
THE WEB-BASED SLA MONITORING AND REPORTING
(WSMR) SYSTEM
Eunjin Ko, Junwoo Lee*, Gilhaeng Lee, Youngsun Kim
SLA Team, ETRI, 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 305-350 Korea
Keywords: Service Level Management, Service Level Agreement, SOAP, COM/CORBA.
Abstract: To provide high-level quality of network service and prevent contract dissension, a Service Level Agree-
ment (SLA) is an essential key factor in telecommunication industry. While most network service providers
normally offer an SLA communicating with legacy monitoring or reporting systems, it is needed to suggest
new architecture of an SLA system for accommodating legacy network management systems without
considering operating environment of each system. To guarantee level of network service, it is important to
gather raw data from legacy systems or other Operating Support Systems and exactly manage it in time. In
this paper, we suggest architecture of an integrated SLA system that is operated on the web-based
communicating technology with legacy systems, i.e. Web-based Service Level Agreement Monitoring and
Reporting (WSMR) system. The proposed architecture offers the way to gather raw data and process it
using web-based communicating technology.
1 INTRODUCTION
As growing of Information Technology (IT)
industry, Internet Protocol (IP) is a de facto
telecommunication technology instead of
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) or Frame
Relay (FR). IP is designed to transfer data from one
site to others without complicated technologies and
the simplicity of IP has explored the size of IT
business. While Quality of Service (QoS) is
considered as a minor factor to communicate in the
early of network era, there is a requirement of
accurate quality of network service depending on the
business rules from both Network Service Providers
(NSP) and customers.
Among these efforts to improve network service
quality, the concept of Service Level Management
(SLM) is emerged. SLM is the disciplined, proactive
methodology and procedures used to ensure that
adequate levels of service are delivered to all (IT)
users in accordance with business priorities and at
acceptable cost. And the instrument for enforcing
SLM is Service Level Agreement (SLA) (Rick
Sturm 2000).
An SLA emerged in the early 1990s as a way for
Information Technology (IT) departments and
service providers within private (usually, corporate)
computer networking environments to measure and
manage the QoS which they were delivering to their
internal customers. Service level agreements are the
contractual component of QoS and are usually
implemented as part of a larger service level
management (SLM) initiative (John J. Lee 2002).
An SLA is a formal negotiated agreement
between two parties. It is a contract that exists
between the Service Provider (SP) and the
Customer(TM Forum, 2001). In the view of NSPs, a
SLA let them have a chance to control and manage
their whole network resource more precisely. There
are five phases used to analyze SLA management;
Product/Service Development, Negotiation and
Sales, Implementation, Execution and Assessment as
Product/Se
r
vice
D
e
vel
o
pm
e
nt
N
egotiati
o
n a
n
d
Sales
I
mp
le
mentation
Ex
ec
uti
o
n
Assessm
en
t
Develop
Templates and
Parametric
Boundaries
Negotiate
Individual
Contracts
Take
Line/Service
Orders and
Provision
Monitor,
Surveillance,
Maintain, Bill
Reassess
Figure 1: Service and associated SLA life cycle
293
Ko E., Lee J., Lee G. and Kim Y. (2005).
THE WEB-BASED SLA MONITORING AND REPORTING (WSMR) SYSTEM.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on e-Business and Telecommunication Networks, pages 293-297
DOI: 10.5220/0001413902930297
Copyright
c
SciTePress

shown in Figure 1. When developing an SLA,
consideration must be given to the life cycle as it
may affect SLA requirements(TM Forum, 2001).
2 RELATED WORKS
To Implement and execute a SLA, there are a lot of
attempts to propose a framework for constructing
and managing quality-of-service (QoS)-centered
service level agreement (SLA) between service
providers and their customers. In these attempts,
SLA is provided through the off-line designing steps
and real-time SLA management steps which are
good solutions to provide real-time SLA in multi-
service packet networks (Eric Bouillet, 2002).
However, there is also needed to gather information
from other legacy systems to provide several SLA.
To communicate with legacy systems for
collecting information, there are some of trial efforts
to use legacy monitoring or reporting systems for
SLA monitoring and reporting. One of these is an
integrated Customer Network Management (CNM)
architecture. This architecture provides SLA with
extending legacy CNM concept. In this architecture,
all functional modules are designed and
implemented as a CORBA object and it adapts
COM/CORBA communicating mechanism (E.C.
Kim, 2000). While COM/CORBA communication
provides the way to access objects, it is easier to
transfer XML via Simple Object Access Protocol
(SOAP).
Recently, as growing web service technologies,
XML web services architecture is recommended and
used when there is a need to communicate with each
other. One of the primary advantages of the XML
Web services architecture is that it allows
applications written in different languages on
different platforms to communicate with each other
in a standards-based way (Roger Wolter, 2001).
Also, all of network services do not have a common
network specification and many research groups or
telecommunication companies have tried to
categorize and classify the SLA metrics to provide
adaptable SLA to network service providers and
their customers (Nathan J Muller, 1999).
In this paper, we suggest the web-based SLA
system, i.e. WSMR system, depending on the XML
Web services architecture. This paper is written in
the following steps. In section 3, we suggest
architecture of WSMR system and explain the
components of WSMR system. It shows the result of
experimental test of WSMR in section 4. In section
5, we mention about the conclusions and present the
further works.
3 WEB-BASED SLA MONITOR-
ING AND REPORTING (WSMR)
SYSTEM
To support an SLA, it is important to categorize all
of contract elements because of managing and
controlling easily. There are normally three
categories in the SLA.
The first SLA category is Open Metrics. Open
Metrics is related with a process that checks whether
NSP provides network service in time or not. If there
is a delay of open service, SLA system has to
monitor the open process, verify the violation of
open metrics and notify NSP and customers of the
violation.
The Second is Trouble Metrics. Trouble Metrics
is related with a process which monitors how long
NSP spends a time to recover network trouble and
how many times it has been occurred during
charging period.
The third is Performance Metrics. Performance
Metrics is the important metrics category in the view
of IT business. Performance Metrics is related with
QoS of network and there are many testing methods
in various network services.
In the case of world leading IT companies, some
of them present several performance metrics that are
network latency, packet delivery, network
availability and so on (MCI).
The WSMR system has been designed and
developed to provide and manage a contract between
network service providers and their customers based
on the web-based XML technology. In WSMR
system, it is communicating with each network
performance gathered system for collecting network
performance data and monitoring network
performance data which is produced by Data
Statistic Module (DSM) in WSMR every midnight.
To receive raw data, a WSMR system has to
communicate with other OSS systems periodically,
i.e. Customer Open Processing (COP) System,
Customer Service Guarantee (CSG) System, each
Network Management System (NMS) and
Equipment Control (EC) System. The COP system
manages customer open request and The CSG
system controls and manages every network trouble
data. NMS manages the status of network and the
EC system manages network equipments. To
consider these conditions, we design WSMR system
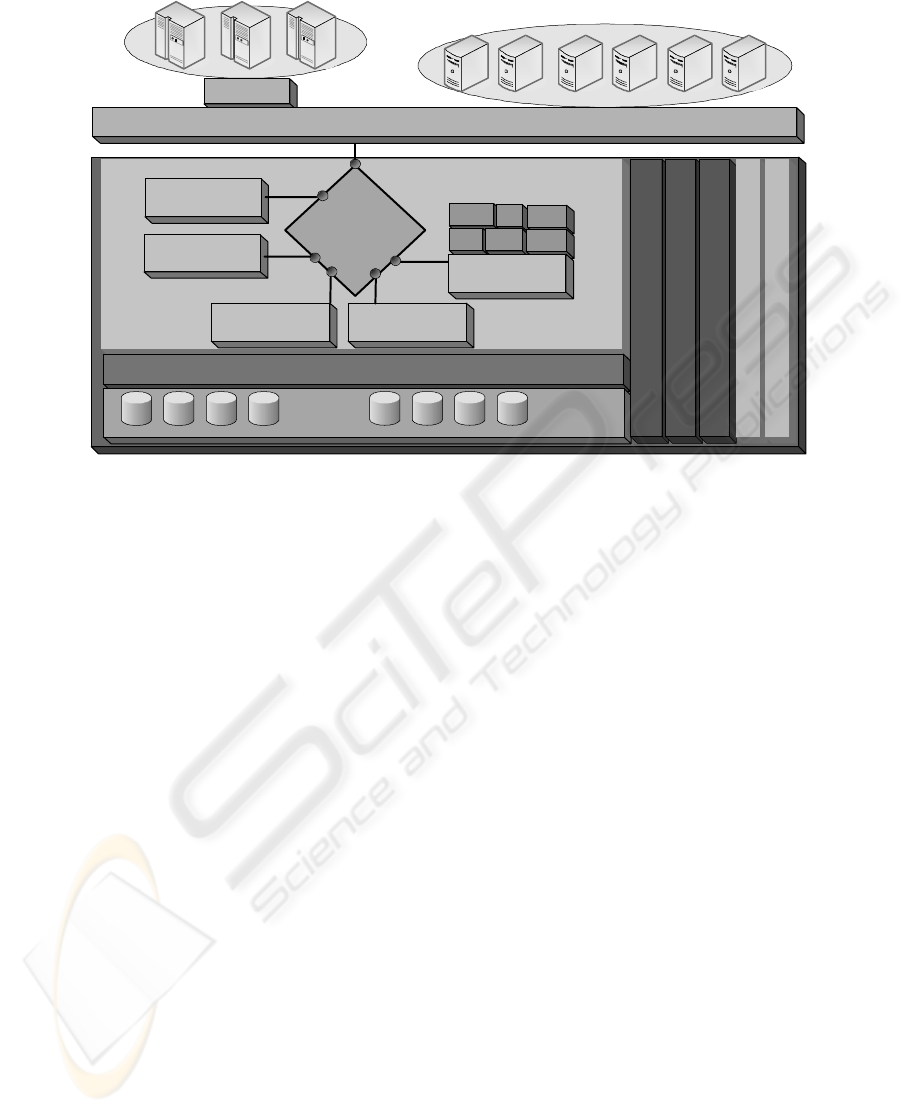
consisted of communication module as shown in
figure 2; data management module, data statistic
module, monitor module, data gathering module,
service specific processing module.
ICETE 2005 - SECURITY AND RELIABILITY IN INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
294
To communicate with other systems, WSMR
system uses XML which is one of standard to
present the documentation in different
telecommunication environment to persistent data
consistency and accuracy. Each XML document has
specific attributes which are able to distinguish it
from other documents. Using specific attributes, the
WSMR system verifies and manages raw data from
other systems.
3.1 Data Dispatcher module
The main role of DDM is control and management
of raw data depending on the individual case
because there are many systems which have their
own operating environment and specific operating
process.
The first role of DDM is providing
communication interface to other OSS systems or
NMS systems with web-based communication
technology.
To support web-based communication, DDM
defines web interfaces using Web services
Description Language (WSDL) and registers these
interfaces in the Universal Discovery Description
and Integration (UDDI). Through pre-defined web
interfaces, DDM communicates with other systems
based on the XML-based Simple Object Application
Protocol (SOAP). With these technologies, we do
not consider the environment of each system but just
define the interworking XML data format.
The second is translating external data into
internal common data format. In the case of open
metrics, each NMS interworked with WSMR system
has its own open data format. In the view of WSMR
system, if WSMR system accommodates a new
network service, each module of WSMR system
redefines all of process for the new network service.
So, it is overhead process to every modules
depended on the each open data format. To translate
original data format into internal common data
format, operator has to register mapping information
in the following steps;
z Define common data format
z Check original data format
z Select elements from original XML
document
z Decide mapping rules
z Register mapping information
Through above 5 steps, it is possible to use
common data format in the WSMR system while an
original data format is various.
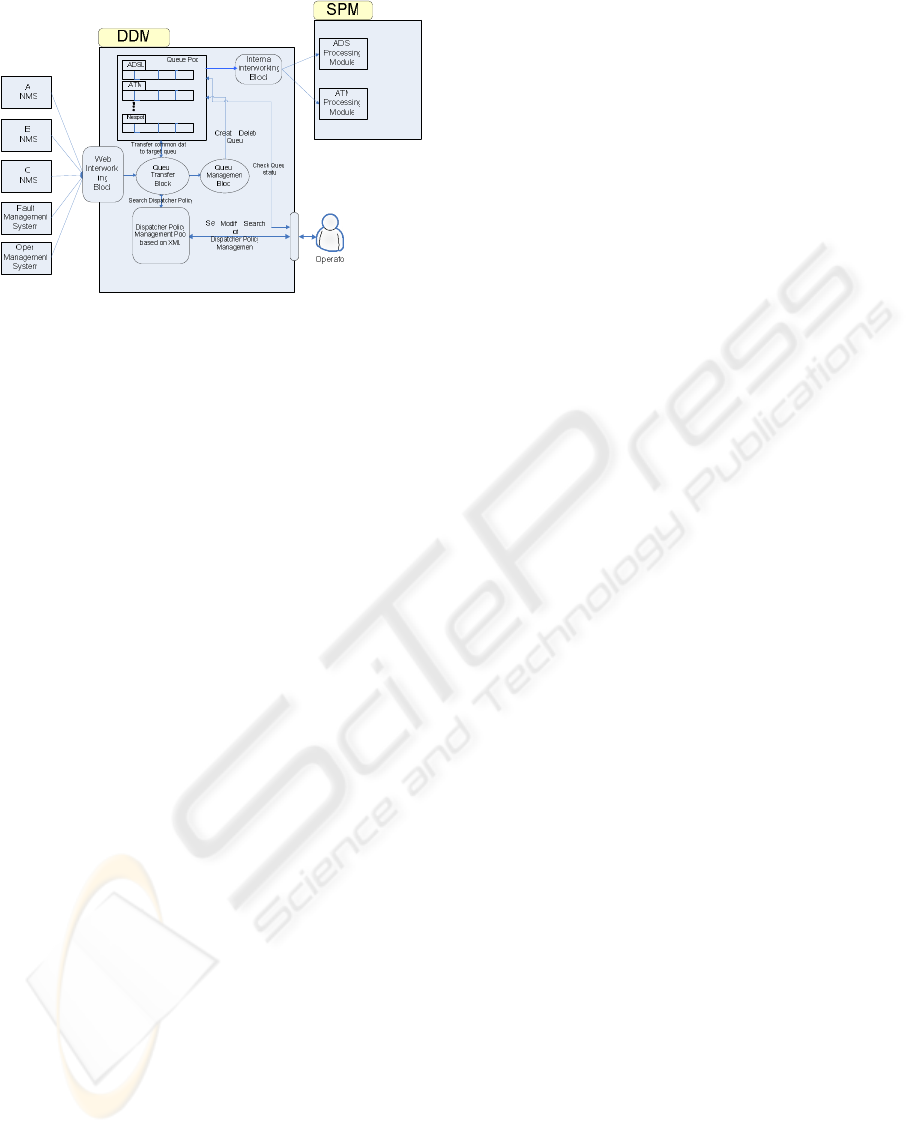
The third is transferring raw data to target
modules depending on the mapping information
which is managed by SLA operator in the DDM.
Transferring function is worked through queue pool
which is controlled by queue management block as
shown in figure 3.
Figure 2. The components of WSMR system
.NET Framework
Database
Database Data bas e Database Database Database Database Da tab ase Database
Data Monitoring
Module
Data Gathering
Module
Data Supporting
Module
Data Statistics
Module
Portal(GUI & WEB)
Web Server (IIS)
Security & Directory Service
XML
SOAP/HTTP/MSMQ
Biztalk(EAI)
Wireless
Internet
VPN
Internet
Frame
Relay
IP-VPN
ATM
Service Specific
Module
Data
Dispatcher
Module
OSS 1 OSS 2 OSS 3
FrameRelay
NMS
Wireless
Internet
NMS
VPN
NMS
IP-VPN
NMS
IP
NMS
ATM
NMS
Web Service
Figure 2: The components of WSMR system
THE WEB-BASED SLA MONITORING AND REPORTING (WSMR) SYSTEM
295
3.2 Service Specific Module
The Service Specific Module (SSM) checks contents
of XML document and retrieves information from it
what SSM has to control. In the case of processing
open metrics, SSM saves information using library
provided by Data Supporting Module (DSM) in the
WSMR database.
In the case of receiving Open Completed Order or
Open Changed Order, SSM finds out initial open
order which is related with the received order. If
there is any unmatched information in the Open
Completed or Open Changed Order, SSM throws it
to the DSM to save log information of error.
Also, SSM sends it to the service-specific process
web service if there is a need to process service
specific control. In that case, SSM receives the result
of processing service-specific process web service
and request DSM to save the information and log. In
the processing of open metric, it is important to keep
the status of processing each customer and SSM
manages it.
Because WSMR system has to accommodate
network service dynamically, we design that SSM
consists of common web service part and service
specific web service part. So, if WSMR system
receives a XML document, SSM checks the type of
XML document, finds out the mapping information
in the XML creation web service list table and calls
related web service for processing service specific
scenario. Otherwise, if there is no need to use a web
service, SSM deletes a web service that is no more
used
3.3 Data Supporting module
Data Supporting Module (DSM) provides libraries
related with Data Base to other modules in WSMR
system. In WSMR system, there are a lot of
information from other systems and are many
database tables depended on the type of information.
So, if there is allowed to access database directly,
every access routine has a dependency on the status
of database tightly.
Because it is inefficient policy that all of modules
in WSMR system control database individually, we
design the module that wholly controls database to
guarantee information consistency in database.
Using DSM, it is easy to access data base without
considering the structure of DB table or other things
and possible to access database efficiently.
3.4 Data Monitoring Module
The WSMR system monitors all information related
with SLA metrics and forecasts the violation of
contract between two parties. If there is a sign to
violate the contract, WSMR system alarms it to the
operator or other systems that control each network.
To support these operations, DM (Data
Monitoring) module monitors periodically all of data
which are saved in data base. The standard value of
each metrics is already saved in metric table before
WSMR system supporting network services.
To monitor all of information is very difficult, so
DM module has a monitoring policy which is based
on the time when each data occurred and generated
by SSM.
3.5 Data Statistics module
DST (Data Statistics) module generates statistic
information. The statistic units are day, week and
month because normal billing unit is month. In
statistic information, there are two types. The first
type is general information which is needed to
represent the state of WSMR operation. The other
type is specific information that is used to manage
Trouble or Network metric. When WSMR system
checks and finds out whether there is a violation or
not, statistic information produced by DST module
is used.
Because it is not necessary to operate all day long,
DST module works on every midnight to generate
statistic information based on gathered information
which is collected.
3.6 Data Gathering module
In providing an SLA in WSMR system, WSMR
system has to gather bulk data from other systems.
The amount of bulk data is very huge and each
interworked system has its own interworking
method. Considering these conditions, we design
Figure
3
:
The structure of data dispatcher
module
ICETE 2005 - SECURITY AND RELIABILITY IN INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
296
DG (Data Gathering) module which has a charge to
gather information with adapting individual
interworking method instead of ID module. There
are several types to communicate with other
systems, i.e. NMS. DG module provides a container
which accommodates interworking sub-modules
4 THE RESULT OF EXPERI-
MENTAL TEST
In this paper, we set a test server to test the
performance of WSMR system; P4 2.8GHz * 8, 32G
Memory, Windows XP professional, generate
incoming raw data and increase it.
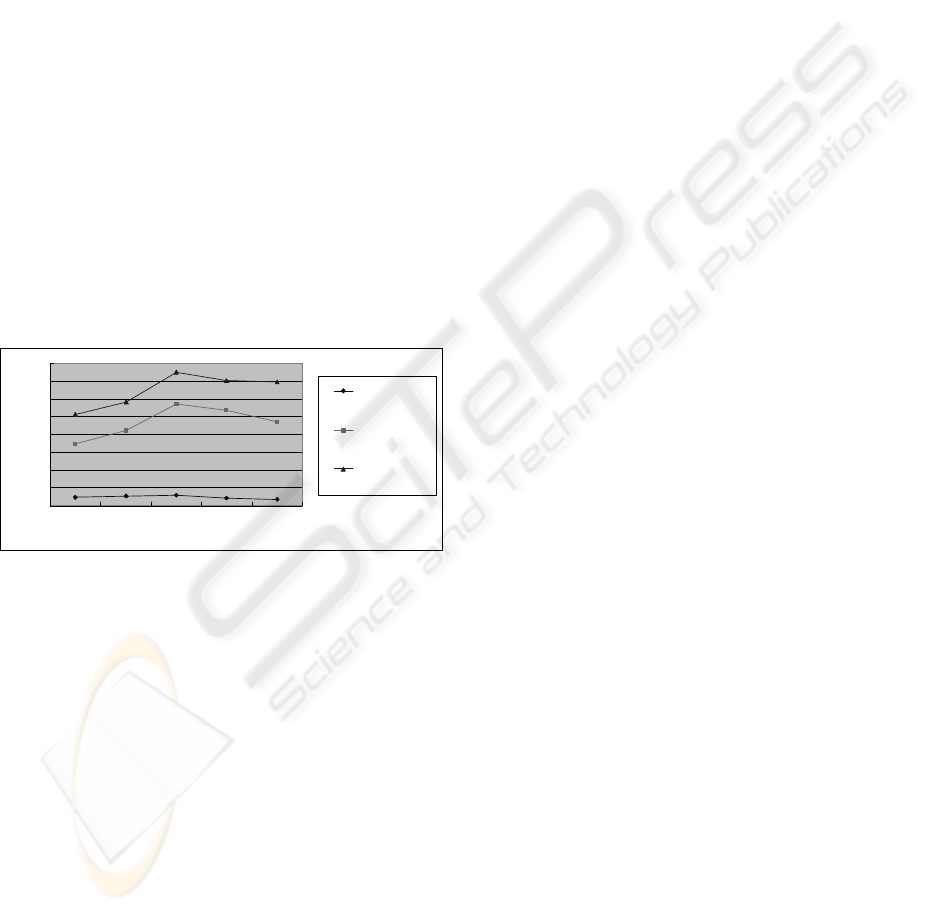
As shown in figure 4, the processing time is not
related to the number of concurrent incoming raw
data. From a case of 500 up to 3000 incoming data,
the processing count in a second is climbing up but
the count is climbing down over 3000. In the result
of test, we know that the default processing time is
needed whether concurrent count is many or not.
Over 10000 counts, the processing capability is
stabilized and the WSMR system is more adjusted
large scale processing conditions.
Figure 4: The experimental result of the WSMR system
and DDM’s performance
5 CONCLUSIONS
In the early of 2000s, there are several suggestions
of providing SLA in the view of several ways. One
of them is QoS-centered SLA architecture and the
other is a legacy-extension architecture depended on
the extension of legacy reporting or monitoring
system. In these suggestions, there is no way to
communicate with other Operating Support Systems
which don’t provide specific interworking
technologies like CORBA. To overcome this
problem, this paper provides architecture of SLA
system which is operated on a web-based
communication technology to communicate with
other systems which are operated in the different
operating environment.
Supporting SLA means to report or monitor the
status of network service quality in time for each
network service customer and if there is no way to
provide SLA in time, SLA function doesn’t have its
right role. To provide in-time service, it is needed to
build several modules to manipulate raw data and
transfer it to target modules.
This paper design and develop the WSMR system
which is consisted of several blocks to manipulate
raw data in times.
In the future, we will design not only web-based
communication mechanism but also other type of
communication mechanism.
REFERENCES
Rick Sturm, Wayne Morris and Mary Jander, 2000,
Foundations of Service Level Management, SAMS. 1st
edition.
John J. Lee, Ron Ben-Natan, 2002,
Integrating Service
Level Agreements
, WILEY. Indiana
TM Forum, 2001,
SLA Management Handbook (GB 917),
TMF
Eric Bouillet, Debasis Mitra, K. G. Ramakrishnan, 2002,
The Structure and Management of Service Level
Agreements in Networks
, IEEE Journal on selected
areas in communications, vol. 20, No 4
E.C. Kim, J.G. Song, C.S. Hong, 2000,
An Integrated
CNM Architecture for Multi-layer Networks with
Simple SLA Monitoring and Reporting Mechanism
,
IEEE Network Operations and Management
Symposium (NOMS)
Roger Wolter, 2001,
XML Web Services Basics,
“http://msdn.microsoft.com/webservices/understanding
/webservicebasics/default.aspx?pull=/library/enus/dnw
ebsrv/html/webservbasics.asp”
Nathan J Muller, 1999,
Managing service level
agreements
, International Journal of Network
Management Volume 9, Issue 3
MCI,
MCI advantage SLA,
“http://global.mci.com/terms/us/products/advantage/”
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
500 1500 3000 10000 20000
Concurrent co unt of inc omin
g
raw data
(
count
)
(count/sec)
WSMR system
DDM(w/ single
thread)
DDM(w/ multi
thread)
THE WEB-BASED SLA MONITORING AND REPORTING (WSMR) SYSTEM
297
