
Continuous Blood Pressure Measurements in Stress
Situations
Cord Volker Bauch
1
, Dieter Barschdorff
2
1
Light Laboratory L-LAB, Salzkottener Str. 1, Paderborn, Germany
2
Electrical Measurement, Faculty EIM-E, University of Paderborn, Paderborn, Germany
Abstract. When a person is exposed to physical and psychological challenge,
the autonomic nervous system reacts in a way to cope the situation. Stress con-
ditions are usually characterized by heart frequency or skin resistance changes.
Though also the blood pressure is known to increase in stress situations, its
measurement was not meaningful because of the insufficient time resolution of
instruments using inflatable cuffs. We present the first model based continuous
blood pressure determinations during stress tests. The measuring technique is
based on the dependency of the systolic blood pressure on the pulse transit time
and on individualized mathematical models. The Vienna Test System and car
driving situations in the driving simulator "Nightdriver" are examined. With the
new technique the blood pressure can be determined without interfering with
the persons cognitive perceptions. It clearly correlates to different stress levels.
1 Introduction
Due to today's fast changing lifestyle and working conditions a majority of people feel
that they are permanently in a state of physical and psychological stress. They speak
of work-related tensions and burnout effects. An increased heart frequency, an accel-
erated blood circulation and, due to sweating, a decrease of the skin resistance are
typical symptoms. Reactions of the autonomic nervous system are the release of the
hormones adrenalin and noradrenalin which lead to a dilatation of blood vessels and
an increased blood pressure. In order to characterize a person's physiological reaction
in situations of special physical efforts and under emotional stress the heart rate, the
heart rate variability and the skin resistance serve as measurable parameters. Blood
pressure variations under such circumstances have not been investigated in detail
because of the lack of an adequate measuring method with high time resolution which
does not interfere with the person's cognitive perception.
Blood pressure measurements in stress situations so far are only possible utilizing
the procedure of Riva-Rocci or with fully automated instruments, utilizing the oscil-
lometric method. Due to the in- and deflating of the cuffs around the upper arm and
the associated pump noise, the measurement highly influences on the persons atten-
tion, which also affects on the blood pressure. Even if an experienced person executes
the measurement, it lasts about 30 seconds. Moreover, a time interval of about one
minute should exist between two measurements. So the time resolution is rather poor
Volker Bauch C. and Barschdorff D. (2006).
Continuous Blood Pressure Measurements in Stress Situations.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Biosignal Processing and Classification, pages 126-134
DOI: 10.5220/0001225401260134
Copyright
c
SciTePress

and registrations of fast blood pressure variations, especially during exercise activities
are not possible. If no movements of the subjects occur the accuracy is in the range of
±3 mmHg.
As "gold standard" the direct invasive measurement using an intra-arterial catheter
is regarded. This technique measures the blood pressure continuously but it is con-
nected with a high instrumental expenditure and significant risks for the patient. Thus
it but cannot be used under laboratory conditions or in real life situations.
There exist non-invasive continuously operating blood pressure measuring systems
using finger cuffs [1] like the Peñáz-method or piezoelectric pressure sensors placed
above exposed arteries [2]. Disadvantage is that squeezing of the fingers by the cuffs
can lead to pain and deafness. Beyond that, due to the movement sensitivity and be-
cause of their size these instruments could not be used in the present investigation.
Finally, the systolic beat-to-beat blood pressure can be computed utilizing a mathe-
matical model with the heart frequency and the pulse transit time as physiological
parameters. While former investigations in this context were based on assuming a
linear dependency between blood pressure and pulse wave velocity [3] or used artifi-
cial neural networks trained with a great variety of patient data [4], we found, that a
high accuracy and long term stability of the model based blood pressure determina-
tion can only be achieved using personalized mathematical models [5, 6]. This
method is used for the present investigation on the influence of stress on the arterial
blood pressure.
2 Method
On the basis of an idealized artery model a relationship between blood pressure and
pulse transit time can be derived [7, 8, 9]. A quadratic equation is the basis for the
blood pressure determination, utilizing normalized values of the pulse transit time
T
R_P
as input and the systolic blood pressure P
sys
as output. In order to calculate the
blood pressure continuously, the beat-to-beat pulse transit time, the individual model
coefficients and the initial blood pressure values of the test person at rest are needed.
The measurement requires appropriate sensors. As already shown in [5], a chest belt
is suitable for detecting the QRS-complex in the ECG, which corresponds to the be-
ginning of the pulse transit time interval. An optical ear sensor serves as pulse wave
arrival indicator. After a few minutes the subjects were not aware of the sensors any
more. So the method can be applied without interfering with the person's attention.
To define the model coefficients, the blood pressure and the pulse transit time have
to be measured at different load conditions. Therefore we use the stair climbing test
after Schellong [10] where the subject has to ascend and descend steps for a certain
time. An immediate rise of the heart frequency, a decrease of the pulse transit time
and a steep rise of the systolic blood pressure occurs after the test begins, Fig. 1. Dur-
ing recovery initial values from prior to the test are reached. Due to the different time
constants of the pressure rise in the exercise phase and the pressure drop during re-
covery two sets of parameters characterizing exercise and recovery are being deter-
mined.
127
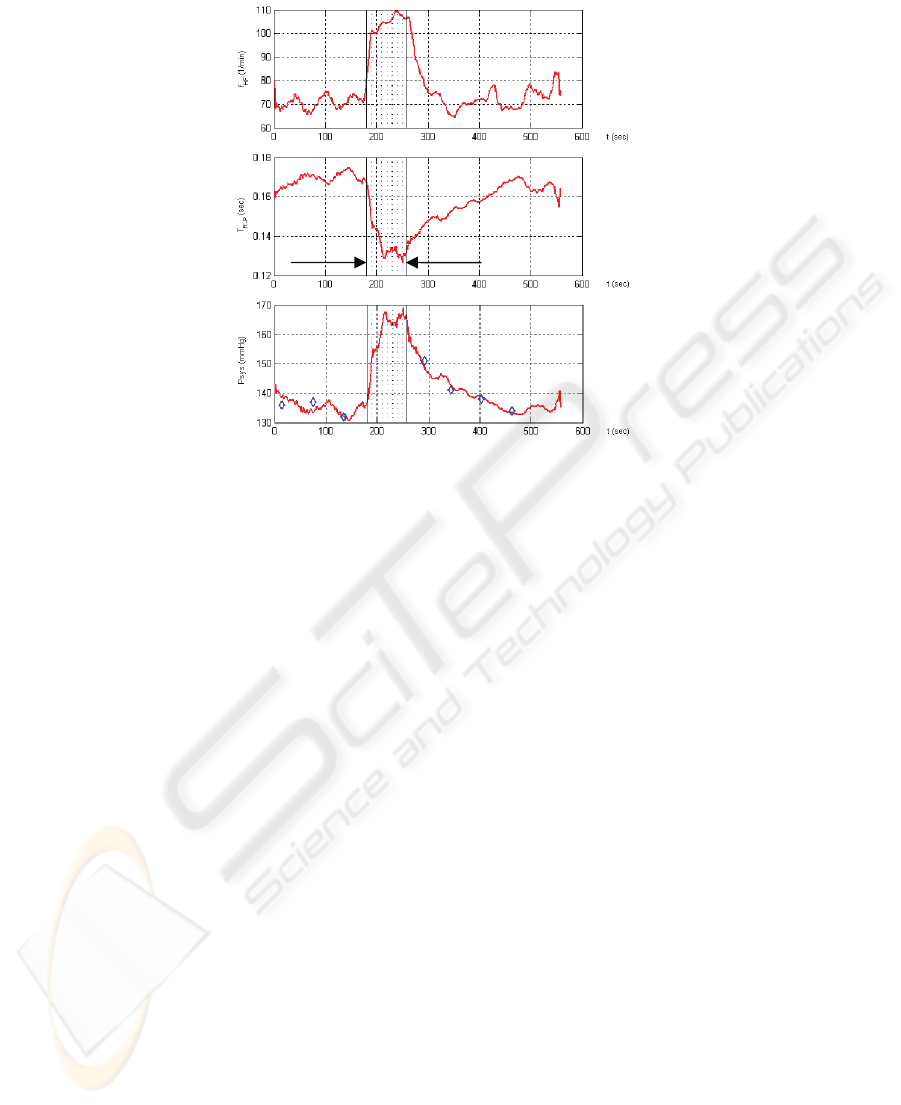
Fig. 1. Heart frequency, pulse transit time and computed systolic blood pressure together with
measured systolic blood presure values, measured with Omron 705 IT.
Reliable reference values utilizing an oscillometric instrument can only be obtained if
the test person is not moving. Therefore, measured values are available only during
the resting and in the recovery phase. The maximum blood pressure at the end of the
exercise phase also cannot be determined but is estimated using a polynomial ap-
proximation with the measured pressures during recovery. This maximum pressure is
used together with the recovery values as additional point for the approximation func-
tion, yielding the recovery model (subscript: rec), see Eq. 1 and Fig. 2. As no meas-
urements with the oscillometric device are possible during the exercise phase, we
estimate the gradient of the pressure dp/dt for t = t
A
at the beginning of the step test,
yielding the exercise model for strain activities (subscript: str):
sys,str
R_P R_P
1,str 2,str 3,str
sys,rec
R_P R_P
1,rec 2,rec 3,rec
2
2
PaTaTa
PaTaTa
ΔΔΔ
ΔΔΔ
=⋅ +⋅ +
=⋅ +⋅ +
(1)
The a
i
are the separately to determine and subject specific model coefficients.
Δ
T
R_P
and
Δ
P
sys
refer to the normalized input and output values with respect to the subject at
rest (subscript: rest), see Eq. 2:
sys sys sys,rest R_P R_P R_P,rest
PPP T T TΔΔ= − ; = − (2)
This increases the robustness of the model coefficients concerning fluctuations of the
physiological and psychological conditions and is in correspondence with the deriva-
tion of the linearized model equation [9]. The assumption is also supported by the
t
A
t
A
Exercise phase
128
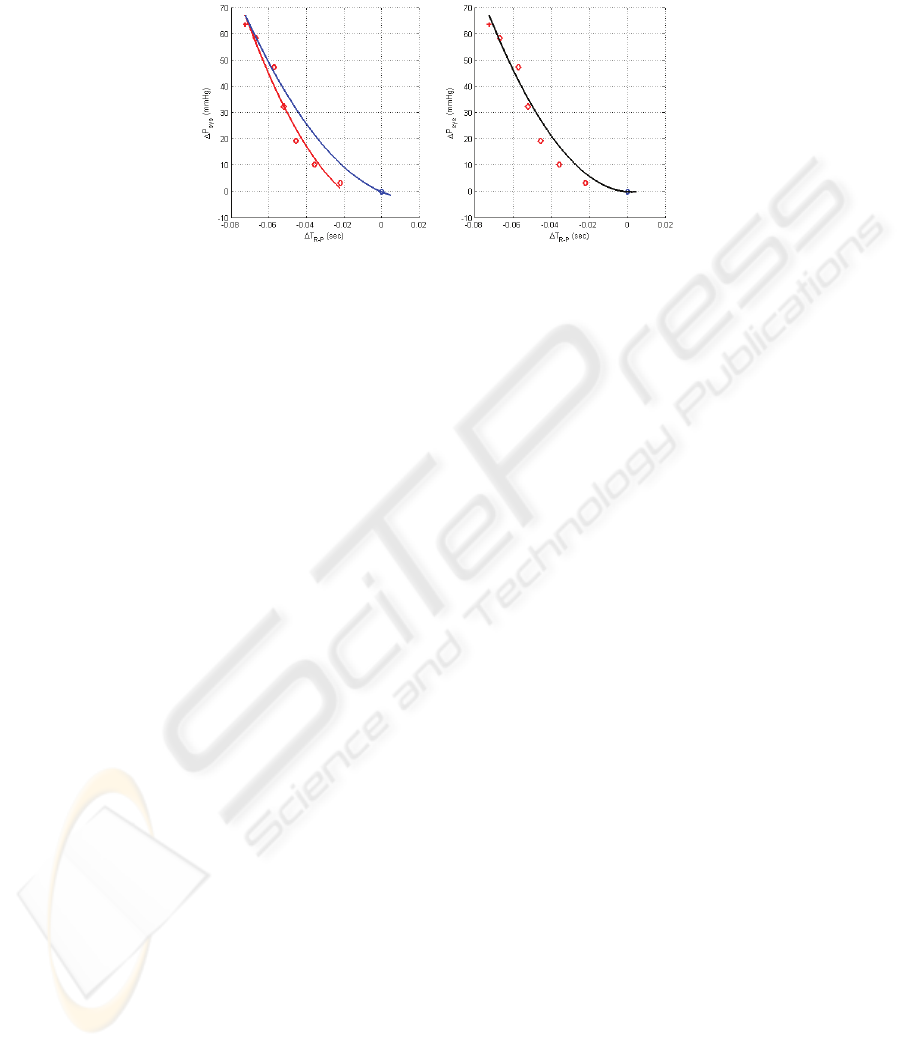
observation, that quite different quiescent blood pressures can be determined, depend-
ing on previous activities and the general health condition of the person under test.
Fig. 2. Exercise and recovery model determined via step test (left) and mean model, used for
systolic pressure determination (right).
The calibration test has to be carried out only once by each participant to determine
the model coefficients which then can be applied at other applications. In most practi-
cal applications we cannot, however, a priori differentiate between exercise and re-
covery phases. We therefore have developed a mean model approach. A suitable
pressure model is obtained by averaging the coefficients, yielding a mean blood pres-
sure model equation for the person under test, Fig. 2. The inevitable error remains in
most cases within the error of the oscillometric instruments, i.e. ±3 mmHg.
3 Applications
Stress usually is experienced as disturbing sensations. It leads to an activation of the
organism and causes reactions [11]. It must be regarded, that factors, which lead to
stress, can be very different from person to person. Stress reactions depend on the
subjective judgement of the situation, earlier experiences and many further aspects
[12]. Therefore, it is hardly possible to define a "standard stress factor". This leads to
difficulties in the assessment, if several persons in a test are exposed to comparable
stress situations. For the proof of stress reactions in the human organism most trigger-
ing indicators of activation are also suitable for the characterization of the reactions.
3.1 Investigations Using the Vienna Test System
The Vienna Test System (VTS) [13] is a computerized psychological testing system
which provides a sophisticated method to evaluate and to train cognitive abilities,
such as attention, memory or logical thinking. The system has also become a global
standard in traffic psychology. Using the VTS we examined whether and how the
blood pressure changes, if a test person is confronted with specific stress-inducing
tasks. The test runs consist usually of a screen-supported instruction phase, a training
phase and finally the actual exercise phase.
129
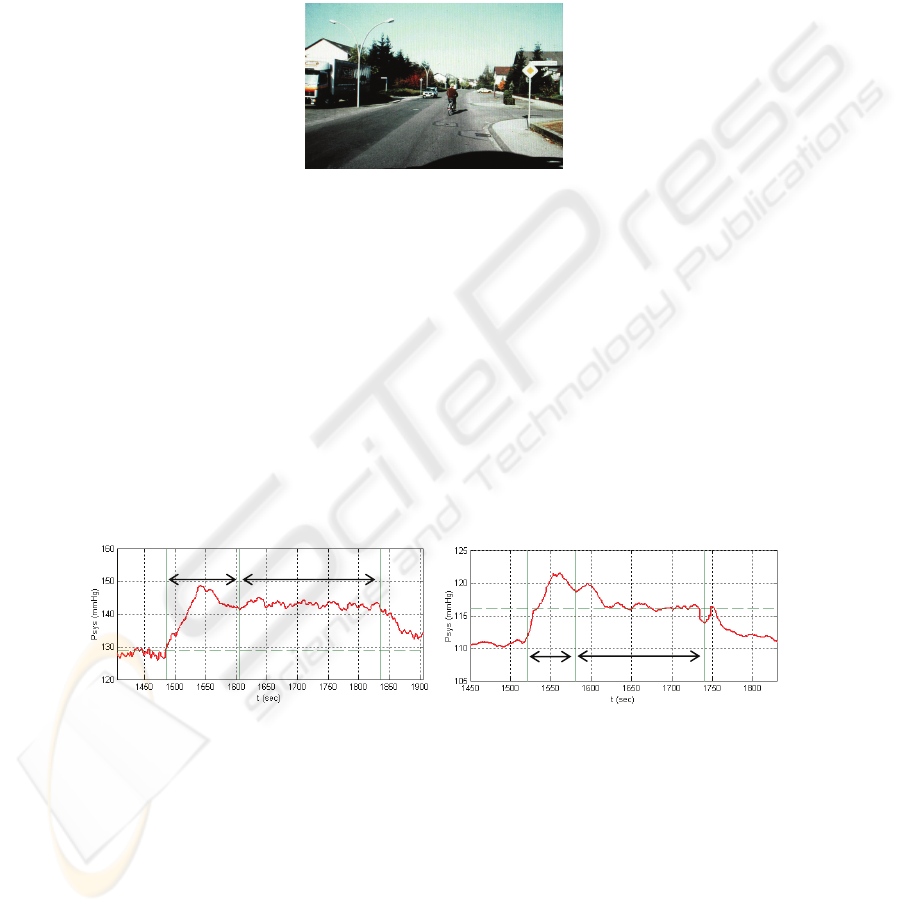
The "Tachistoscopic Traffic Test" is used to examine the optical perception on short
time presentations of traffic scenes. The test persons are exposed to twenty pictures,
Fig. 3, with a presentation time of one second each. Subsequently the person has to
decide in a multiple choice among five possible answers what was to be seen in the
picture: people, cars, bicycles, traffic signs and traffic lights. The task sounds simple,
but due to the short presentation time the decision between the different objects given
in the traffic situations seems quite difficult. Thus easily an uncertainty arises during
the selection of the correct answers, which can lead to a stress sensation.
Fig. 3. Example from the Tachistoscopic Traffic Test.
The blood pressure graphs of two persons, Fig. 4 are found in a similar form for all
test participants performing the Traffic Test. They show a more or less pronounced
pressure maximum during the initial training phase, in which already situations occur
like in the following test. For both persons the pressure remains after the first change
practically constant for the test duration then falling to values before test begin. This
indicates that after a first stage of insecurity about the forthcoming events a continu-
ous strain is present. Compared with the initial pressure before test begin a mean
pressure rise of approximately 14 mmHg for a person not familiar with the test and
approximately 6 mmHg in the second case can be seen accompanied by some oscilla-
tions due to variable learning stress.
In summary systolic blood pressure changes up to 20 mmHg were observed with a
tendency to higher changes between quiescent and test phase mean blood pressure for
younger participants.
Fig. 4. Systolic blood pressure at Tachistoscopic Traffic Test (left: test unknown to test person,
right: test is known from former experiments).
3.2 Investigation Using the Driving Simulator “Nightdriver"
In the following a potentially stressful everyday life situation is examined: driving a
motor vehicle. Here the question arises to what extent one can judge from the recor-
ded physiological signals, in particular from the blood pressure, on different mental
Exercising
Training
Exercising
Train.
130
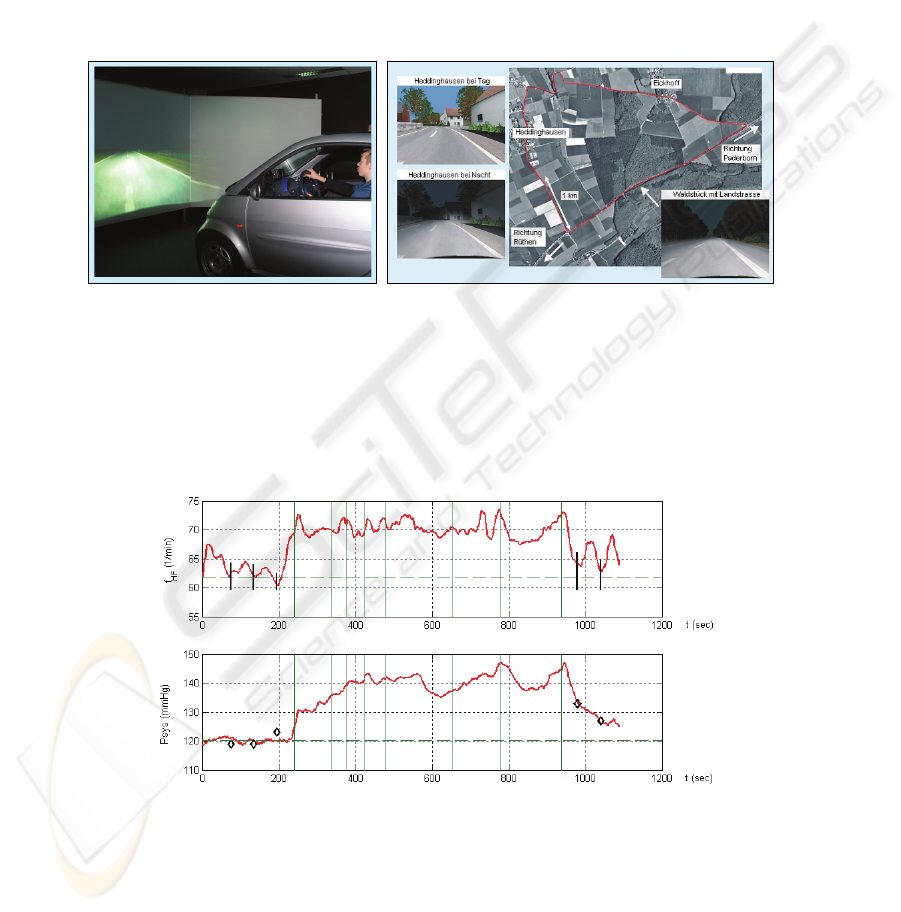
load phases. And further it is to be examined, which factors lead to stress in the car
driving situation at all.
In our investigation for the first time a continuous blood pressure determination
could be performed during driving a car. To explore this topic the night driving simu-
lator "Nightdriver" was used, which provides identically laboratory conditions for all
participants. It consists of a "Smart"-vehicle and a three beamer projection of the
traffic scenes. In the interactive virtual reality system, Fig. 5, the test participants can
drive comparably to a normal passenger car. The landscape-street model with differ-
ent scenarios like small villages, narrow streets as well as a short highway passage
extends over a length of about 8 km. The participants were instructed to drive the dis-
tance as briskly as possible considering the traffic rules and not leaving the road.
Fig. 5. Car Simulator "Nightdriver" and cockpit/ aerial view of test track (Source: L-LAB).
Fig. 6 shows the measured values from a test person to whom the simulator and the
test track was unknown, while in Fig. 7 the simulation setup was known to the sub-
ject. At the beginning and after reaching the destination oscillometric blood pressure
measurements () were performed. The numbers above the P
sys
-graph indicate spe-
cific track points to correlate the traffic situations with corresponding physiological
reactions.
Fig. 6. Heart frequency and systolic blood pressure at driving (average speed: 45,3 km/h; simu-
lator and track unknown to test person).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
131
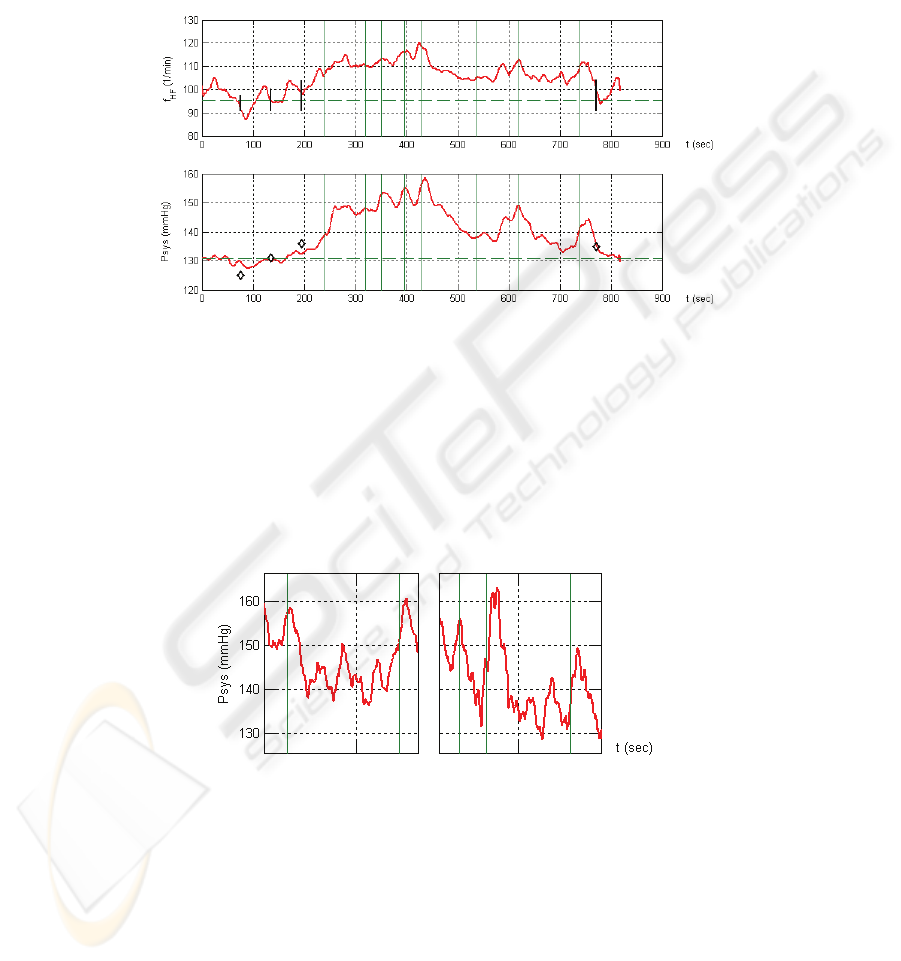
The signal waveforms of the two participants show interesting similarities. At the
beginning of the ride at "1" the blood pressure of both drivers rises more or less ra-
pidly. Interesting are the corresponding pressure maxima when entering and leaving a
short highway passage ("7" and "8") and the pressure decrease, while steadily driving
on a straight road and on the highway. The excellent correspondence of oscillometric
and continuously measured blood pressure is remarkable.
Fig. 7. Heart frequency and systolic blood pressure at driving (average speed: 63,5 km/h, simu-
lator and track known from previous drives).
The driving results of further test participants exhibit very similar blood pressure
graphs. In general it can be seen in Figs. 6 and 7, that the systolic blood pressure as
well as the heart frequency respond to traffic situations. Pressure rises up to 30 mmHg
are typical for normal traffic situations. With increasing experience in handling the
simulator the influence on the individual pressure curves becomes smaller. The heart
frequency also shows related variations but the changes in systolic blood pressure can
more clearly be assigned to the specific traffic situations.
Fig. 8. Systolic blood pressure changes at same track part, first without and second with sud-
denly braking car in front (Numbers: "5" sharp curve, "7" turning point, "b" braking car).
In a second series of experiments the test persons had to follow another car on the
same parcours. During the drive the car ahead suddenly changes the speed and the
driver had to handle suddenly occurring obstacles. Fig. 8 shows the systolic blood
pressure of a driver at the same part of the track first without any special occurrence
and second with the car in front of him braking suddenly at point "b". The subject had
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
5 7 5 b 7
132

no chance to avoid a simulated crash. A pressure rise of about 30 mmHg can be ob-
served directly after the accident. Thinking of dangerous situations in real traffic
much higher changes could be expected.
4 Discussion
Our investigations using the Vienna Test System and the driving simulator "Night-
driver" demonstrate the first continuous blood pressure measurements in realistic
stress situations, pointing out the suitability of the systolic blood pressure as a reliable
stress indicator. Arising stress leads to an increase of the blood pressure as discussed
before. Other experiments calming down the subject with quiet and slow music show
contrary results. The pressure keeps at the initial value or even drops below during the
presentation.
Utilizing individual exercise-recovery and averaged model functions the systolic
blood pressure could be determined continuously and non-invasively with high tem-
poral resolution. Also brief fluctuations are indicated, which remain unidentified if
classical cuff based instruments are applied. With the new method it is no problem
any more to determine the blood pressure during exercise phases. The measuring
system must be calibrated individually for the subjects under investigation using the
Schellong stair climbing test. This calibration is to be accomplished only once for
each person. The model parameters are stable at least for several days if no medica-
tion is taken. In all practical applications one cannot differentiate between strain and
recovery, so that a single model with coefficients achieved by averaging is preferred.
The preceding considerations are applied to the systolic blood pressure. Due to the
relatively small pressure changes and the dispersion of the measured values, the error
in defining an appropriate model for the diastolic pressure was found too high.
Since the pressure values during the calibration are measured using an advanced
oscillometric device, a comparable accuracy of at least ±3 mmHg can be achieved.
For a detailed failure analysis comparative invasive measurements would be meaning-
ful. According to statements of medical experts, however, such measurements cannot
be carried out due to the dangers for the subjects.
In order to investigate the psychological and physiological conditions of the
subjects in greater detail, more than one parameter meaningfully would have to be
evaluated. It has to be considered that not all parameters which correspond to
physiological reactions could be measured in special test situations because of their
unsufficient accuracy in field experiments or the high instrumental expenditure. Also,
the fact that the subject is disturbed too much, has to be considered. Heart frequency
changes correlate with the systolic blood pressure variations in general and could
serve as stress indicators. However, the blood pressure variations give a more precise
insight in the influencing reasons of the visible changes of the physiological signals
and therefore in the situations which were analysed. Furthermore, the heart rate seems
to be more affected by physical efforts than the blood pressure. Another parameter
which is often used and relatively simple to register is the electrodermal activity or
skin resistance. Disadvantage in this case is that quite often reactions can be observed
which objectively are not correlated with any stressful situation.
133

Because the sensor technique of the continuous beat-to-beat measurement method is
not at all influencing on the persons attention, the continuous model based blood
pressure measurement proves as valuable additional indicator for the psychological
conditions and the stress levels of the test participants. Although intraindividual dif-
ferences in the reactions to special situations can be observed, in general it can be
quoted that all participants show similar results. Due to personalized models our
blood pressure determination method is sensitive even to small signal changes.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Jürgen Locher and Regina Sprenger from L-LAB Paderborn for
providing the Vienna Test System and making test drives with the “Nightdriver”
Simulator possible. We are also grateful to Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd Henning and Dipl.-
Ing. Stefan Schlößer from the Institute of Electrical Measurement of the University of
Paderborn and to Prof. E. Trowitzsch, University of Witten-Herdecke/Vestic Chil-
drens Hospital, Datteln, for helpful discussions.
References
1. Finapres Medical Systems, "Datasheet Finometer and Portapres",
http://www.finapres.com/index.php?pid=4200, 2002.
2. Medwave, "Vasotrac APM 2005A System Features and Specifications", 2005,
http://www.pmsinstruments.co.uk/vasotrac.htm
3. D. Barschdorff, M.Erig, "Kontinuierliche Blutdruckbestimmung während des Belastungs-
EKG", Biomedizinische Technik, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 34-39, 1998.
4. D. Barschdorff, M. Erig, E. Trowitsch, "Noninvasive continious blood pressure determina-
tion", XVI IMEKO World Congress, Proceedings VII, Wien, 25.-28. Sep. 2000.
5. D. Barschdorff, C. Bauch, "High resolution beat-to-beat measurement of systolic blood
pressure using personalized models ", Proc. 10 th IMEKO TC 10 Int. Conf. on Techn. Di-
agnostics, Budapest, 9.-10. June 2005.
6. D. Barschdorff, C. Bauch, "Application of high resolutionblood pressure measurement to
stress and traffic situations "Proc. 10
th
IMEKO TC 10 Int. Conf. on Techn. Diagnostics,
Budapest, 9.-10. June 2005.
7. R. Busse, "Kreislaufphysiologie", Thieme, Stuttgart, 1982.
8. R.F. Schmidt, G. Thews, "Physiologie des Menschen", Springer, 1997.
9. P. Elter, "Methoden und Systeme zur nichtinvasiven, kontinuierlichen und belastungsfreien
Blutdruckmessung", Diss., Univ. Karlsruhe, pp. 1-162, 2001.
10. Roche "Lexikon Medizin: Schellong-Test", 2003,
http://www.gesundheit.de/roche/ro32500/r34385.000.html
11. R. Schandry, "Psychophysiologie", Urban & Schwarzenberg, 1981.
12. K. Rogge, "Physiologische Psychologie", Urban & Schwarzenberg, 1981.
13. G. Schuhfried: "Vienna Test System", http://www.schuhfried.at/eng/wts/wts_index.htm
134
