
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR
MOBILE SELF-TRAINING
M. Ennaji*, H. Boukachour*, P. Gravé**
Laboratoire d’Informatique du Havre*, CIRTAI-NTIC**
25, rue Ph. Lebon
76058 Le Havre Cedex, France
Keywords: Multi-agent and multi-layer system, Case-Based Reasoning, teaching agent, Semantic features.
Abstract: This article is the result of an interdisciplinary meeting between sociologists and didacticiens on the one
hand and data processing specialists on the other hand. To develop the theoretical and methodological
principles of the design of a training environment, by putting the needs and the difficulties of the student at
the center of the design process and data-processing modeling, constitutes the common action of these two
research laboratories within the framework of this collaboration. To design a virtual tutor called “teaching
agent” in a system of remote formation implies the implementation of a flexible and adaptive system. We
propose an multi-agent multi-layer architecture able to initiate the training and to manage a teaching and an
individualized follow-up.
1 INTRODUCTION
A Computer Environment of Human Learning
(EIAH) is a computer system which has for
objective to favor the learning of a domain of
knowledge by a learning. The computer systems of
the learning assistant are traditionally structured
around an only educational module: an artificial
tutor. It possesses a domain expertise of knowledge
and applies a strategy of education to interact with a
student to help him to resolve a given problem. This
principle of functioning in autonomy of the couple
student-tutor can be satisfying until the moment
when the system reaches its limits; the presence of a
human teacher, even another student becomes then
essential. So, these systems can be used as a
supplement to the traditional teaching, in a class for
example. However, with the evolution of the
networks of communication such the Internet and
the services associated as the information servers
like Web type for example, the teaching and the
situations of learning move from the institutional
frame to the room of lessons towards the place of
residence, the company, etc.
So, it is now necessary to design EIAH which
take into account the mobility of the students, as to
ensure them an individualized follow-up to respect
their rhythm of learning and put in their arrangement
the human presence among all the accessible
educational resources.
This work is the result of an interdisciplinary
meeting between sociologists and didacticiens on
one hand and computer science specialists on the
other hand. It articulates around the pooling of the
skills of two research laboratories of the university
of the harbour: the Computer Science Laboratory of
Le Havre (LIH), and more particularly the research
group ARM (agents and major risk) and the
laboratory CIRTAI-NTIC which has experimented
some tools of learning and noted their limits. Our
contribution, in the field of the distance learning,
consists in designing and in realizing a computer
system able to introduce the learning and the
managing an individualized teaching and follow-up.
This article develops the multi-agent multi-layer
architecture resulting from the work of the computer
science specialists on the systems of decision
making for dynamic situations, which is adapted to
the conception and to the realization of an
"intelligent" virtual tutor also called "teaching agent
" in mobile learning.
2 TEACHING AGENT
The learning situation based on computer is thought
like a Human-Machine system. Classically it
343
Ennaji M., Boukachour H. and Gravé P. (2006).
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR MOBILE SELF-TRAINING.
In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - AIDSS, pages 343-350
DOI: 10.5220/0002461003430350
Copyright
c
SciTePress
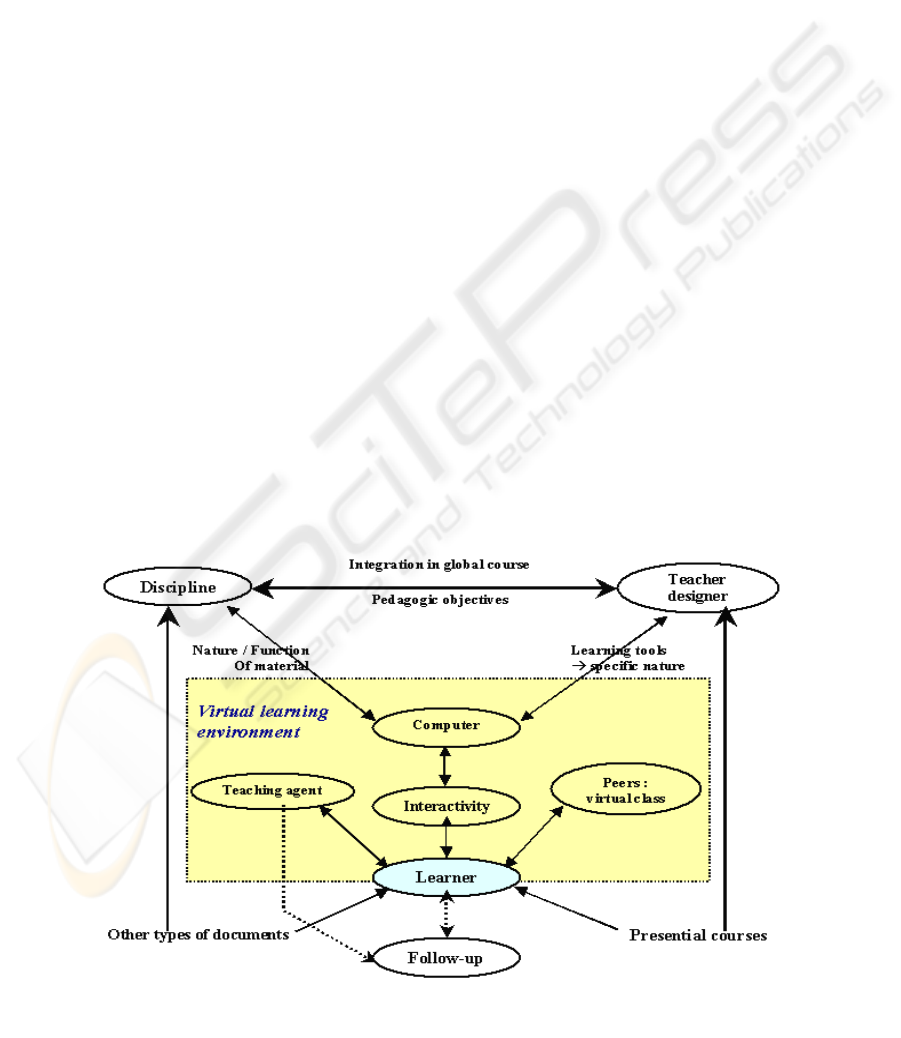
consists in examining the relations between different
components: teacher, learner, learning object and
computer. Sometimes it also includes a reflexion on
these relations and the institutional environment.
These learning system are focused on content but do
not attach importance to the career of acquiring
content. These learning systems generally rest on a
transmissive model rather than learning model. It
often reduces the e-learning to a learning activity
sequential organisation. So the interactivity of the
learner is limited by using simple navigation based-
function with the tool.
The working party NTIC of the CIRTAI
(ANNOOT et al. 2004) (BERTIN, 2004) (BERTIN
et GRAVÉ, 2004a) (BERTIN et GRAVÉ, 2004b)
shows, for the distant learning system, the specific
interactions between different components of an
ergonomic model based on a constructivist approach
(VYGOTSK, 1978). New interactions add to the
usually recognized learning interactions (teacher,
learner, learning object), because of the introduction
of the distance. Furthermore we have to add the
necessity of transferring in a virtual environment
interaction whose observation in a presential
learning have revealed the importance, particularly
peers relations, pedagogic tutoring and follow-up.
About this pedagogic tutoring, we enrich our
interactionist and ergonomic model (outline 1) by
addition of dimensions that allows the development
of learner cognitive and metacognitive abilities: this
main line research moves towards the conception of
“teaching agent”. We lean on the concept of
teaching agent, described by Philip Hubbard
(Hubbard, 1999), (Hubbard, 2000). It is an
informatic entity which, by its graphic, its
conception and its dynamic and well-timed
apparition mode, plays the virtual tutor role.
Together with Hubbard, such an agent has to
present certain characteristics:
• A physical presence and a personality,
• An expertise in the reference field,
• An aptitude for individualised learning,
• An ability to initiate learning.
The following outline situates the teaching agent
in the distant learning mediatized systems.
By its appearance and its operating mode, the
teaching agent is a sort of technological mediation of
human presence which might allow different uses:
• Aid in using activities and software;
• Methodological advices for learning better at
distance;
• Selective aid (dictionary, encyclopaedia…);
• Aid production and redaction (thesaurus for
language for example);
• Supply additional references;
• Watch learning operation in the background
(follow-up functions).
At the same time teaching specialist (the
pedagogue), expert and tutor (or companion), the
teaching agent is receptive at any time, without any
evaluative connotation unlike the teacher. “The
pedagogue in classical times was the slave who
escorted the children to school, uneducated slave
whose main task was to serve as bodyguard but who
could also help the learner in his homework, answer
Figure 1: Didactic ergonomic interactionist model (Berlin, 2001, 2004).
ICEIS 2006 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
344

questions, play games, or even give tests. But the
pedagogue never initiates: he comes forward when
summoned and, when the learner has had enough,
he goes back to his place. This is the role which
seems in some ways a natural one for the computer
to assume. After all, computers were built in the first
place to answer questions, not to ask them”
(HIGGINS, 1986). Its role is essentially formative.
This is a less explored domain of research for two
main reasons:
• The difficulty to formalize the theoretical nature of
a computing agent, capable giving the learner this
“cognitive scaffolding” (VIGOTSKI,1978),
• The problems for developing an appropriate
technology to these needs. We lean on an
experiment, carried out at the University of Le
Havre (France), with students in Economics and
Social Administration Bachelor’s Degree, who
received instruction in Organisation Sociology, in
two modes: part time in traditional presential
learning with the teacher, part time in self-training
situation with a CD-ROM. The same contents
were given. At the end of the training, students
filled a questionnaire about their perceptions of the
two pedagogic modes (processing of this data is
still in progress). As far as we are concerned, this
CD-ROM automatically generates follow-up files,
which memorize the student’s individual paths.
career during it self-training. The analysis of this
data files help understand the student’s path and
examine the pertinence to add a teaching agent or a
computing system, that can ensure these pedagogic
tutoring functions.
3 OUR APPROACH: DESIGN
AND IMPLEMENTATION
3.1 Introduction
There are numerous research works as well as
teaching practices coming from the teaching and the
computer experiments led in mobile learning and,
more particularly, in online training. These works
are interested in the conception and the
implementation of computer systems allowing to
attend the student in his training, BAGHERA
(Webber et Pesty, 2002), SIGFAD (Mbala and al,
2003).
The current platforms of e-learning do not have
tools allowing to make an individualized follow-up
of the student. This follow-up is essential because of
the great number of students which do not finish the
training. They use a more technical approach, by
proceeding to a simple transposition of a traditional
pedagogy in a computer portal, than a didactics one,
by integrating the contributions of the most recent
theories without limiting itself to the structures of
behaviourist kind.
In the framework of a self-training, the student must
have the freedom and the choice of the course to
follow in order to assimilate the object of the
learning by a building approach of the knowledge
instead of a massive use of documents. This freedom
must be assisted by a regular and continuous follow-
up. Traditionally, the follow-up is insured by a
teacher. The main objective of our training
environment, opened and distant (FOAD) is to
propose an alternative in the traditional teaching.
Consequently, the computer tool has to integrate the
assistance and the follow-up among its features.
This expected computer tool is an opened,
evolutionary system and a "translation" of the
training agent, described in the interaction model of
didactic ergonomics according to (Bertin, on 2001)
(Figure 1). To meet the needs of didacticiens, it
consists in conceiving and realizing a computer
system which has to take into account the following
characteristics:
Opened: the structure can change dynamically.
Evolutionary: because the components of such a
system are not known in advance, change during
time, and are essentially heterogeneous.
Autonomous: such a system has to take the role of
the teacher and to may be able to initiate the
learning.
Adaptive: the system is intended for an
individualized learning, so it is needed to take into
account the various profiles of the students.
The system is complex. This complexity, which
is also translated by the important number of data to
be treated and the dynamics of the situation to be
treated, led to us to choose the multi-agent systems
(MAS) as the modelling (Jennings and al., on 1998).
4 ANALYSING AND
DECOMPOSITION OF THE
NEEDED
4.1 Introduction
We are making closer the questioning on the
analysis of the career of the students in self-training,
and the decision system support which have to allow
to represent, to follow and to analyze the evolution
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR MOBILE SELF-TRAINING
345

of a dynamic situation. Such a system allows to
represent the observed situation but also its
evaluation.
Evaluating the situation can be performed by
calculating its possible consequences. This can be
carried out using previous situations whose
consequences are known. So, a reasoning based on
analogy can be used relying on the following
hypothesis: if a A situation looks like a B
situation, the consequences of the A situation
ought to be similar to those of the B situation.
The Case Based Reasoning (CBR) (Kolodner,
1993) is a methodology of resolution of problems
leaning on the re-use of the experiences spent to
resolve new problems. The decision making system
is one of the most promising domains of application
of the CBR. It allows to put in synergy the capacity
of resolution of problem of the man with the
capacity of the computer system. Memory of the one
and the other one strengthen mutually to participate
in the resolution of the problem.
In the framework of a mobile self training
offering the individualized follow-up of students, a
decision making system, allows to analyze the
course and the work of learning it to anticipate a
possible finishing of learning it or a "bad" learning
of this one.
The system which we propose, has to take into
account moreover, the evolutionary character and
the dynamics of the course to be analyzed. The
analysis is supported by the link which the system is
going to make, in a continuous way, between the
way of learning it and the past career .
The past tracks are described by scenarios
grouped together in a base called "base of
scenarios". They characterize, for every past career ,
all the determining aspects in its progress. We call
here determining aspect, a fact which played a
current role in the career the events have taken
place. So, every scenario contains a temporal list of
semantic features associated to the important aspects
of the careers.
The analysis of the career s has to be made in a
continuous career , in which we must use a multi-
agent architecture allowing the implementation of a
dynamic and incremental case reasoning for the
situations evaluation. This architecture allows the
real-time comparison of the situation observed with
past situations stored in a base of case.
4.2 Existing Works
In parallel, in this collaboration between computer
specialists and didacticiens, the areas of research of
the computer specialists of the LIH working on the
distance learning, concern the systems of decision
making that must estimate a dynamic situation.
Numerous applications of computer systems must
allow to represent an evolving situation in order to
be able to analyse it. This problem exists in different
application domains such as road traffic,
meteorology, risks management, etc. The
implementation of these systems requires to answer
to the following questions:
Which tools to model the situation?
Which tools to model and manage time?
Which architecture to manage the monitoring of the
evolution of the situation?
How to allow the users to have a clear and
understandable view of the state of the situation and
of its possible evolution?
The observed situation generally contains a great
number of dynamic parameters, that is to say
parameters whose value change over time. Systems
allowing the management of such situations must be
dynamic in order to be able to handle these
evolutions. As a consequence, to design these
systems, a flexible and adaptive architecture is
needed. This led us to choose a multi-agent
architecture(Jennings and al ., on 1998). We are thus
interested in the development of multi-agent systems
dedicated to the modelization and the evolution
forecast of dynamic situations.
Such a system must not only allow to represent
the observed situation, but also has to allow its
evaluation. Evaluating the situation can be
performed by calculating its possible consequences.
This can be carried out using previous situations
whose consequences are known. So, a reasoning
based on analogy can be used relying on the
following hypothesis: if a A situation looks like a B
situation, the consequences of the A situation ought
to be similar to those of the B situation. To perform
such a reasoning, we must elaborate:
• a multi-agent CBR. The representation of the
current situation is, in our context, based on a set
of agents.
• a dynamic CBR. The target case of the CBR
process is an evolving situation, so the CBR has to
take this evolution into account incrementally. In
other words, when the situation changes, it must not
be considered as a new target case.
Using such a dynamic multi-agent CBR, the
aim
of the system is to select as soon as possible the
cases of the base which seem to be the most similar
ICEIS 2006 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
346
to the current situation in order to be able to
anticipate its consequences. Of course, this selection
must adapted to the evolution of the situation over
time. Indeed, new information on the situation can
eventually modify the set of cases which have been
selected during the previous steps.
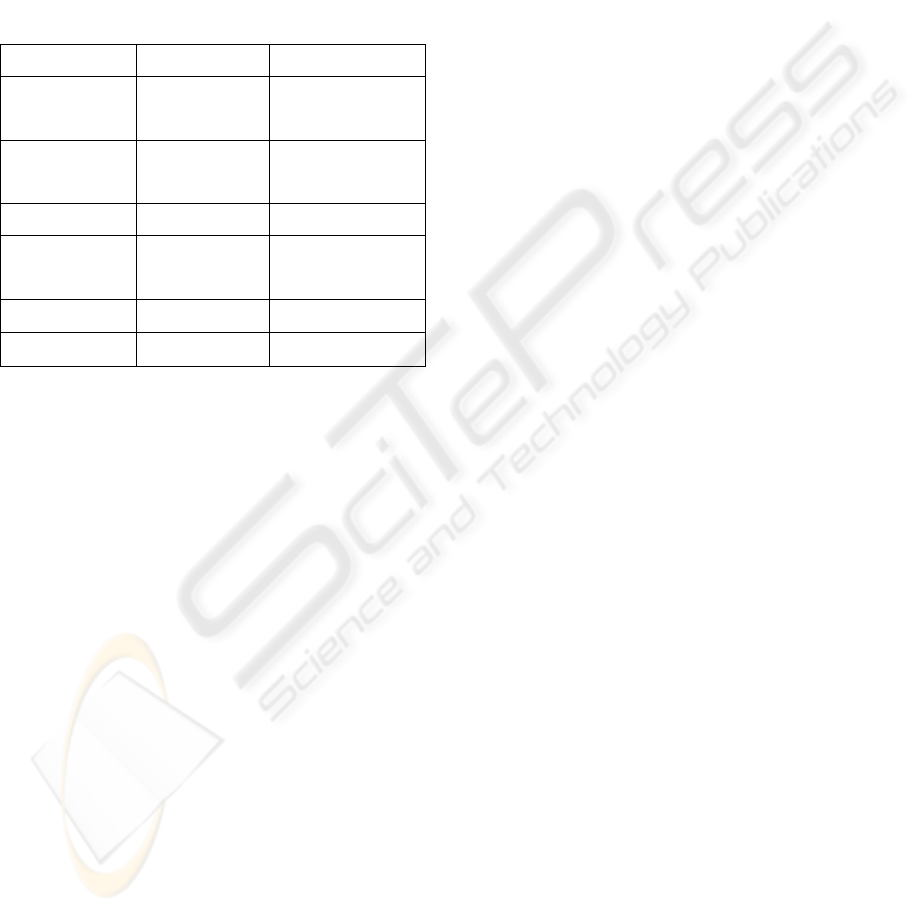
In the following figure (see figure 2), we present a
synthesis of the similarities and differences between
our approach and the CBR for dynamic situations.
More information can be found in (Simon and
Boukachour, 2004).
Standard CBR dynamique CBR Our approach
Target Case = set
of attributes
Target Case=
temporal description
Target Case =
temporal description
Static elaboration Static elaboration
continuous and
multi-agent
elaboration step
Indexation None None
Static recall step Static recall step
Multi-agent and
continuous recall
step
Adaptation Adaptation make by expert
Learnning Learnning Learnning
Figure 2: Similarities and differences between our
approach and the CBR for dynamic situations.
5 OUR PROPOSAL: PRINCIPLES
AND IMPLEMENTATION
5.1 Principles: The Different Kinds of
Agents Used
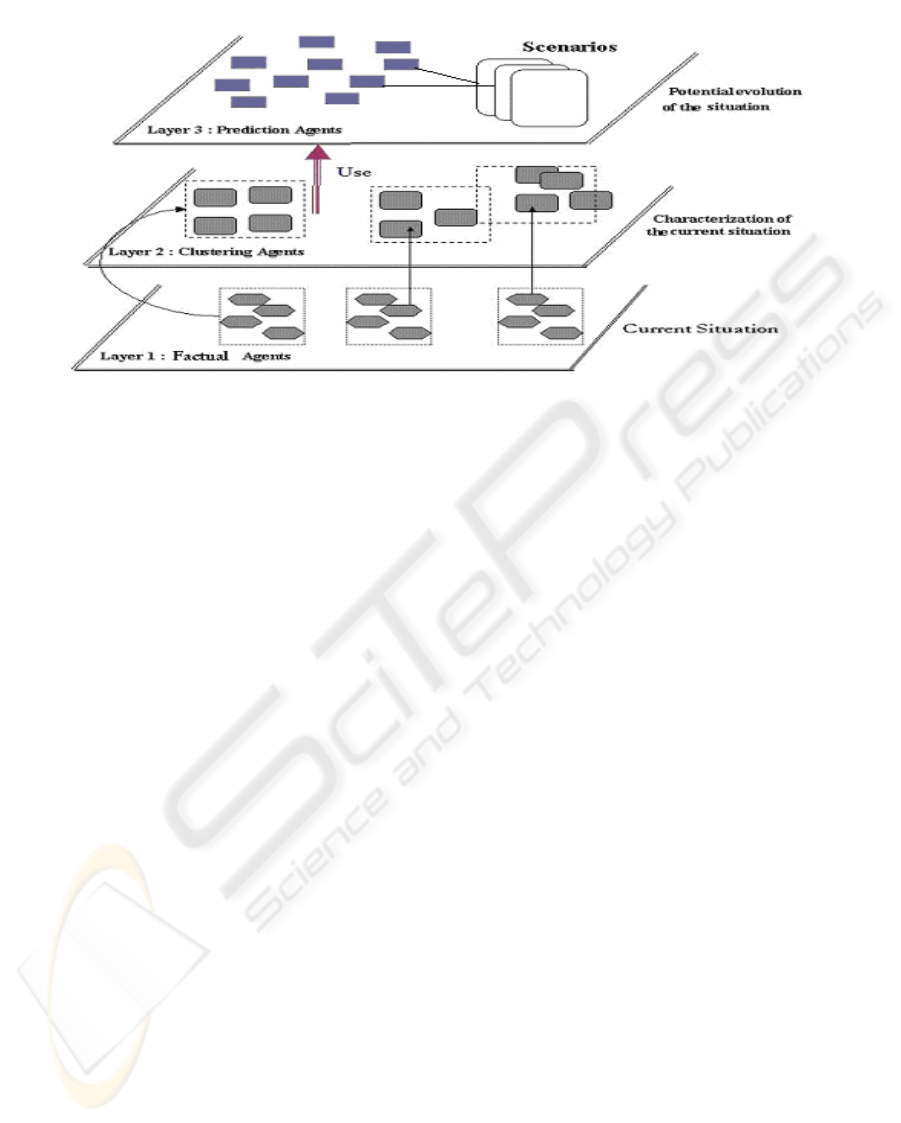
Our architecture is based on a multi-agent
architecture as proposed by Marcenac in (Marcenac,
1997). This kind of architecture uses several
hierarchical agent layers, a layer of the level n
having a view on the layer of the level n-1. Our
system use three different layers (see figure 3) :
the lowest one : it contains the agents allowing to
model the current state of the situation, that is to say
the informational agents,
the intermediate one : it contains synthesis agents
used to analyse the previous layer,
the highest one : it contains prediction agents which
must provide information about the potential
evolution of the situation using dynamic CBR
techniques.
5.2 Factuals Agents
First of all, the observed situation is modelled by a
set of "factuals" agents. This set of agents receives
pieces of information about the situation which are
sent to the system by actors or by distributed data
bases. Each factual agent is supposed to represent
one of these pieces of information which is called
“semantic features (SF)” (Jackendoff, 1993)
(Denhière and Baudet, 1992).. A SF is a three-part-
relation <object, qualification, value> representing a
partial aspect of the situation. A SF is also the
atomic data structure, i.e. the smallest piece of
information the system could deal with. (for more
details, see (Person and al., 2005) (Boukachour and
al., 2002). The main advantage to use agents to
represent information about the current situation is
that it allows to obtain a flexible representation
which can be easily adapted as the situation evolves
(ie as new pieces of information about the situation
are introduced in the system). Each agent must also
provide a temporal validity measure allowing to
evaluate the "freshness" of the piece of information
associated to its semantic features.
Each informational agent must provide numerical
measures of its evolution over time. More precisely,
these measures must allow to evaluate the level of
reinforcement of the agent inside the organisation it
belongs to. Indeed, it is supposed that the more an
agent is reinforced, the more its semantic features
must be taken into account in the evaluation of the
situation. This reinforcement must be based on a
similarity measure between items which can use
semantic, temporal and spatial aspects (Pesron and
al., 2005). These mechanisms allow to take into
account the fact that, for example, a piece of
information introduced very early in the system can
turn out to be non relevant later. On the contrary,
some can be given later to the system and finally be
judged as very representative of the current state of
the situation. More information can be found in
(Person and al., 2005).
5.3 Synthesis Agents
The goal of these agents is to provide a synthetic
view of the global behaviour of the factuals agents
layer in order to facilitate the comparison with past
situations stored in the scenarios base. This layer
helps to implement the standard target case
elaboration step of the case-based reasoning cycle.
This elaboration is, however, specific because of its
dynamic property.
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR MOBILE SELF-TRAINING
347
More precisely, the goal is to classify factuals agents
into groups. This operation can be done using
reinforcement and temporal validity measures
provided by factuals agents. Indeed, if one consider
a particular factual agent, the values of its measures
are not very significant. On the contrary, if these
measures are compared with those of the other
factuals agents, it allows to build groups of agents
with similar measures values. Theses groups can be
representative of important aspects of the current
situation which will be used by prediction agents to
manage the comparison with past situations.
The goal of synthesis agents is to dynamically
build these groups called clusters. In (Coma and al.,
2003), we propose a dynamic techniques for agents
clustering. Each cluster is modified over time
according to factuals agents evolution. For example,
it can increase if new informational agents seem to
be similar (from the measures point of view) to those
belonging to it. On the contrary, it can decrease, or
even disappear, if too few factuals agents belong to
it.
5.4 Prediction Agents
In order to be able to use CBR techniques, the
system must contain cases describing past situations.
Such cases are called "scenarios". These scenarios
must allow to characterize, for each past situation,
the set of decisive factors which seem to be related
to the career the situation went on. As a
consequence, each scenario contains a list of
semantic features associated to the decisive factors
of the past situation. This list can, eventually, be
organized temporally. These factors can be found
using experience feedback provided by domain
experts.
A prediction agent is associated to each scenario
stored in the system. The goal of the prediction
agent is to compare the course of the current
situation represented by the factuals agents with the
one described in the scenario. This comparison,
which must be made in real time, consists in
determining if the factors which seem to be
important in the current situation are similar to the
decisive factors of the situation described in the
scenario. In order to do that, the prediction agent
must know the factors, that is to say the items
associated to them, which are considered to be the
most representative of the current state of the
situation. Calculating these factors is the job of the
synthesis agents belonging to the intermediate
agents layer of the system.
The goal of the prediction agents layer is to
provide a continuous recall process of cases of the
case base, unlike the one used in CBR for dynamic
situations described before. Notice that, for the
moment, the adaptation step will be done by domain
experts which will be in charge to evaluate if the non
matched part of the recognised scenario can be used
for the current situation. Indeed, the continuous
evolution of the analysed situation may decrease the
relevance of the adaptation process result. That's
why, after having discussed with experts, it has been
chosen to give, to the expert, elements about the
main similarities and differences between the
Figure 3: Multi-agent and multi layer architecture.
ICEIS 2006 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
348

scenario and the current situation which he can use
in order to manage his own adaptation. More
information can be found in (Simon and
Boukachour, 2004).
6 MULTI-LAYER MAS
GENERICITY AND
SPECIFICATION
In the previous section, we have presented the multi-
agent architecture allowing the implementation of a
dynamic and incremental CBR for the evaluation of
the potential evolution of an dynamic observed
situation. The architecture is based on two parts:
• a generic part: 3 layers of agents;
• a bound part to the domain: ontology, measure of
nearness.
The genericity is one of the objectives of the multi-
layer system. The genericity of the system must be
understood here as being the separation between a
part of the mechanisms considered as being relevant
independently from the domain. The generic aspect
covers:
• the use of semantic features as atomic granules
of information piece: at a given time, the current
situation is representable by a collection of
semantic features;
• a factual agent takes care of a semantic feature;
• a factual agent arranges several internal
indicators which inform its states.
Some aspects of the internal indicators of a factual
agent are generic. For example, an evolution of the
speed will induce an update of the acceleration
independently from the domain.
Automaticaly, the ontology is specific to the domain.
The categorization of the semantic features is
specific too, as the choice of the valid transitions
from the generic automaton, the setting parameter of
thresholds and the actions were associated to the
transitions.
The collaboration between didacticiens and
computer specialists allow a clarification of the
concepts and the vocabulary of the common domain.
To initiate the learning and to manage an
individualized teaching in a multimedia environment
supposes to translate the characteristics of the
teaching agent into multi-agent system. Hubbard
isolates four characteristics of the virtual tutor which
we suggest to take into account in the multi-agent
system in the following career :
the "physical" presence and the personality of the
virtual tutor correspond to an adaptive and
intelligent human-machine interface;
the expertise in the field of reference corresponds in
the MAS to a knowledge base (base of scenarios and
ontology);
the capacity in an individualized teaching
corresponds to the implementation of a reasoning by
dynamic CBR supported by the architecture in three
layers;
the capacity to introduce the learning corresponds to
an autonomy of the system and the intrinsic
proactivity of its agents.
The low layer of the system, the factual agents,
contains agents carrying the semantic features bound
to the various actions of student. The career of the
student is so represented by a set of agents draw.
The ontology of the domain and particularly, the
object of the learning, allows to define the semantic
features.
The intermediate layer, the synthesis agents, consists
in placing the agents or the groups of factual agents
in regard each others. This layer participates in the
phase of elaboration of the target case of the CBR,
by keeping that the striking elements of the career
of student.
The highest layer, the prediction agents, its role is
to build a continual process and incremental of recall
step. At each scenario is associated a prediction
agent. The purpose of an agent of prediction is to
estimate continuously the degree of similarity
between the career of the student and the scenario to
which it is associated. A scenario contains the
determining facts of a known career as well as the
result of the evaluation of this career .
7 CONCLUSION
In this article, we have presented a multi-agent
architecture allowing the implementation of a
dynamic CBR for the evaluation of the potential
evolution of an observed situation. This architecture
relies on 3 layers of agents with a pyramidal
relation. The lower layer allows to build a
representation of the target case, i.e. the current
situation. The second layer allows to implement a
dynamic elaboration of the target case. Finally, the
upper layer implements a dynamic process of source
cases recall allowing the search for past situations
similar to the current one.
The system bases itself on heterogeneous data. It
is a question of going from an exhaustive and factual
description of the situation ( current work) in a level
A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR MOBILE SELF-TRAINING
349

description knowledge allowing to characterize
synthetically this situation. The continuous treatment
of the information from the environment allows to
suggest to the actors (students and tutors) the
possible evolutions of the current situation. For that
purpose, we have to formalize the representation of
the successful information. To represent the current
situation, it is necessary to proceed to the
construction of an ontology of the domain to be able
to categorize the various semantic features
(elementary information).
The experiment of a tool of self-training by the
sociologists of the university of Le Havre produce a
set of files tracks. These files represent the career s
of a student to make a study case. The current work
consists in analyzing these files, to build the
ontology of the domain and specify the low layer by
identifying the semantic features.
REFERENCES
Annoot Emmanuelle, Bertin Jean-Claude, Gravé
Patrick,2004 « Quelles médiations dans les formations
à distance avec les nouvelles technologies dans
l’Enseignement Supérieur ? », Rapport de recherche
dans le cadre du CPER Pôle SHS, Universités du
Havre et de Rouen..
Bertin Jean-Claude, 2004 « L’ergonomie didactique face
au défi de la formation ouverte et à distance », ASP,
numéro spécial RANACLES.
Bertin Jean-Claude, Gravé Patrick, 2004a « Didactic
ergonomics and Web-based materials design »,
communication à CALICO 2004, Carnegie Mellon
University, Pittsburgh, USA.
Bertin Jean-Claude, Gravé Patrick, 2004b « Didactic
ergonomics and Web-based materials design: in
favour of a conceptual model », communication à Xith
International CALL Conference, CALL & Research
Methodologies, University of Antwerp (Belgique).
Boukachour H 2002. Système de veille préventive pour la
gestion de situations d'urgence: une modélisation par
organisations d'agents. Application aux risques
industriels. PhD Thesis, University of Le Havre.
Boukachour H., Simon G., Coletta M., Galinho T., Person
P., Serin F.,2002 Preventive Monitoring Information
System: a Model Using Agent Organizations SCI2002,
Orlando, USA.
Boukachour H., Simon G., Serin F., Galhino T., Coletta
M., Person P. and Fournier D.,2003 Vers une
architecture multi-agent pour la représentation et
l'évaluation de situations dynamiques, CCGEI'03
Montréal.
Cardon A.,1997. Les systèmes d'information et de
communication de gestion de crise: une modélisation
par agents. Ingénierie des Systèmes d'Information,
5(2), p. 167-193.
Coma R., Simon G, Coletta M., 2003 « A multi-agent
architecture for agents clustering » Agent Based
Simulation ABS’2003, Montpellier.
Denhière, G. and Baudet, S. (1992). Compréhension de
texte et science cognitive . Editions Puf.
Durand S., 1999. Représentation des points de vues
multiples dans une situation d'urgence : une
modélisation par organisations d'agents. PhD Thesis,
University of Le Havre.
Higgins John, 1986 « Smart learners and dumb machines
», Systems, vol. 14, n° 2,1986 pp. 147-50.
Hubbard Phillip, 1999 « Teaching agents in CALL
tutorials », CALICO’99, Oxford, Ohio, USA.
Hubbard Phillip, 2000 « Taming teaching agents, meaning
technologies and participatory dramas”, CALICO
2000, University of Arizona, Tucson, USA
Jackendoff, R., 1993. Semantics and Cognition
Cambridge, M.I.T.Press.
Jennings N., Wooldridge M., Sycara K., 1998 A roadmap
of agent research and development. Autonomous Agent
and Multi-Agent Systems, 1(5), p 7-38.
Kolodner J., 1993 Case-based reasoning, San Mateo CA :
Morgan Kaufman.
Mbala A., Reffay C. and Chanier T. 2003 SIGFAD : un
système multi-agents pour soutenir les utilisateurs en
formation à distance. In Actes de la conférence
Environnements Informatiques pour l'Apprentissage
Humain (EIAH'2003), Strasbourg, France, pages 319-
330.
Marcenac P., 1997 Modélisation de systèmes
complexes par agents. Techniques et sciences
informatiques, p 1013-1037.
Person P., Boukachour H., Coletta M., Galinho T.
and Serin F, 2005. From Three Multi-agent
Systemsto One Decision Support System.
IICAI’05. Inde
Simon G and Boukachour H, 2004 Towards a Multi-Agent
Architecture for Dynamic Case-based Reasoning".
ICKEDS'04. International Conference on Knowledge
Engineering and Decision Support.Porto (Portugal).
Simon G, Boukachour H., and M. Coletta, 2002. Vers une
architecture multi-agent pour la modélisation et
l’évaluation de situations dynamiques. Technical
report, LIH, Université du Havre.
Vygotski Lev Sémionovitch, 1978 Mind in society : the
development of higher psychological processes,
Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Webber, C., Pesty, S. 2002 Emergence de diagnostic par
formation de coalitions - Application au diagnostic
des conceptions d'un apprenant. In: Journées
Francophones pour l'Intelligence Artificielle
Distribuée et les Systèmes Multi-Agents
J.P.Muller(ed), Hermes, Lille, pp.45-57.
Wooldridge M., Jennings N.R., 1998 Pitfalls of
agentoriented development, 2nd International
Conference on Autonomous Agents, pp. 385-391,
Minneapolis.
ICEIS 2006 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
350
