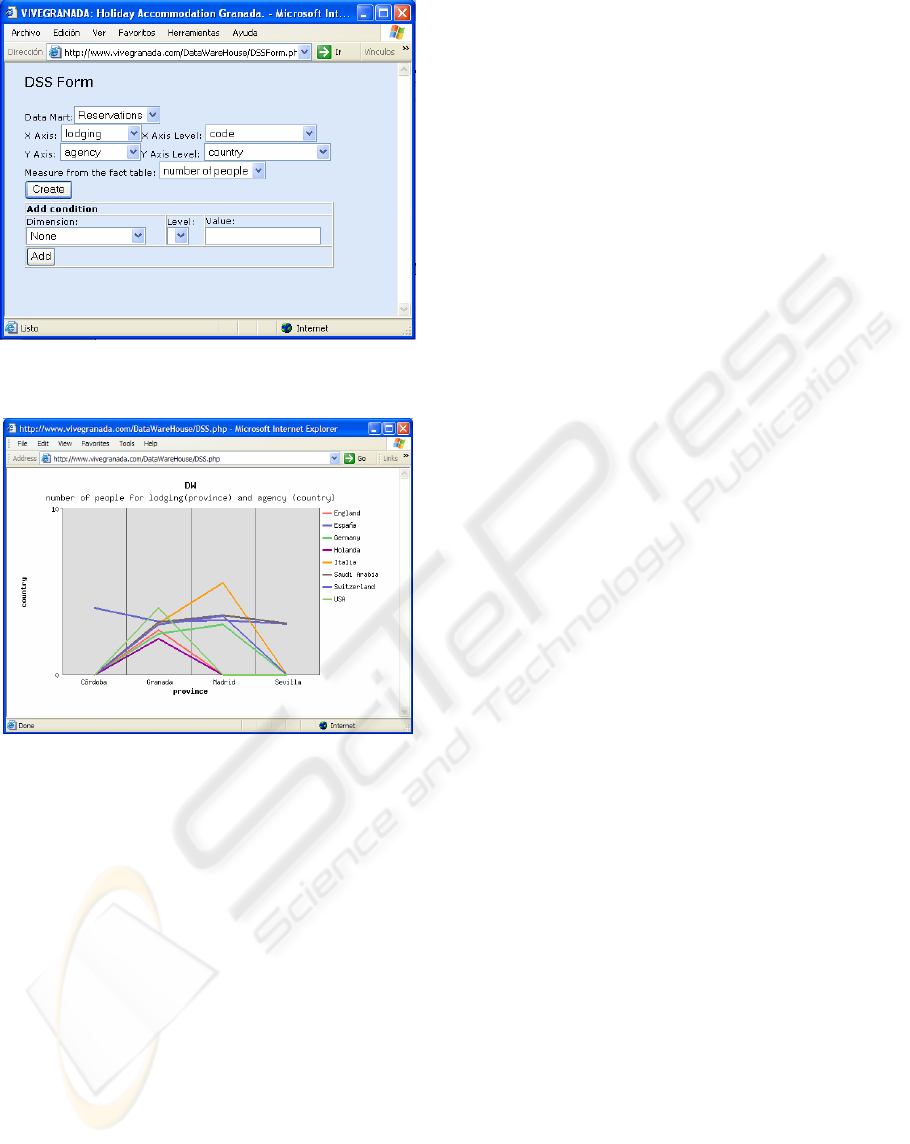
Figure 3: A DSS form for a parametric query of the KMS
WebTour.
Figure 4: Plot returned by the DSS system for the
parametric query in Figure 3.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported by the Spanish
CICYT projects TIN2005-09098-C05-03 (research
program PRONTIN), TIN2004-08000-C03-02
(research program AMENITIES), TIN2004-07672-
C03-02 and the travel agency ViveGranada S.L.L.
REFERENCES
Abad-Grau, M. M. and Arias-Aranda D. (2006).
Operations Strategy and Flexibility: modeling with
Bayesian classifiers. Industrial Management and Data
System. To appear.
Araque, F. and Samos, J. (2003). Data warehouse
refreshment maintaining temporal consistency. 5th
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems, ICEIS´03. Angers. France.
Araque, F., Salguero, A. and Abad-Grau, M. M. (2006).
Application of data warehouse and Decision Support
System in Soaring site recommendation. Proceedings
of the Thirteenth Conference on Information and
Communication Technologies in Tourism, ENTER
2006, M. Hitz, M. Sigala and J. Murphy (eds.), Wien-
NewYork: Springer-Verlag Computer Science, pp.
308-319.
Bartenstein, O., Geske, U., Hannebauer, M. and Yoshie,
O. (2003). Web Knowledge Management and Decision
Support, Springer.
Castillo, E., Gutiérrez, J. M. and Hadi, A. S. (1997) Expert
Systems and Probabilistic Networks Models, Springer
Verlag.
Chau, K. W., Cao, Y., Anson, M. and Zhang, J. (2002).
Application of data warehouse and Decision Support
System in construction management, Elsevier.
Chaudhuri, S. and Dayal, U. (1997). OLAP technology
and data warehousing, ACM SIGMOD Records.
Hewlett-Packard Labs, Vol 26, 1, March.
Haller, M., Pröll, B., Retschitzegger, W., Tjoa, A. M. and
Wagner, R. R. (2000). Integrating Heterogeneous
Tourism Information in TIScover - The MIRO-Web
Approach. Proceedings Information and
Communication Technologies in Tourism, ENTER
2000. Barcelona, Springer Verlag, pp. 71-80.
Hammer, J., García-Molina, H., Widom, J., Labio, W. and
Zhuge, Y. (1995). The Stanford Data Warehousing
Project. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, June.
Harinarayan, V., Rajaraman, A. and Ullman, J. (1996).
Implementing Data Cubes Efficiently. Proc. of ACM
SIGMOD Conference. Montreal, Vol 25, 2, pp 205-
216.
Inmon, W. H. (2002). Building the Data Warehouse. John
Wiley.
Kimball, R. and Ross, M. (2002). The Data Warehouse
Toolkit: The Complete Guide To Dimensional
Modeling. John Wiley, 2nd Edition.
Kirkgöze, R. and Tjoa, A. M. (1998). The Use of Data
Warehouses as a Basis for Strategic Decision in
Tourism. Proc. Information and Communication
Technologies in Tourism, ENTER 98. Springer Verlag,
pp. 162-169.
Sveiby, K.E. (2001). A knowledge-based theory of the
firm to guide strategy formulation, Journal of
Intellectual Capital, 2, 344-258.
ICEIS 2006 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
244
