
SIMILARITY MEASURES FOR SKILL-PROFILE MATCHING IN
ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
Ernst Biesalski
DaimlerChrysler AG, Plant Wörth, Daimlerstrasse 1, D-76742 Wörth, Germany
Andreas Abecker
FZI Research Center for Information Technologies at the University of Karlsruhe, 76131 Karlsruhe, Germany
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Ontology, Skill Management.
Abstract: At DaimlerChrysler’s truck plant in Wörth, we are currently implementing a comprehensive IT solution for
integrated and synergistic processes in personnel development. In this paper, we sketch some ontology-
based software modules – as well as their interdependencies and synergies – which support streamlined and
integrated, comprehensive personnel-development processes. A central element in the software architecture
is ontology-based similarity assessment for skill-profile matching which is exemplarily discussed for
software-supported project staffing.
1 MOTIVATION
In the coming 10 years, Human Resource
Management (HRM) departments in large
companies in Germany and most parts of Europe
will face radically new challenges and tasks.
Already today, demographic studies and prognoses
show clearly, that in the long-term, the number of
young people will significantly decrease (Federal
Statistical Office Germany, 2003). Even with a
realistically estimated amount of immigration, the
share of citizen under 20 years will reduce from 20%
(2001) to 16% (2050) of the overall population
while the share of people above 60 years increases
from about 25% to about 33%. Consequently, the
working population will run through a continuous
aging process (in the average), and from ca. 2015
on, the number of persons available for employment
will more and more run short. Under such
conditions, a coordinated, long-term personnel
development strategy gains increasing importance.
Such a strategic personnel development must be part
of a comprehensive HRM strategy which should in
turn be embedded into an overall, holistic
Knowledge Management (KM) approach (Biesalski;
Abecker, 2005).
From the IT point of view, HRM departments
mainly use IT applications for the management of
personnel data (standing data, performance reviews),
for junior employee development, or for training
planning, seldom also for assessment of training
needs. Real-world system landscapes are often
characterized by manifold heterogeneous systems,
evolved over time, showing pretty non-uniform
features – which hinders interoperability of those
applications. Further problems come from massively
redundant data storage, as well as complex
interfaces between systems. Since such system
landscapes are typically a combination of standard
software and proprietary developments of the HR
software department, they seldom support an
integrated personnel development approach, i.e., a
coordinated behaviour of different applications.
Modern views on knowledge and skills of
employees are normally not realized. The purpose of
such systems is to manage the single employee, not
to model and manage an integrated view on
employee, tasks and organizational context.
At DaimlerChrysler’s truck plant in Wörth, we
are currently developing such an integrated system
and process landscape. In Section 2, we sketch the
respective software architecture. In Section 3, we
focus on one module of the system, designed for
supporting project staffing. At the hand of this
example, we discuss in more detail the ontology-
based matching of skill profiles – which is a central
functionality also for the other modules. Finally, in
11
Biesalski E. and Abecker A. (2006).
SIMILARITY MEASURES FOR SKILL-PROFILE MATCHING IN ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 11-16
DOI: 10.5220/0002462700110016
Copyright
c
SciTePress
Section 4, we briefly summarize, sketch some
related work and report on the current
implementation status of the system.
2 AN APPLICATION
FRAME-WORK FOR
PERSONNEL DEVELOPMENT
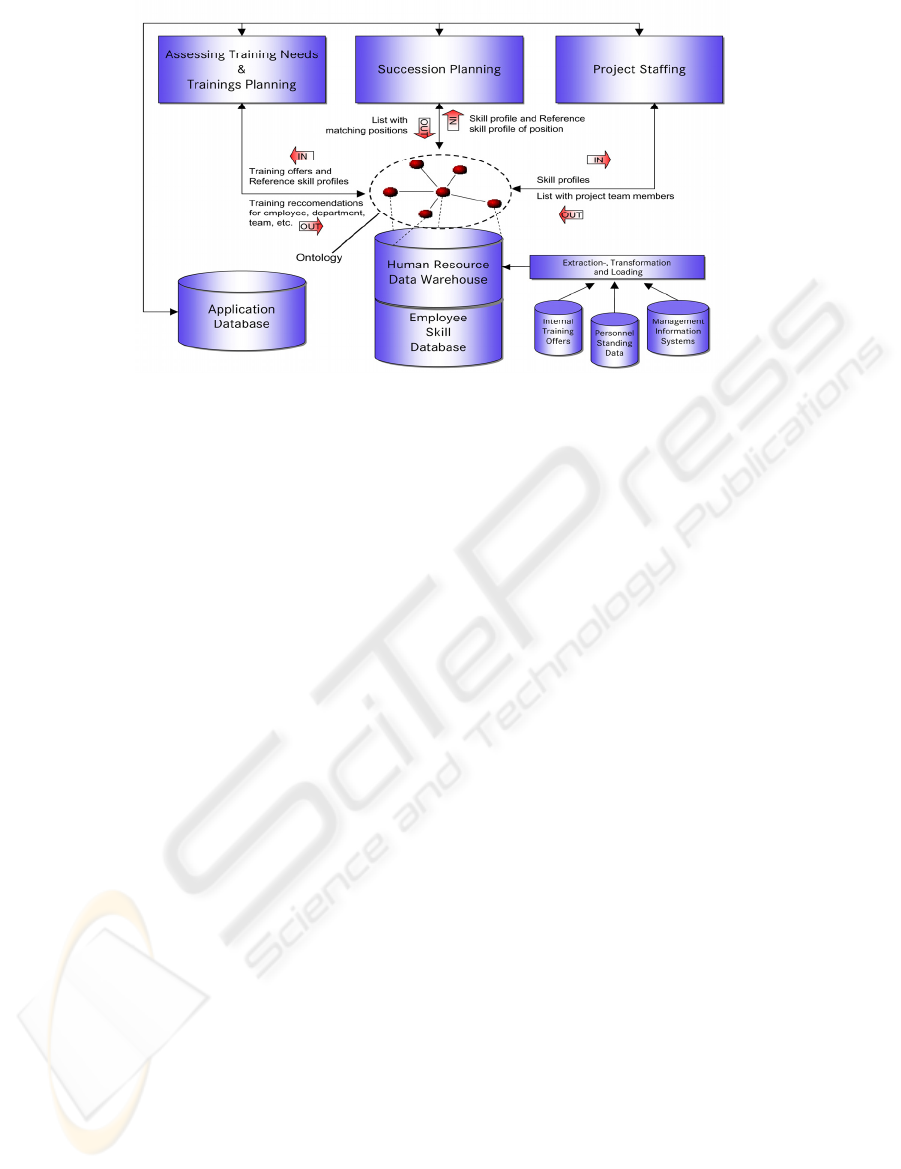
We propose an integrated software and process
framework for personnel development (PD
Framework) as depicted in Figure 1. It contains
business processes for personnel development
(Biesalski; Abecker, 2005a), a Human Resource
Data Warehouse (HR DWh) which integrates data
from different legacy systems, an ontology-based
employee-skill database, as well as different new
application modules.
In this article, we focus on the application
module for project staffing. A core idea of this and
all the other modules is the ontology-based
modelling of employees’ skill profiles. This is based
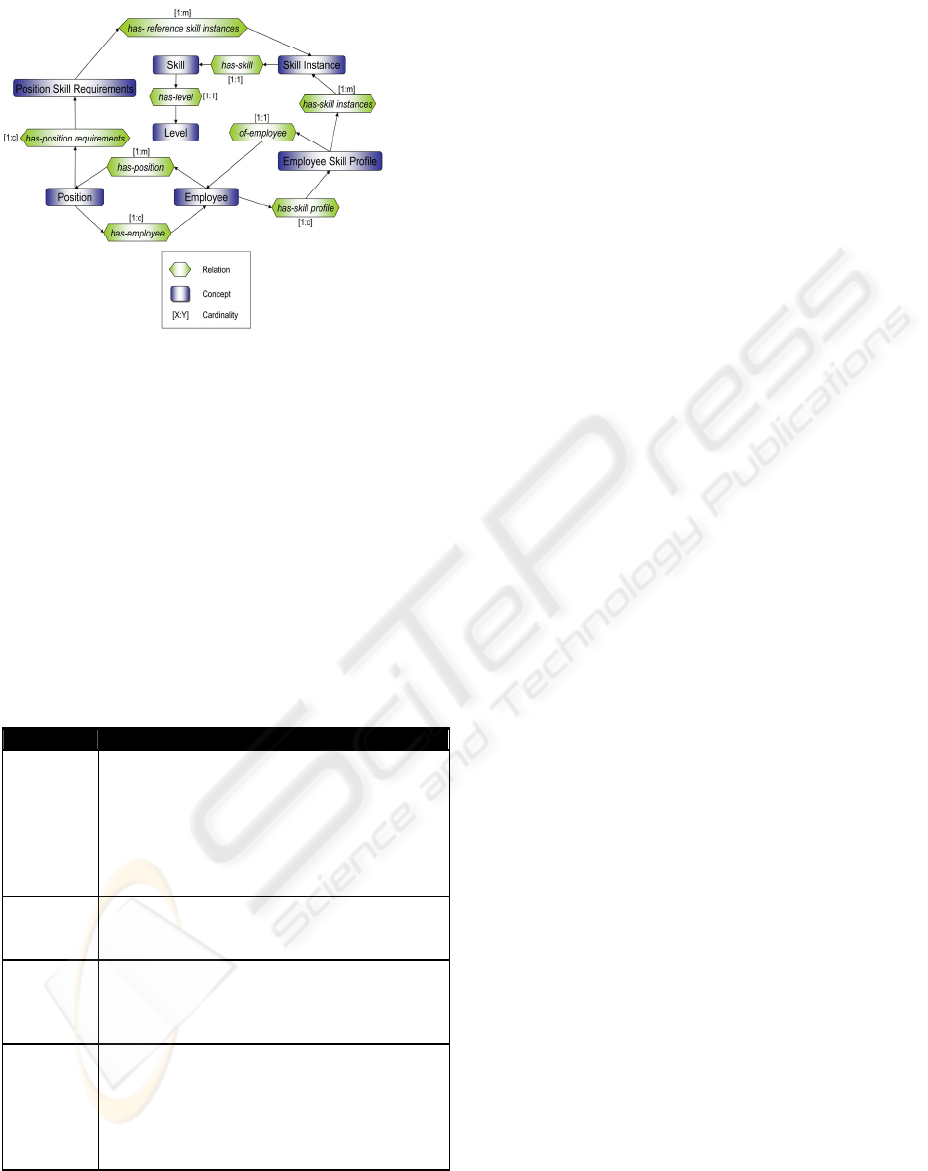
upon an ontology which formalizes the former skill
catalogue that describes all different personal skills
occurring or required in the company (cp. Figure 2).
Each software module employs an ontology-based
matching procedure which is able to compare skill
profiles (i.e. bundles of skills which characterize an
employees’ knowledge, skills, and qualifications, or,
the competences required for a specific job,
respectively). For the “Succession Planning”
module, this means to compare the to-be skill profile
of an open position with the as-is profiles of a
number of employees – in order to find out the most
suited candidate. To this end, we compare bundles
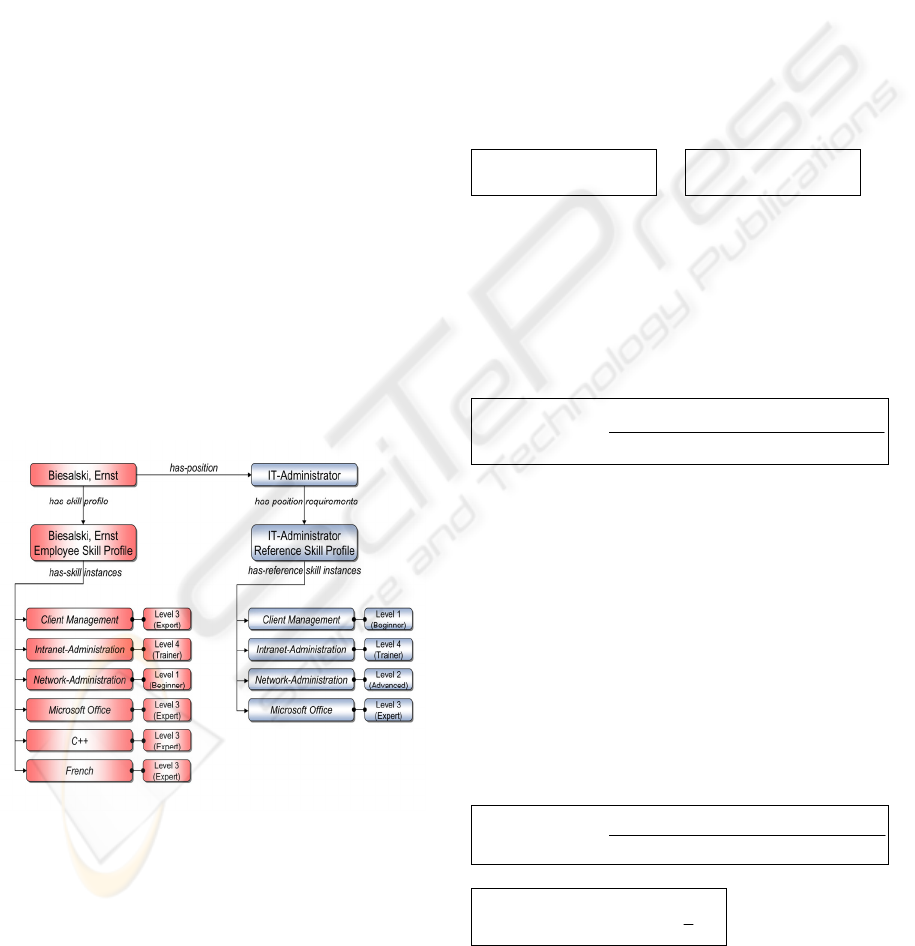
of ontology instances, as indicated in Figure 3.
In the same manner, in the module “Detection of
training needs / Training planning”, we compare
competence profile of jobs with the as-is profile of
employee in order to identify qualification gaps.
Such a comparison can also regard strategic
directions, e.g. of the department, thus leading to a
training planning and behaviour which is closer to
the company’s overall strategic needs. When having
identified strategic training gaps, they can be
compared with training offers, and suggestions for
filling gaps can be made, also regarding time
restrictions of employees, budget restrictions, etc.
Such suggestions can then be offered by the
department manager to the employees. In the
module “Project and job staffing”, the matching
procedure searches best available employees for
vacancies in project teams, based upon matching
between to-be (project / job requirements) and as-is
(personal profile) comparisons.
3 THE MODULE: PROJECT
STAFFING
In industrial practice, open jobs are seldom staffed
along a structured procedure. Personal networks and
preferences often play the major role. Of course, this
guarantees neither a fast nor an optimized result, in
particular when staffing a large project team with a
number of heterogeneous required skills and
competencies. Since large enterprise usually have
electronic data about the competences and
experience of their employees, a (partial) automation
seems feasible and desirable.
In order to support project staffing, we need on
one hand position skill requirements and on the
other hand employees’ skill profiles. We want to
find – with a minimum staffing effort – the best
Figure 1: Overall Perspective - Personnel Development Software Framework.
ICEIS 2006 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
12
suited employees who fulfil the position skill
requirements as well as other constraints, such as
availability. For integrating project staffing into a
comprehensive HRM approach, we particularly need
the standardized skill catalogue which allows for a
unified semantic description of position skill
requirements and employee skill profiles, and a
skill-matching procedure. For addressing these
issues, we adopted the approach of (Hefke;
Stojanović, 2004), introduced a comprehensive
ontology-based skill catalogue at DaimlerChrysler
plant Wörth / Rhine, as well as ontology-based
similarity measures for profile matching.
Table 1: Some Central Concepts of the Skill Ontology.
Concept Description
Skill The ability to produce solutions in some
problem domain. In Enterprise Skill
Management, the identified, named, trainable
competence of some employee, often
required to perform a specific organizational
task (well), to fill a position, or to enact an
organizational role.
Weight Achieved or required level of expertise
which indicates to which extent the given
competence is or shall be mastered.
Skill
instance
A skill together with a level of expertise
(e.g., “expert in C++ programming”,
“beginner in English”). As a unit of reference
only needed for internal technical reasons.
Skill
Profile
A list of skill instances. As an employee skill
profile describing as-is situation regarding an
individual’s personal qualifications, as
position skill requirements describing
necessary qualifications to do a job
successfully.
3.1 Ontology Based Skill Modelling
In general, a skill catalogue contains skills relevant
for the company. In a structured skill catalogue, the
skills can be equipped with a weight, describing the
achieved level of expertise. In the DaimlerChrysler
Wörth case, about 700 single skills have been
modeled. For an employee, a personal skill profile
lists his or her actual skills, together with weights for
the achieved level of expertise. A profile for position
skill requirements is a list of weighted skills which
are important for successfully doing the required
tasks in a given position (here the weight expresses
the relevance of having achieved the specified level
of expertise). Both profiles refer to the same, unified
vocabulary specified in the skill catalogue (cp.
Figure 2 and Table 1).
3.2 Project Staffing with Ontology
Based Similarity Measures
As an efficient and expressive data structure for
processing skill profiles, we use an ontology-based
approach (Staab; Studer, 2004) which stores,
manages, and compares profiles with the help of the
KAON (Mädche; Motik; Stojanović, 2003) ontology
management framework. For supporting the
selection of qualified employees, our „project
staffing“ module is a web-based tool which allows
to define project-specific position skill requirements
and – based upon those – gives dedicated project
staffing advice. To this end, decision-supporting
information is taken into account from sources such
as employee-skill profiles, job catalog, time
recording system, etc. Since a multitude of
perspectives must be fed into the complex employee
selection process, the matching procedure which
compares job profiles and potential candidates’
profiles should be capable of semantically assessing
the similarity of ontology instances. For realizing
such a candidate selection procedure, we employed
the similarity framework introduced in (Ehrig;
Haase; Stojanović; Hefke, 2004). However, while
(Ehrig; Haase; Stojanović; Hefke, 2004) focus on
text-dominated application areas (comparison of
vocabularies and terminologies), the comparison of
skill profiles requires more advanced combination
and expression means for similarity measures. So,
we extended the framework such that the user can be
provided with different metrics for assessing a
candidates’ suitability for a given job profile. Our
requirements analysis and analysis of existing HRM
systems showed that different similarity metrics for
Figure 2: Top-Level Structure of Skill Ontology
(simplified).
SIMILARITY MEASURES FOR SKILL-PROFILE MATCHING IN ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
13
profile comparison should be used to express
different aspects relevant for different tasks. For
project staffing, an aggregated metric is used which
combines the following four aspects:
• Direct skill comparison: we require an
exact match of as-is and to-be. So we can
specify K.O. criteria for the central
requirements, especially in strategically
important jobs.
• Proportional similarity: we identify also
partially fulfilled requirements. This is also
important if we can plan for additional
teaching and qualification measures or for
“training on the project”.
• Compensatory similarity: we identify not
only partially fulfilled requirements, but also
overqualifications; so, additional expertise
on one hand may compensate deficiencies on
the other hand. If several employees fulfil the
K.O. criteria, this can be useful to find the
most suited one.
• Taxonomic similarity: the taxonomic
structure of the skill ontology is taken into
account to find “close matches” in the case
that no employee has exactly the required
qualifications. Also usable for deciding
between several candidates, and for refining
profile specifications.
Figure 3: Example: Part of Ontology-based Employee-
Competence Database.
Let us now discuss these similarity measures in
some more detail.
3.3 Similarity Measures for Skill
Profiles
The basis of our skill-profile matching is the
mapping of all competence metrics to a four-level
scale (beginner, advanced, expert, teacher).
Comparison of skill profiles is reduced to the
comparison of skill instances. Let:
• R be a profile for some position-skill
requirements consisting of a non-empty list
of skill instances r with skill name rs and
expertise level rl, and
• E be an employee-skill profile consisting of a
list of skill instances e with skill name es and
expertise level el
()
⎩
⎨
⎧
=
=
else ,0
esrs if , 1
:,
name skill
ersim
()
⎩
⎨
⎧
=
=
else0,
elrl if 1,
:,
level skill
ersim
3.3.1 Direct Skill Comparison
Often we want to specify special skill instances as
K.O. criteria. This requires an extension of our skill
modelling. Then we can define the direct skill
comparison metrics for a position skill requirements
profile R and an employee skill profile E as follows:
()
∑
∑
∈
∈∈
∗
=
Rr
EeRr
ameskilskilllevel
rweight
ersimersimrweight
ERsim
)(
),(*),()(
:,
,
ln
comparisondirect
3.3.2 Proportional Similarity
The idea of direct comparison leads to the effect that
each underfulfillment of a skill requirement finally
results in a complete disqualification of the
respective employee. It does not allow to assess the
possibly differing extent to which the requirements
where not fulfilled (only marginal deficiencies
versus complete misqualification). In reality, project
leaders need a metrics which is suited to assess
partial fulfillment of requirements in an appropriate
manner. To this end, we define the proportional
similarity:
()
∑
∑
∈
∈∈
−
∗
=
Rr
EeRr
levelalproportion
rweight
ersimersimrweight
ERsim
)(
),(*),()(
:,
,
name skill
similarity-alproportion
with:
()
()
else ,
4
1
elrl-1
el rl if 1
:,
level-alproportion
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎨
⎧
∗−
≤
=ersim
ICEIS 2006 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
14
3.3.3 Compensatory Similarity
Proportional similarity is an extension of the
compensatory similarity which addresses not only
under-, but also overqualifications. These can be
especially valuable when several candidates have
fully satisfied the requirements of the other
similarity measures and cannot yet further be
distinguished.
()
∑
∑
∈
∈∈
−
∗
=
Ss
EeRr
levelrycompensato
sweight
ersimersimrweight
ERsim
)(
),(*),()(
:,
,
name skill
similarity-rycompensato
with:
() ( )
4
1
el rl-1:,
level-rycompensato
∗−=ersim
This metrics must be interpreted differently from
the other two presented before. In contrast to the
situation with an exact match or a proportional
similarity, a “1” is here not anymore an indicator
that all requirements are fulfilled completely.
Instead, overqualifications in some skill-profile
facets may compensate for underqualifications in
other facets.
3.3.4 Taxonomic Similarity
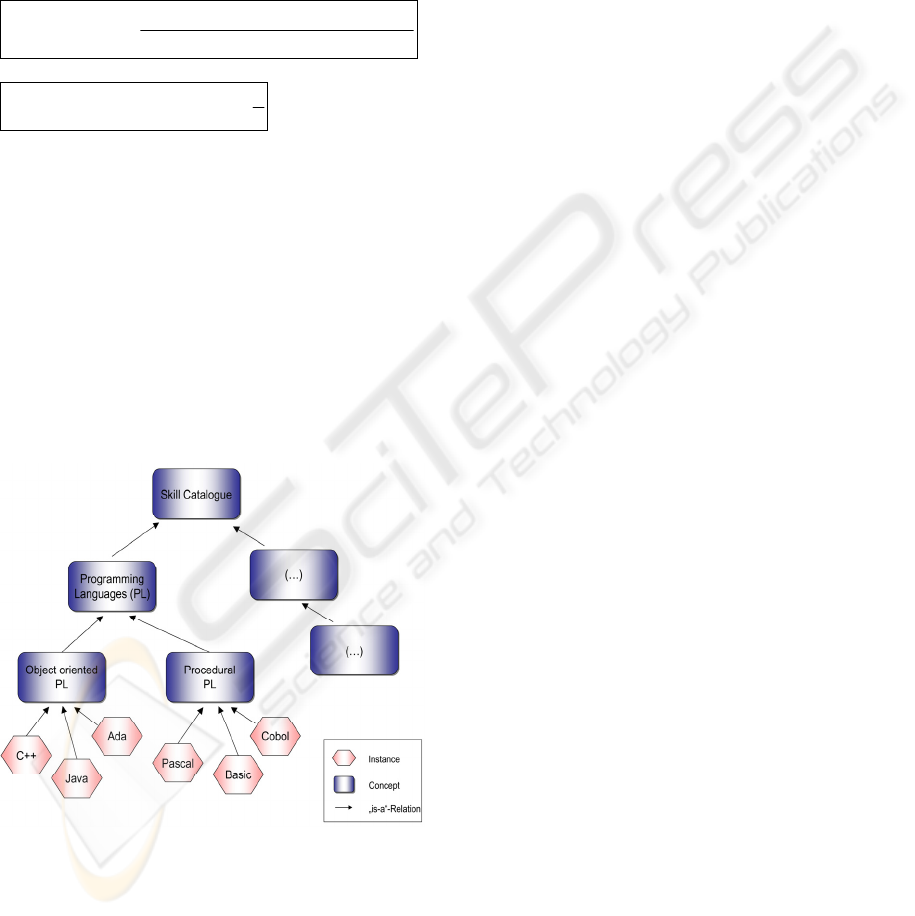
It is often difficult to find employees which fit
relatively exact into a given profile specification.
Figure 4: Example Taxonomic Similarity.
This comes also from the fact that it is not always
trivial to specify the expected requirements
unequivocally if there are different possible opinions
how to characterize the required profile in terms of a
complex skill catalogue which might provide many,
slightly different, but related skills in a certain
competence area. For instance, knowledge about
„Spreadsheet software“ might also be proven by a
certificate about using „Microsoft Excel“.
Depending on the perspective, profile models may
differ, both when employees describe themselves,
and when project leaders define a required skill
profile.
Taxonomic similarity can be derived from
semantic cotopy of two ontology instances. Figure 4
gives an example as a small excerpt from a
hypothetical skill catalogue: the skills „Object
oriented programming“ and „Procedural
programming“ are closely related since the have the
same parent concept. While “Java programming”
and “C++ programming” are very similar, “Pascal
programming” is still related, but far more loosely.
Such sophisticated comparisons of profiles based on
the taxonomic skill catalogue as background
knowledge, allows far-reaching detailed assessments
of whole project team staffs, if required. In
particular, they allow for fine-granular ranking of
candidates. Due to space limitations, we don’t go
into details about the computation of taxonomic
similarity, here. For more information, see, e.g.
(Ehrig; Haase; Stojanović; Hefke, 2004).
4 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
The idea of detailed ontology-based modelling of
personal skills is not new (Stader, Macintosh, 1999;
Liao; Hinkelmann; Abecker; Sintek, 1999), but has
found just recently more practical interest. Our own
work within DaimlerChrysler, but also for instance
(Hefke; Stojanović, 2004; Lau; Sure, 2002;
Dittmann, 2003; Hiermann; Höfferer, 2005) show
that such an approach – if appropriately supported
by organizational processes – can lead to more
efficient and more effective project staffing in real-
world, large-scale industrial application scenarios.
As sketched in Section 2, even more impact can be
achieved by designing a comprehensive ontology-
based skill-management infrastructure, joining up
existing systems, adding new functionalities, and
designing suitable support processes. The focus of
this paper was the use of ontology-based similarity
measures for skill-profile matching. Many academic
approaches for using advanced reasoning for skill
matching (like: Colucci; Di Noia; Di Sciascio;
Donini; Mongiello; Mottola, 2003) apparently have
not yet been applied in large-scale real-world
scenarios. Similarity-based approaches seem not yet
very widespread in this area, but they have proven
their practical usefulness in a vast amount of Case-
Based Reasoning (CBR) applications (see, e.g.,
Watson, 1997). CBR tools have also been
SIMILARITY MEASURES FOR SKILL-PROFILE MATCHING IN ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
15

successfully applied in Expert Finder systems which
can be seen as a very specific partial instance of a
skill management system (Vivacqua; Lieberman,
2000). The specific contribution of the work
presented in this paper is to settle the CBR ideas
upon a state-of-the art ontology infrastructure – thus
combining the advantages of similarity based search
(good retrieval results in vaguely specified query
situations and complex domains) with those of
ontology-based systems (clear semantics, good
application potential for integration of different
legacy systems).
When writing this paper, the software framework
is fully specified, the HR Data Warehouse and the
employee-skill database are already implemented,
and the three application modules are under
implementation.
REFERENCES
Federal Statistical Office Germany, 2003. Pressestelle
Wiesbaden. Bevölkerung Deutschlands bis 2050 –
Ergebnisse der 10. Koordinierten
Bevölkerungsvorausberechnung. Statistisches
Bundesamt, Wiesbaden 2003. In German.
Biesalski, E.; Abecker, A., 2005. “Ansätze zum
ontologiebasierten Human Resource Management”.
Workshop on IT Tools for Knowledge Management
Systems: Applicability, Usability, and Benefits @
WM2005, Kaiserslautern, April 2005. In German.
Biesalski, E.; Abecker, A., 2005a. „Integrated Processes
and Tools for Personnel Development“. In: 11th Int.
Conf. On Concurrent Enterprising ICE-2005, Munich,
June 2005.
Hefke, M.; Stojanović, L., 2004. “An Ontology-Based
Approach for Competence Bundling and Composition
of ad-hoc Teams in an Organisation”. In K.
Tochtermann & H. Maurer (eds.), I-KNOW’04, Graz /
Austria, June 2004.
Lau, T.; Sure, Y., 2002. “Introducing Ontology-based
Skills Management at a large Insurance Company”. In
Modellierung-2002, Modellierung in der Praxis –
Modellierung für die Praxis, pp. 123-134, March 2002.
Stader, J.; Macintosh, A., 1999. “Capability Modelling
and Knowledge Management.” In Applications and
Innovations in Expert Systems VII, Proc. ES’99 – 19th
Int. Conf. of the BCS Specialist Group on Knowledge-
Based Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence, pp
33–50. Springer-Verlag.
Staab, S.; Studer, R., 2004. “Handbook on Ontologies”.
Springer-Verlag, 2004.
Mädche, A.; Motik, B.; Stojanović, L., 2003. “Managing
Multiple and Distributed Ontologies in the Semantic
Web“. VLDB Journal 12(4): 286-302, Springer-
Verlag, 2003.
Ehrig, M.; Haase, P.; Stojanović, N.; Hefke, M., 2004.
”Similarity for Ontologies – a Comprehensive
Framework”. In Workshop Enterprise Modelling and
Ontology: Ingredients for Interoperability, at PAKM
2004.
Liao, M.; Hinkelmann, K.; Abecker, A.; Sintek M., 1999.
“A Competence Knowledge Base System for the
Organizational Memory”. In F. Puppe (ed.): XPS-99 /
5. Deutsche Tagung Wissensbasierte Systeme,
Springer LNAI 1570, 1999.
Colucci, S.; Di Noia, T; Di Sciascio, E.; Donini, F;
Mongiello, M.; Mottola, M., 2003. “A Formal
Approach to Ontology-Based Semantic Match of
Skills Descriptions”. In J. Universal Computer Science
9(12):1437-1454, 2003. Springer Verlag
Watson, I., 1997. “Applying Case-Based Reasoning:
Techniques for Enterprise Systems”. Morgan
Kaufman Publishers, 1997.
Vivacqua, A.; Lieberman, H., 2000. “Agents to Assist in
Finding Help”. In ACM Conf. on Computers and
Human Interface (CHI-2000), the Hague, Netherlands,
April 2000.
Dittmann, L., 2003. “Towards Ontology-based Skills
Management”. Project Report 8/2003, Project
KOWIEN, University Duisburg-Essen 2003.
Hiermann, W.; Höfferer, M., 2005. “Skills Management:
Searching Highly Skilled Employees for
Teambuilding and Project Management Tasks”. In K.
Tochtermann & H. Maurer (eds.), I-KNOW’05, Graz /
Austria, June 2005.
ICEIS 2006 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
16
