
Development of a Model of Financial Stability of Universities
Tatyana Miroshnikova
1a
and Natalia Taskaeva
2b
1
Vladivostok State University of Economy and Service, 41, Gogolya str., Vladivostok, Russia
2
National Research Moscow State University of Civil Engineering, 26, Yaroslavskoye Shosse, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Financial Stability of the University, Financial Stability Indicators, Education System, Educational Quality.
Abstract: The financial stability of state universities is the basis for the sustainable progressive development of this area.
The most important direction of the strategic policy of state administration is the management of the
educational process. The relevance of the topic of the work is due to the need to ensure the financial stability
of educational organizations, which seems to be an important task in the framework of increasing the
efficiency and effectiveness of the activities of organizations subordinate to the Ministry of Science and
Higher Education in terms of financial and economic activities. The subject of the research is the development
of a model of financial stability of a public institution. The existing methods for assessing the financial
condition of commercial organizations cannot be applied to the analysis of the financial condition of budgetary
structures. The information base of budgetary institutions differs in many respects in the content of a number
of indicators of the balance sheet from commercial organizations. The authors used an analytical approach in
the study of existing approaches to assessing financial stability. The result of the work is a model for assessing
the financial stability of universities. It allows you to determine the level of financial stability of any university
and identify those areas of activity where there are negative results that have affected the indicators of
financial stability in general. This will ensure effective planning in the formation and allocation of resources.
The methodological basis of the study was methodological recommendations for the analysis and diagnostics
of financial stability, as well as publications of leading experts in the field of economics.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the Ministry of Science and Higher
Education of the Russian Federation, the Federal
State Statistics Service and the National Research
University "Higher School of Economics", the
dynamics of the number of state, municipal and
private universities in 2000–2019 changed as follows
(Figure 1). During the period under review, the
number of state and municipal Russian universities
exceeded the number of private ones by 1.4 - 2 times
(Bondarenko, 2019).
Figure 1: Change in the number of state, municipal and private universities in Russia in 2000–2019.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3998-3633
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1792-0562
Miroshnikova, T. and Taskaeva, N.
Development of a Model of Financial Stability of Universities.
DOI: 10.5220/0010597007490756
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 749-756
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
749

Statistics of the last twenty years confirm that
Russian higher education is provided largely by state
and municipal universities. Higher education in the
Russian Federation is one of the priority areas for the
state.
The financial stability of state universities is the
basis for the sustainable progressive development of
this sphere. The efficiency of the formation and
distribution of resources, financial results and the
level of solvency determine financial stability.
Considering the essence of financial stability, it
should be noted that it implies not only maintaining a
positive level of indicators characterizing it, but also
includes development, which is manifested in
economic growth. Namely, there are tendencies of
positive changes taken together indicators of the
economic and financial development of the
organization over a certain period (Kovaleva, 2019).
The object of our research is to assess the financial
sustainability of public universities.
The most important direction of the strategic
policy of state administration is the management of
the educational process. The scientific, industrial,
ecological, cultural and political potential of the
country directly depends on the quality of education
of the population.
Along with organizations and commercial
enterprises, budgetary institutions, based on the
results of work for the reporting period, determine
economic or financial indicators (results) of
economic activity. The economic indicators of the
activities of budgetary institutions are used for
economic planning of the activities of the institution
in the analysis of economic activities, as well as to
determine the tax base.
The most important indicators of the activities of
a budgetary institution include:
receipts by income;
payments for expenses;
the amount of subsidies for the fulfillment of
the state assignment.
When making managerial decisions and
conducting financial and economic activities of state
institutions, its directions may change, and as a result,
they may face the problem of ensuring and
maintaining financial stability.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The technology of the process of managing a
budgetary organization includes closely interrelated
functions: planning, accounting, analysis and
regulation (Aidemirova, 2017).
The instability of the financial state of the budget
of a state organization is characterized by a low level
of its own sources of budgeting, imbalance, inability
to correctly distribute revenues and a low share of
social spending in their total amount.
With a stable financial condition, there is a
sufficient amount of own sources of income, the
budget is balanced; the priority is to finance the social
and cultural sphere.
In terms of its structure, the information base of
budgetary institutions differs in many respects in the
content of a number of balance sheet indicators from
the base of commercial organizations, and it should
be noted that in order to improve financial stability, it
is necessary to take into account changes in the
structure of property and sources.
In this regard, it should be noted that the methods
for assessing the financial condition of commercial
organizations could not be applied to the analysis of
the financial condition of budgetary structures in a
more or less long-term perspective. This is largely
due to the restrictions related to the specifics of
budgetary institutions, and is expressed in the fact
that:
when calculating the autonomy ratios (the ratio
of own and borrowed sources), the cost of
equity capital is used, whose value is displayed
as part of the liability of the balance sheet of a
commercial organization. The state budgetary
institution does not form its own capital, and
the liabilities of its balance sheet include only
two sections: "Liabilities" and "Financial
result".
the calculation of financial stability ratios (the
ratio of own and borrowed sources of
financing) is carried out on the basis of the
classical methodology, using the value of long-
term liabilities. Nevertheless, relying on clause
14 of Article 9.2 of the Federal Law of
12.01.1996 No. 7-FZ (as amended on
08.06.2020) "On non-profit organizations":
"Budgetary institutions are not entitled to place
funds on deposits with credit institutions, as
well as make transactions with securities,
unless otherwise provided by federal laws”
(Frolkin, 2016).
Based on the proposed methods for calculating
financial stability indicators applicable for a state
university, we can propose an integrated approach
that combines all methodological approaches, but
excludes duplication.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
750
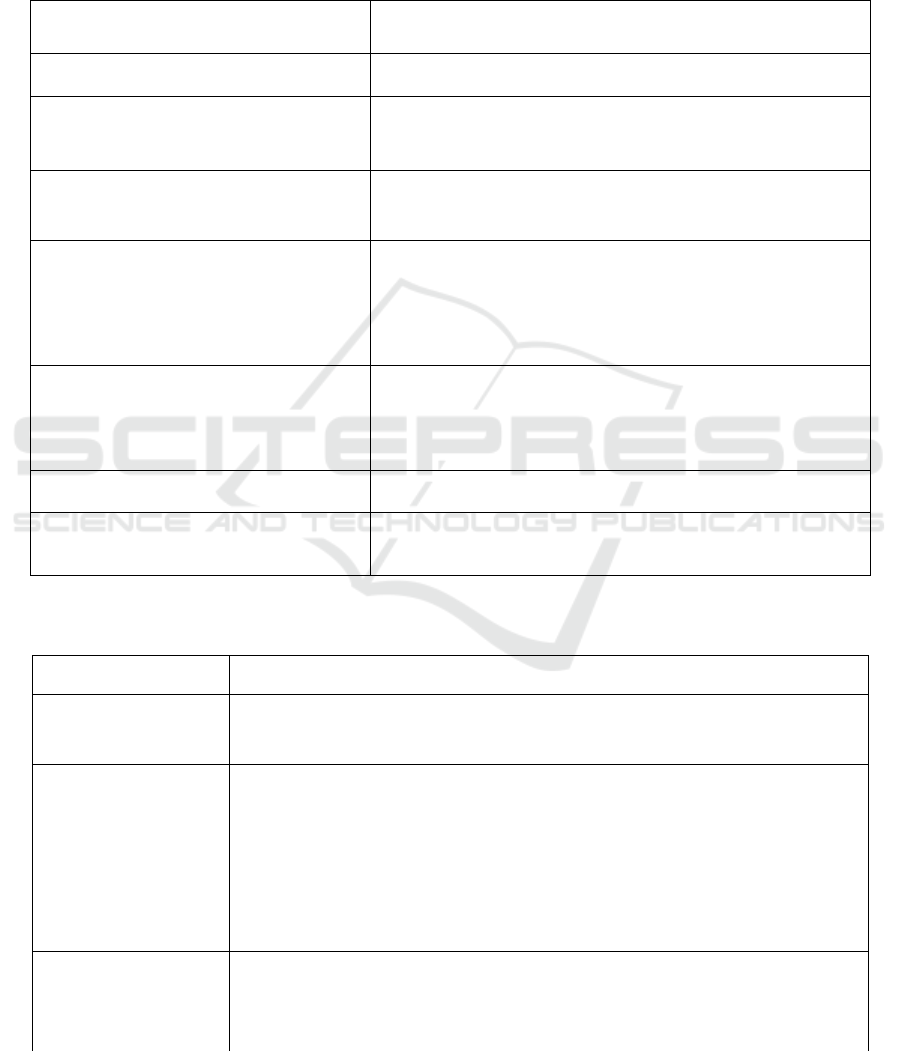
3 RESULTS
To develop a model of financial stability, we present
the absolute and relative indicators borrowed from the
models of the Ministry of Education, as well as the
methods used to analyze the financial stability of
commercial organizations (Financial sustainability,
2016). Table 1 presents the absolute indicators
applicable to characterize the financial stability of a
public university.
Table 1: Accumulated absolute indicators of the financial stability of the university.
Indicators Value
Total number of students in undergraduate,
s
p
ecialist and
g
raduate
p
ro
g
rams
The sum of the number of students enrolled in educational
p
ro
g
rams of bachelor's, s
p
ecialist's and master's de
g
rees
The number of enlarged groups of
specialties and directions (hereinafter -
UGSN)
Share of UGSN in the total amount
The total number of the teaching staff
(hereinafter PPS)
The total number of teaching staff excluding internal part-time
workers
̆
and working under civil contracts, excluding the
occupied rates, expressed as a percentage.
The proportion of the number of students
enrolled in master's programs and programs
for the training of scientific and
pedagogical workers (hereinafter - SPW) in
graduate school in the total number of the
g
iven contin
g
ent
The ratio of the reduced contingent of students to the reduced
contingent of students in Master's programs and postgraduate
teaching staff training programs
The number of publications of the
organization, indexed in the information
and analytical system of scientific citation -
Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI), per
100 academic staff
The ratio of the number of publications published in the reporting
year, included in the RSCI, to the number of teaching staff,
multiplied by 100
The amount of income from educational
activities
The amount of funds of the organization received during the
re
p
ortin
g
y
ear from educational activities
The amount of subsidies for the fulfillment
of a state task (hereinafter referred to as the
GZ
)
This subsidy is provided to institutions in accordance with
paragraph one of clause 1 of Article 78.1 of the Budget Code of
the Russian Federation
(
Kuznetsova, 2016
)
.
Table 2: Accumulated relative indicators of the financial stability of the universityю
Indicators Value
The volume of research
and development work
per 1 academic staff
The ratio of the total amount of funds received during the reporting year from the
implementation of research and development work to the number of teaching staff.
Average score of the
Unified State Exam
The ratio of the sum of the average Unified State Exam scores of students enrolled in
full-time studies based on the Unified State Exam results, adopted based on the
results of targeted admission in all areas and specialties of bachelor's and specialty
programs, multiplied by the number of such students enrolled in the corresponding
areas and specialties of bachelor's and specialty programs to the total number of such
students.
The results of students eligible for admission without entrance examinations are
recognized as the highest Unified State Exam results (100 points) in the relevant
general education subjects (Improving the financial, 2018).
Income from all sources
calculated on the
number of students
(reduced contingent)
The ratio of the amount of the organization's funds received during the reporting year
from budgetary and non-budgetary sources to the reduced contingent of students
enrolled in bachelors, specialists, and master's programs.
Development of a Model of Financial Stability of Universities
751
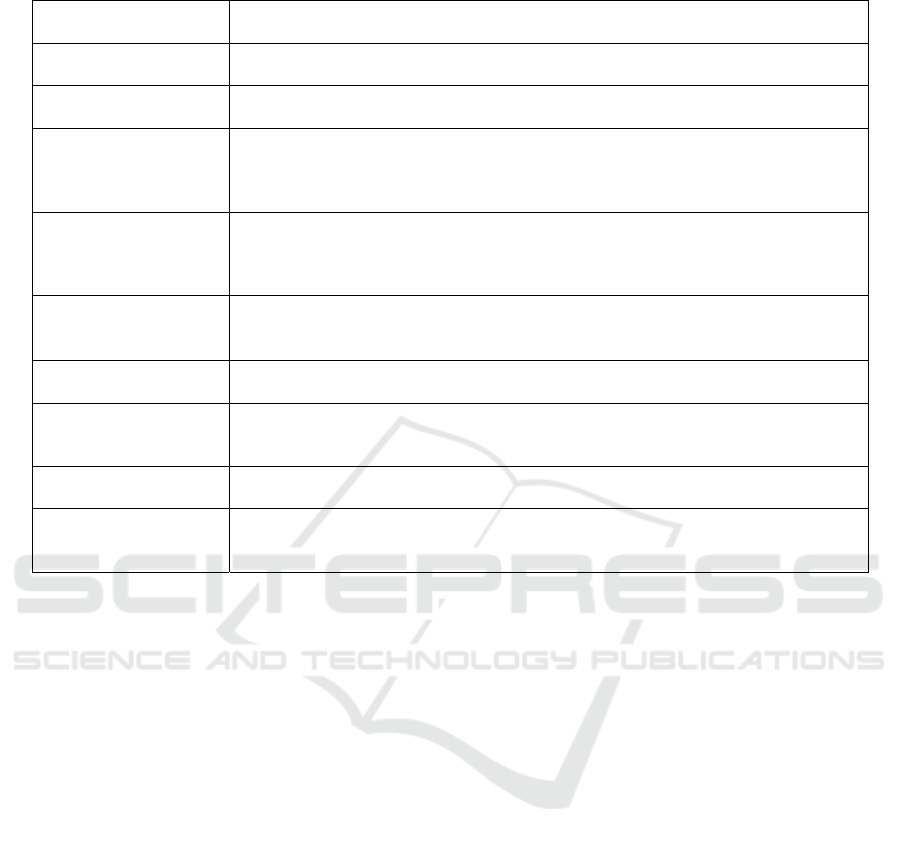
Continuation of table 2
Accumulation of
deterioration
Shows the degree of depreciation of fixed assets
Autonomy ratio Financial result (own funds) / The total amount of sources of formation of the
p
ro
p
ert
y
of the universit
y
(
excludin
g
obli
g
ations to the founder
)
(
Batkovsk
y
, 2017
)
Dependency ratio Obligations to creditors / The total amount of sources of formation of the property of
the university (excluding obligations to the founder)
(Improving the financial, 2018)
Coefficient of provision
of non-current assets
with long-term sources
of financin
g
The total amount of sources of formation of non-current assets / Total non-current
assets
Autonomy indicator
(PFY-1)
PFY - an indicator of
financial stabilit
y
The share of receipts from income-generating activities in the total volume of
receipts from income-generating activities and subsidies for financial support for the
fulfillment of the state task
Increase in receipts
from income-generating
activities (PFY -2)
Increase in receipts from income-generating activities in the reporting period in
relation to the period preceding the reporting period
Debt burden ratio (PFY
-3
)
Dependence of educational activities on borrowed funding sources
Share of overdue
accounts payable (PFY
-4
)
The ratio of the volume of accounts payable to the total volume of accounts payable
(excluding income payables)
Share of overdue
receivables (PFY -5)
The ratio of the amount of overdue receivables to the total amount of receivables
Deficit of funds from
income-generating
activities
(
PFY -6
)
Assessment of the indicator of accounts payable to funds from income-generating
activities
Table 2 shows the relative indicators of the financial
stability of the university. Analysis in these areas
involves the use of available information contained in
public reports. This makes it possible to conduct a
comprehensive assessment of the financial stability of
a state university. In general, the actual financial
condition of the organization can be represented only
by the integrated use of the results of absolute and
relative indicators.
4 DISCUSSION
Of great importance in the analysis of the financial
stability of an organization is the use of absolute
indicators:
the total number of students in undergraduate,
specialist and graduate programs,
the amount of income from educational
activities,
the total number of teaching staff, the
proportion of students in graduate programs
and postgraduate teaching programs in
postgraduate studies in the total number of
contingent,
the number of publications of the organization,
indexed in the information and analytical
system of scientific citation, per 100 academic
staff,
the amount of subsidies for the implementation
of the State Task, the number of enlarged
groups of specialties and directions. These
indicators are criterial, since they are used to
form metrics that allow you to determine the
quality of the financial condition (Flagship
Universities of Russia, 2020).
Relative values play an extremely important role
in modern conditions in the analysis of financial
stability, since they smooth out the distorting effect of
inflation on the reporting material. Their prevalence
is due to a certain advantage over absolute indicators,
since they allow one to compare objects that are
incomparable in absolute values, are more stable in
space and time, characterize homogeneous variation
series, and also improve the statistical properties of
indicators. The choice of indicators for the analysis of
financial stability should contribute to solving the
problem: to assess the financial stability on the basis
of accounting data.
As a result of the work done, we propose a model
for analyzing the financial stability of a state
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
752
budgetary educational institution of higher education,
created as a result of using all the above indicators,
taken from the classical methods of calculating
financial stability and indicators of the Ministry of
Education.
Using this technique, you can analyze the
company's activities throughout its existence and
carry out calculations annually to observe and analyze
the dynamics of the indicator. In the future, we
transferred all indicators to a point estimate, which
helped to draw a general conclusion about the level of
financial stability based on the results of assessing
both absolute and relative indicators.
The peculiarity of this model is that the financial
stability of the company is divided into the factors
that describe it. The factors represent the properties of
the first level, to which we attributed such
characteristics as - educational activities, research
activities, the state of fixed assets and financial and
economic activities. Further below the level are
indicators describing these factors, they constitute the
second level of indicators. Figure 2.2 shows the tree
of properties of the model for assessing the financial
stability of the state budgetary educational institution
of higher education.
The model includes the properties of three levels,
0 - the level is the main property, the indicator to the
definition, which our model aspires to. Below the
level, the enlarged properties are indicated, which
represent those areas of activity to which the
indicators we have highlighted belong.
The model presents the absolute and relative
indicators of the second level in the amount of
twenty-one.
For the best perception of the results, we suggest
using weight-adjusted scores, that is, each indicator
will have a weight of 0.048 for each of the 21
indicators out of a total ideal result of 1 or 100
percent. Each of the indicators of the university
receives a point taking into account the compliance
with one of the assessment factors. The calculation is
based on the ratios, where 2 points in a 3-point
gradation is 2/3 of the maximum mark, 1 point,
respectively, 1/3, in a 2-point system a similar
calculation. Accordingly, the scores adjusted for their
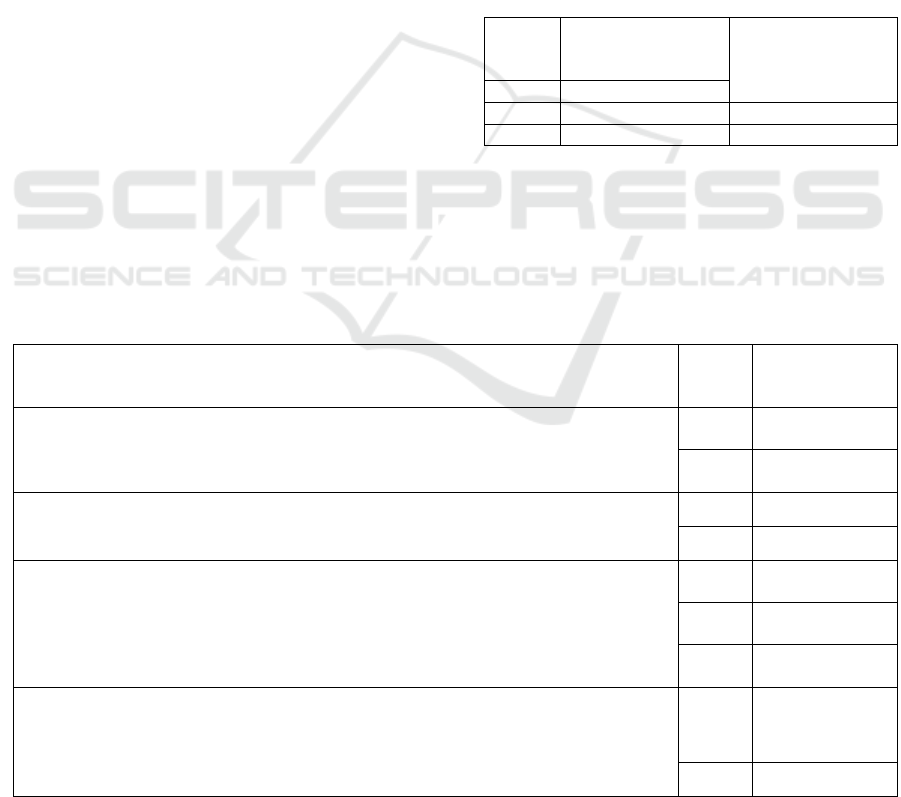
weight are presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Scores of the model for assessing the financial
stability of a state university, taking into account the
weight.
Point
score
Point weight in a 3-
point grading
s
y
stem
Point weight in a 2-
point grading
system
3 0,048
(
4,8%
)
2 0,032 (3,2%) 0,048 (4,8%)
1 0,016 (1,6%) 0,024 (2,4%)
Table 4 shows the scoring of the 2-level factors that
describe the property of the 1-level “Educational
activity”. Each point can be "obtained" according to
the condition indicated in the column for the absolute
value of the factor.
Table 4: Indicators of the scoring of factors of the 2nd level of the category "Educational activity".
Indicator name
Point
score
The absolute
value of the
facto
r
Total number of students in undergraduate, specialist and graduate programs 2 more than
10.000 students
1 less than 10,000
students
The number of enlarged groups of specialties and directions (UGSN) 2 more than 20
1 less than 20
Total number of teaching staff 3 The indicator
has increase
d
2 Indicator has not
chan
g
e
d
1 The indicator
has decrease
d
The share of the number of students enrolled in Master's programs and postgraduate
teaching staff training programs in the total number of the given contingent
2 more than 20%
1 less than 20%
Development of a Model of Financial Stability of Universities
753
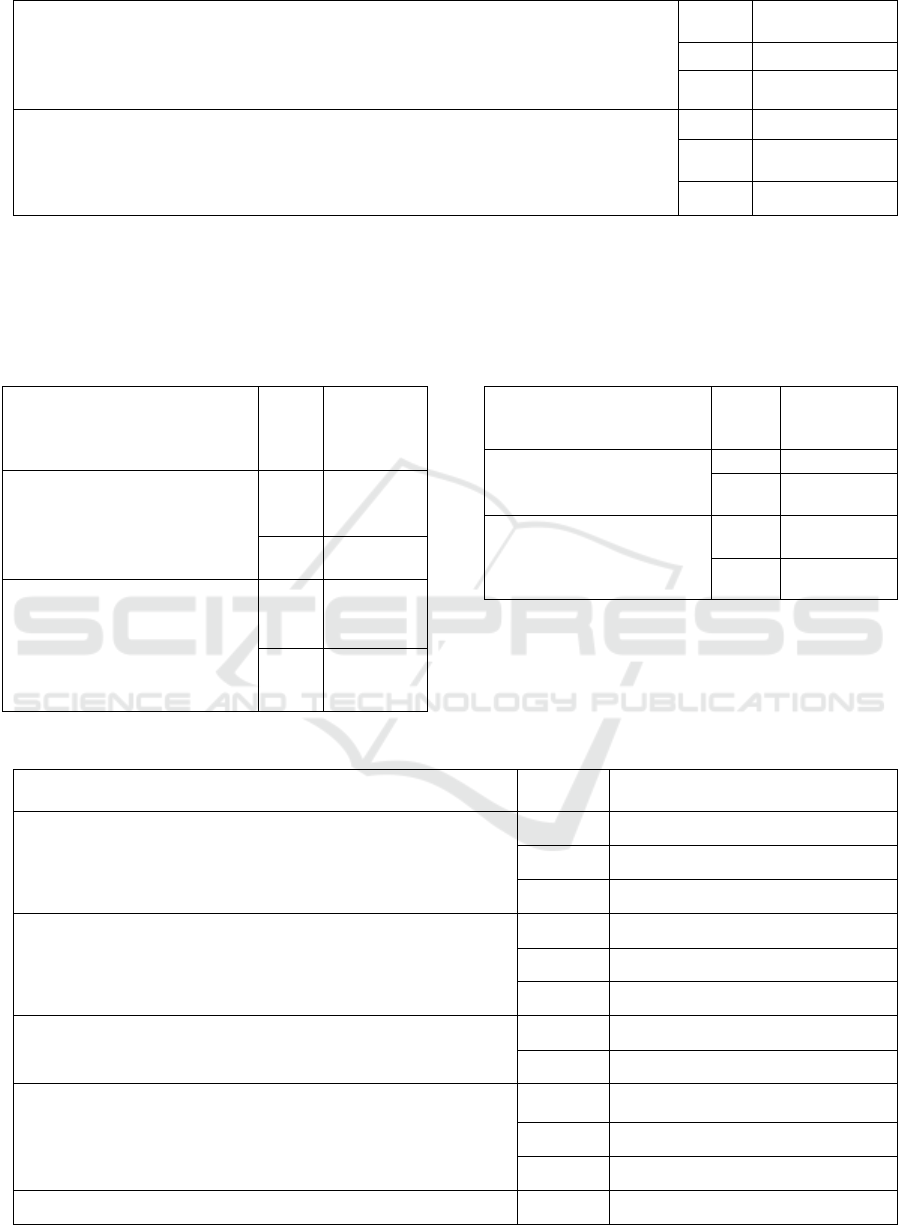
The average score of the "unified state exam" of students taken on the basis of the results
of the "unified state exam" for full-time education at the expense of the corresponding
budgets of the budgetary system of the Russian Federation
3 from 80 to 100
2 from 60 to 80
1 from 40 to 60
The average score of the "unified state exam" of students taken on the basis of the results
of the "unified state exam" for full-time training with payment of the cost of training by
individuals and legal entities
3 61.63 and up
2 from 53.8 to
61.63
1 44 to 53.8
Table 5 shows the scoring of the 2-level factors
that describe the property of the 1-level "Research
activity".
Table 5: Indicators of the scoring of factors of the 2nd level
of the category "Research activity".
Indicator name
Point
score
The
absolute
value of
the facto
r
The number of publications of
the organization, indexed in the
information and analytical
system of scientific citation, per
100 academic staff
2
More than
20
1
Less than
20
R&D revenues (excluding funds
from the budgets of the
budgetary system of the Russian
Federation, state funds for the
support of science) per one
academic staff
2
More than
150 th,
rubles.
1
Less than
150 th.
rubles
A feature of this table is the use of only two-point
gradation. The following Table 6 lists the metrics for
the Basic Properties State property.
Table 6: Indicators of scoring of factors of the 2nd level of
the category "State of basic properties".
Indicator name
Point
score
The absolute
value of the
facto
r
Accumulation of
deterioration
2
Less than 0.5
1
More than
0.5
Coefficient of provision of
non-current assets with
long-term sources of
financin
g
2
More than
0.6
1
Less than 0.6
The final table describes the property "Financial
and economic activity".
Table 7: Indicators of scoring of factors of the 2nd level of the category "State of basic properties".
Indicator name
Point
score
The absolute value of the factor
The amount of income from educational activities
3
The dynamics are positive
2
The volume did not change (± 5%)
1
Dynamics is negative
The amount of subsidies for the execution of the state order
3
The dynamics are positive
2
The volume did not change (± 5%)
1
Dynamics is negative
Income from all sources calculated on the number of students
(reduced contingent)
2
More than 200 thousand rubles.
1
Less than 200 thousand rubles
Autonomy ratio
3
from 0.5 to 0.7
2
more than 0.71
1
less than 0.49
Dependency ratio
3
from 0.4 to 0.5
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
754
2
from 0.5 to 0.7
1
more than 0.71 and less than 0.4
Autonomy indicator (PFY-1)
3
Maximum value 70% or more
2
Satisfactory value: 30% - 69%
1
Minimum value 30% or less
Increase in receipts from income-generating activities (PFY -2)
3
Maximum value 8% or more
2
Satisfactory value: 0% - 8%
1
Minimum value 0% or less
Debt burden ratio (PFY -3)
3
Minimum value from 0% to 10%
2
Satisfactory value: 11% - 24%
1
Maximum value 25% or more
Share of overdue accounts payable (PFY -4)
3
Minimum value 0%
2
Satisfactory value: more than 0% -
u
p
to 1%
1
Maximum value 1% or more
Share of overdue receivables (PFY -5)
3
Minimum value 0%
2
Satisfactory value: more than 0% -
up to 1%
1
Maximum value 1% or more
Deficit of funds from income-generating activities (PFY -6)
3
Maximum value 0% or more
2
Satisfactory value: -15% - 0%
1
Minimum value -15% or less
5 CONCLUSION
The paper proposes the absolute and relative
indicators of financial stability used in the author's
model. The authors presented a model for assessing
the financial stability of a higher educational
institution. For a more visual result, one or 100
percent was taken as an ideal indicator, while all
indicators were assigned points in accordance with
whether they correspond to the standard value or not.
Thus, using this methodology, a state university is
able to quickly and qualitatively analyze its activities
from the point of financial stability and then
determine which indicators should be emphasized in
the future when planning their activities. In order to
develop the university in the future and increase its
prestige among applicants, one should take into
account those areas of activity in which negative
values of indicators were obtained. In conclusion, we
note that the analysis of the financial stability of a
public institution of higher education in modern
conditions is extremely important in the framework
of increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of the
activities of a higher educational institution.
Development of a Model of Financial Stability of Universities
755

REFERENCES
Aidemirova, Z.A. (2017). The role of the analysis of the
financial state of the financial in the management
system. Aeterna Scientific Publishing Center, pages 4–
8.
Batkovsky, M.A. (2017). Ensuring the financial stability of
the university.
Bondarenko, N.V. (2019). Education in numbers: short
statistical collection.
Financial sustainability of the university or how to
“balance” the quality? (2016) LLC "Editorial office of
the journal Accreditation in Education", 6: 58-60.
Flagship Universities of Russia (2020).
http://flagshipuniversity.ntf.ru/project
Frolkin, A.V. (2016). The concept of financial stability in
budgetary and autonomous institutions. Bulletin of the
Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, pages
127-132.
Improving the financial stability of universities. (2018).
Projects of Russian universities, 212. M.: FGBOU VO
"PRUE im. G.V. Plekhanov".
Improving the financial stability of universities. (2018).
Projects of Russian universities: scientific publication.
Ural Federal University named after the first President
of Russia B. N. Yeltsin (Yekaterinburg), Ministry of
Education and Science of the Russian Federation,
Russian University of Economics. G.V. Plekhanov,
212.
Kovaleva, V. 2019. NRU HSE, 96.
Kuznetsova, A.L. (2016). On the issue of assessing the
financial sustainability of a state university taking into
account financing from non-budgetary sources, 1(5): 29
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
756
