
FEATURES EXTRACTION AND TRAINING STRATEGIES IN
CONTINUOUS SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR ROMANIAN
LANGUAGE
Corneliu Octavian Dumitru
1,2
1
Politehnica University Bucharest, Faculty of Electronics Telecommunication and Information Technology,
Splaiul Independentei 313, Bucharest, Romania
2
ARTEMIS Department, GET/INT 9, rue Charles Fourier, 91011, Evry, France
Inge Gavat
1
1
Politehnica University Bucharest, Faculty of Electronics Telecommunication and Information Technology,
Splaiul Independentei 313, Bucharest, Romania
Keywords: HMM, MFCC, PLP, LPC, context dependent modeling, continuous speech.
Abstract: This paper describes continuous speech recognition experiments for Romanian language, by using HMM
(Hidden Markov Models) modeling. The following questions are to be discussed: the realization of a new
front-end reconsidering linear prediction, the enhancement of recognition rates by context dependent
modeling, the evaluation of training strategies ensuring speaker independence of the recognition process
without speaker adaptation procedures, by speaker selection for training. The experiments lead to a
development of the initial system with a promising front-end based on PLP (Perceptual Linear Prediction)
coefficients, second ranked for the recognition performance obtained, near the first ranked front-end based
on mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC), but far better as the last ranked, based on simple linear
prediction. Concerning the implemented algorithm for context dependent modeling, it permits in all
situations enhanced recognition rates. The experiments made with gender speaker selection enhanced under
certain conditions the recognition rate, proving good generalization properties especially by training with
the male speakers database.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper presents experiments that continue our
work in Romanian continuous speech recognition,
based on statistical modeling at the acoustical level
applying Hidden Markov Models. By this
experiment, we have tried to add new possibilities to
our system, initially based on a front-end with mel-
cepstral parameterization, on acoustic modeling of
independent phonemes as constituents of uttered
phrases and on training or testing with a database in
which male and female speakers were balanced
represented.
In order to realize speech recognition for mobile
applications, a reconsideration of the linear
prediction for the front-end would be interesting. In
our experiments, the modest performance of LPC
could be enhanced in a promising manner by
perceptual linear prediction (PLP), beginning with
only five PLP coefficients (Dumitru, 2005).
A continuous speech recognition algorithm was
further experimented applying the context dependent
modeling in order to improve recognition rates
realized in our system that simplify the model quasi
independent phonemes as constituents of spoken
words sequences.
In the end, the training procedure was tested,
based on speaker selection ensuring speaker
independence of the recognition process without
special speaker adaptation procedures
The remainder of the paper is structured as
follows: chapter 2 is dedicated to speech
parameterization; chapter 3, to Hidden Markov
Models (HMM) with context dependent modeling
114
Octavian Dumitru C. and Gavat I. (2006).
FEATURES EXTRACTION AND TRAINING STRATEGIES IN CONTINUOUS SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR ROMANIAN LANGUAGE.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 114-121
DOI: 10.5220/0001198901140121
Copyright
c
SciTePress
and phonetic decision trees. The subject of the
chapter 4 concerns training strategies. Database and
experimental results are exposed in chapter 5 and 6.
Conclusion and references close the paper.
2 SPEECH
PARAMETERIZATION
METHODS
In ASR systems designed by specialists, feature
extraction seems to be a solved issue, but alternative
solutions are still proposed especially for distributed
systems in trend to make speech recognition
affordable for everyone. In such systems, the easier
processing tasks, like collecting speech and
parameterize the obtained data are realized in a
distributed manner, at each user. Tasks requiring
higher knowledge like training the recogniser or
decisions making are reserved to a central computer,
which assist the distributed users. A communication
system ensures the necessary data transfers between
users and computer (Furui, 2000), (Gold, 2002).
An important challenge in this case is to realize the
user processing stages as simple as possible. Having
in mind to simplify the feature extraction, we turned
to linear prediction, whose simplicity held this
method in the top of feature extraction methods over
a long time.
The PLP (perceptual linear prediction) audio
analysis method is more adapted to human hearing,
compared to the classic linear prediction coding
(LPC).
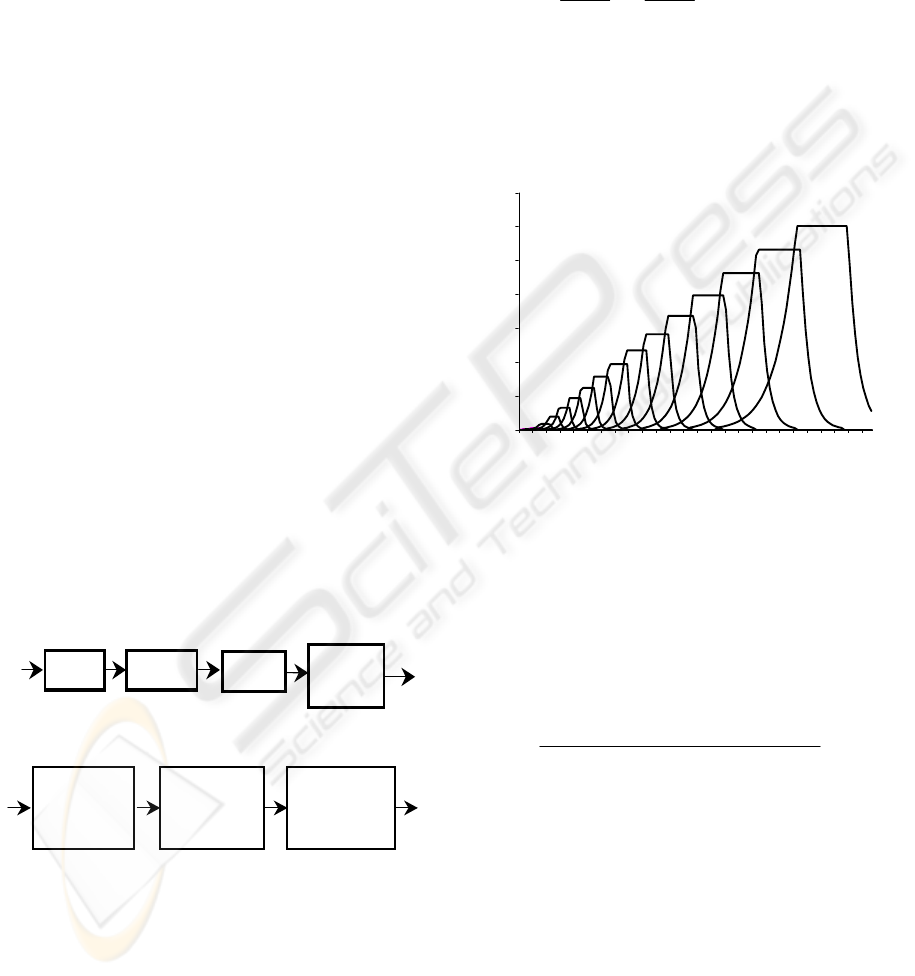
s (n)
FFT
S
p
. M.
IFFT
Du rb i n
Rec ur si on
PLP
coef
.
Figure 1: Perceptual linear prediction analysis.
Critical Band
Analysis
Ω
(
ω
)
Equal Loudness
Curve
E(
ω
)
Intensity-
Loudness
()
3/1'
)(ω=ω SS
Figure 2: Block representation for Sp. M.
The block scheme of the processor PLP
(Hermansky, 1990) is shown in figure 1, and the
spectral manipulation (SP. M.) is represented in
figure 2.
The power spectrum is computed as follows:
22
))(SIm())(SRe()(P ω+ω=ω (1)
The first step is a conversion from frequency to
bark, which is a better representation of the human
hearing resolution in frequency. The bark frequency
corresponding to an audio frequency is:
()
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
π
ω
+
π
ω
=ωΩ
5.0
1
2
12001200
ln6
(2)
The resulting warped spectrum is convoluted with
the power spectrum of the critical band-masking
curve, which acts like a bank of filters centered on
i
Ω
, having the shape shown in figure 3.
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
1 10192837465564738291100109118127
Frequency (FFT point)
Figure 3: The weighting functions with equal loudness
pre-emphasis.
The spectrum is pre-emphasized by an equal
loudness curve, which is an approximation to the
non-equal sensitivity of human hearing at different
frequencies, at about 40dB level. The following
curve is given by a filter having the transfer
function:
()
(
)
(
)
(
)
92
2
62
462
1038.0103.6
108.56
E
×+ω××+ω
ω×+ω
=ω
(3)
The last operation prior to the all-pole modeling
is the cubic-root amplitude compression (Intensity –
Loudness Conversion), which simulates the non-
linear relation between the intensity of sound and its
perceived loudness. Together with the
psychophysical equal-loudness pre-emphasis, this
operation also reduces the spectral amplitude
variation of the critical-band spectrum so that the
following all-pole modeling can be done by a
relatively low model order.
Autoregressive modeling is the final stage of
the PLP analysis, and consists of approximating the
FEATURES EXTRACTION AND TRAINING STRATEGIES IN CONTINUOUS SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR
ROMANIAN LANGUAGE
115
spectrum by an all-pole model, using the
autocorrelation method. An Inverse Discrete Fourier
Transformation is applied to the spectrum samples,
resulting the dual autocorrelation function. For a M-
th order all-pole model, we need only the first M+1
autocorrelation values. The Levinson - Durbin
recursive algorithm is used to solve the Yule –
Walker equations.
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
+−
−
−
=
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
×
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
−
−
)1N(R
...
)3(R
)2(R
)N(A
...
)3(A
)2(A
)1(R...)1N(R)N(R
............
)1N(R...)1(R)2(R
)N(R
...)2(R)1(R
(4)
where
()
nR
are the autocorrelation coefficients, and
()
nA
are the all-pole model’s coefficients (the
predictor), and
()
11A =
.
The ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition)
performance for LPC based front-ends (Milne, 2002)
will be analyzed comparatively with the
performance obtained with MFCC based front-ends
(Vergin, 1999), considered as standard at present.
3 HIDDEN MARKOV MODELS
(HMM)
HMMs are finite automates, with a given number of
states; passing from one state to another, it is made
instantaneously at equally spaced time moments. At
every passing from one state to another the system
generates observations, two processes taking place
into the automate: the transparent one and the hidden
one, which cannot be observed, first represented by
the observations string (parameter sequence) and
second, represented by the states string.
Concerning the HMMs, there are three main
problems to discuss:
The first problem is the evaluation one. Given the
model and the observation (parameter) sequence, we
have to analyze if the sequence is produced by the
given model. The probability to produce an
observation sequence with a Markov model is
calculated by the “forward” and “backward”
algorithms.
The second problem is about establishing the
correct state sequence. The “Viterby” algorithm is
one of the most used algorithms to this purpose.
The third problem is the parameter optimization
of the model to describe the observation sequence as
good as possible. Training allows optimal adaptation
of the model parameters to training data by re-
estimating them. The “Baum-Welch” algorithm is
the most used re-estimation algorithm parameter.
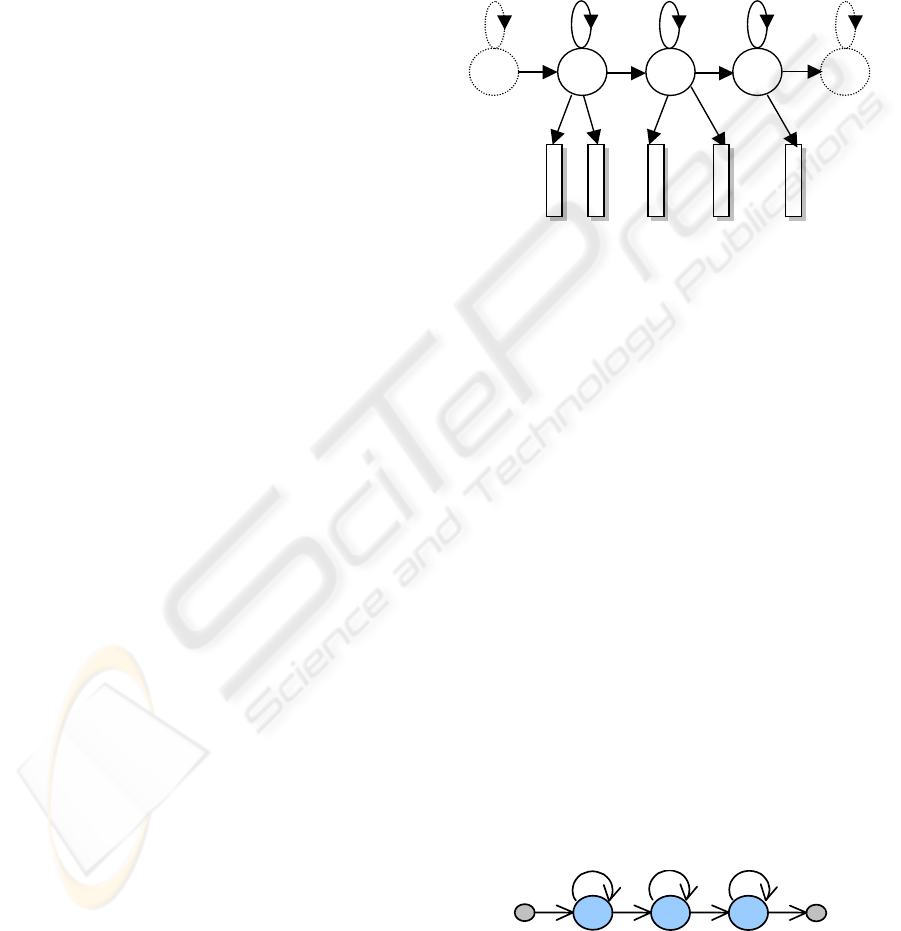
In figure 4 there is represented the left - right model
(Bakis), which is considered the best choice for
speech. For each phoneme, called monophone, such
a model is constructed; a word string is obtained by
connecting corresponding HMMs together in
sequence, the extension to continuous speech being
realized in a simple manner.
s
1
s
2
s
3
a
12
a
23
a
11
a
22
a
33
o
1
o
2
o
3
o
4
o
5
b
1
(o
1
)
b
1
(o
2
)
b
2
(o
3
)
b
2
(o
4
)b
3
(o
5
)
Figure 4: Left-right model or Bakis model.
3.1 Context – Dependent Modeling
In the simplified hypothesis of context independent
phoneme modelling, each word results as a
concatenation of the component phonemes; for each
phoneme a model is construct. In Romanian
language, as phoneticians claim, there are 34
phonemes, requiring 34 different models.
In real speech, the words are not simple strings
of independent phonemes: as effect of co-
articulation, the immediate neighbour – phonemes,
for instance the preceding and the following one,
affect each phoneme in the word. This immediate
neighbour – phonemes are called respectively the
left and the right context; a phoneme constitutes
with the left and right context a triphone. For
example in the triphone “a - z + i_o”, (SAMPA-
Speech Assessment Methods Phonetic Alphabet -
transcription for the Romanian word ”azi”), the
phoneme “z” has as left context “a” and as right
context “i_o”, like is shown in figure 5.
Figure 5: The word internal triphone “a - z + i_o”.
a - z + i_o
ICINCO 2006 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
116
For each such a triphone a model must be trained: in
Romanian it would give a number which equals
3930434
3
= models, which is totally unacceptable
for a real world system. In our speech recognition
task we have modeled only internal – word triphones
and the adopted state tying procedure has conducted
to a controllable situation (Young, 1992).
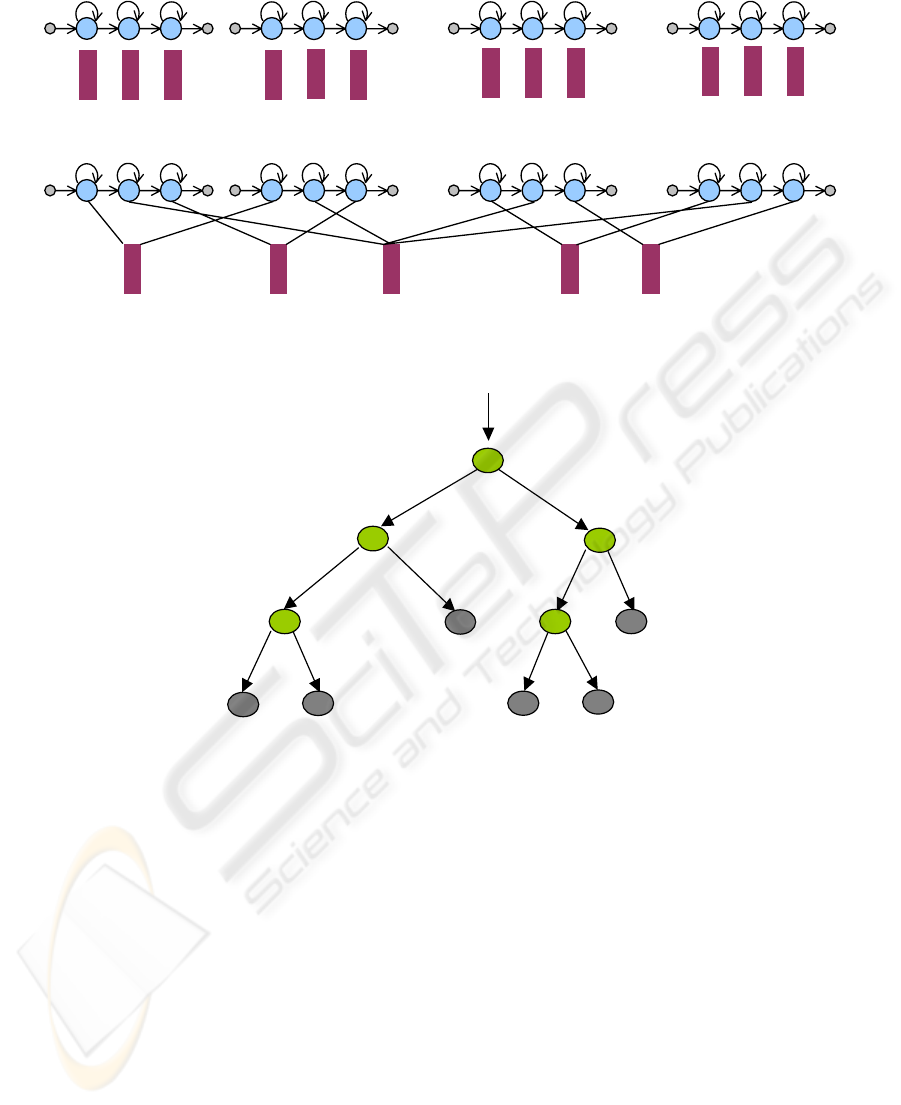
3.2 State Tying on Phonetic Decision
Trees
If triphones are used in place of monophonemes, the
number of needed model increases and the problem
of insufficient training data may occur. To solve this
problem, tying of acoustically similar states of the
models built for triphones corresponding to each
context- there is an efficient solution. For example,
in figure 6a four models are represented for four
different contexts of the phoneme “a”, namely the
triphones “k – a + S”, “g – a + z”, “n – a + j”, “m – a
+ j”. In figure 6b the clusters formed with
acoustically similar states of the corresponding
HMMs are represented.
The choice of the states and the clustering in
phonetic classes are achieved by mean of phonetic
decision trees. A phonetic decision tree built as a
binary tree, as it is shown in figure 7 and has in the
root node all the training frames to be tied, in other
words all the contexts of a phoneme. To each node
of the tree, beginning with the parent – nodes, a
question qi is associated concerning the contexts of
the phoneme (Odell, 1992).
Possible questions are, for example: is the right
context a vowel (R = Consonant?), is the left context
a phoneme “a” (L = a?); the first answer designates a
a
)
k - a + S g - a + Z n - a + j m - a +j
b)
k - a + S g - a + Z n - a + j m - a +j
Figure 6: a) Different models for triphones around the phoneme “a”, b) Tying of acoustically similar states.
Figure 7: Phonetic tree for phoneme m in state 2.
R=Consonant?
y
n
L=Vowel?
y
n
L=a?
y
n
L=Vowel_medial?
yn
R=Vowel?
L=p?
n
y
FEATURES EXTRACTION AND TRAINING STRATEGIES IN CONTINUOUS SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR
ROMANIAN LANGUAGE
117

large class of phonemes, the second only a single
phonetic element. Depending on the answer, yes or
no, child nodes are created and the frames are placed
in them. New questions are further made for the
child nodes, and the frames are divided again.
The questions are chosen in order to increase the
log likelihood of the data after splitting. Splitting is
stopped when increasing in log likelihood is less
than an imposed threshold, resulting a leaf node. In
such leaf nodes are concentrated all states having the
same answer to the question made along the path
from the root node and therefore states reaching the
same leaf node can be tied as regarded acoustically
similar. For each leaf node pair the occupancy must
be calculated in order to merge insufficient occupied
leaf nodes (Young, 1994).
A decision tree is built for each state of each
phoneme. The sequential top down construction of
the decision trees was realized automatically, with
an algorithm selecting the questions to be answered
from a large set of 130 questions, established after
knowledge about phonetic rules for Romanian
language.
4 TRAINING STRATEGIES
In speaker independent speech recognition for large
vocabularies, the training strategies for the
acoustical models are very important: a well trained
model has high generalization properties and leads
to acceptable word and phrase recognition rates,
even without special speaker adaptation procedures.
This purpose can be simply realised by speaker
selection in the training phase (Goronzy, 2002),
(Hanson, 1990), (Huang, 2001).
In our experiments made on the continuous speech
recognition system we have assessed the speech
recognition performance configuring the training
database in three manners: only with female
speakers, only with male speakers, combining male
and female speakers. In order to find out which
training strategy ensure the highest generalization
capacity, the tests were made with two kinds of
databases: only with female speakers, and only with
male speakers.
5 DATABASE
For continuous speech recognition, usually our
database is constituted for training by 3300
utterances, spoken by 11 speakers, 7 males and 4
females, each speaker reading 300 utterances, and
for testing by 880 utterances spoken by the same
speakers, each of them reading 80 utterances. The
training database contains over 3200 distinct words,
while the testing database contains 1500 distinct
words and we used for phonetic transcription
SAMPA (Speech Assessment Methods Phonetic
Alphabet).
The data are sampled by 16 kHz, quantified with 16
bits, and recorded in a laboratory environment.
6 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Our first experiments performed on a Romanian
language corpus prove that context-dependent
models perform better than context-independent
models. The recognition system was trained with
3000 phrases collected from ten speakers (more than
3000 distinct words). Gaussian output probability
distribution was assumed for the 36 mel-frequency
cepstrum coefficients (12 MFCC and first and
second order variation).
Firstly, the 34 context-independent models
(monophones) were trained, and the system was
tested with an unrolled speaker. The testing
utterances contained over 140 distinct words and a
loop-grammar was assumed, i.e. any word could
occur after any word, anytime. The word recognition
rate (WRR) is around 60-65%. The results are
slightly better for the enrolled speakers (around
70%) (Woodland, 1994), (Oancea, 2004).
The core of our experiments is the construction
of the decision tree for each state of the triphones
derived from the same monophone. The
monophones were cloned initially, and the resulted
triphones were trained by embedded Baum-Welch
procedure. Then, the decision tree was build for
different thresholds (TL) in terms of log-likelihood
resulting different size systems. The results are
presented in Table 1. For a small threshold (TL) of
300, the trees are big and the system is large having
2954 tied states with a huge number of parameters.
For a big threshold of 6000, the trees are much
smaller, implying a great reduction in the system
size, from 7521 triphone states to 416 states, (5,5%
remained size) while the performance is degrading
with less than 1%. In Table 1, are given also the
word recognition rate (WRR), the accuracy and
phrase recognition rate (PRR).
In the second experiment, we have carried out a
series of experiments in order to establish the
performance realized under various conditions
concerning on one hand the feature extraction, on
ICINCO 2006 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
118
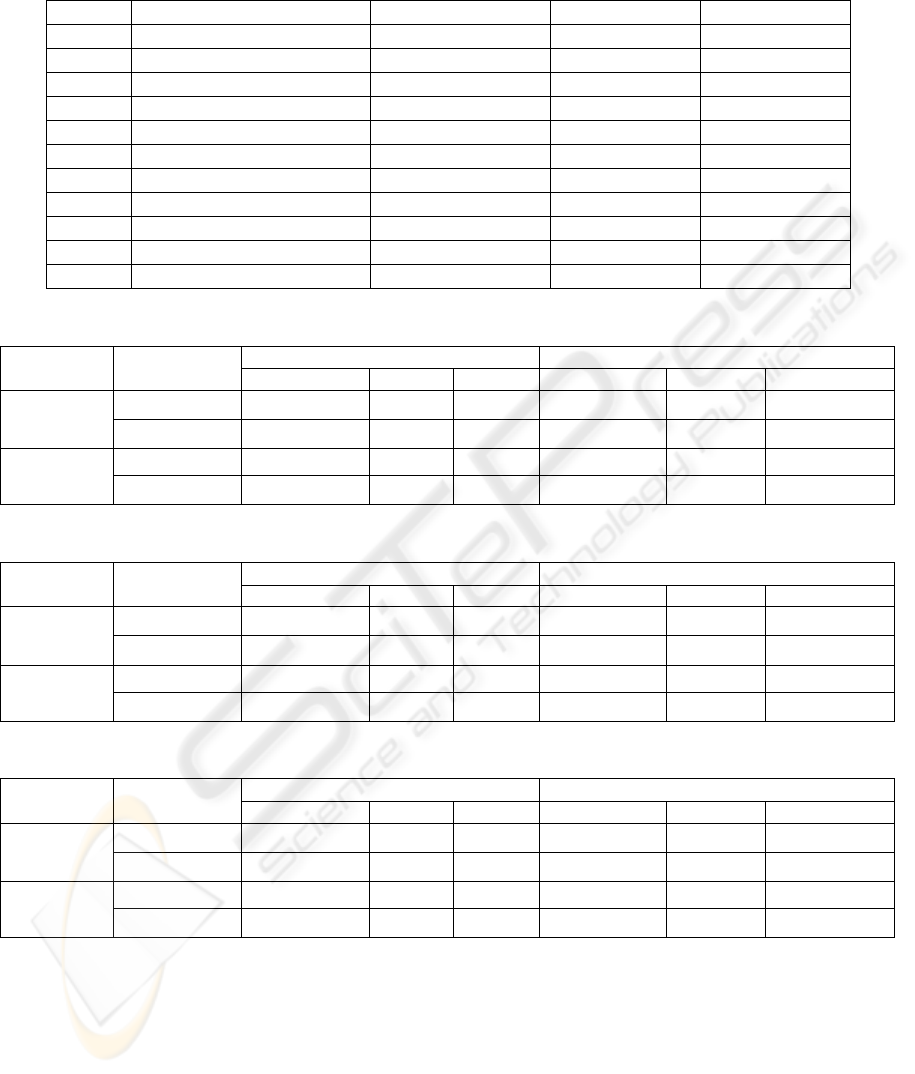
Table 1: The results obtained for different thresholds for constructing the phonetic trees.
Table 2: Word Recognition Rate and Phrase Recognition Rate (PRR): training MS testing MS or FS.
Word Recognition Rate (WRR) Phrase Recognition Rate (PRR)
Training
MS
Type
MFCC_D_A LPC PLP MFCC_D_A LPC PLP
Monophone 65,47% 32,61% 40,53% 20,00% 5% 10%
Testing MS
Triphone 90,41% 51,32% 72,42% 66,25% 11,25% 37,50%
Monophone 51,81% 25,18% 31,65% 21,25% 6,25% 16,25%
Testing FS
Triphone 83,21% 49,16% 63,55% 48,75% 12,50% 32,50%
Table 3: Word Recognition Rate and Phrase Recognition Rate (PRR): training FS testing MS or FS.
Word Recognition Rate (WRR) Phrase Recognition Rate (PRR)
Training FS Type
MFCC_D_A LPC PLP MFCC_D_A LPC PLP
Monophone 63,07% 28,06% 29,26% 21,25% 3,75% 6,26%
Testing MS
Triphone 78,42% 51,32% 56,35% 37,50% 11,25% 21,25%
Monophone 67,39% 33,09% 40,29% 30% 12,5% 22,50%
Testing FS
Triphone 89,45% 63,55% 62,35% 57,50% 33,75% 30%
Table 4: Word Recognition Rate and Phrase Recognition Rate (PRR): training MS and FS testing MS or FS.
Word Recognition Rate (WRR) Phrase Recognition Rate (PRR)
Training
MS and FS
Type
MFCC_D_A LPC PLP MFCC_D_A LPC PLP
Monophone 68,35% 27,58% 52,52% 23,75% 3,75% 18,75%
Testing MS
Triphone 88,97% 53,24% 75,78% 60% 10% 36,25%
Monophone 60,19% 25,42% 48,44% 31,25% 6,25% 20%
Testing FS
Triphone 85,69% 52,28% 74,86% 55% 11,25% 46,25%
the other hand the training strategies. The
performance is expressed in word recognition rate –
WRR and in phrase recognition rate (PRR). The
conditions for feature extraction are: perceptive
cepstral analysis giving a 36-dimensional vector
having as components 12 MFCCs with the
corresponding first and second order derivatives,
perceptual linear prediction giving a 5-dimensional
feature vector having as components five PLP
coefficients, and linear prediction, giving a 12-
dimensional feature vector having as components
the LP coefficients.
The training conditions are as follows: three
databases, one for male speakers (MS), one for
female speakers (FS) and one for both male and
female speakers (MS and FS). In all cases we
TL Initial states / final states Remained size WRR PRR
300 7521 / 2954 39.3% 90.14% 88.88%
900 7521 / 1448 19.3% 89.60% 88.56%
1200 7521 / 1164 15.5% 90.31% 89.28%
1800 7521 / 908 12.1% 90.51% 89.61%
2400 7521 / 747 9.9% 90.02% 89.06%
3000 7521 / 643 8.5% 89.97% 88.91%
3600 7521 / 573 7.6% 90.07% 88.85%
4200 7521 / 522 6.9% 89.79% 88.56%
4800 7521 / 480 6.4% 89.60% 88.55%
5400 7521 / 446 5.9% 88.85% 86.91%
6000 7521 / 416 5.5% 88.75% 86.78%
FEATURES EXTRACTION AND TRAINING STRATEGIES IN CONTINUOUS SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR
ROMANIAN LANGUAGE
119
excluded one male speaker and one female speaker
from the training and used the data for testing. The
results expressed in WRR and PRR obtained in the
experiments realized under these conditions are
summarized in Table 2, Table 3, and Table 4. From
the performance point of view we are especially
interested in WRR, stronger influenced by feature
selection and acoustical model training strategy than
PRR. On the other hand, in our experiments, the
only reason for PRR variation is the WRR
variations.
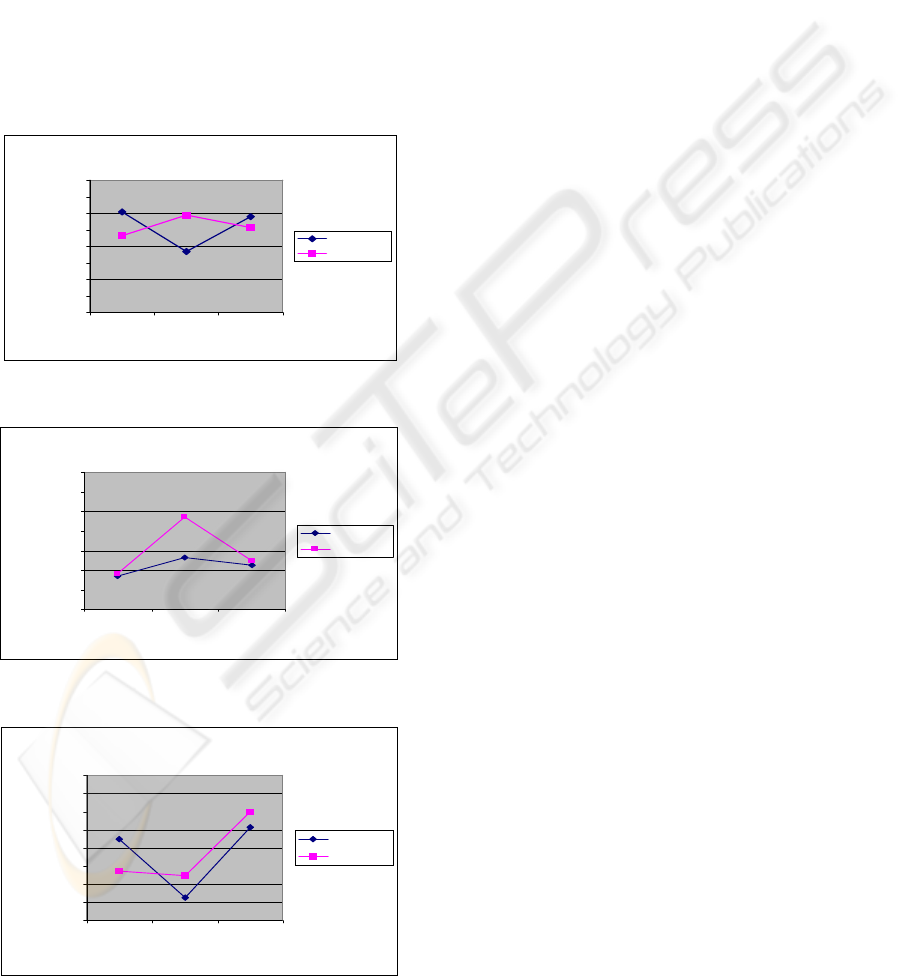
In the graphics represented in figure 8, 9, 10 are
given the WRR (for triphones) dependencies for
different testing conditions of the MS, FS and MS
and FS trained databases.
Case MFCC_D_A
90,41%
88,97%
78,42%
83,21%
89,45%
85,69%
60,00%
65,00%
70,00%
75,00%
80,00%
85,00%
90,00%
95,00%
100,00%
MS FS MS and FS
Training
WRR
Testing MS
Testing FS
Figure 8: WRR – case MFCC_D_A.
Case LPC
51,32%
48,32%
53,24%
49,16%
52,28%
63,55%
40,00%
45,00%
50,00%
55,00%
60,00%
65,00%
70,00%
75,00%
MS FS MS a nd FS
Training
WR
R
Testing MS
Test ing FS
Figure 9: WRR – case LPC.
Case PLP
72,42%
56,35%
75,78%
63,55%
62,35%
79,86%
50,00%
55,00%
60,00%
65,00%
70,00%
75,00%
80,00%
85,00%
90,00%
MS FS MS and FS
Training
WRR
Testing MS
Testing FS
Figure 10: WRR – case PLP.
The results for WRR are:
- for LPC feature extraction the attained word
recognition rates are low: 32,61% (monophone)
training and testing with MS and 48,32% (triphone);
28,06% (monophone) training and testing with FS
and 63,55% (triphone); 27,58% (monophone)
training MS and FS and testing with FS and 51,32%
(triphone).
- for PLP feature extraction, with 5 coefficients
the obtained results are very promising, giving word
recognition rates about 62,35% (triphone training
and testing FS), 72,42% (triphone training and
testing MS) and 75,78% (triphone training MS and
FS and testing MS).
- for MFC feature extraction we obtained the best
results, as we expected, considering that the MFCC
are currently standard features in speech recognition:
monophone 65,47% and triphone 90,41% -training
and testing with MS; monophone 67,39% and
triphone 89,45% training and testing with FS;
monophone 68,35% and triphone 88,97% -training
MS and FS and testing with MS.
7 CONCLUSIONS
As concerns the first experimental results one may
find an optimum threshold while building the ASR
in order to maintain a balance between the system
size and the system performance. We may conclude
that context-dependency (CD) is very important for
phoneme based ASRs and CD models are clearly
superior to context-independency CI models (over
40% relative increase). The computational
requirements (memory and speed) disadvantages can
be overcome by tree-based clustering of the model
states.
In the case of the second experiments, evaluating
the efficiency of feature extraction on WRR, one can
say that the highest recognition rate was obtained
using cepstral analysis (65,47% - monophone,
90,41% - triphone), and the lowest recognition rates
were obtained for LPC analysis (32,61% -
monophone, 51,32% - triphone). Although in PLP
analysis we only use a very small number of
parameters (5), the results obtained are satisfactory
(40,53% - monophone, 72,42% - triphone), the
recognition rates being situated between the two
cases mentioned above.
Concerning the training strategies, we can
observe two different behaviours. In the case of PLP
coefficients, the best WRR are obtained on the
database combined-trained with MS and FS for both
ICINCO 2006 - SIGNAL PROCESSING, SYSTEMS MODELING AND CONTROL
120

cases of tests with MS or FS, this proving a high
generalization capacity of the combined system. In
the case of LPC and MFC coefficients, the
combined-trained database is not so efficient, the
best results being obtained if the tests are made on
the same type of database used in the training
processes.
The PRR variation follows the WRR variation,
which was expected, because nothing was especially
done to enhance PRR.
It is also obvious the improvement of the results
when using HMM modeling triphones compared to
the case of HMM modeling monophones.
REFERENCES
Dumitru, C.O., Gavat, I., 2005. Features Extraction,
Modeling and Training Strategies in Continuous
Speech Recognition for Romanian Language, Proc.
EUROCON, Belgrade, Serbia & Montenegro, pp.
1425-1428.
Dumitru, C.O., Gavat, I., 2005. A Comparative Study of
Features for Continuous Speech Recognition by
Statistical Modeling with Monophones and Triphones,
Proc. SPED, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, pp.73-78.
Furui, S., 2000. Digital Speech Processing, Synthesis and
Recognition, 2-end, rev and expanded Marcel Dekker,
N.Y.
Gold, B., Morgan, N., 2002. Speech and audio signal
processing, John Wiley and Sons, N.Y.
Goronzy, S., 2002. Robust Adaptation to Non-Native
Accents in Automatic Speech Recognition, Springer –
Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Germany.
Hanson, B.A., Applebaum, T.H., 1990. Robust Speaker-
Independent Word Features Using Static, Dynamic
And Acceleration Features, Proc. ICASSP, pp. 857-
860.
Hermansky, H., 1990. Perceptual Linear Predictive
Analysis of Speech, J. Acoust. Soc. America, Vol.87,
No.4, pp. 1738-1752.
Huang, X., Acero, A., Hon, H.W., 2001. Spoken Language
Processing – A Guide to Theory, Algorithm, and
System Development, Prentice Hall.
Huang, C., Chen, T., Chang, E., 2002. Speaker Selection
Training For Large Vocabulary Continuous Speech
Recognition, Proc. ICLSP Vol. 1, pp. 609-612.
Milner, B.A., 2002. Comparison of Front-End
Configurations for Robust Speech Recognition, ICLSP
2002 Proceedings, Vol. 1, pp. 797-800.
Oancea, E., Gavat, I., Dumitru, C.O., Munteanu, D., 2004.
Continuous speech recognition for Romanian language
based on context-dependent modeling, Proc.
COMMUNICATION 2004, Bucharest, Romania, pp.
221-224.
Odell, J.J., 1992. The Use of Decision Trees with Context
Sensitive Phoneme Modeling, MPhil Thesis,
Cambridge University Engineering Department
SAMPA - Speech Assessment Methods Phonetic
Alphabet,
http://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/home/sampa/home.htm
Vergin, R D., O’Shaughnessy, Farhat, A., 1999.
Generalized Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients for
Large Vocabulary Speaker Independent Continuous
Speech Recognition, IEEE Trans. Speech Audio
Processing, Vol. 7, No.5, pp. 525-532.
Woodland, P.C., Odell, J.J., Valtchev, V., Young, S.J.,
1994. Large Vocabulary Continuous Speech
Recognition Using HTK, Proc. ICASSP 1994,
Adelaide.
Young, S.J., 1992. The General Use of Tying in Phoneme-
Based HMM Speech Recognizers, Proc. ICASSP’92,
Vol. 1, pp. 569-572, San Francisco.
Young, S.J., Odell, J.J., Woodland, P.C., 1994. Tree Based
State Tying for High Accuracy Modeling, ARPA
Workshop on Human Language Technology,
Princeton.
FEATURES EXTRACTION AND TRAINING STRATEGIES IN CONTINUOUS SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR
ROMANIAN LANGUAGE
121
