
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR ADAPTED INFORMATION
RETRIEVAL IN UBIQUITOUS ENVIRONMENTS
Angela Carrillo-Ramos, Marlène Villanova-Oliver, Jérome Gensel and Hervé Martin
LSR Laboratory, SIGMA Team, 681 rue de la Passerelle, 38402 Saint Martin D’Hères, France
Keywords: Agents, Knowledge Management, Query Routing, Adaptation.
Abstract: PUMAS is a framework based on agents which provides nomadic users with relevant and adapte
d
information. Using PUMAS, information delivered to nomadic users is adapted according to, on the one
hand, their preferences and history in the system and, on the other hand, the limited capacities of thei
r
Mobile Devices (MDs). This framework is composed of four Multi-Agent Systems (MAS, Connection MAS,
Communication MAS, Information MAS and Adaptation MAS) for handling adaptation. In this paper, we
illustrate how the PUMAS agents augment user queries with information about her/his characteristics an
d
those of her/his MD and, how the Router Agent (which belongs to the Information MAS) redirects the use
r
queries towards the different Web based Information System (WIS) which contain all or part of the
information for answering them and which execute on servers or MDs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ubiquitous Computing is defined by the W3C
(http://www.w3.org/TR/webont-req/) as an emerging
paradigm of personal computing characterized
mainly by the use of Mobile Devices (MDs). The
term MD refers generally to small, handheld and
wireless computing devices, used to access Web
based Information System (WIS). WIS are systems
which enable collecting, structuring, storing,
managing and diffusing information, like traditional
Information Systems (IS) do, but over a Web
infrastructure. WIS provide users with complex
functionalities which are activated through a Web
browser in a hypermedia interface. WIS designers
must be provided with mechanisms and architectures
that cope with the reduced capabilities of the MDs,
in order to efficiently retrieve and deliver data using
these devices. The WIS must provide users with
useful information retrieved from an intelligent
search and presented in a suitable way. We believe
that the agent paradigm is an interesting approach
for this purpose. The Multi-Agent System (MAS)
approach is defined in (El Fallah-Seghrouchni et al.,
2004) as a credible paradigm to design distributed
and cooperative systems based on the agent
technology.
The interest of MAS, when the Internet is used to
access and exchange information through MDs (that
they call “smart devices”), is shown in (Ramparany
et al., 2003). In this case, agents can be useful to
represent user characteristics inside the system and
the MDs can work like “cooperative devices”. The
W3C defines an agent as “a concrete piece of
software or hardware that sends and receives
messages”. In our context, these messages can be
used to access a WIS and to exchange information.
The MD applications require network architectures
able to support automatic and ad hoc configuration
which consider features of the ubi
quitous computing
environment such as heterogeneity, mobility,
autonomy, high distribution, etc. Such environment
is defined in (Pirker et al., 2004) as a dynamic
distributed network of embedded devices and
systems that can interact with humans to satisfy their
requirements and provide a variety of information,
communication, and collaboration services.
In order to provide nomadic users only with the most
relevant information (i.e. “the right information in
the right place at the right time"), a MD application
must embed mechanisms for propagating the user
queries towards the “right” information sources
(stored in one or several devices) which can answer
these queries considering user preferences, features
of her/his MDs, her/his location, etc. This is the
21
Carrillo-Ramos A., Villanova-Oliver M., Gensel J. and Martin H. (2006).
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR ADAPTED INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN UBIQUITOUS ENVIRONMENTS.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Internet Technology / Web
Interface and Applications, pages 21-29
DOI: 10.5220/0001237900210029
Copyright
c
SciTePress
main purpose of the Query Routing process. (Xu et
al., 1999) define this process as the general problem
of, on the one hand, evaluating the query using the
most relevant data sources and, on the other hand,
integrating results returned from data sources. In
order to optimize the Query Routing process,
(Agostini et al., 2004) and (Park et al., 2004)
propose to use some metrics related to the
trustworthiness of the information sources, their
capability to satisfy user information needs and their
timeliness of information delivery.
PUMAS (Carrillo et al., 2005a) is a framework for
retrieving information distributed between several
WIS and/or different types of MDs. The architecture
of PUMAS is composed of four MAS (Connection
MAS, Communication MAS, Information MAS and
Adaptation MAS), each one encompassing several
ubiquitous agents which cooperate to achieve the
different tasks handled by PUMAS (e.g., MD
connection/disconnection, communications between
agents, information exchange, storage and retrieval,
etc.). In this paper, we present the activities of
representation and data exchange of the PUMAS
agents (activities based on XML files). Through
PUMAS, the final objective is to build and propose a
framework which additionally to the management of
accesses to WIS performed through MDs, is also in
charge of performing an adaptation of information
according to user profiles (which refers to their
needs, preferences, histories in the system, current
location, etc.) and, the technical capabilities of
her/his MD. This paper focuses on the representation
of knowledge managed by PUMAS agents (to
achieve the adaptation tasks and support the Query
Routing process executed by the Router Agent) in
order to redirect queries formulated by users towards
the different WIS. We show here how the Knowledge
Bases (KBs) managed by PUMAS agents are used by
this process. We also explain and illustrate each
activity of the Query Routing process using as
example an airport WIS and a scenario we briefly
describe:
A passenger equipped with her/his MD must take a
plane. Let us suppose that she/he must arrive three
hours before for checking in and that she/he also
must buy some gifts at the duty free shops. Let us
assume that, at the airport, each airline and shop
has a WIS which provides customers with
information about their services (e.g., departure and
arrival schedule) and their products (e.g., sales, new
products). The passenger wants to know the closest
duty free shops to the departure gate of her/his flight
which sell each article of her/his gift list (at the
lowest price). Let us suppose that several shops sell
the same products (e.g., souvenirs, books, post
cards, liquors) which correspond to what the user
would like to buy.
The paper is organized as follows. We present in
section 2, the goal and the architecture of the
PUMAS framework. We describe more particularly
the data representation and data exchange of the
agents and their managed information. In section 3,
we present Knowledge Management, especially that
performed by agents which belong to the
Information and Adaptation MAS for adaptation
purposes. In section 4, through the example scenario
described above, we explain the Query Routing
process performed by the Router Agent. Finally, we
present some related works before we conclude in
section 6.
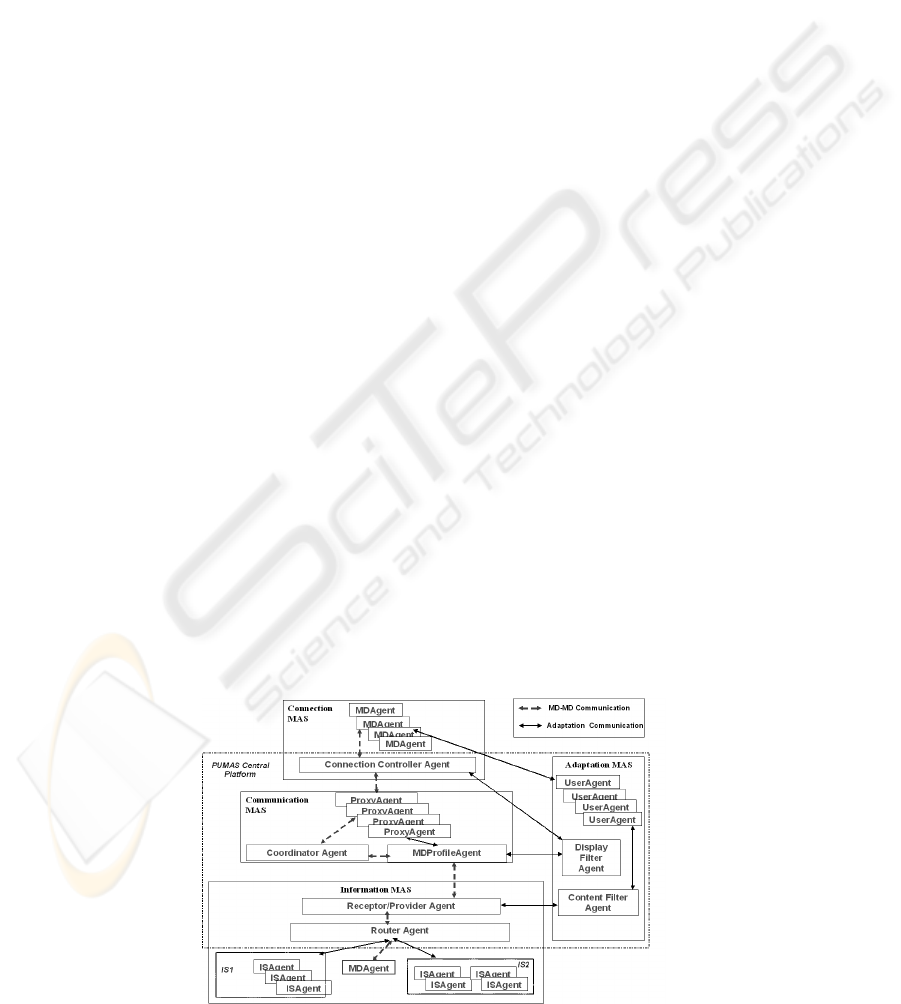
2 THE PUMAS FRAMEWORK
The architecture of PUMAS is composed of four
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) which will be explained
in the following subsections (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: The PUMAS Architecture.
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
22

The PUMAS framework has been extended
compared to the architecture presented in (Carrillo et
al., 2005a). We have introduced in (Carrillo et al.,
2005b) a new MAS, called the Adaptation MAS, in
the architecture of PUMAS. The agents belonging to
the Adaptation MAS have as responsibilities to
manage specific XML files which contain
information about the user and her/his MD. Its
knowledge allows selection and filtering of
information for users. This paper focuses, on the one
hand, on the managed knowledge and the exchanged
information between agents of PUMAS, especially,
those belonging to the Information and the
Adaptation MAS for adaptation purposes, and on the
other hand, on the strategies followed by the Router
Agent in order to perform the Query Routing
process. The following subsections give a short
description of each MAS, focusing on the
information exchanged between PUMAS agents. A
detailed description of the Connection MAS, the
Communication MAS and the Information MAS can
be found in (Carrillo et al., 2005a) while the
Adaptation MAS is presented in detail in (Carrillo et
al., 2005b).
2.1 The Connection MAS
This MAS includes several Mobile Device Agents
and one Connection Controller Agent.
A Mobile Device Agent is executed on the user’s
MD. This agent manages the Device Profile XML
file, located on the user’s MD, which describes the
characteristics of the MD, using OWL (Ontology
Web Language, http://www.w3.org/2004/OWL/) in
order to define a common ontology for all agents
which share this information (e.g., the
DisplayFilterAgent which belongs to the Adaptation
MAS, see section 2.4). This file contains some
information about hardware and software
requirements, network status, type of hypermedia
files supported by the MD, conditions for
disconnecting (i.e. finishing sessions), etc. A Mobile
Device Agent also manages the Session XML file
which describes characteristics of the user sessions:
who is the user connected, when the session begun
and what MD is connected. This file will be
exchanged with the UserAgent (belonging to the
Adaptation MAS).
The Connection Controller Agent executes on the
central platform of PUMAS. This agent checks
connections established by users and agent status
(e.g., connected, disconnected, killed, etc.). It also
gets the user’s location and the MD type (e.g., PDA)
from the User Location XML file (which contains
physical and logical location features) and from the
Device Profile XML file (which contains MD
features). Both files are provided by the Mobile
Device Agents and locally managed by the
Connection Controller Agent.
The XML files (i.e., User Location, Session and
Device Profile XML files) managed by the Mobile
Device Agent and the Connection Controller Agent
have been defined using
OWL and the extensions
introduced by (Indulska et al., 2003) to CC/PP.
These extensions include some user characteristics
like location (physical and logical location),
requirements of available applications (hardware,
software, browser and WAP requirements),
characteristics of sessions (user, device, application)
and user profiles (general user’s requirements,
preferences).
2.2 The Communication MAS
This MAS is composed of several Proxy Agents, one
MDProfile Agent and one Coordinator Agent. These
agents are located in the central platform of PUMAS.
There is one Proxy Agent for each connection from
a Mobile Device Agent. The main task of this agent
is to represent a Mobile Device Agent within the
system and has the same properties and behaviour as
the Mobile Device Agent except those concerning
the connection.
The MDProfile Agent has to check the user profiles
according to her/his MD. This agent shares
information about specific MD features for user
session with the DisplayFilterAgent (which belongs
to the Adaptation MAS).
The Coordinator Agent is in permanent
communication with the Connection Controller
Agent in order to verify connection status of the
agent which searches for information. This agent
knows all agents connected in the system using a
yellow pages mechanism. If there are some
problems with the Connection Controller Agent
(e.g., if the Connection Controller Agent fails or, if
there is a lot of connections), the Coordinator Agent
can play the role of the Connection Controller Agent
up until problems are fixed. At that moment, the
Connection Controller Agent and the Coordinator
Agent must synchronize information about the
connected agent and check current connections.
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR ADAPTED INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN UBIQUITOUS
ENVIRONMENTS
23

2.3 The Information MAS
The Information MAS is composed of one or several
Receptor/Provider Agents, one or several Router
Agents and one or several ISAgents.
The Receptor/Provider Agents which are located in
the central platform of PUMAS own a general view
of the whole system. They receive requests that are
transmitted from the Communication MAS and
redirect them to the Router Agents. Once a query has
been processed by the ISAgents, a Receptor/Provider
Agent checks whether the query results consider the
user profile according to her/his preferences, history
in the system, etc.
In order to redirect a query to the “right” WIS, the
Router Agent applies a strategy which depends on
one or several criteria (see section 4). This agent
also compiles results returned by the ISAgents and
analyzes them (according to defined criteria in the
user preferences) to decide whether the whole set of
results or only a part of it has to be sent to the
Receptor/Provider Agents.
An ISAgent associated with a WIS (and which
executes on the same device that the WIS) receives
user queries from the Router Agent and is in charge
of searching for information. Once a result for a
query is obtained, the ISAgent returns it to the
Router Agent. An ISAgent can execute a query by
itself or delegate this task to the adequate WIS
component.
2.4 The Adaptation MAS
This MAS is composed of one or several
UserAgents, one DisplayFilterAgent and one
ContentFilterAgent. They are located in the central
platform of PUMAS.
Each UserAgent manages a User Profile XML file
(defined using OWL) which contains personal
characteristics of a user (e.g., user ID, location, etc.)
and her/his preferences (e.g., the user wants only
video files). This file is obtained by means of the
Mobile Device Agent (which executes on the user’s
MD). There is only one UserAgent which represents
a user at the same time and centralizes all the
characteristics of the same user who can have
several sessions opened. The UserAgent
communicates with the ContentFilterAgent to send
the User Profile XML file in order to update user
preferences.
The DisplayFilterAgent manages a Knowledge Base
which contains general information about the
characteristics of different types of MDs (e.g.,
format files supported) and knowledge acquired
from previous connections (e.g., problems and
capabilities of networks according to data
transmissions).
The ContentFilterAgent manages a Knowledge Base
which contains preferences and characteristics of the
users. It communicates with the UserAgent, asking
for user preferences defined for a specific session
(e.g., the current session).
3 KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
IN PUMAS
In this section, we describe the knowledge managed
by agents of the Information and the Adaptation
MAS of PUMAS to achieve their adaptation tasks
and support the Query Routing process. This
knowledge is stored in Knowledge Bases (KBs) in
the shape of pieces of knowledge called “facts” and
defined using JESS (which is a rule engine and
scripting environment for building Java applications
which has the capacity to "reason" using knowledge
supplied in the form of declarative rules.
http://herzberg.ca.sandia.gov/jess/). We declare
these facts as instances of JESS Templates in order
to represent user preferences, features of the MD, the
WIS, etc. as described in the following subsections.
3.1 Knowledge of the Information
MAS
The Router Agent stores in its KB a fact for each
WIS. This agent exploits these facts to redirect user
queries. A fact which represents a WIS describes
characteristics of the WIS like its name, managed
information, the type of device where it is executed
(e.g., server, MD) and the ISAgent associated with
the WIS (i.e., the ISAgent which execute on the WIS
and can be asked for information and consequently
answers queries). The following template defines a
WIS:
(deftemplate WIS
(slot name)
(slot agentID)
(slot device)
(multislot info_items)) ; fact (1)
The following fact (instance of the template defined
above) represents the WIS of a store. The WIS is
called StoreWIS and executes on a server. The
ISAgent which executes on this WIS is called
StoreISA. The StoreWIS contains information (a list
of info_items) about the articles, sales, and new
products which are sold in the store:
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
24

(assert (WIS
(name StoreWIS)(agentID StoreISA)
(device server)
(info_items “articles” “sales” “new
products”)))
3.2 Knowledge of the Adaptation
MAS
The ContentFilterAgent (CFA) manages a KB which
contains user preferences. These preferences are
represented as facts defined as follows:
(deftemplate User_Preference
(slot userID)
(slot required_info)
(multislot complementary_info)
(multislot actiontodo)
(slot problem)
(multislot actionforrecovering))) ; fact
(2)
The User_Preference fact is composed of a userID
(which identifies the owner of this preference),
required information (required_info) and
complementary_info which is added to the
User_Preference definition by the CFA and is
inferred from queries of previous sessions (i.e.
information frequently asked simultaneously with
the required_info). This fact is also composed of
information about what and how the user would like
the system to present results (list of actionstodo for
displaying information to her/him) and in the case of
problems, what the system has to do
(actionsforrecovering).
We consider that queries also depend on several
criteria (criteria managed by the CFA): user location,
her/his history in the system, activities developed
during a time period, etc. Such Criterion is defined
as:
(deftemplate Criterion
(slot userID)(multislot criteria)
(multislot attributes)) ; fact (3)
Here is an example of Criterion which expresses
that all of John Smith’s queries depend on his
location, especially if he is in the airport:
(assert (Criterion
(userID “John Smith”)
(criteria location)
(attributes “airport” )))
In the next section, we describe the Query Routing
process which is performed by the Router Agent
exploiting the knowledge we have described in this
section.
4 QUERY ROUTING IN PUMAS
The Query Routing (QR) process in PUMAS is
achieved by the Router Agent (RA) which receives
queries together with user characteristics and those
of their MDs. In order to redirect a query to the
“right” WIS, the strategy chosen by the RA depends
on several criteria: user location, peer similarity,
time constraints, preferences, etc. The strategy can
lead to sending the query to a specific WIS, or to
sending the query through broadcast, or to splitting
the query in sub-queries, each one being sent to one
or several ISAgents (ISAs, agents which belong to
the Information MAS and execute on the WIS). The
RA is also in charge of compiling results returned by
the ISAs and of analyzing them (according to the
defined criteria for the queries, see section 3.2) to
decide whether the whole set of results or only a part
of it will be sent to the user.
In PUMAS, the QR process consists of three
activities, based on the work of (Xu et al., 1999)
which are described and illustrated in the next
subsections, using the airport scenario presented in
introduction.
4.1 Analyzing the Query
This activity is related to the possible split of a query
into sub-queries. The RA analyzes the complexity of
a query. A query is considered as simple if it can be
answered by only one agent and complex if several
agents are required. This analysis is more precisely
based on facts, stored in the KB of the RA, about the
WIS (which notably contains knowledge about
information managed by this WIS). The RA also
analyzes criteria of a query (e.g., location, user’s
activities, etc.), knowledge of the query receivers
(e.g., if the query is directed to specific known
receivers), etc. After this analysis, the RA decides
whether it has to divide a query in sub-queries or
not.
For the scenario, the RA must split the query (“all
the shops which sell the articles of my gifts list”) in
several sub-queries (“all the shops which sell each
article of my gifts list”). The number of sub-queries
depends of the number of articles. If there is only
one article, the query is simple (only one agent will
answer). Otherwise, the query is complex. The RA
must also consider two criteria: proximity of the
departure gate and price of the article in the shop.
For that, the RA asks the CFA for the user
preferences and criteria of the query (i.e., fact (2,3)
and its instances; see section 3.2). The RA could
receive from CFA facts as the following which
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR ADAPTED INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN UBIQUITOUS
ENVIRONMENTS
25

expresses that when the passenger “John Smith”
consults the “closest shops”, he also wants those
which sell their products at the “lowest prices”:
(assert (User_Preference
(userID “John Smith”)
(required_info “closest shops”)
(complementary_info “lowest prices”)
(actiontodo show)
(problem “empty list of shops”)
(actionforrecovering cancel)))
4.2 Selecting the Information
Sources
A query could be directed to a specific agent or to a
group of agents; if the query receivers are known,
the selection is simple (the potential information
sources are the specific agents). Otherwise, the RA
selects information sources and computes the
network of neighbours, based on ideas of (Yang et
al., 2004). These authors propose an efficient QR
approach for information retrieval in unstructured
P2P networks. The QR policies are utilized to
determine to how many nodes and to which nodes,
the query should be forwarded in the network. This
work introduces the Routing Guide (RG) concept
which is based on results returned for queries
previously processed, and is used to determine
routing directions for queries. In the information
retrieval process in P2P systems, each node owns a
collection of data that is shared with other nodes.
When a user submits a query, her/his node becomes
the source of the query (requestor). Such node may
send query messages to any number of its
neighbours. Then any neighbour receiving the query
message firstly processes the query over its local
information. If the node finds some results, it sends
back its address to the requestor node so that it
fetches data directly.
In our proposal, a peer is neighbour of some others
if it satisfies a set of characteristics (criteria defined
in user preferences of an application). For example,
close location, same activities, same role, similar
knowledge, colleagues who work in group. The
characteristics are not restricted to proximity criteria.
We can consider several cases for composing a
network of neighbours in which each node is an
information source:
First case, there could be one or several agents
which answer the same query. The simplest way of
composing this network is to group all these agents.
This gathering is useful, for example, when the RA
does not have information about the sources or when
it is the first time that the RA works with the
neighbours. In order to avoid unnecessary,
redundant or useless communications and select the
most relevant neighbours, the RA applies criteria of
dependency of the query. For instance, if the
criterion is location, the network is composed of the
nearest neighbours; if user queries depend on her/his
previous queries, the RA must redirect them to the
most trusted neighbours; if the criterion is similarity,
the network could be composed of the neighbours
with a similar profile, tasks, etc. If no criteria are
established, the RA analyzes the trust level of these
neighbours. The RA associates a trust level to each
neighbour from answers to previous queries, based
on the work of (Agostini et al., 2004). In these
authors’ work, when a peer receives a query, it
analyzes the result of its queries and increases the
trust of those peers who reply with more appropriate
semantic contents. This work explains the process
for sending queries from a peer to other ones. After
query formulation, a peer named “seeker” checks
what peers are connected (“active”) and chooses,
among those connected, which peers send the query.
A query session is then opened to manage the
answer from each peer, or from peers that are
connected with the peer in charge of solving the
query. The strategy used by the seeker in order to
select a provider and referrals from providers to
solve the query is a Trust and Reputation Strategy.
The Trust and Reputation Strategy proposed by
(Agostini et al., 2004) consists of the following
process: the seeker faces the problem of selecting
which one among the peers is able to solve a query
Q with highest probability, or who makes the most
progress towards solving the query. To decide, the
seeker constructs and manages a list <p1, p2,…pk>
of trusted peers to which submit the query. The list
is conventionally ordered according to decreasing
trust level. The seeker strategy of query resolution is
the following: first, it asks p1, then p2, and
continues up to pk until it receives relevant answers
from previous peers in the list. It is important to note
that the list of trusted peers evolves with the system.
The Trust of a peer is acquired by its Reputation.
Second case, a query could be only answered by one
agent which is known. The RA uses its KB
(describing what are the WIS, their ISAs and their
managed information) to contact the WIS from
which it could obtain the answer to this query. This
is a specialization of the first case.
Third case, the query has been split in several sub-
queries in the analysis step. The RA analyzes which
agents can answer each one. The network of
neighbours is then composed by the agents which
could answer the sub-queries. The process applied in
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
26

order to select information sources (ISAs) for each
sub-query is the same that the process defined in the
first case. Finally, the network of neighbours is
composed of the union of the different sub-networks
generated for each sub-query.
For the scenario, the RA could include in the
network of neighbours all ISAs executing on WIS of
the duty free shops which sell the products she/he
searches (based on fact (1) and its instances; see
section 3.1). The RA must also analyze the trust level
associated with these neighbours (e.g., the first shop
which answers). If it is the first time that the RA
executes this query or that works with these ISAs,
the RA sends the query to them through a broadcast
message. The RA must compose the network of
neighbours of the agents which could answer the
sub-queries of the query (“the closest shops to the
departure gate which sell the wanted article at the
lowest price”). In order to select the WIS of those
shops, the RA must apply criteria for the queries
(based on fact (3) and its instances; see section 3.2),
in this case, the proximity of the shops to the
departure gate and the lowest price for the articles.
For this case, the RA could store facts in its KB like
the ones presented below. These facts express that
all queries from passenger “John Smith” depends on
both his location, particularly if he is at the airport,
and, the proximity of the departure gate:
(assert (Criterion
(userID “John Smith”)
(criteria location)
(attributes “airport” )))
(assert (Criterion
(userID “John Smith”)
(criteria proximity)
(attributes “departure gate” )))
4.3 Redirecting the Query
Once the RA has identified potential information
sources (neighbours), it redirects the query, sending
a message which includes the query to its
neighbours. The RA can use an oriented message
(for specific receivers) or broadcast it to all
neighbours (e.g., waiting for the first one to reply,
obtaining all the answers and analyzing which are
the most trusted ones). If the RA has a trust schema
for the agents which compose the network of
neighbours, the RA could send the message in a
sequential way, starting with the most trusted one. If
it answers, the process is finished. Otherwise, the RA
has to continue sending messages until the least
trusted agent has been contacted, according to the
ideas of (Agostini et al., 2004).
For the scenario, the network is composed of ISAs
which execute on the WIS of the duty free shops. If
there is only one shop WIS, the RA sends it the
query. Otherwise, the RA sends the query to each
ISA, beginning with the most trusted one.
If the RA knows that neighbor1 can answer sub-
query1, neighbor2 can answer sub-query2 and so on,
it sends the oriented messages to each neighbour
(based on fact (1) about the WIS and its instances;
see section 3.1). For example, if the passenger would
like to know if her/his flight is on time, the RA sends
the query to the ISA which executes on the WIS of
the airline (for this example, we call it “OneISA”)
and to the ISA which executes on the WIS of the
airport and manages flight departure and arrival
schedules (for this example, we call it
“DAFlightsISA”). In this case, we can find in the KB
of the RA the following facts which allow it to
redirect the query to the OneISA and the
DAFlightsISA:
(assert (WIS
(name AirlineOneIS)(agentID OneISA)
(device server)
(info_items “departures” “arrivals”
“prices”)))
(assert (WIS
(name AirportIS)(agentID DAFlightsISA)
(device server)
(info_items “departures” “arrivals”)))
The RA must then compile answers obtained from
different agents and select the most relevant ones
according to the established dependency criteria.
The mechanisms for compiling results are not
explained in this paper.
5 RELATED WORKS
We present here some agent-based architectures or
frameworks for adapting information to users.
CONSORTS Architecture (Kurumatani, 2003) is
based on ubiquitous agents and designed for a
massive support of MDs. It detects user locations
and defines user profiles to adapt their information.
The CONSORTS architecture proposes a mechanism
to define the relations that hold between agents (e.g.,
communication, hierarchy, role definition), with the
purpose of satisfying user requests. Unlike PUMAS,
it does not consider distribution of information
between MDs (which could improve response time)
nor user preferences.
The work of (Gandon et al., 2004) proposes a
Semantic Web architecture for context-awareness
and privacy. This architecture supports automated
discovery and access of a user’s personal resources
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR ADAPTED INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN UBIQUITOUS
ENVIRONMENTS
27

subject to user-specified privacy preferences.
Service invocation rules along with ontologies and
profiles enable identification of the most relevant
resources available to answer a query. However, it
does not consider that information which can answer
a query can be distributed between different sources.
The PIA-System (Albayrak et al., 2005) is an agent-
based personal information system for collecting,
filtering and integrating information at a common
point, offering access to information by WWW, e-
mail, SMS, MMS and J2ME clients. It combines
push and pull techniques in order to allow the user
on the one hand, to search explicitly for specific
information and, on the other hand, to be informed
automatically about relevant information. However,
the PIA System only searches information in text
format. It does not consider the adaptation of
different kinds of media to different MDs, nor user
location.
(Sashima et al., 2004) propose an agent-based
coordination framework for ubiquitous computing. It
coordinates services and devices to assist a particular
user in receiving a particular service in order to
maximize her/his satisfaction. This framework
chooses proper resources from numerous sources,
coordinates those resources on behalf of users and
assists them in accessing resources of ubiquitous
computing environments. These authors take into
account the contextual features of nomadic users,
especially, the location. Unlike PUMAS, this
framework does not consider the adaptation of
information according to the access devices nor the
possible distribution of data among devices.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we have described knowledge
managed and exchanged by the Information and the
Adaptation MAS of PUMAS to support the
adaptation capabilities and the Query Routing
process. PUMAS is a framework which retrieves
adapted information according to user profiles and
technical capabilities of MDs used to access the Web
Information Systems (WIS). We have also described
the strategies followed by the Router Agent to
perform the Query Routing process. In PUMAS, this
process is composed of three activities: analysis of
the query, selection of the information sources and
redirection of the query. Finally, we have presented
each activity and we have also illustrated them
through a scenario supported by a WIS in an airport.
We are currently implementing and testing each
MAS of PUMAS. For this purpose, we have chosen
JADE-LEAP (http://jade.tilab.com/), a FIPA
compliant platform. We intend to define, on the one
hand, algorithms for each activity of the Query
Routing process and, on the other hand, extensions
of an Agent Communication Language (ACL,
http://www.fipa.org/specs/fipa00061/SC00061G.htm
l) in order to consider nomadic user characteristics
like location and connection time. For this purpose,
we want to introduce in ACL, primitives like query-
when, query-where, query-close.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author Angela Carrillo-Ramos is partially
supported by the Universidad de los Andes
(Colombia). She thanks Nicolas Lopez-Giraldo for
his comments.
REFERENCES
Agostini, A., Moro, G., 2004. Identification of
Communities of Peers by Trust and Reputation. In
AIMSA 2004, 11th Int. Conf. in Artificial Intelligence:
Methodology, Systems, and Applications. LNCS,
3192, Springer Verlag, 85-95.
Albayrak, S., Wollny, S., Varone, N., Lommatzsch, A.,
Milosevic D., 2005. Agent Technology for
Personalized Information Filtering: The PIA-System.
In SAC 2005, 20th ACM Symposium on Applied
Computing. ACM Press, 54-59.
Carrillo-Ramos, A., Gensel, J., Villanova-Oliver, M.,
Martin, H., 2005a. PUMAS: a Framework based on
Ubiquitous Agents for Accessing Web Information
Systems through Mobile Devices. In SAC 2005, 20
th
ACM Symposium on Applied Computing. ACM Press,
1003-1008.
Carrillo-Ramos, A., Gensel, J., Villanova-Oliver, M.,
Martin, H., 2005b. A Peer Ubiquitous Multi-Agent
Framework for providing nomadic users with adapted
information. In AP2PC 2005, 4th Int. Workshop on
Agents and P2P Computing. Eds: Despotovic, Z.,
Joseph, S. and Sartori, C., 166-179.
El Fallah-Seghrouchni, A., Suna, A., 2004. CLAIM: A
Computational Language for Autonomous, Intelligent
and Mobile Agent. In PROMAS 2003, 1st Int.
Workshop on Programming Multi-agent Systems
Languages and Tools. LNAI, 3067, Springer-Verlag,
90-110.
Gandon, F., Sadeh, N., (2004, Oct). Semantic Web
Technologies to Reconcile Privacy and Context
Awareness. In Journal of Web Semantics, 1 (3).
Retrieved Nov. 9, 2005, from
http://www.websemanticsjournal.org/ps/pub/2004-17.
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
28

Indulska, J., Robinson, R., Rakotonirainy, A., Henricksen
K., 2003. Experiences in Using CC/PP in Context-
Aware Systems. In MDM 2003, 4th Int. Conf. in
Mobile Data Management. LNCS, 2574, Springer-
Verlag, 247-261.
Kurumatani, K., 2003. Mass User Support by Social
Coordination among Citizen in a Real Environment. In
MAMUS 2003, Int. Workshop in Multi-Agent for Mass
User Support. LNAI, 3012, Springer-Verlag, 1–16.
Park, J., Barber, S., 2004. Finding Information Sources by
Model Sharing in Open Multi-Agent System. In
UbiAgents04, Workshop on Agents for Ubiquitous
Computing. Retrieved Nov. 9, 2005, from
http://www.ift.ulaval.ca/~mellouli/ubiagents04/
Pirker, M., Berger M., Watzke, M., 2004. An approach for
FIPA Agent Service Discovery in Mobile Ad Hoc
Environments. In UbiAgents04, Workshop on Agents
for Ubiquitous Computing. Retrieved Nov. 9, 2005,
from http://www.ift.ulaval.ca/~mellouli/ubiagents04/
Ramparany, F., Boissier, O., Brouchoud, H., 2003.
Cooperating Autonomous Smart Devices. In
sOc’2003, the Smart Objects Conference, 182-185.
Sashima, A., Izumi, N., Kurumatani, K., 2004. Bridging
Coordination Gaps between Devices, Services, and
Humans in Ubiquitous computing. In UbiAgents04,
Workshop on Agents for Ubiquitous Computing.
Retrieved Nov. 9, 2005, from
http://www.ift.ulaval.ca/~mellouli/ubiagents04/.
Xu, J., Lim, E., Ng, W.K., 1999. Cluster-Based Database
Selection Techniques for Routing Bibliographic
Queries. In DEXA 99, 10th Int. Conf. on Database and
Expert Systems Applications. LNCS, 1677, Springer-
Verlag, 100-109.
Yang, D., Xu, L., Cai, W., Zhou, S., Zhou, A., 2004.
Efficient Query Routing for XML Documents
Retrieval in Unstructured Peer to Peer Networks. In
APWeb 2004, 6th Asia Pacific Web Conf. LNCS,
3007, Springer-Verlag, 217-223.
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT FOR ADAPTED INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN UBIQUITOUS
ENVIRONMENTS
29
