
COMPARISON OF MATCHING STRATEGIES FOR COLOUR
IMAGES
Bogusław Cyganek, Łukasz Socha
AGH – University of Science and Technology, Department of Electronics
Al. Mickiewicza 30, Kraków, Poland
Keywords: Stereo, Image matching, Colour processing.
Abstract: The paper addresses the ubiquitous problem of matching of colour images. Colour plays very important role
in human visual system and the question arises how it can influence image matching in case of a computer
based vision systems. In this paper the area based matching methods are investigated. Several matching cost
functions and different colour spaces (RGB, HSI, YCrCb) are examined. Obtained results for colour are
compared with monochromatic methods. Quality of dense disparity maps was verified in two ways: by
number of points rejected after cross-checking and by PSNR value between original reference image and its
reconstruction from the second reference and disparity map. The main objective of this research is to verify
benefits and drawbacks of using colour information for matching versus inevitable costs associated with
processing of greater amounts of data.
1 INTRODUCTION
Image matching plays a very important role in vision
systems – it is used in computer based stereovision,
motion analysis, video indexing, etc. The key
problem is finding corresponding points in images.
If the corresponding areas are determined the depth
of the scene can be computed by triangulation
(Cyganek, 2002)(Scharstein, 1998).
Most of the matching techniques use only
monochrome (one channel) images (Scharstein,
2002). However, there is still an open question how
colour information (more than one channel of data)
can help in this task. It is obvious that colour can
provide useful information for matching, e.g. red
pixel cannot mach witch blue one although their
values can be the same. If so, then what colour space
and cost measures are the most appropriate and
under what conditions.
In this paper we address these questions by
providing an overview of the comparison measures
appropriate for matching of the colour images and in
different colour representations (RGB, HSI, and
YCrCb). Matching results were verified by counting
number of points rejected after cross-checking as
well as by computing the PSNR value between
original reference image and its reconstruction
obtained from the second reference image and a
disparity map.
2 OVERVIEW OF MATCHING
TECHNIQUES FOR COLOUR
IMAGES
The main idea of area matching is based on
estimation of similarity between regions of n×m
pixels from the left and right image, respectively. In
case of grey scale images, similarity of two blocks is
computed based on some relation between intensity
of corresponding pixels. Let us now recall some
measures for matching of monochrome and colour
images, as follows.
A command is the basic instruction that a script
file contains. Some commands require parameters
that further define what the command should do. An
expression is a combination of operators and
arguments that create a result. Expressions can be
used as values in any command. Examples of
expressions include arithmetic, relational
comparisons, and string concatenations.
364
Cyganek B. and Socha Ł. (2006).
COMPARISON OF MATCHING STRATEGIES FOR COLOUR IMAGES.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 364-369
DOI: 10.5220/0001369603640369
Copyright
c
SciTePress

M_SAD
∑
∈
++++−++
Uji
yx
jdyidxIjyixI
),(
21
),(),(
(1)
M_SSD
()
∑
∈
++++−++
Uji
yx
jdyidxIjyixI
),(
2
21
),(),(
(2)
M_ZSAD
()()
∑
∈
++−++++−−++
Uji
yxyx
dydxIjdyidxIyxIjyixI
),(
2211
),(),(),(),(
(3)
M_ZSSD
()()
[]
∑
∈
++−++++−−++
Uji
yxyx
dydxIjdyidxIyxIjyixI
),(
2
2211
),(),(),(),(
(4)
M_GRAD
()
()
(
)
()
()
∑
∈
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
++++∇−++∇−++++∇+++∇
Uji
yxyx
jdyidxIjyixIcjdyidxIjyixI
),(
2121
,,,,
2
1
(5)
where I
1
, I
2
stand for intensities in the left and right
image, d
x
, d
y
are disparities between matching
regions U in the left and right image, is the average
value of intensity in a region U. Measure (5) was
introduced by (Scharstein, 1998).
Comparison of colour images requires
calculations in the multi-channel signal space. To
simplify notation of the formulas let us define the
following abbreviations:
),(
11
jyixRR ++=
),(
22 yx
djydixRR
+
+
+
+
=
(6)
),(
11
jyixGG ++=
),(
22 yx
djydixGG
+
+
+
+
=
(7)
),(
11
jyixBB ++=
),(
22 yx
djydixBB
+
+
+
+
=
(8)
Based on (1)-(4) and with notation (6)-(8)
we define the first group (prefix RGB_1_) of
measures for the RGB colour space, as follows:
RGB_1_SAD
∑
∈
++−++
Uji
BGRBGR
),(
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
(9)
RGB_1_SSD
(
)
∑
∈
++−++
Uji
BGRBGR
),(
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
(10)
RGB_1_ZSAD
()()()
(
)
(
)
(
)
∑
∈
−+−+−−−+−+−
Uji
BBGGRRBBGGRR
),(
2
22
2
22
2
22
2
11
2
11
2
11
(11)
RGB_1_ZSSD
()()()()()()
∑
∈
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−+−+−−−+−+−
Uji
BBGGRRBBGGRR
),(
2
2
22
2
22
2
22
2
11
2
11
2
11
(12)
The second group (RGB_2_) of measures for
the RGB colour space is as follows:
RGB_2_SAD
()
∑
∈
−+−+−
Uji
BBGGRR
),(
212121
(13)
RGB_2_SSD
()()()
()
∑
∈
−+−+−
Uji
BBGGRR
),(
2
21
2
21
2
21
(14)
RGB_2_ZSAD
()()()()()()
()
∑
∈
−−−+−−−+−−−
Uji
BBBBGGGGRRRR
),(
221122112211
(15)
RGB_2_ZSSD
()()()()
(
)()
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
∑
∈
−−−+−−−+−−−
Uji
BBBBGGGGRRRR
),(
2
2211
2
2211
2
2211
(16)
For the HSI space and with the abbreviations
analogous to (6)-(8), the first group
(prefix HSI_1_) of measures is defined as follows:
FOR ACHROMATIC REGIONS: FOR CHROMATIC REGIONS:
HSI_1_SAD
∑
∈
−
Uji
II
),(
21
()
∑
∈
−+−
Uji
HHII
),(
2121
(17)
HSI_1_SSD
()
∑
∈
−
Uji
II
),(
2
21
()( )
(
)
∑
∈
−+−
Uji
HHII
),(
2
21
2
21
(18)
HSI_1_ZSAD
()()
∑
∈
−−−
Uji
IIII
),(
2211
(
)
(
)
(
)
∑
∈
−+−−−
Uji
HHIIII
),(
212211
(19)
HSI_1_ZSSD
()()()
∑
∈
−−−
Uji
IIII
),(
2
2211
(
)
(
)
(
)
()
(
)
∑
∈
−+−−−
Uji
HHIIII
),(
2
21
2
2211
(20)
COMPARISON OF MATCHING STRATEGIES FOR COLOUR IMAGES
365

where the achromatic regions are these where more
than 60% of pixels meet the following conditions
(Koshan, 1996)(Tseng, 1992): (I>0.95 ∨ I≤0.25) or
(0.8<I≤0.95 ∧ S<0.18), or,(0.6<I≤0.8 ∧ S<0.2), or
(0.5<I≤0.6 ∧ S<0.3), or,(0.4<I≤0.5 ∧ S<0.4), or
(0.25<I≤0.4 ∧ S<0.6), or, The second group
(HSI_2_) of measures, operating on the separate
channels of the HSI colour space, are defined as
follows:
HSI_2_SAD
∑
∈
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
+
−
+−
Uji
HHSS
II
),(
2121
21
βα
(21)
HSI_2_SSD
()
∑
∈
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
+
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
+−
Uji
HHSS
II
),(
2
21
2
21
2
21
βα
(22)
HSI_2_ZSAD
()()
(
)
(
)
∑
∈
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
+
−−−
+−−−
Uji
HHSSSS
IIII
),(
212211
2211
βα
(23)
HSI_2_ZSSD
()()()
(
)
(
)
∑
∈
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
−−−
+−−−
Uji
HHSSSS
IIII
),(
2
21
2
2211
2
2211
βα
(24)
where
α
and
β
are scaling coefficients (for 8 bits per
channel,
α
=
β
=16 what means that only 5 oldest bits
are taken into consideration).
For the YCrCb space the two measures are
introduced based on the following scheme:
YCrCb_k_SAD
()
∑
∈
−+−+−
Uji
br
CbCbwCrCrwYY
),(
212121
(25)
The YCrCb_1_SAD is derived from (13) with w
i
defined as follows:
⎩
⎨
⎧
>
=
otherwise
Ciif
w
i
0
1
τ
(26)
where τ is a threshold value.
The second measure YCrCb_2_SAD is derived
from (25) with w
i
defined as follows:
α
/1=
i
w
(27)
where
α
is a scaling coefficients (for 8 bits per
channel,
α
=8 means that only 5 oldest bits are taken
into consideration).
Formula (5) for the M_GRAD measure has
been extended to cope with different colour spaces:
_GRAD
∑∑∑∑
∈===
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
∇−∇−
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
∇+∇
Uji kkk
kCkCkCkC
),(
3
1
21
3
1
2
3
1
1
)()()()(
βα
(28)
where C
1
(k) and C
2
(k) stand for the k-th colour
channel (e.g. R, G, and B) for the first and second
image, respectively, with the assumptions introduced
by formulas (6)-(8);
α
and
β
are scaling coefficients
(in experiments:
α
=0.5 and
β
=1). From (28) we
obtain the specific measures for each of the colour
spaces: RGB_GRAD, HSI_GRAD, and
YCrCb_GRAD.
Finally we incorporate the two additional
measures which define yet another kind of distances
between colour vectors C
1
and C
2
. For the RGB
colour space it takes the following form (Loo, 2002):
RGB_ DST
()
∑
∈Uji
CCdist
),(
21
,
(29)
where:
()
σ
+++= ''',
21
bgrCCdist
212121
',',' BBbGGgRRr −=−=−=
()
3/'''''' bgbrgr −+−+−=
σ
For matching in the HSI space Wei et.al. (Wei,
2003) propose a modified measure that is based on
the well known Minkowski’s formula. This
modification is given as follows:
HSI_ DST
(30)
∑
∈
−+−+−
Uji
IISSHH
),(
21
2
21
3
21
HSI_DST reflects meaning of each of the
components from the HSI space as perceived by
humans. We incorporated this measure to our
experiments as well.
Displacements in (29) and (30) between colour
vector with indices 1 and 2, with respect to the (i,j)
indices, follow the assumptions introduced in (6)-
(8). 3 Experimental Results
Figure 1 depicts disparity maps for Relaxing Jack
test pair. Size of the matching window is 8x8 pixels.
VISAPP 2006 - MOTION, TRACKING AND STEREO VISION
366
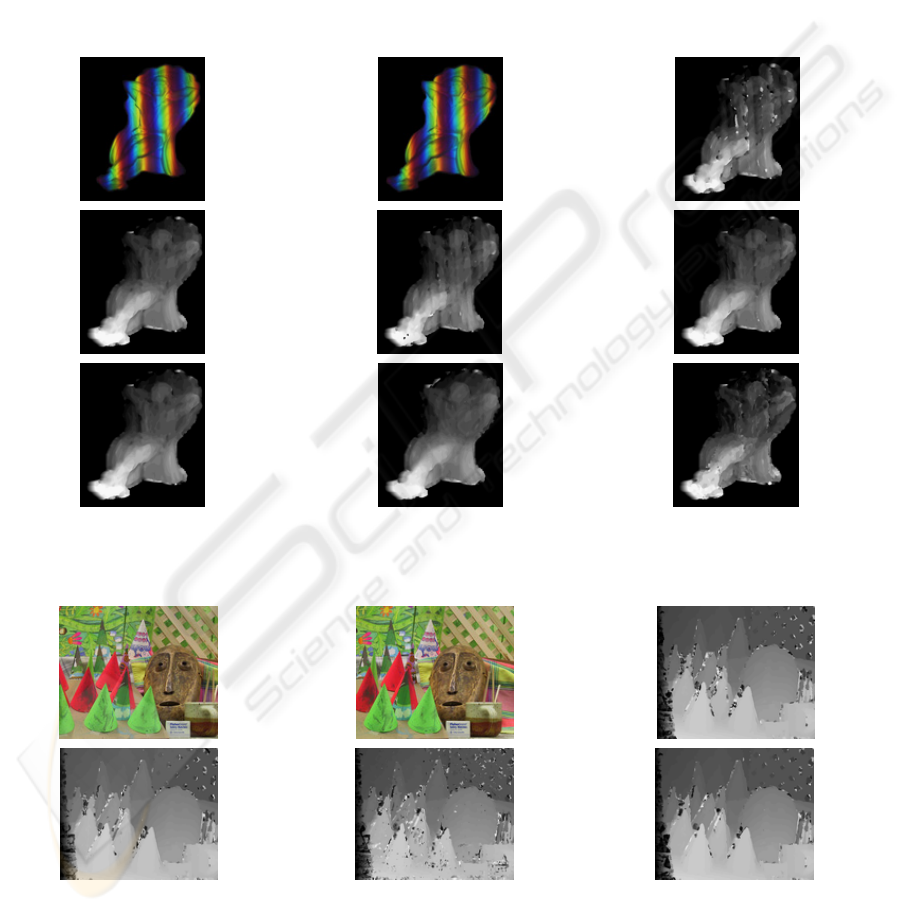
The acquired maps are presented for monochromatic
and some colour correlation measures. Number of
mismatched points defined by mutual validation of
disparity maps, is lowered by 20%-30%. Quality
improvement of the results is measured also by a
difference between the original image and the image
reconstructed from the disparity map; PSNR ratio is
improved approximately by 1dB. In this case colour
information results in significant improvement in
image matching.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 depict depth maps for
Cones and Tsukuba stereo pairs. In both cases there
are not evident benefits of using colour data.
Comparing results for monochrome and colour
signals there is no significant improvement for the
latter. The number of mismatched points in cases of
the best cost functions varies approximately by 5%.
In case of the HSI colour space the number of
mismatched points increases up to 50%. Results
acquired by the mutual validation of depth maps are
affirmed by the measurement of the PSNR ratio
between the original and reconstructed images.
a
b c
d
e f
g
h i
Figure 1: Disparity maps for the Relaxing Jack, block size 8x8. (a) left image, (b) right image, (c) disparity map for
M_SAD, false matches: 16,49%, (d) disparity map, RGB_2_SAD, false matches: 13,2%, (e) disparity map, HSI_2_SAD,
false matches: 15,25%, (f) disp. map, YCrCb_2_SAD, false matches: false matches: 14,99%, (g) disp. map, RGB_GRAD,
false matches: 20,18%, (h) disp. map, RGB_DST, false matches: 13,23%, (i) disp. map, HSI_DST, false matches: 11,93%.
a b c
d
e f
Figure 2: Disparity maps for Cone, block size 8x8 (a) left image, (b)right image, (c) disparity map, M_ZSAD, false
matches: 14,93%, (d) disparity map, RGB_2_ZSAD, false matches: 14,8%, (e) disparity map, HSI_2_ZSAD, false matches:
22,86%, (f) disparity map, YCrCb_2_ZSAD, false matches: 14,53%.
COMPARISON OF MATCHING STRATEGIES FOR COLOUR IMAGES
367
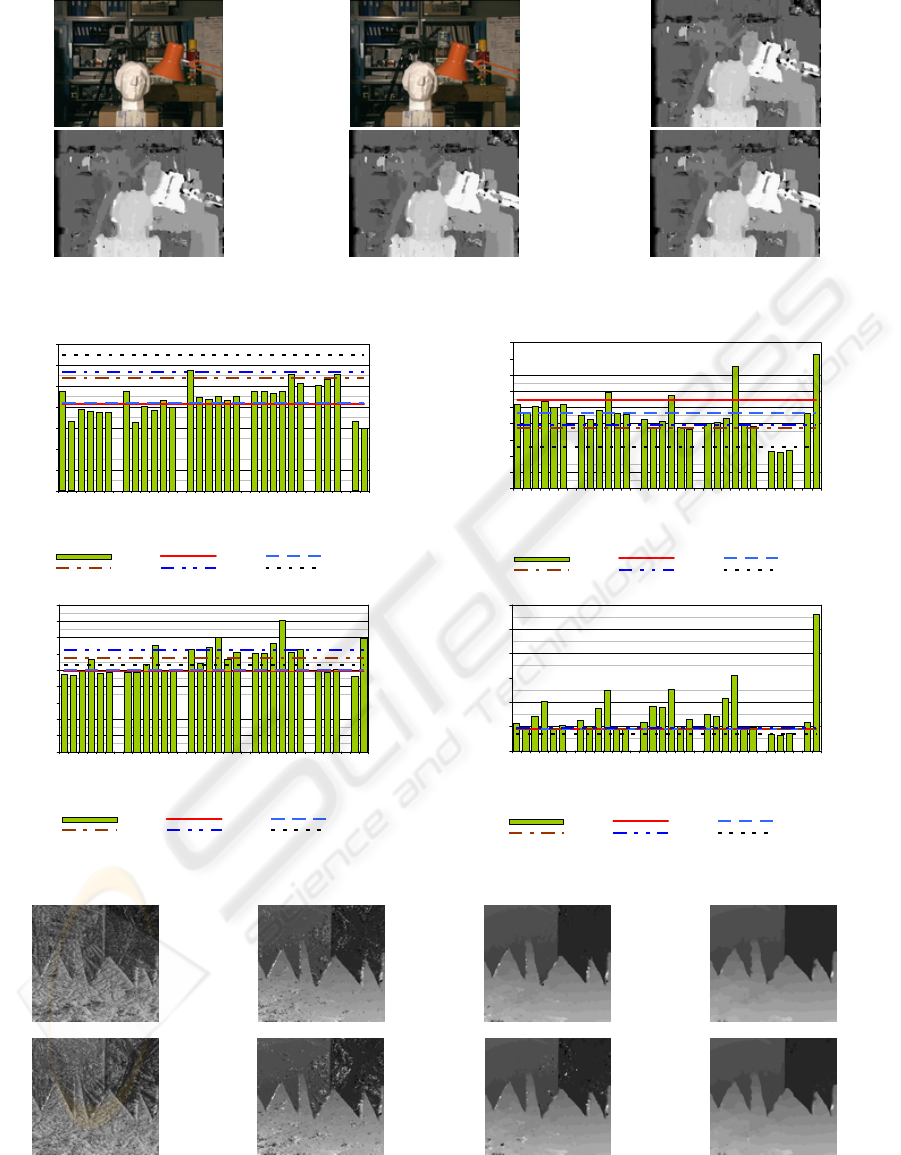
a
b c
d
e f
Figure 3: Disparity maps for Tsukuba, block size 8x8 (a) left image, (b)right image, (c) disparity map, M_SAD, false
matches: 19,62%, (d) disparity map, RGB_1_SAD, false matches: 19,09%, (e) disparity map, YCrCb_1_SAD, false
matches: 19,3%, (f) disparity map, RGB_DST, false matches: 18,92%.
a
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
RGB_1_SAD
RGB_2_SAD
HSI_1_SAD
HSI_2_SAD
YCrCb_1_SAD
YCrCb_2_SAD
RGB_1_SSD
RGB_2_SSD
HSI_1_SSD
HSI_2_SSD
YCrCb_1_SSD
YCrCb_2_SSD
RGB_1_ZSAD
RGB_2_ZSAD
HSI_1_ZSAD
HSI_2_ZSAD
YCrCb_1_ZSAD
YCrCb_2_ZSAD
RGB_1_ZSSD
RGB_2_ZSSD
HSI_1_ZSSD
HSI_2_ZSSD
YCrCb_1_ZSSD
YCrCb_2_ZSSD
RGB_GRAD
HSI_GRAD
YCrCb_GRAD
RGB_DST
HSI_DST
[%]
COLOR M_SAD M_SSD
M_ZSAD M_ZSSD M_GRAD
b
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
RGB_1_SAD
RGB_2_SAD
HSI_1_SAD
HSI_2_SAD
YCrCb_1_SAD
YCrCb_2_SAD
RGB_1_SSD
RGB_2_SSD
HSI_1_SSD
HSI_2_SSD
YCrCb_1_SSD
YCrCb_2_SSD
RGB_1_ZSAD
RGB_2_ZSAD
HSI_1_ZSAD
HSI_2_ZSAD
YCrCb_1_ZSAD
YCrCb_2_ZSAD
RGB_1_ZSSD
RGB_2_ZSSD
HSI_1_ZSSD
HSI_2_ZSSD
YCrCb_1_ZSSD
YCrCb_2_ZSSD
RGB_GRAD
HSI_GRAD
YCrCb_GRAD
RGB_DST
HSI_DST
[%]
COLOR M_SAD M_SSD
M_ZSAD M_ZSSD M_GRAD
c
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
RGB_1_SAD
RGB_2_SAD
HSI_1_SAD
HSI_2_SAD
YCrCb_1_SAD
YCrCb_2_SAD
RGB_1_SSD
RGB_2_SSD
HSI_1_SSD
HSI_2_SSD
YCrCb_1_SSD
YCrCb_2_SSD
RGB_1_ZSAD
RGB_2_ZSAD
HSI_1_ZSAD
HSI_2_ZSAD
YCrCb_1_ZSAD
YCrCb_2_ZSAD
RGB_1_ZSSD
RGB_2_ZSSD
HSI_1_ZSSD
HSI_2_ZSSD
YCrCb_1_ZSSD
YCrCb_2_ZSSD
RGB_GRAD
HSI_GRAD
YCrCb_GRAD
RGB_DST
HSI_DST
[%]
COLOR M_SAD M_SSD
M_ZSAD M_ZSSD M_GRAD
d
0
8
16
24
32
40
48
RGB_1_SAD
RGB_2_SAD
HSI_1_SAD
HSI_2_SAD
YCrCb_1_SAD
YCrCb_2_SAD
RGB_1_SSD
RGB_2_SSD
HSI_1_SSD
HSI_2_SSD
YCrCb_1_SSD
YCrCb_2_SSD
RGB_1_ZSAD
RGB_2_ZSAD
HSI_1_ZSAD
HSI_2_ZSAD
YCrCb_1_ZSAD
YCrCb_2_ZSAD
RGB_1_ZSSD
RGB_2_ZSSD
HSI_1_ZSSD
HSI_2_ZSSD
YCrCb_1_ZSSD
YCrCb_2_ZSSD
RGB_GRAD
HSI_GRAD
YCrCb_GRAD
RGB_DST
HSI_DST
[%]
COLOR M_SAD M_SSD
M_ZSAD M_ZSSD M_GRAD
Figure 4: Comparison of matching quality between colour (vert. bars) vs. monochrome matching (horz. lines) – as a
function of number of points rejected after cross-checking: (a) Relaxing Jack, (b) Cone, (c) Tsukuba, (d) Sawtooth.
a b c d
e
f
g
h
Figure 5: Disparity maps for Sawtooth (a) M_SAD, block size 1x1, false matches: 48,78%, (b) M_SAD, size 3x3, false
matches: 21,99%,(c) M_SAD, size 7x7, false matches: 7,99%, (d) M_SAD, size 13x13, false matches: 6,16%, (e)
RGB_2_SSD, size 1x1, false matches: 51,01%, (f) RGB_2_SSD, size 3x3, false matches: 27,75%, (g) RGB_2_SSD, size
7x7, false matches: 10,9%, (h) RGB_2_SSD, size 13x13, false matches: 6,28%.
VISAPP 2006 - MOTION, TRACKING AND STEREO VISION
368

a
10
14
18
22
26
135791113151719
[%]
M_SSD RGB_2_SSD
HSI_2_SAD YCrCb_1_SAD
b
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
135791113151719
[%]
M_ZSAD RGB_2_ZSAD
HSI_1_ZSAD YCrCb_1_ZSAD
c
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
135791113151719
[%]
M_SAD RGB_2_SAD
HSI_1_SAD YCrCb_1_SAD
Figure 6: False matches after validation as a function of block size for different methods: (a) Relaxing Jack, (b) Cones,
(c) and Sawtooth stereo pairs.
Figure 4 presents bar graphs comparing matching quality
between colour (vertical bars) versus monochrome
matching (horizontal lines), in terms of the number of
rejected points after cross-checking, for different methods
and images. Analyzing this collection, it is clear that
results acquired by corresponding methods are similar,
except for HSI colour space, where results are
significantly worse.
Figure 5 presents depth maps for the Sawtoots pair
acquired by matching regions of different size. The two
matching measures were used: M_SSD and RGB_2_SSD.
Independent of a size of matching regions, the former gave
better matching results. However, the latter case is just
opposite.
Figure 6 presents plots of false-matches rate, after the
validation with cross-checking, as a function of matching
block size, for different methods and stereo pairs.
From the presented sets of data we see that for
different images there is no significant advantage of
colour matching in comparison to the monochrome
version. Needless to say, that the latter computations
are much more time efficient.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The paper analyses several methods of matching of
the colour versus monochrome images. Additional
employment of colour information in the area-based
matching methods does not give satisfactory results.
Although there is thrice more information in colour
images, improvement of matching quality (false
matches and PSNR after reconstruction from the
depth map) is slight or paradoxically it is even
aggravated.
In general case incorrect matching of points in
monochromatic images is not a result of lack of
information in places where matching is possible.
Incorrect matching occurs mainly in areas of images
with insufficient texture for match discrimination or
in occluding places. Unfortunately, addition of
colour information does not help in these situations,
what was verified by the presented experiments. To
the detriment of these simple matching methods the
computational complexity is greatly increased.
Apparently the inherent correlation among
colour channels cannot result in significant
improvements of quality of the resulting disparities.
Thus, if higher quality is expected then more
advanced methods are recommended than presented
in this paper. Alternatively, an acceptable in many
applications compromise can be achieved with the
simple matching methods presented in this paper and
monochrome images.
REFERENCES
Cyganek, B., 2002. Three Dimensional Image Processing,
(in Polish) EXIT Warsaw, Poland.
Koshan, A., 1997. Improving Robot Vision by Colour
Information, Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Artificial
Intelligence, Slovakia.
Koshan, A., 1996. Using perceptual attributes to obtain
dense depth maps, Proc. of the IEEE Southwest
Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation,
USA, pp. 155-159.
Koshan A., Rodehorst V., Spiller K., 1996. Colour Stereo
Vision Using Hierarchical Block Matching and Active
Colour Illumination, ICPR `96, Austria, Vol. I, pp.
835-839.
Scharstein, D., 1998. View Synthesis Using Stereo Vision,
Lecture Notes on Computer Science No. 1583,
Springer, Berlin.
Scharstein, D., Szeliski, R., 2002. A Taxonomy and
Evaluation of Dense Two-Frame Stereo
Correspondence Algorithms. International Journal of
Computer Vision, Vol. 47, No. 1-3, pp. 7-42.
Tseng, D., Chang, C., 1992. Colour segmentation using
perceptual attributes, Proc. 11th Int. Conference on
Pattern Recognition, the Netherlands, pp. 228-231.
Wei, B., Liu, Y., Pan, Y., 2003. Using Hybrid Knowledge
Engineering and Image Processing in Colour Virtual
Restoration of Ancient Murals, IEEE Trans. on
Knowledge and Data Eng., Vol. 15, No. 5, pp. 1338-
1343.
Loo P.K., Tan C.L., 2002. Adaptive Region Growing
Colour Segmentation for Text using Irregular
Pyramid, Technical Report.
COMPARISON OF MATCHING STRATEGIES FOR COLOUR IMAGES
369
