Personnel Needs Regional Map as a Planning Element for Territories
Sustainable Development
Svetlana M. Kurbatova
1,2,3 a
and Alexey G. Rusakov
1b
1
Law Institute, Krasnoyarsk State Agrarian University, Mira Av. 90, Krasnoyarsk, Russia
2
Law Institute, Siberian Federal University, Svobodny ave. 79, Krasnoyarsk, Russia
3
Krasnoyarsk State Medical University named after Professor V. F. Voino-Yasenetsky, 1 Partizana Zheleznyaka str.,
Krasnoyarsk, Russia
Keywords: Human Resources, Sustainable Development, Region, Legal Regulation.
Abstract: The article analyzes regional personnel problems in the context of regions sustainable development concept
and essence analysis. The place and role of the personnel issue for regions sustainable development policy
implementation are considered. The specifics of human resources distribution in the region, taking into
account their socio-economic characteristics, are noted. It is proposed to create and maintain a regional
personnel map as a way to minimize the young specialists personnel distribution problem across the region
territories, on the higher education specific educational institution example. To implement this, as well as to
solve other tasks related to ensuring the regions sustainable development, it is proposed to create regional
Analytical personnel centers.
1 INTRODUCTION
State policy aimed at the territories sustainable
development is one of the most important tasks faced
by modern states, including Russia. State stable and
sustainable development ensures national stability
and creates reliable conditions for the further country
development as a whole (Kuzmenkova, 2016).
Measures for the sustainable development formation
and further development should be implemented by
highly professional and knowledgeable specialists.
Kuttubayeva, T.A., in addition to the qualification,
professionalism and education level, also additionally
highlights territorial and professional mobility
(Kuttubayeva, 2006)
This leads to the relevance of raising the personnel
issue, which is hindered by the situation between the
standard of living and large settlements infrastructure,
which are not so many in the Russian Federation, and
rural areas, that make up a large part of it (Ivanova,
2012), and the resulting economic imbalance
(Scheblyakov, Farafontova, Kurbatova and
Kuzhleva, 2020). The reasons are obvious. Low
standard of living, low salaries, lack of comfortable
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8518-9233
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0453-6657
housing, unclear prospects for career growth and self-
realization, etc. This is especially true in relation to
the so-called "prestigious professions" like lawyer,
economist, programmer, designer, psychotherapist,
etc.
Modern research has shown that an extremely
small number of young professionals who receive
legal education or work in the legal field have a desire
to work and live in rural areas and in region remote
areas.
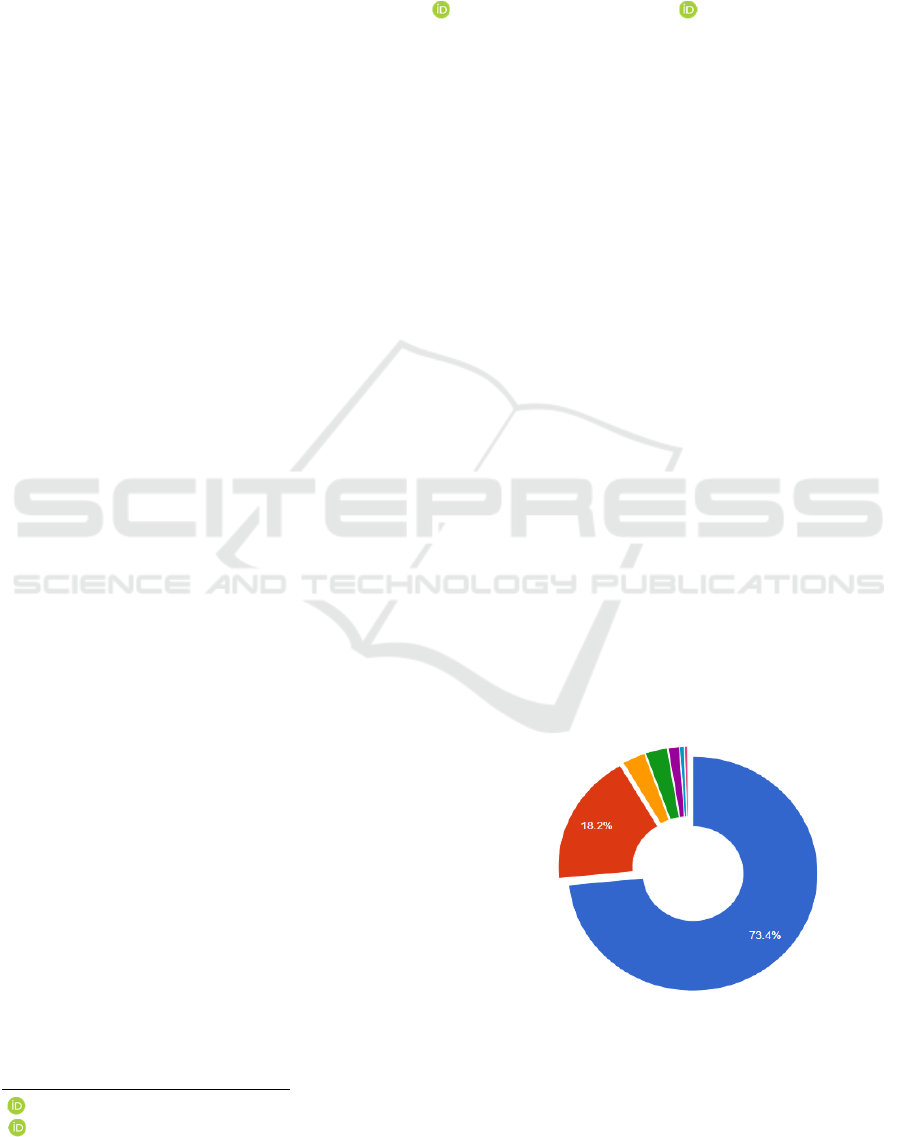
Figure 1: Distribution of the vacancy "Lawyer" by the
Krasnoyarsk Region districts (Statistics, 2020).
810
Kurbatova, S. and Rusakov, A.
Personnel Needs Regional Map as a Planning Element for Territories Sustainable Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0010598008100815
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 810-815
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
So, in 2020, the distribution of the vacancy
"Lawyer" in the Krasnoyarsk Region was as follows:
73.4% - Krasnoyarsk (the regional center);
18.2% - Berezovsky district (the territory that
actually became part of Krasnoyarsk);
The remaining 8.2% account for vacancies in
all other territories of the Krasnoyarsk Region,
on the area of which as many as 5 Frances can
be located (!).
This is due to a whole range of socio-economic
problems that significantly affect the quality of life in
rural areas (Kurbatova and Aisner, 2020). Young
legal professionals do not see any prospects for
professional and career growth. They often perceive
their work in rural areas as a temporary, short-term
phenomenon, and try to change their residence, try to
live in urban settlements, where the quality of life and
professional prospects are higher than in rural and
remote areas of the Krasnoyarsk Region. As a result,
rural and remote areas of the region are experiencing
a "personnel shortage" in young lawyers, who, along
with other professions young representatives, are the
intellectual, economic and social reserve of society,
its strategic human resources and human capital that
can ensure the regions sustainable development.
2 METHODOLOGY
The research was based on scientific works, including
fundamental ones (Salgiriev, 2019; Shchedko, 2016;
Gusev, 2014; Minullina, 2008) on this and similar
topics, as well as government bodies and
organizations statistical data, the results of surveys
and interviews conducted by the authors themselves
and allowed us to formulate our own position on the
issues under study. This allowed us to consider the
issues raised in the article at the empirical and
theoretical levels.
For this purpose, such general scientific methods
as observation, comparison, analysis and synthesis,
analogy and modeling, abstraction and
concretization, etc., as well as private scientific-
statistical analysis, monographic analysis, graphic
and other methods were used.
3 RESULTS
Under sustainable development, the authors
understand the state policy multidimensional
direction, where a special role is assigned to the
personnel issue solution, organized according to the
following scheme:
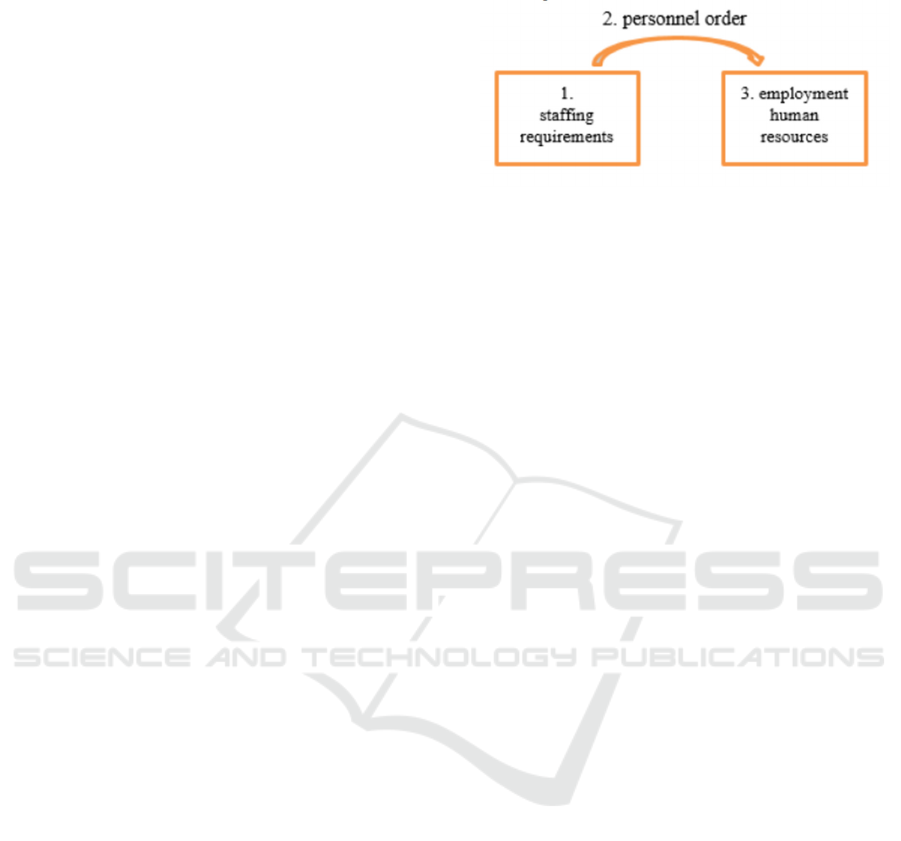
Figure 2: Stages of solving the personnel issue.
The stages content is built on the wave of a certain
logic:
1) First, it is necessary to identify the region
territories personnel needs for individual professions
(and this should be done, including in the short,
medium and long term);
2) Placing an order to regional educational
institutions for the legal and other personnel training
(while interacting with specific educational
institutions, including the modernization of existing
and the creation of new educational training
programs);
3) Employment in the region.
An effective mechanism for their implementation
is the use of an integrated approach that will reveal
the problem from different sides, form the most
optimal specific measures combination. This leads to
the need for open, broad-format discussions involving
regional and municipal authorities representatives,
employers and employees, higher and secondary
vocational educational institutions, students and the
public, using the positive experience of other regions,
including foreign countries.
However, in order for this not to be chaotic, it is
necessary to create a regional center created at the
level of a specific subject of the federation, which is
designed to accumulate information about the supply
and demand for certain professions, the necessary
territories, acting as a coordinator, and in some cases,
such interactions organizer. This Center is designed
to:
Develop a map of personnel needs for the
region territories for the short-term (up to 3
years), medium-term (up to 5 years) and long-
term (up to 10 or more years) perspective;
Coordinate the personnel orders formation and
distribution for educational institutions in the
region.
To update the issue of the need to develop and
adjust educational programs aimed at training
specialists, taking into account the region
specifics and peculiarities, which should be
Personnel Needs Regional Map as a Planning Element for Territories Sustainable Development
811

reflected in the curricula variable part, i.e. in
the academic disciplines names and content.
For example, the Krasnoyarsk State Agrarian
University trains bachelors in the field of
"Jurisprudence" in the profile "Legal regulation of
rural areas and agriculture sustainable development",
within the framework of which the graduates are
trained for the following activities types:
Rule-making;
Law application;
Law enforcement;
Expert advisory.
At the same time, Krasnoyarsk State University
takes into account the Krasnoyarsk Region regional
specifics and the university agricultural profile.
Similarly, the master's degree program in the field
of "Jurisprudence" is developed: the profile "Land
relations State legal regulation" is implemented in
relation to the lawyers for rural areas training, based
on the special socio-economic significance of land as
legal relations resource and subject, as well as the
university specifics.
The university administration is doing a lot to
ensure that law graduates (as well as graduates of
other fields of studies and specialties prepared at the
agrarian university) are employed throughout the
Krasnoyarsk Region, however, there is an acute lack
of strong state support that would cover the political,
economic and social aspects of this issue.
4 DISCUSSION
Territories sustainable development is understood by
different authors as a combination of different
elements. So, Antonova, M.A. understands the
regions sustainable development as a combination of
three elements: economic efficiency; ensuring equal
living conditions; and environmental sustainability
(Antonova, 2012). Tretyakova, E.A. Osipova, M. Y.
distinguish economic, social and environmental
elements (Tretyakova and Osipova, 2018).
Minullina, N.V. defines sustainable development
as a transition from the economy of using natural
resources to the economy of their reproduction, in
which the future generations interests are ensured,
highlighting the educational component as a separate
element (Minullina, 2008).
This is facilitated by the lack of uniformity in the
legal regulation of the Russian Federation state policy
area. For example, the Urban Planning Code of the
Russian Federation defines "territories sustainable
development" as "ensuring ... safety and favorable
conditions for human life, limiting the negative
impact of economic and other activities on the
environment and ensuring the natural resources
protection and rational use in the interests of present
and future generations" (p. 3, p. 1).
The rural territories of the Russian Federation
sustainable development concept for the period up to
2020 (approved by the decree of the Government of
the Russian Federation No. 2136-р of November 30,
2010) was focused on rural territories and meant by
their sustainable development "rural territories stable
socio-economic development, increasing the
production of agricultural and fish products,
improving the agriculture and the fisheries complex
efficiency, achieving the rural population full
employment and improving their standard of living,
as well as rational land usage". Almost word for word
(but not completely!) this definition is repeated by the
Strategy for Sustainable Development of Rural
Territories of the Russian Federation for the period up
to 2030 (approved by the decree of the Government
of the Russian Federation on February 02, 2015 No.
151-р): "rural territories stable socio-economic
development, increasing the agricultural production
volume, increasing the agriculture efficiency,
achieving the rural population full employment and
improving their standard of living, rational use of
land". Recognizing the role of the state in shaping the
territory sustainable development, it should be
recognized that in Russia there is no federal law that
would comprehensively regulate these issues,
combining urban planning, social, economic,
personnel, educational and other foundations for such
development.
The authors support the legislators position. They
pay special attention to the personnel issues solution
(which is reflected in the current regulatory legal
acts). They agree with the opinion of the authors, who
believe that staffing is the basis for the territories
development and is multidimensional in nature.
(Gorbunova and Shashlova, 2009; Vlasova, 2016;
Gainov, 2015). At the same time, the authors
understand the sustainable development of the
Krasnoyarsk Region as a organizational, legal,
economic and social measures complex system that
allow for the prompt and effective resolution of
economic, organizational, social and legal issues of
ensuring vital activity and maintaining an adequate
quality of life in the region territory.
The human factor is one of the most important
elements of this measures system, as it manifests
itself both at the organizational and executive levels
(Kurbatova, Aisner and Naumov, 2020).
And this determines the importance of training
personnel who could implement these functions.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
812

For the territory (and the country as a whole)
sustainable development in the legal sphere (law-
making, law arrangement and enforcement), it is
necessary:
1) To create the high-quality and material-
supported normative legal acts at the level of the
Russian Federation subject and at the municipal level.
At the same time, these regulatory legal acts should
not simply duplicate the provisions contained in the
federal level acts, but should take into account the
territories specific needs, ensuring their timely
implementation by law enforcement agencies.
2) To assign tasks of providing the territory with
appropriate highly professional personnel, first of all,
to regional educational institutions. This applies both
to the personnel training in narrow-profile
professions (agronomist, veterinarian, etc.), and
others, for example, in the field of law. To do this, it
is necessary to adapt existing and develop new
educational programs that take into account this
specificity. An example is the Krasnoyarsk State
University, which teaches lawyers for bachelor's and
master's degrees, in profiles that have a regional
aspect.
3) It is necessary to build a clear interaction
between employers, educational institutions and the
public (potential and real students, employees in the
region).
At the moment, this is being prevented by:
"Weak feedback from business structures that
do not make specific requirements for the level
and quality of training;
The employers unwillingness to participate in
the formation of practical skills in students, to
provide their resources for the educational
programs implementation;
Business insufficient participation in the
innovations development and replication
received within the walls of educational
institutions;
Weak interest (largely due to a lack of
understanding of the benefits) in creating a
single educational, scientific and industrial
space" (Gulyaeva, Buraeva, Vlasova and
Grishaeva, 2014). It can be recommended that
regional employers should adopt the foreign
colleagues experience when they seek out
future employees from school, paying for their
further education at universities with the
obligation of these students to work a certain
minimum number of years with these
employers in the future.
It is necessary to recall the positive experience of
targeted training that existed in Russia earlier and
implied a similar approach. At the same time, special
attention should be paid to local youth, based on the
calculation that in the future, having graduated, many
do not want to leave their small homeland for good,
lose family ties (67% of the respondents answered
this in the authors studying at the Law Institute of the
Krasnoyarsk State Agrarian University from rural
areas).
We believe that we should return to the young
specialists distribution system, especially when it
comes to students studying on a budget basis.
4) Regional authorities should independently
develop programs of assistance to young
professionals, fixing them by law, providing for the
funds allocation for this from the budget
5) It is important to develop personal motivation
and form value, cultural, civic-patriotic and other
personal attitudes, and this should be done from the
kindergarten stage. In the future these qualities should
be developed more.
In particular, in relation to the legal profession, it
is noted that its prestige in terms of promoting justice,
protecting people in difficult life situations, etc. is
currently very low in Russia; and lawyers themselves
are often perceived by the population as "reshalas",
cynical and corrupt people.
6) The desire for a decent salary and the need for
housing are not the only conditions that determine the
graduates willingness to go to work in the region.
High wage in the absence of opportunities to spend it,
as well as housing, which often needs to be repaired,
offset these two conditions with the third one, that is
the need for infrastructure. This was expressed by
21% of junior students and 78% of senior students
from among the 220 students studying at the Law
Institute of the Krasnoyarsk State Agrarian
University, interviewed by the authors during the
study. These are high-quality healthcare institutions,
a variety of shops and shopping centers, sports and
other cultural and leisure facilities, cafes and
restaurants, etc. Thus, this puts the availability of
appropriate infrastructure in these territories among
the priority conditions for the young personnel
distribution across the region territories.
Therefore, it is necessary to raise its value in the
eyes of society (and the lawyers themselves), through
a number of measures:
To increase the number of public appearances
by lawyers;
To popularize the jurisprudence through
modern technologies that allow the population
free legal education development, i.e. casts,
podcasts, video clips, video lectures, mobile
applications created under the guidance of
Personnel Needs Regional Map as a Planning Element for Territories Sustainable Development
813

persons who are well-known and deservedly
respected in the field of jurisprudence;
To conduct legal lectures for the population on
the basis of educational institutions;
To use civil society institutions for this
purpose;
To expand the "legal clinics" capabilities (for
example, there are only two of them in the
Krasnoyarsk Region, on the basis of the Law
Institutes of the Krasnoyarsk State University
and the Siberian Federal University).
7) Along with the region specifics, it is necessary
to take into account the specifics of the profession in
certain areas and spheres.
For example, agriculture is often characterized by
a more complex management system compared to
other sectors of economy. This affects the
organization and content of the legal service itself in
rural areas, which has historical prerequisites. Thus,
according to the Instructions on the procedure for
legal services to collective farms, approved by Order
No. 265/25 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the
USSR and the Ministry of Justice of the USSR dated
November 16, 1984, various forms of legal services
to collective farms were previously used in
agriculture, i.e. a collective farm legal adviser, a head
collective farm (state farm) lawyer (legal group), a
legal advice to the bar association lawyer and other
forms.
In connection with the abovementioned, we
consider it appropriate to form a personnel
distribution map for each region in the territory. It is
advisable to implement the following model:
The personnel needs awareness in the short-
term (up to 3 years), medium-term (up to 5
years) and long-term (up to 10 years or more)
perspective;
The development of a program to meet these
needs by analyzing the services educational
market, the specific employers financial
capabilities and (or) regional and (or)
municipal budgets;
Drawing up a map of personnel needs based on
geographical, demographic and other maps of
the region;
The roadmap development (estimates
preparation, calculation, the planned number of
people employed for specific jobs, the
mechanism for organizing this, educational
institutions involved in the project, etc.).
This activity should be carried out by relevant
specialists working on a permanent basis, with the
involvement of employers and employees
representatives in certain types of professions, as well
as educational institutions located in the region and
their students. In this connection, we propose to
create a regional Analytical personnel center in each
Russian Federation subject, with the appropriate
competence for solving this type of tasks, but also
responsibility for the improper execution.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Of course, such a direction of Russian state policy as
the sustainable regional development formation as the
basis for creating an economically strong, socially
protected and politically stable state is a reflection of
the natural development level that the Russian
Federation has achieved to date.
However, there are still many unresolved
problems in this area, there is a lack of regulatory
legal acts at different levels, and there is a lack of
understanding on the part of different subjects and,
primarily, authorities, in solving quite certain issues.
We believe that it is necessary to conduct scientific
research on this topic, that will help to identify
problems and find ways to overcome them and
contribute to the regions sustainable development
formation.
REFERENCES
Antonova, M.A. (2012). Theoretical and methodological
foundations for the study of sustainable development of
regions. Regional Economics and Management, 4 (36):
46-52
Vlasova, T.A. (2016). Conditions for the formation and
assessment of the state of human resources in the
agricultural sector of the economy. Regional economy:
theory and practice, 12 (435): 107-121
Gainov, A.A. (2015). Sustainable development of
territories: the main factors and problems of the regions
of Russia. Socio-economic sciences and humanities
research, 6: 51-55.
Gorbunova, I.I., Shashlova, N.M., (2009). Staffing is the
basis for sustainable development of rural areas.
Bulletin of the Tull State University. Economic and
legal sciences, 2-1: 153-160.
Gulyaeva, T.I., Buraeva, E.V., Vlasova, T.A. and
Grishaeva, O. Yu. (2014). Securing young specialists in
the countryside as a priority direction of the regional
personnel policy). Economic Analysis: Theory and
Practice, 11 (362): 59-66.
Gusev, V.V. (2014). Improvement of methodological
support for sustainable socio-economic development of
the region on the basis of its system diagnostics: author.
dis. ... Cand. econom. sciences. Barnaul, 26 p.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
814

Ivanova, N.A. (2012). Theoretical aspects of the concept of
the infrastructure of the region. Modern high
technologies. Regional Supplement, 3(32): 30-36.
Kuzmenkov, V.D. (2016). Sustainable development of
Russian regions. Bulletin of the Voronezh State
University of Engineering Technologies, 2 (68): 257-
261.Kurbatova, S.M. and Aisner, L.Y. (2020).
Innovative Socially Oriented Type of Economic
Development as State Policy in Agriculture. E3S Web
of Conferences, 161, 01050
Kurbatova, S.M., Aisner, L.Y. and Naumov, O.D.(2020).
Labor resource as a factor of modern agricultural
production. E3S Web of Conferences, 161, 01088.
Kuttubaeva, T. A. (2006). Formation of a strategy for the
development and use of human resources at the
regional level: abstract. diss. ... candidate of economic
sciences. Barnaul, 23 p.
Minullina, N. V. (2008). Human resource Management as
a basis for sustainable development of the region (on
the example of the Republic of Tatarstan): autoref.dis.
... candidate of economic sciences. Kazan. 22 p.
Osipova, M. Yu. (2017). Development of a static-dynamic
approach to the assessment and management of
sustainable development in the region. Candidate of
Economic Sciences, Perm.
Salgiriev, R. R. (2019). Sustainable development of the
municipality: methodological foundations and
implementation mechanism: abstract. diss. ... Dr.
economy. sciences'. Moscow.
Statistics of salaries of a Lawyer in the Krasnoyarsk
Territory Electronic resource. Trud.com
Tretyakova, E. A. and Osipova, M. Yu. (2018). Assessment
of indicators of sustainable development of Russian
regions. Problems of forecasting, 2(167): 24-35.
Scheblyakov, E.S., Farafontova, E.L., Kurbatova, S.M.,
Rakhinsky, D.V. and Kuzhleva, A.A. (2020). On the
concept and types of harm to the environment. IOP
Conference Series: Earth and Environmental
Science 548(6), 062025
Shedko, Yu. N. (2016). Improving the mechanisms for
managing the sustainable development of the region:
diss. ... doctor of Economics. Moscow, 361 p.
Personnel Needs Regional Map as a Planning Element for Territories Sustainable Development
815
